Abstract
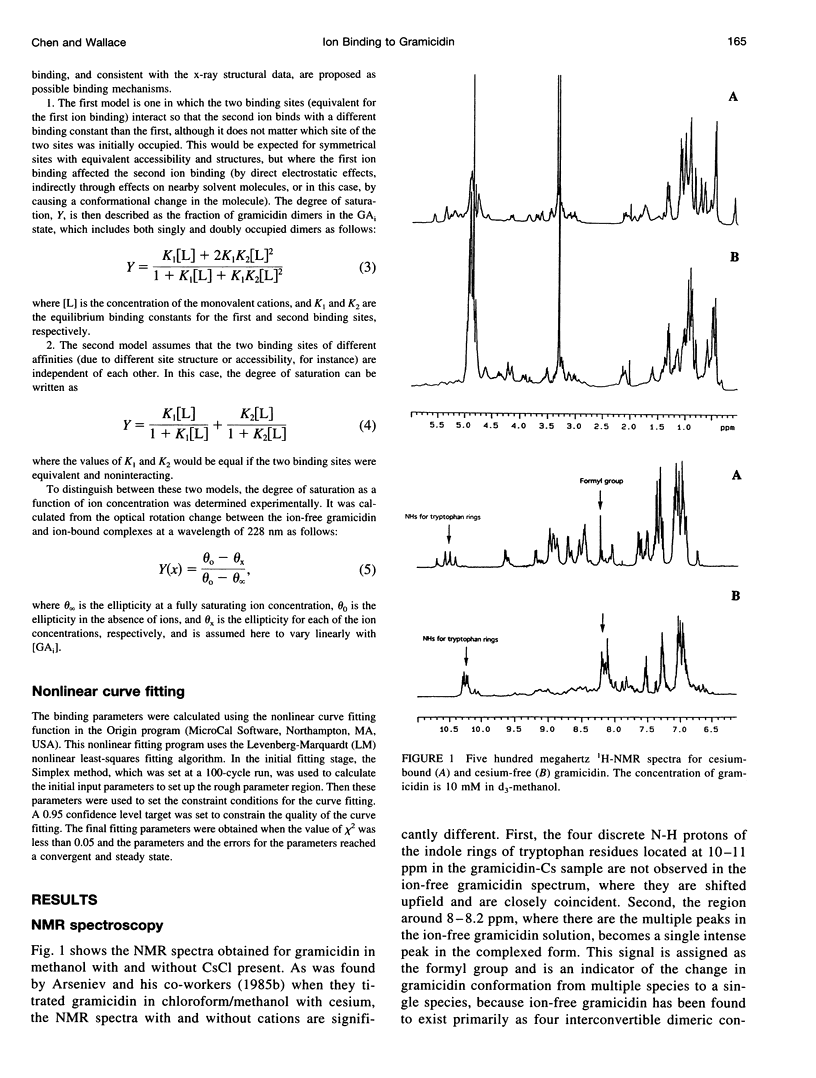
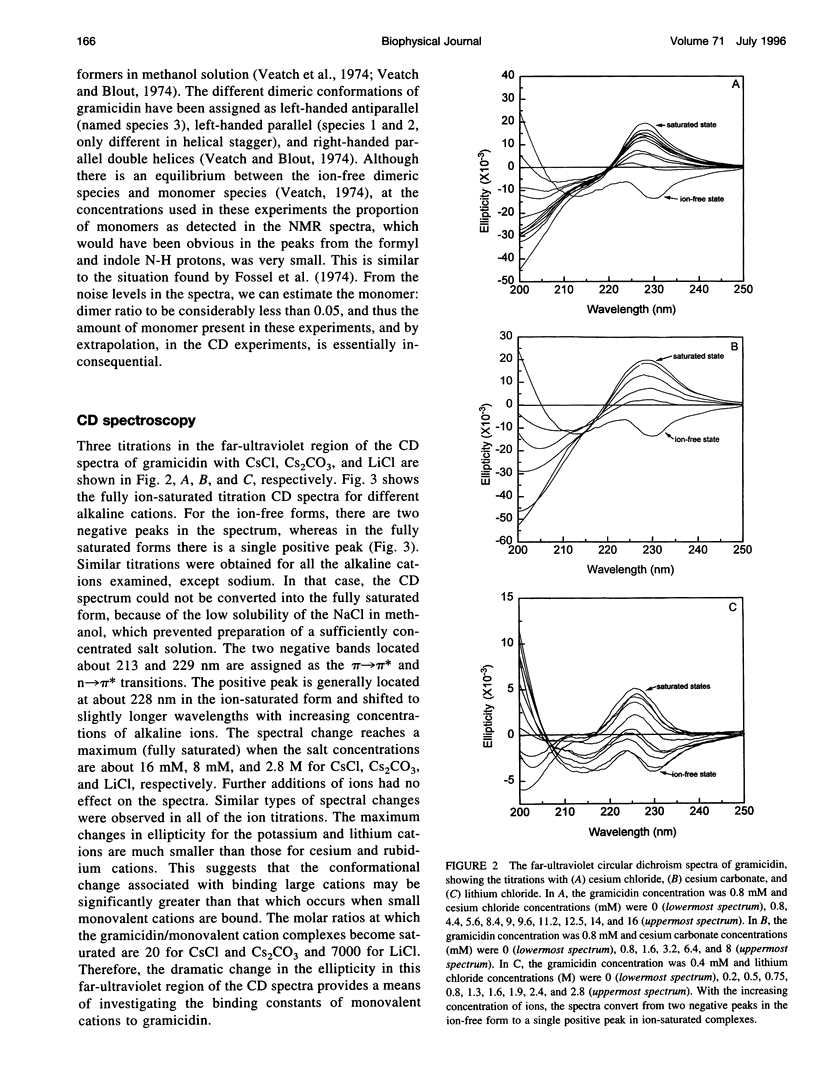
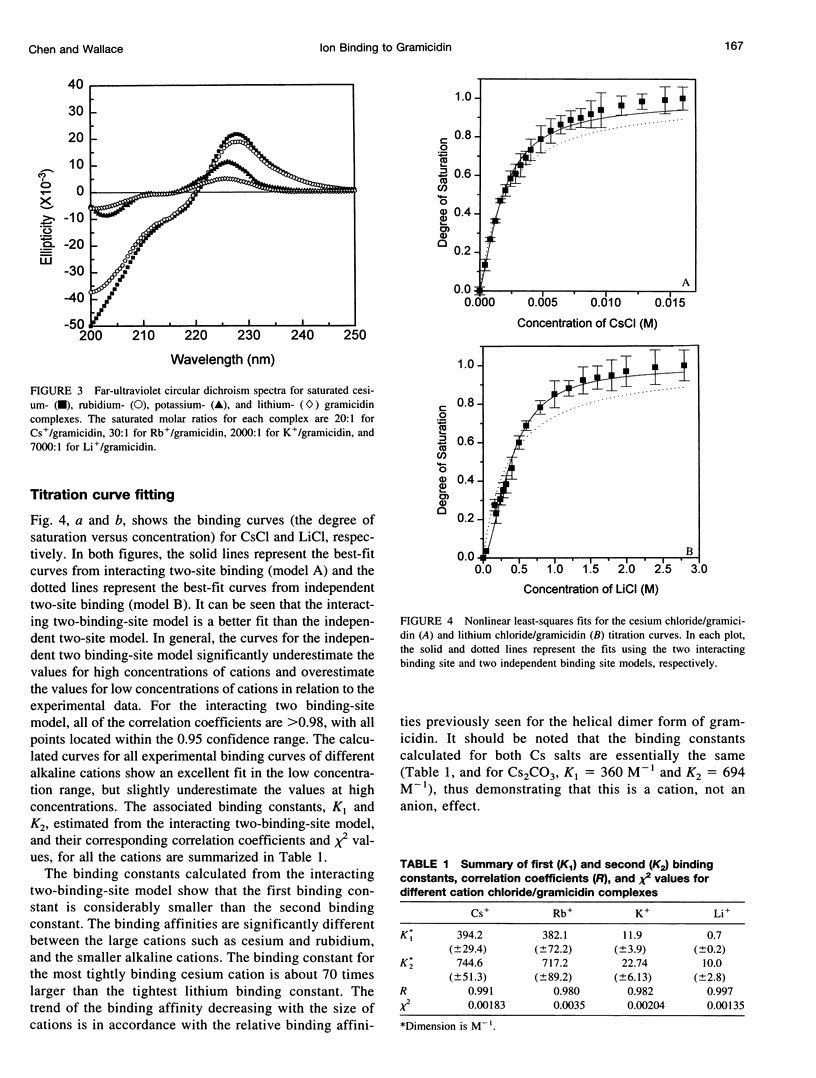
Gramicidin is a polypeptide antibiotic that forms monovalent cation-specific channels in membrane environments. In organic solvents and in lipids containing unsaturated fatty acid chains, it forms a double-helical "pore" structure, in which two monomers are intertwined. This form of gramicidin can bind two cations inside its lumen, and the crystal structures of both an ion complex and an ion-free form have been determined. In this study, we have used circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy to examine the binding mechanism and the binding constants (K1 and K2) of cations to gramicidin in the double helical form in methanol solution. The dramatic change in optical rotation in the far-ultraviolet CD spectrum of gramicidin provides a useful tool for monitoring the binding. The binding mechanism appears to involve a large conformation change associated with the binding of ions to the first of the two sites. The calculated values for the K1 binding constants for alkaline cations are considerably smaller than the K2 binding constants. The order of binding affinity for alkaline cations is similar to that for the helical dimer "channel" form of gramicidin, i.e., Cs+ approximately Rb+ > > K+ > Li+, but in comparison to the helical dimer form, the binding to double-helical dimers is dominated by a cation size-dependent conformational change in the gramicidin structure.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S. Gramicidin channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:531–548. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arseniev A. S., Barsukov I. L., Bystrov V. F., Lomize A. L., Ovchinnikov YuA 1H-NMR study of gramicidin A transmembrane ion channel. Head-to-head right-handed, single-stranded helices. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):168–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80702-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohg A., Ristow H. DNA-supercoiling is affected in vitro by the peptide antibiotics tyrocidine and gramicidin. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 3;160(3):587–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornélis A., Laszlo P. Sodium binding sites of gramicidin A: sodium-23 nuclear magnetic resonance study. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):2004–2007. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani J. A., Levitt D. G. Binding constants of Li+, K+, and Tl+ in the gramicidin channel determined from water permeability measurements. Biophys J. 1981 Aug;35(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84804-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman G., Horn R. Ionic selectivity revisited: the role of kinetic and equilibrium processes in ion permeation through channels. J Membr Biol. 1983;76(3):197–225. doi: 10.1007/BF01870364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman G., Sandblom J., Neher E. Interactions in cation permeation through the gramicidin channel. Cs, Rb, K, Na, Li, Tl, H, and effects of anion binding. