Abstract
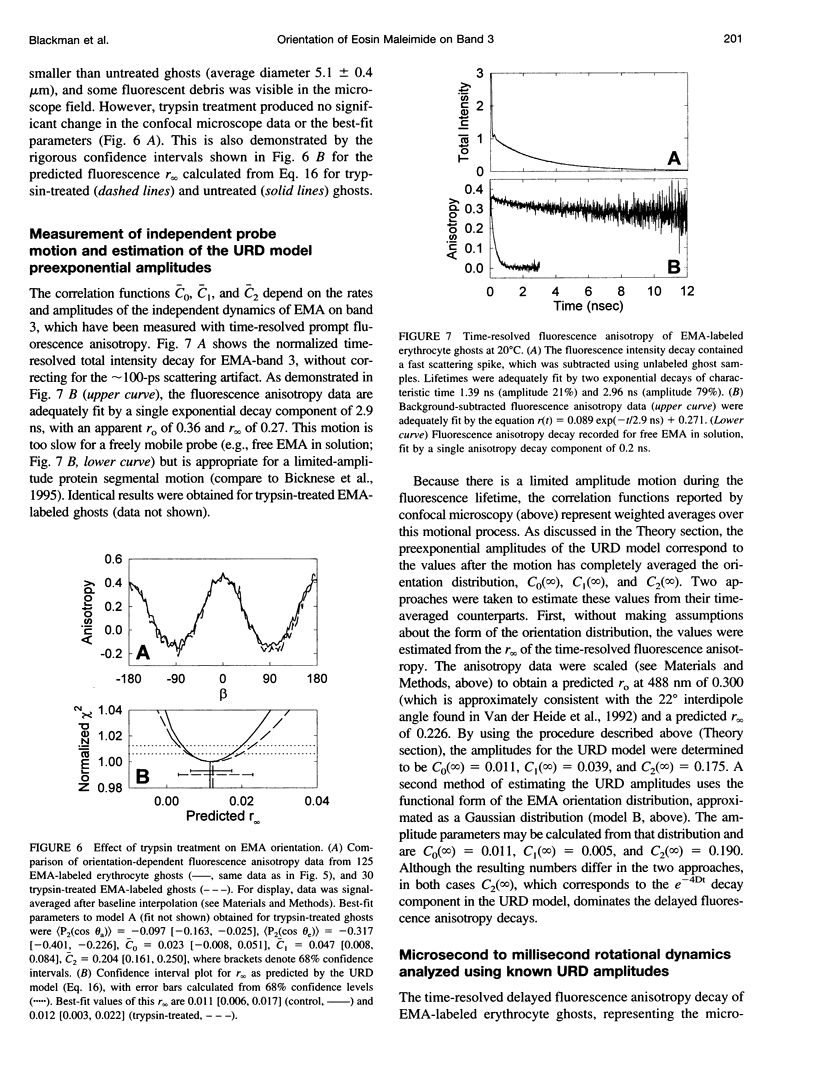
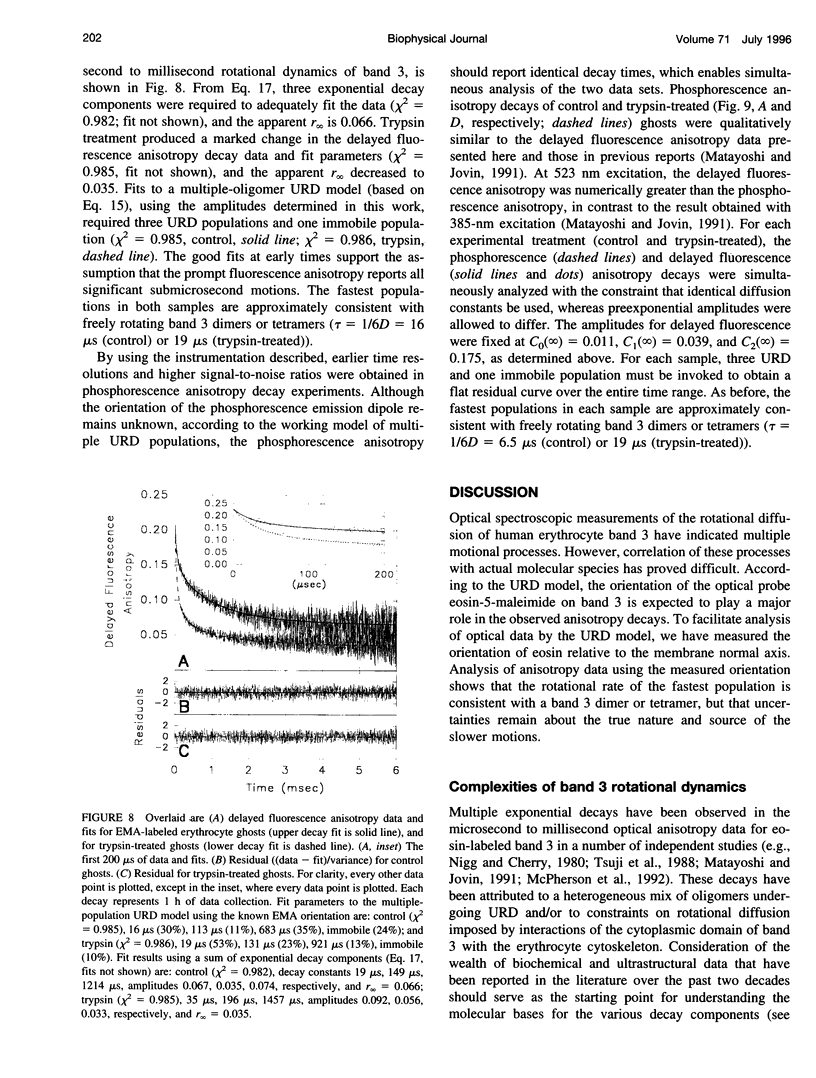
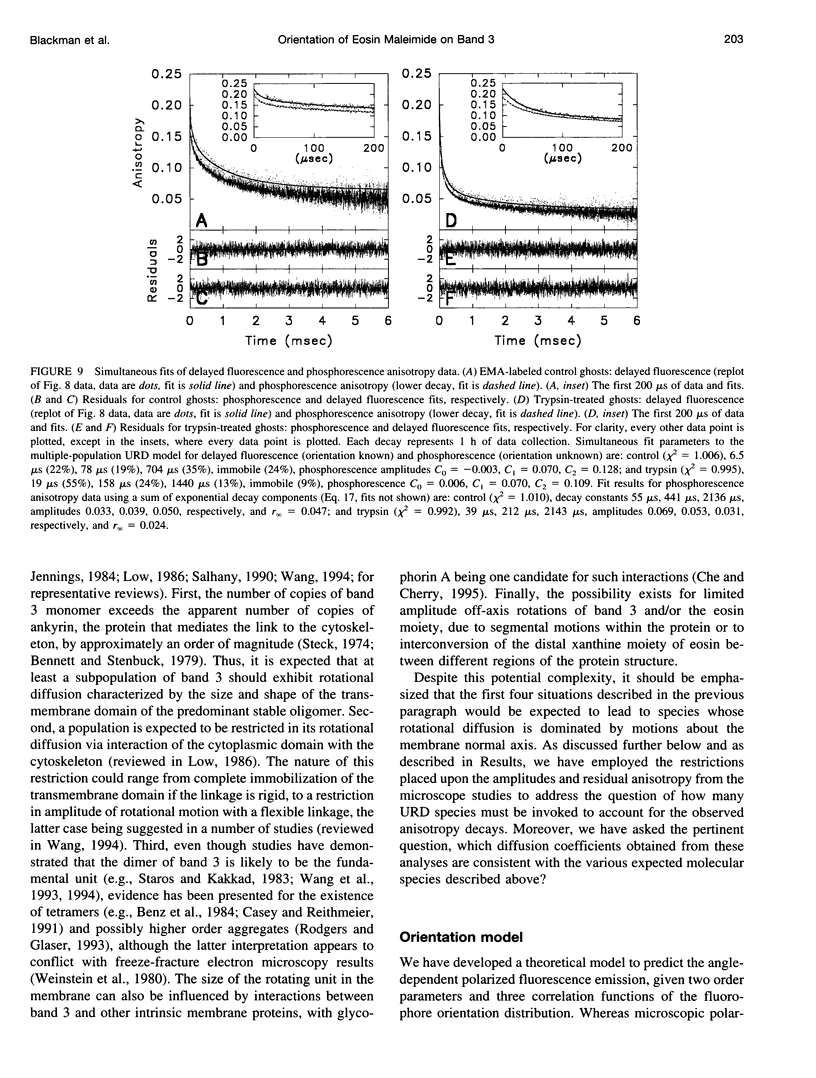
The dominant motional mode for membrane proteins is uniaxial rotational diffusion about the membrane normal axis, and investigations of their rotational dynamics can yield insight into both the oligomeric state of the protein and its interactions with other proteins such as the cytoskeleton. However, results from the spectroscopic methods used to study these dynamics are dependent on the orientation of the probe relative to the axis of motion. We have employed polarized fluorescence confocal microscopy to measure the orientation of eosin-5-maleimide covalently reacted with Lys-430 of human erythrocyte band 3. Steady-state polarized fluorescence images showed distinct intensity patterns, which were fit to an orientation distribution of the eosin absorption and emission dipoles relative to the membrane normal axis. This orientation was found to be unchanged by trypsin treatment, which cleaves band 3 between the integral membrane domain and the cytoskeleton-attached domain. this result suggests that phosphorescence anisotropy changes observed after trypsin treatment are due to a rotational constraint change rather than a reorientation of eosin. By coupling time-resolved prompt fluorescence anisotropy with confocal microscopy, we calculated the expected amplitudes of the e-Dt and e-4Dt terms from the uniaxial rotational diffusion model and found that the e-4Dt term should dominate the anisotropy decay. Delayed fluorescence and phosphorescence anisotropy decays of control and trypsin-treated band 3 in ghosts, analyzed as multiple uniaxially rotating populations using the amplitudes predicted by confocal microscopy, were consistent with three motional species with uniaxial correlation times ranging from 7 microseconds to 1.4 ms.
