Abstract
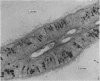
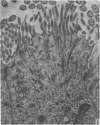
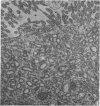
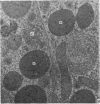
Ultrastructural studies were undertaken on the efferent ductules of the testis of the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus), Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica) and guinea-fowl (Numida meleagris). Four cell types were identified and described: ciliated cells which were found in the epithelium of both the proximal and distal segments of the efferent ductules, non-ciliated Type I cell which, together with the ciliated cell, formed the epithelium of the proximal efferent ductule and the non-ciliated Type II cell which, together with the ciliated cell, formed the epithelium of the distal efferent ductule. Intraepithelial lymphocytes were the fourth cell type found in the epithelium of both segments of the efferent ductule of the fowl only.
Full text
PDF


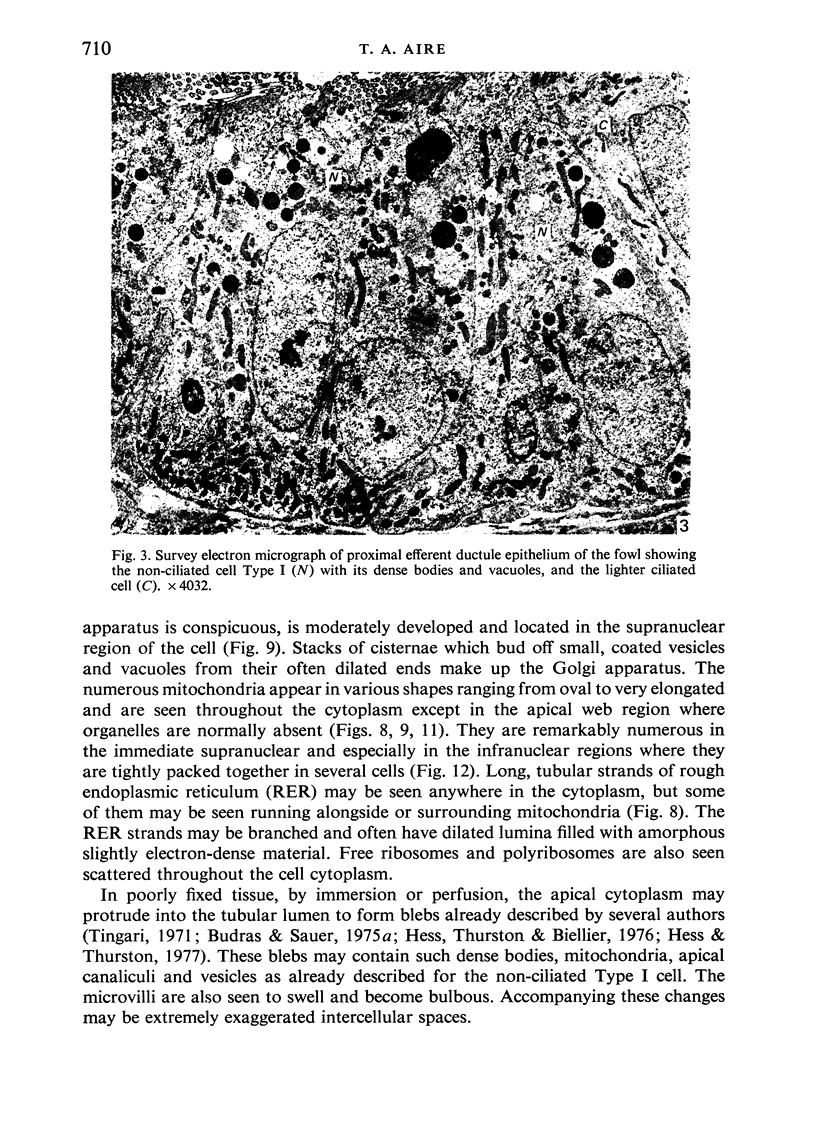









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aire T. A., Ayeni J. S., Olowo-Okorun M. O. The structure of the excurrent ducts of the testis of the guinea-fowl (Numida meleagris). J Anat. 1979 Oct;129(Pt 3):633–643. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aire T. A., Malmquist M. Intraepithelial lymphocytes in the excurrent ducts of the testis of the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus). Acta Anat (Basel) 1979;103(2):142–149. doi: 10.1159/000145005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budras K. D., Sauer T. Morphology of the epididymis of the cock (Gallus domesticus) and its effect upon the steroid sex hormone synthesis. I. Ontogenesis, morphology and distribution of the epididymis. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1975 Dec 23;148(2):175–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00315268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budras K. D., Sauer T. Morphology of the epididymis of the cock (Gallus domesticus) and its effect upon the steroid sex hormone synthesis. II. Steroid sex hormone synthesis in the tubuli epididymidis and the transformation of the ductuli aberrantes into hormone producing noduli epididymidis in the capsule of the adrenal gland of the capon. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1975 Dec 23;148(2):197–213. doi: 10.1007/BF00315269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Duve C., Wattiaux R. Functions of lysosomes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1966;28:435–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.28.030166.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell R. T., Stacy R. D. Effects of colchicine on the ovine corpus luteum: role of microtubules in the secretion of progesterone. J Reprod Fertil. 1977 Jan;49(1):115–117. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0490115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Acebo J., Hermida O. G. Morphological relations between rat -secretory granules and the microtubular-microfilament system during sustained insulin release in vitro. J Anat. 1973 Apr;114(Pt 3):421–437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess R. A., Thurston R. J., Biellier H. V. Morphology of the epididymal region and ductus deferens of the turkey (Meleagris gallopavo). J Anat. 1976 Nov;122(Pt 2):241–252. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess R. A., Thurston R. J. Ultrastructure of epithelial cells in the epididymal region of the turkey (Meleagris gallopavo). J Anat. 1977 Dec;124(Pt 3):765–778. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LADMAN A. J., YOUNG W. C. An electron microscopic study of the ductuli efferentes and rete testis of the guinea pig. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Mar 25;4(2):219–226. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladman A. J. The fine structure of the ductuli efferentes of the opossum. Anat Rec. 1967 Apr;157(4):559–575. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091570403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martan J., Hruban Z., Slesers A. Cytological studies of the ductuli efferentes of the opossum. J Morphol. 1967 Feb;121(2):81–102. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051210202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita I. [Some observations on the fine structure of the human ductuli efferentes testis]. Arch Histol Jpn. 1966 May;26(4):341–365. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.26.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tingari M. D. Histochemical localization of 3 - and 17 -hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases in the male reprodutive tract of the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus). Histochem J. 1973 Jan;5(1):57–65. doi: 10.1007/BF01012045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tingari M. D. On the structure of the epididymal region and ductus deferens of the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus). J Anat. 1971 Sep;109(Pt 3):423–435. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tingari M. D. The fine structure of the epithelial lining of the ex-current duct system of the testis of the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus). Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1972 Jul;57(3):271–295. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1972.sp002162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON M. L. Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):475–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama M., Chang J. P. An ultracytochemical and ultrastructural study of epithelial cells in ductuli efferentes of Chinese hamster. J Histochem Cytochem. 1971 Dec;19(12):766–774. doi: 10.1177/19.12.766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]