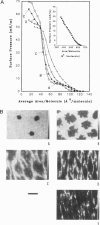
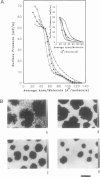
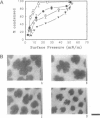
Abstract
Pulmonary surfactant, a lipid-protein complex, secreted into the fluid lining of lungs prevents alveolar collapse at low lung volumes. Pulmonary surfactant protein C (SP-C), an acylated, hydrophobic, alpha-helical peptide, enhances the surface activity of pulmonary surfactant lipids. Fluorescein-labeled SP-C (F-SP-C) (3, 6, 12 wt%) in dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), and DPPC:dipalmitoylphosphatidylglycerol (DPPG) [DPPC:DPPG 7:3 mol/mol] in spread monolayers was studied by epifluorescence microscopy. Mass spectometry of F-SP-C indicated that the protein is partially deacylated and labeled with 1 mol fluorescein/1 mol protein. The protein partitioned into the fluid, or liquid expanded, phase. Increasing amounts of F-SP-C in DPPC or DPPC:DPPG monolayers decreased the size and total amounts of the condensed phase at all surface pressures. Calcium (1.6 mM) increased the amount of the condensed phase in monolayers of DPPC:DPPG but not of DPPC alone, and such monolayers were also perturbed by F-SP-C. The study indicates that SP-C perturbs the packing of neutral and anionic phospholipid monolayers even when the latter systems are condensed by calcium, indicating that interactions between SP-C and the lipids are predominantly hydrophobic in nature.
Full text
PDF

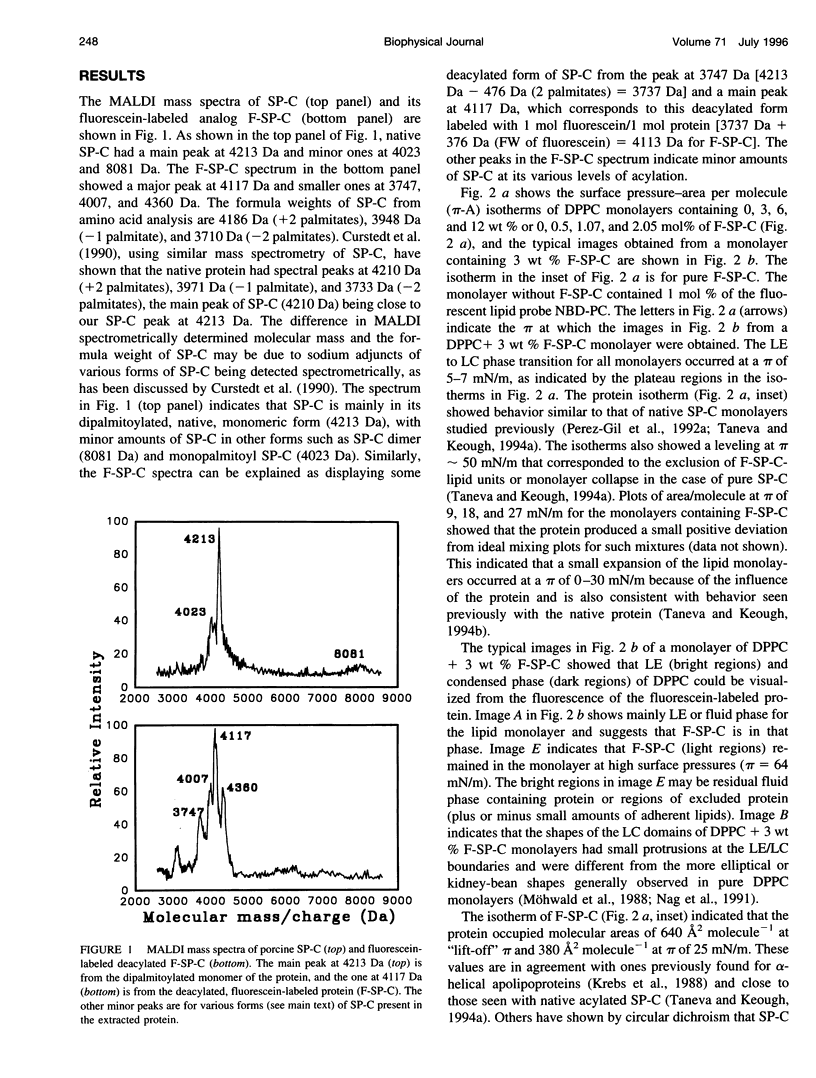
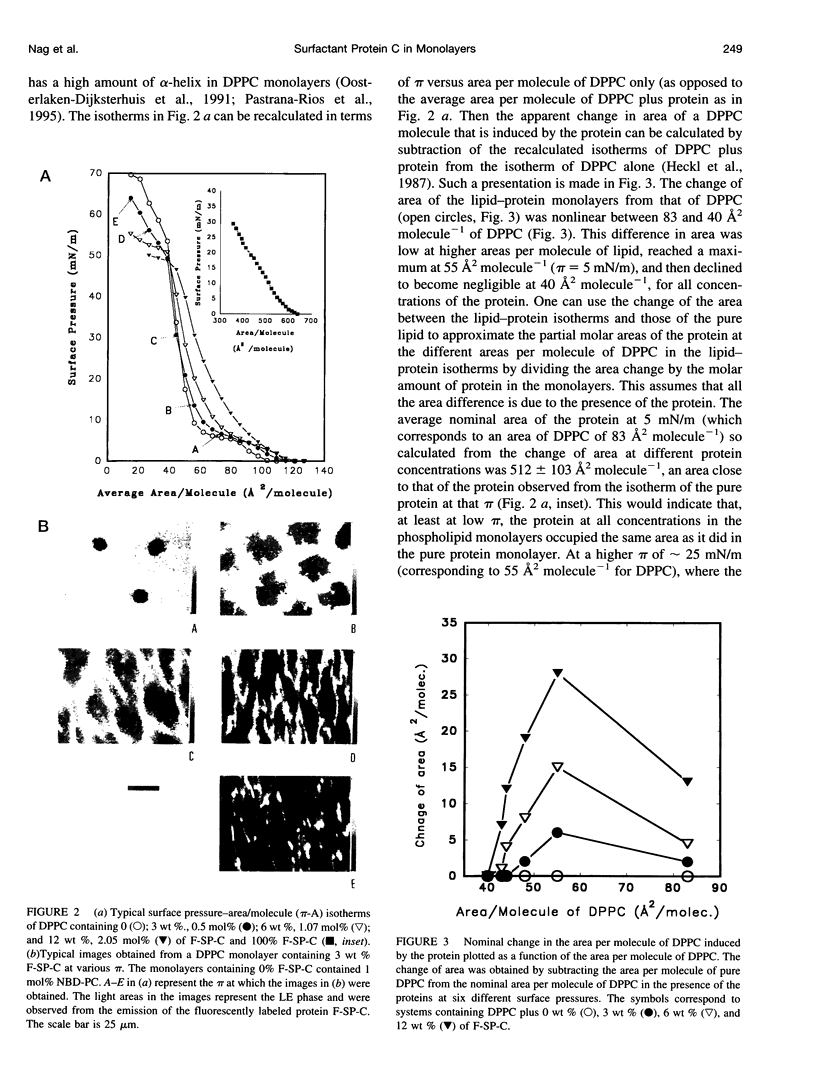
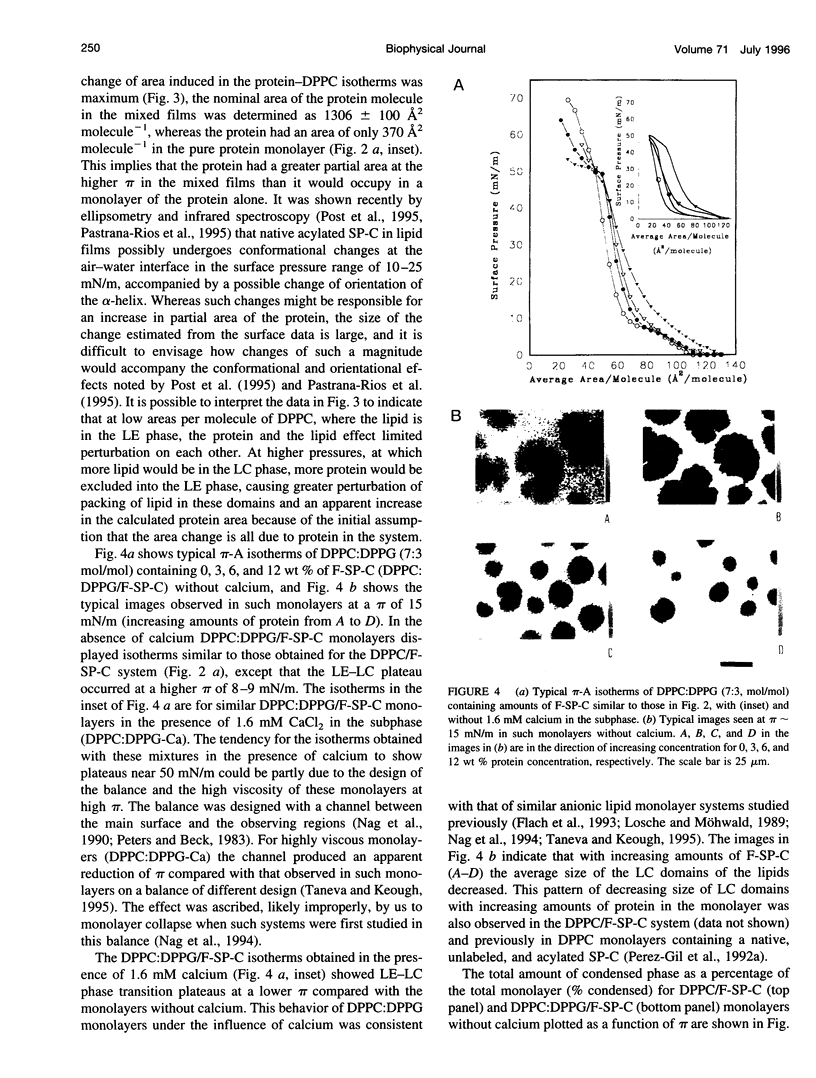
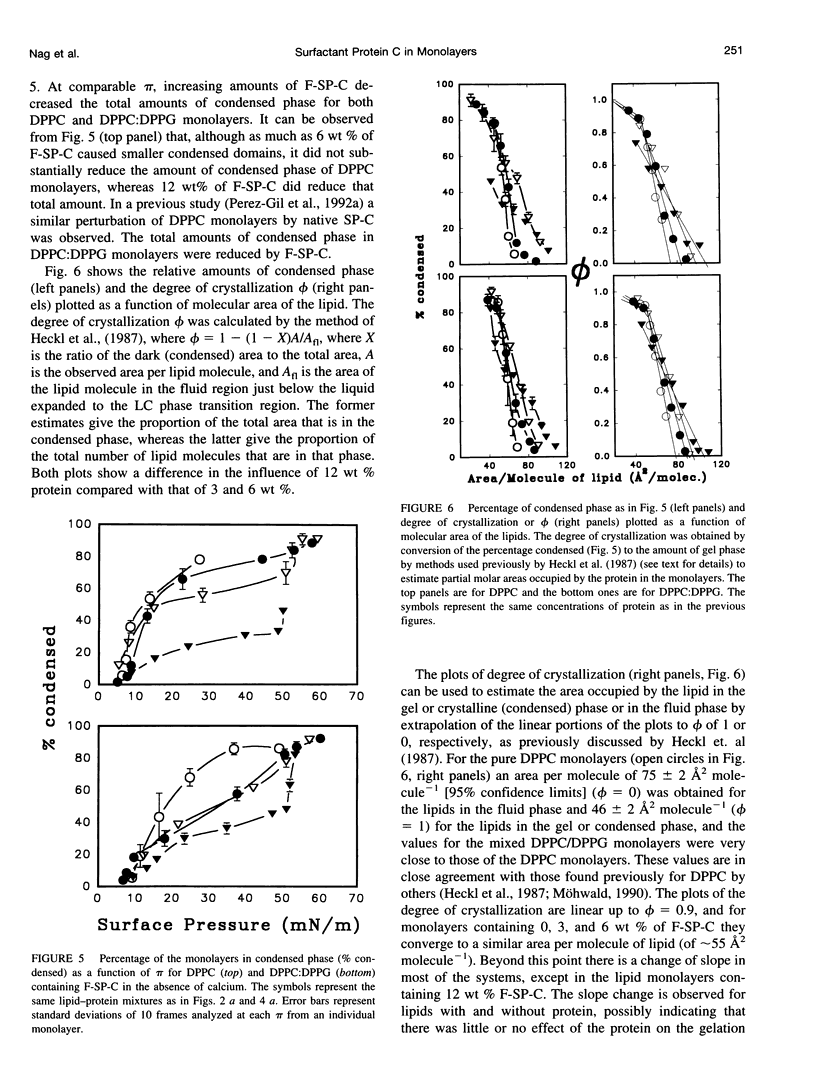
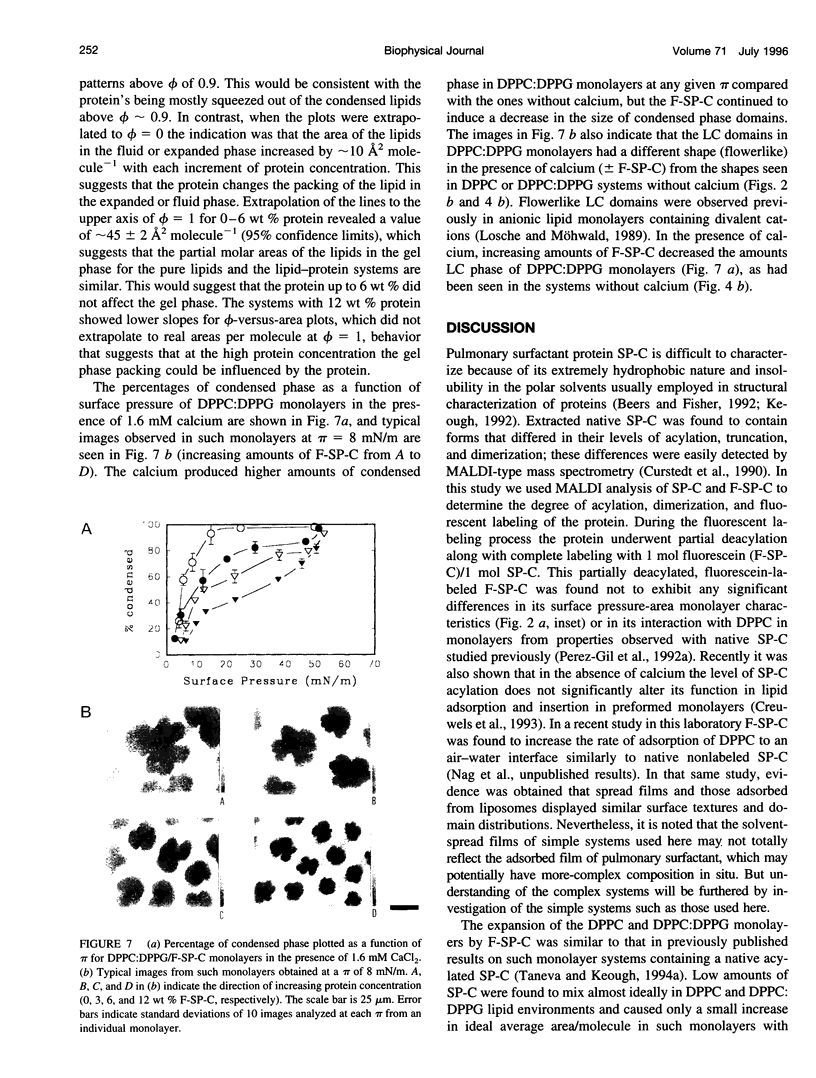




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Müller U., Holenstein C., Heyn M. P. Lateral segregation of proteins induced by cholesterol in bacteriorhodopsin-phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 15;596(1):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90179-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey T. R., Huang E. C., Henion J. D. Structural characterization of protein tryptic peptides via liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry and collision-induced dissociation of their doubly charged molecular ions. Anal Chem. 1991 Jul 1;63(13):1193–1200. doi: 10.1021/ac00013a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creuwels L. A., Demel R. A., van Golde L. M., Benson B. J., Haagsman H. P. Effect of acylation on structure and function of surfactant protein C at the air-liquid interface. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26752–26758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserhåti T., Szögyi M. Interaction of phospholipids with proteins and peptides. New advances IV. Int J Biochem. 1994 Jan;26(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(94)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curstedt T., Johansson J., Persson P., Eklund A., Robertson B., Löwenadler B., Jörnvall H. Hydrophobic surfactant-associated polypeptides: SP-C is a lipopeptide with two palmitoylated cysteine residues, whereas SP-B lacks covalently linked fatty acyl groups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2985–2989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flach C. R., Brauner J. W., Mendelsohn R. Calcium ion interactions with insoluble phospholipid monolayer films at the A/W interface. External reflection-absorption IR studies. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):1994–2001. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81276-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawgood S., Shiffer K. Structures and properties of the surfactant-associated proteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:375–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckl W. M., Zaba B. N., Möhwald H. Interactions of cytochromes b5 and c with phospholipid monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 18;903(1):166–176. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90166-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz A. D., Baatz J. E., Whitsett J. A. Lipid effects on aggregation of pulmonary surfactant protein SP-C studied by fluorescence energy transfer. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 21;32(37):9513–9523. doi: 10.1021/bi00088a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz A. D., Elledge B., Whitsett J. A., Baatz J. E. Effects of lung surfactant proteolipid SP-C on the organization of model membrane lipids: a fluorescence study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jun 11;1107(1):44–54. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90327-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibdah J. A., Lund-Katz S., Phillips M. C. Molecular packing of high-density and low-density lipoprotein surface lipids and apolipoprotein A-I binding. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1126–1133. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson J., Curstedt T., Robertson B. The proteins of the surfactant system. Eur Respir J. 1994 Feb;7(2):372–391. doi: 10.1183/09031936.94.07020372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson J., Szyperski T., Curstedt T., Wüthrich K. The NMR structure of the pulmonary surfactant-associated polypeptide SP-C in an apolar solvent contains a valyl-rich alpha-helix. Biochemistry. 