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):307–340. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85491-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossel E. T., Veatch W. R., Ovchinnikov U. A., Blout E. R. A 13C nuclear magnetic resonance study of gramicidin A in monomer and dimer forms. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5264–5275. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Baarda J. R. Gramicidin, valinomycin, and cation permeability of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):53–60. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.53-60.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton J. F., Koeppe R. E., 2nd, Shungu D., Whaley W. L., Paczkowski J. A., Millett F. S. Equilibrium binding constants for Tl+ with gramicidins A, B and C in a lysophosphatidylcholine environment determined by 205Tl nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):571–577. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83668-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langs D. A. Three-dimensional structure at 0.86 A of the uncomplexed form of the transmembrane ion channel peptide gramicidin A. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):188–191. doi: 10.1126/science.2455345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G., Elias S. R., Hautman J. M. Number of water molecules coupled to the transport of sodium, potassium and hydrogen ions via gramicidin, nonactin or valinomycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 22;512(2):436–451. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers V. B., Haydon D. A. Ion transfer across lipid membranes in the presence of gramicidin A. II. The ion selectivity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulus H., Sarkar N., Mukherjee P. K., Langley D., Ivanov V. T., Shepel E. N., Veatch W. Comparison of the effect of linear gramicidin analogues on bacterial sporulation, membrane permeability, and ribonucleic acid polymerase. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4532–4536. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux B., Karplus M. Molecular dynamics simulations of the gramicidin channel. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1994;23:731–761. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.003503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell E. W., Weiss L. B., Navetta F. I., Koeppe R. E., 2nd, Andersen O. S. Single-channel studies on linear gramicidins with altered amino acid side chains. Effects of altering the polarity of the side chain at position 1 in gramicidin A. Biophys J. 1986 Mar;49(3):673–686. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83694-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARGES R., WITKOP B. GRAMICIDIN A. V. THE STRUCTURE OF VALINE- AND ISOLEUCINE-GRAMICIDIN A. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 May 5;87:2011–2020. doi: 10.1021/ja01087a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart O. S., Goodfellow J. M., Wallace B. A. The pore dimensions of gramicidin A. Biophys J. 1993 Dec;65(6):2455–2460. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81293-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sychev S. V., Barsukov L. I., Ivanov V. T. The double pi pi 5.6 helix of gramicidin A predominates in unsaturated lipid membranes. Eur Biophys J. 1993;22(4):279–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00180262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: a proposed pi(L,D) helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):672–676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Trapane T. L., Walker J. T., Prasad K. U. On the relative lipid membrane permeability of Na+ and Ca2+. A physical basis for the messenger role of Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6659–6661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W. R., Blout E. R. The aggregation of gramicidin A in solution. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5257–5264. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W. R., Durkin J. T. Binding of thallium and other cations to the gramicidin A channel. Equilibrium dialysis study of gramicidin in phosphatidylcholine vesicles. J Mol Biol. 1980 Nov 15;143(4):411–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W. R., Fossel E. T., Blout E. R. The conformation of gramicidin A. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5249–5256. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. A. Gramicidin channels and pores. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:127–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. A., Ravikumar K. The gramicidin pore: crystal structure of a cesium complex. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):182–187. doi: 10.1126/science.2455344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. A., Veatch W. R., Blout E. R. Conformation of gramicidin A in phospholipid vesicles: circular dichroism studies of effects of ion binding, chemical modification, and lipid structure. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 29;20(20):5754–5760. doi: 10.1021/bi00523a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein S., Wallace B. A., Morrow J. S., Veatch W. R. Conformation of the gramicidin A transmembrane channel: A 13C nuclear magnetic resonance study of 13C-enriched gramicidin in phosphatidylcholine vesicles. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 15;143(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]