Full text
PDF

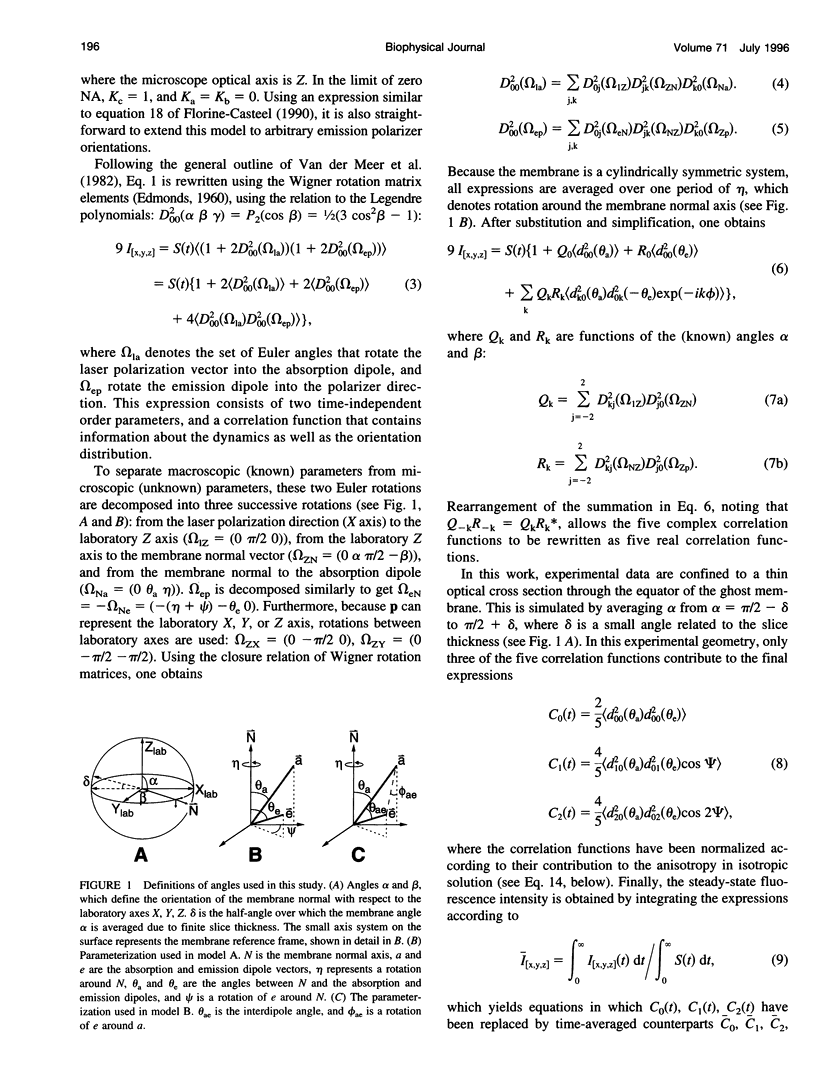



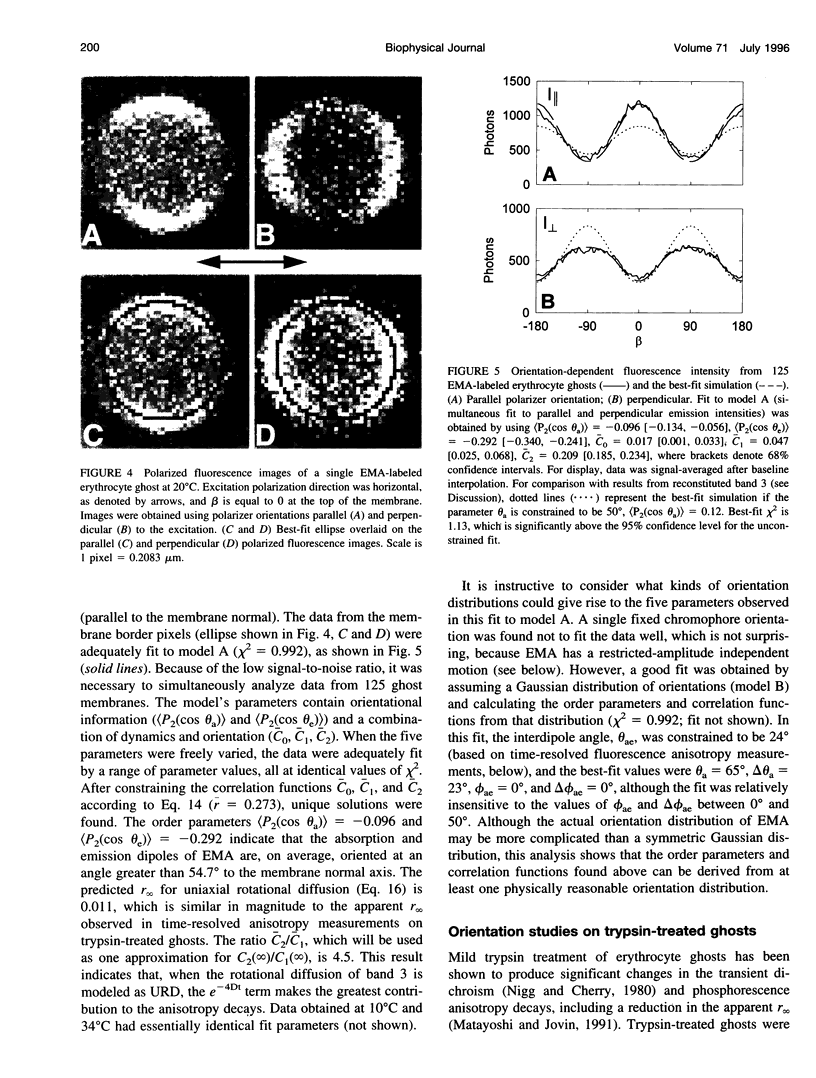





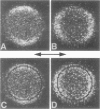
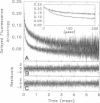
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod D. Carbocyanine dye orientation in red cell membrane studied by microscopic fluorescence polarization. Biophys J. 1979 Jun;26(3):557–573. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85271-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badley R. A., Martin W. G., Schneider H. Dynamic behavior of fluorescent probes in lipid bilayer model membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 16;12(2):268–275. doi: 10.1021/bi00726a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beechem J. M. Global analysis of biochemical and biophysical data. Methods Enzymol. 1992;210:37–54. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)10004-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., Stenbuck P. J. The membrane attachment protein for spectrin is associated with band 3 in human erythrocyte membranes. Nature. 1979 Aug 9;280(5722):468–473. doi: 10.1038/280468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Tosteson M. T., Schubert D. Formation and properties of tetramers of band 3 protein from human erythrocyte membranes in planar lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 5;775(3):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90190-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beth A. H., Conturo T. E., Venkataramu S. D., Staros J. V. Dynamics and interactions of the anion channel in intact human erythrocytes: an electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopic study employing a new membrane-impermeant bifunctional spin-label. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3824–3832. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknese S., Rossi M., Thevenin B., Shohet S. B., Verkman A. S. Anisotropy decay measurement of segmental dynamics of the anion binding domain in erythrocyte band 3. Biochemistry. 1995 Aug 22;34(33):10645–10651. doi: 10.1021/bi00033a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghardt T. P., Ajtai K. Following the rotational trajectory of the principal hydrodynamic frame of a protein using multiple probes. Biochemistry. 1994 May 10;33(18):5376–5381. doi: 10.1021/bi00184a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. R., Reithmeier R. A. Analysis of the oligomeric state of Band 3, the anion transport protein of the human erythrocyte membrane, by size exclusion high performance liquid chromatography. Oligomeric stability and origin of heterogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15726–15737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Che A., Cherry R. J. Loss of rotational mobility of band 3 proteins in human erythrocyte membranes induced by antibodies to glycophorin A. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1881–1887. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80365-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Bürkli A., Busslinger M., Schneider G., Parish G. R. Rotational diffusion of band 3 proteins in the human erythrocyte membrane. Nature. 1976 Sep 30;263(5576):389–393. doi: 10.1038/263389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Godfrey R. E. Anisotropic rotation of bacteriorhodopsin in lipid membranes. Comparison of theory with experiment. Biophys J. 1981 Oct;36(1):257–276. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84727-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb C. E., Beth A. H. Identification of the eosinyl-5-maleimide reaction site on the human erythrocyte anion-exchange protein: overlap with the reaction sites of other chemical probes. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 11;29(36):8283–8290. doi: 10.1021/bi00488a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb C. E., Hustedt E. J., Beechem J. M., Beth A. H. Protein rotational dynamics investigated with a dual EPR/optical molecular probe. Spin-labeled eosin. Biophys J. 1993 Mar;64(3):605–613. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81419-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. D., Golan D. E. Band 3 and glycophorin are progressively aggregated in density-fractionated sickle and normal red blood cells. Evidence from rotational and lateral mobility studies. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):208–217. doi: 10.1172/JCI116172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix J. A., Verkman A. S. Mapping of fluorescence anisotropy in living cells by ratio imaging. Application to cytoplasmic viscosity. Biophys J. 1990 Feb;57(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82526-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florine-Casteel K. Phospholipid order in gel- and fluid-phase cell-size liposomes measured by digitized video fluorescence polarization microscopy. Biophys J. 1990 Jun;57(6):1199–1215. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82639-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellen E. H., Burghardt T. P. Saturation effects in polarized fluorescence photobleaching recovery and steady state fluorescence polarization. Biophys J. 1994 Mar;66(3 Pt 1):891–897. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(94)80865-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyn M. P., Cherry R. J., Müller U. Transient and linear dichroism studies on bacteriorhodopsin: determination of the orientation of the 568 nm all-trans retinal chromophore. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 15;117(3):607–620. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hustedt E. J., Beth A. H. Analysis of saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance spectra of a spin-labeled integral membrane protein, band 3, in terms of the uniaxial rotational diffusion model. Biophys J. 1995 Oct;69(4):1409–1423. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80010-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M. L. Oligomeric structure and the anion transport function of human erythrocyte band 3 protein. J Membr Biol. 1984;80(2):105–117. doi: 10.1007/BF01868768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P., Garland P. B. Depolarization of fluorescence depletion. A microscopic method for measuring rotational diffusion of membrane proteins on the surface of a single cell. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 28;132(2):252–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81172-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M., Vaz W. L. Rotational and translational diffusion in membranes measured by fluorescence and phosphorescence methods. Methods Enzymol. 1989;172:471–513. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)72030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F. The shape of a membrane protein derived from rotational diffusion. Eur Biophys J. 1986;14(1):63–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00260404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolt-Marticorena C., Casey J. R., Reithmeier R. A. Transmembrane helix-helix interactions and accessibility of H2DIDS on labelled band 3, the erythrocyte anion exchange protein. Mol Membr Biol. 1995 Apr-Jun;12(2):173–182. doi: 10.3109/09687689509027505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepke S., Passow H. Effects of incorporated trypsin on anion exchange and membrane proteins in human red blood cell ghosts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 2;455(2):353–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90311-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman D. M., Reithmeier R. A. Localization of the carboxyl terminus of Band 3 to the cytoplasmic side of the erythrocyte membrane using antibodies raised against a synthetic peptide. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):10022–10028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. W., Mathies R. A. Orientation of the protonated retinal Schiff base group in bacteriorhodopsin from absorption linear dichroism. Biophys J. 1989 Oct;56(4):653–660. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82712-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. S. Structure and function of the cytoplasmic domain of band 3: center of erythrocyte membrane-peripheral protein interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 22;864(2):145–167. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(86)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M., Kopito R. R., Lodish H. F. Cloning and characterization of band 3, the human erythrocyte anion-exchange protein (AE1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9089–9093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macara I. G., Kuo S., Cantley L. C. Evidence that inhibitors of anion exchange induce a transmembrane conformational change in band 3. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1785–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matayoshi E. D., Jovin T. M. Rotational diffusion of band 3 in erythrocyte membranes. 1. Comparison of ghosts and intact cells. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 9;30(14):3527–3538. doi: 10.1021/bi00228a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matayoshi E. D., Sawyer W. H., Jovin T. M. Rotational diffusion of band 3 in erythrocyte membranes. 2. Binding of cytoplasmic enzymes. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 9;30(14):3538–3543. doi: 10.1021/bi00228a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson R. A., Sawyer W. H., Tilley L. Band 3 mobility in camelid elliptocytes: implications for erythrocyte shape. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 6;32(26):6696–6702. doi: 10.1021/bi00077a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson R. A., Sawyer W. H., Tilley L. Rotational diffusion of the erythrocyte integral membrane protein band 3: effect of hemichrome binding. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 21;31(2):512–518. doi: 10.1021/bi00117a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Cherry R. J. Anchorage of a band 3 population at the erythrocyte cytoplasmic membrane surface: protein rotational diffusion measurements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4702–4706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palek J., Lambert S. Genetics of the red cell membrane skeleton. Semin Hematol. 1990 Oct;27(4):290–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan R. J., Cherry R. J. Evidence that eosin-5-maleimide binds close to the anion transport site of human erythrocyte band 3: a fluorescence quenching study. Biochemistry. 1995 Apr 11;34(14):4880–4888. doi: 10.1021/bi00014a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimplikar S. W., Reithmeier R. A. Affinity chromatography of Band 3, the anion transport protein of erythrocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9770–9778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao A., Martin P., Reithmeier R. A., Cantley L. C. Location of the stilbenedisulfonate binding site of the human erythrocyte anion-exchange system by resonance energy transfer. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4505–4516. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigler R., Ehrenberg M. Molecular interactions and structure as analysed by fluorescence relaxation spectroscopy. Q Rev Biophys. 