1994 May 17;33(19):6015–6023. doi: 10.1021/bi00185a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller A., Eistetter H. R., Voss T., Schäfer K. P. The pulmonary surfactant protein C (SP-C) precursor is a type II transmembrane protein. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 15;277(Pt 2):493–499. doi: 10.1042/bj2770493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keough K. M., Kariel N. Differential scanning calorimetric studies of aqueous dispersions of phosphatidylcholines containing two polyenoic chains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 7;902(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleemann W., McConnell H. M. Interactions of proteins and cholesterol with lipids in bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 21;419(2):206–222. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90347-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs K. E., Ibdah J. A., Phillips M. C. A comparison of the surface activities of human apolipoproteins A-I and A-II at the air/water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 15;959(3):229–237. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs K. E., Phillips M. C. The helical hydrophobic moments and surface activities of serum apolipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Nov 29;754(2):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90165-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krill S. L., Gupta S. L. Effect of a bovine lung surfactant protein isolate (SP-B/C) on egg phosphatidylglycerol acyl chain order in a lipid mixture with dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine and palmitic acid. J Pharm Sci. 1994 Apr;83(4):539–541. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600830418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leckband D. E., Helm C. A., Israelachvili J. Role of calcium in the adhesion and fusion of bilayers. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 2;32(4):1127–1140. doi: 10.1021/bi00055a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow M. R., Taneva S., Simatos G. A., Allwood L. A., Keough K. M. 2H NMR studies of the effect of pulmonary surfactant SP-C on the 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine headgroup: a model for transbilayer peptides in surfactant and biological membranes. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 26;32(42):11338–11344. doi: 10.1021/bi00093a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhwald H. Phospholipid and phospholipid-protein monolayers at the air/water interface. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 1990;41:441–476. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pc.41.100190.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag K., Boland C., Rich N., Keough K. M. Epifluorescence microscopic observation of monolayers of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine: dependence of domain size on compression rates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Sep 30;1068(2):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90204-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag K., Keough K. M. Epifluorescence microscopic studies of monolayers containing mixtures of dioleoyl- and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholines. Biophys J. 1993 Sep;65(3):1019–1026. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81155-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notter R. H., Shapiro D. L., Ohning B., Whitsett J. A. Biophysical activity of synthetic phospholipids combined with purified lung surfactant 6000 dalton apoprotein. Chem Phys Lipids. 1987 Jun;44(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(87)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastrana-Rios B., Taneva S., Keough K. M., Mautone A. J., Mendelsohn R. External reflection absorption infrared spectroscopy study of lung surfactant proteins SP-B and SP-C in phospholipid monolayers at the air/water interface. Biophys J. 1995 Dec;69(6):2531–2540. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80124-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R., Beck K. Translational diffusion in phospholipid monolayers measured by fluorescence microphotolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7183–7187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Possmayer F. A proposed nomenclature for pulmonary surfactant-associated proteins. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Oct;138(4):990–998. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.4.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post A., Nahmen A. V., Schmitt M., Ruths J., Riegler H., Sieber M., Galla H. J. Pulmonary surfactant protein C containing lipid films at the air-water interface as a model for the surface of lung alveoli. Mol Membr Biol. 1995 Jan-Mar;12(1):93–99. doi: 10.3109/09687689509038502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Gil J., Cruz A., Casals C. Solubility of hydrophobic surfactant proteins in organic solvent/water mixtures. Structural studies on SP-B and SP-C in aqueous organic solvents and lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jul 1;1168(3):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(93)90181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Gil J., López-Lacomba J. L., Cruz A., Beldarraín A., Casals C. Deacylated pulmonary surfactant protein SP-C has different effects on the thermotropic behaviour of bilayers of dipalmitoylphosphatidyl-glycerol (DPPG) than the native acylated protein. Biochem Soc Trans. 1994 Aug;22(3):372S–372S. doi: 10.1042/bst022372s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Gil J., Nag K., Taneva S., Keough K. M. Pulmonary surfactant protein SP-C causes packing rearrangements of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine in spread monolayers. Biophys J. 1992 Jul;63(1):197–204. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81582-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Gil J., Tucker J., Simatos G., Keough K. M. Interfacial adsorption of simple lipid mixtures combined with hydrophobic surfactant protein from pig lung. Biochem Cell Biol. 1992 May;70(5):332–338. doi: 10.1139/o92-051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schürch S., Goerke J., Clements J. A. Direct determination of surface tension in the lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4698–4702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiffer K., Hawgood S., Düzgünes N., Goerke J. Interactions of the low molecular weight group of surfactant-associated proteins (SP 5-18) with pulmonary surfactant lipids. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2689–2695. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiffer K., Hawgood S., Haagsman H. P., Benson B., Clements J. A., Goerke J. Lung surfactant proteins, SP-B and SP-C, alter the thermodynamic properties of phospholipid membranes: a differential calorimetry study. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 19;32(2):590–597. doi: 10.1021/bi00053a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signor G., Mammi S., Peggion E., Ringsdorf H., Wagenknecht A. Interaction of bombolitin III with phospholipid monolayers and liposomes and effect on the activity of phospholipase A2. Biochemistry. 1994 May 31;33(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1021/bi00187a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simatos G. A., Forward K. B., Morrow M. R., Keough K. M. Interaction between perdeuterated dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine and low molecular weight pulmonary surfactant protein SP-C. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5807–5814. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi A., Fujiwara T. Proteolipid in bovine lung surfactant: its role in surfactant function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):527–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taneva S. G., Keough K. M. Calcium ions and interactions of pulmonary surfactant proteins SP-B and SP-C with phospholipids in spread monolayers at the air/water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 May 24;1236(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(95)00046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taneva S. G., Keough K. M. Dynamic surface properties of pulmonary surfactant proteins SP-B and SP-C and their mixtures with dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry. 1994 Dec 13;33(49):14660–14670. doi: 10.1021/bi00253a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taneva S., Keough K. M. Pulmonary surfactant proteins SP-B and SP-C in spread monolayers at the air-water interface: II. Monolayers of pulmonary surfactant protein SP-C and phospholipids. Biophys J. 1994 Apr;66(4):1149–1157. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80896-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbussche G., Clercx A., Curstedt T., Johansson J., Jörnvall H., Ruysschaert J. M. Structure and orientation of the surfactant-associated protein C in a lipid bilayer. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jan 15;203(1-2):201–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb19848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. C., Hawgood S., Hamilton R. L. Changes in lipid structure produced by surfactant proteins SP-A, SP-B, and SP-C. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Jul;5(1):41–50. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. H., Possmayer F. Comparative studies on the biophysical activities of the low-molecular-weight hydrophobic proteins purified from bovine pulmonary surfactant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Aug 12;961(3):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jongh H. H., Goormaghtigh E., Killian J. A. Analysis of circular dichroism spectra of oriented protein-lipid complexes: toward a general application. Biochemistry. 1994 Dec 6;33(48):14521–14528. doi: 10.1021/bi00252a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]