1973 May;6(2):139–199. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000113x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers W., Glaser M. Distributions of proteins and lipids in the erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 30;32(47):12591–12598. doi: 10.1021/bi00210a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffman P. G., Delbrück M. Brownian motion in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3111–3113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staros J. V., Kakkad B. P. Cross-linking and chymotryptic digestion of the extracytoplasmic domain of the anion exchange channel in intact human erythrocytes. J Membr Biol. 1983;74(3):247–254. doi: 10.1007/BF02332127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner M. J., Martin P. G., High S. The complete amino acid sequence of the human erythrocyte membrane anion-transport protein deduced from the cDNA sequence. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 15;256(3):703–712. doi: 10.1042/bj2560703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timbs M. M., Thompson N. L. Measurement of restricted rotational diffusion of fluorescent lipids in supported planar phospholipid monolayers using angle-dependent polarized fluorescence photobleaching recovery. Biopolymers. 1993 Jan;33(1):45–57. doi: 10.1002/bip.360330106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timbs M. M., Thompson N. L. Slow rotational mobilities of antibodies and lipids associated with substrate-supported phospholipid monolayers as measured by polarized fluorescence photobleaching recovery. Biophys J. 1990 Aug;58(2):413–428. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82387-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Kawasaki K., Ohnishi S., Merkle H., Kusumi A. Regulation of band 3 mobilities in erythrocyte ghost membranes by protein association and cytoskeletal meshwork. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 20;27(19):7447–7452. doi: 10.1021/bi00419a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D. N. Band 3 protein: structure, flexibility and function. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jun 6;346(1):26–31. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00468-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D. N., Kühlbrandt W., Sarabia V. E., Reithmeier R. A. Two-dimensional structure of the membrane domain of human band 3, the anion transport protein of the erythrocyte membrane. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2233–2239. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05876.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D. N., Sarabia V. E., Reithmeier R. A., Kühlbrandt W. Three-dimensional map of the dimeric membrane domain of the human erythrocyte anion exchanger, Band 3. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3230–3235. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06624.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener W. A. Fluorescence recovery spectroscopy as a probe of slow rotational motions. Biophys J. 1984 Dec;46(6):795–803. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84078-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heide U. A., Orbons B., Gerritsen H. C., Levine Y. K. The orientation of transition moments of dye molecules used in fluorescence studies of muscle systems. Eur Biophys J. 1992;21(4):263–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00185121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heide U. A., Rem O. E., Gerritsen H. C., de Beer E. L., Schiereck P., Trayer I. P., Levine Y. K. A fluorescence depolarization study of the orientational distribution of crossbridges in muscle fibres. Eur Biophys J. 1994;23(5):369–378. doi: 10.1007/BF00188661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]