Abstract
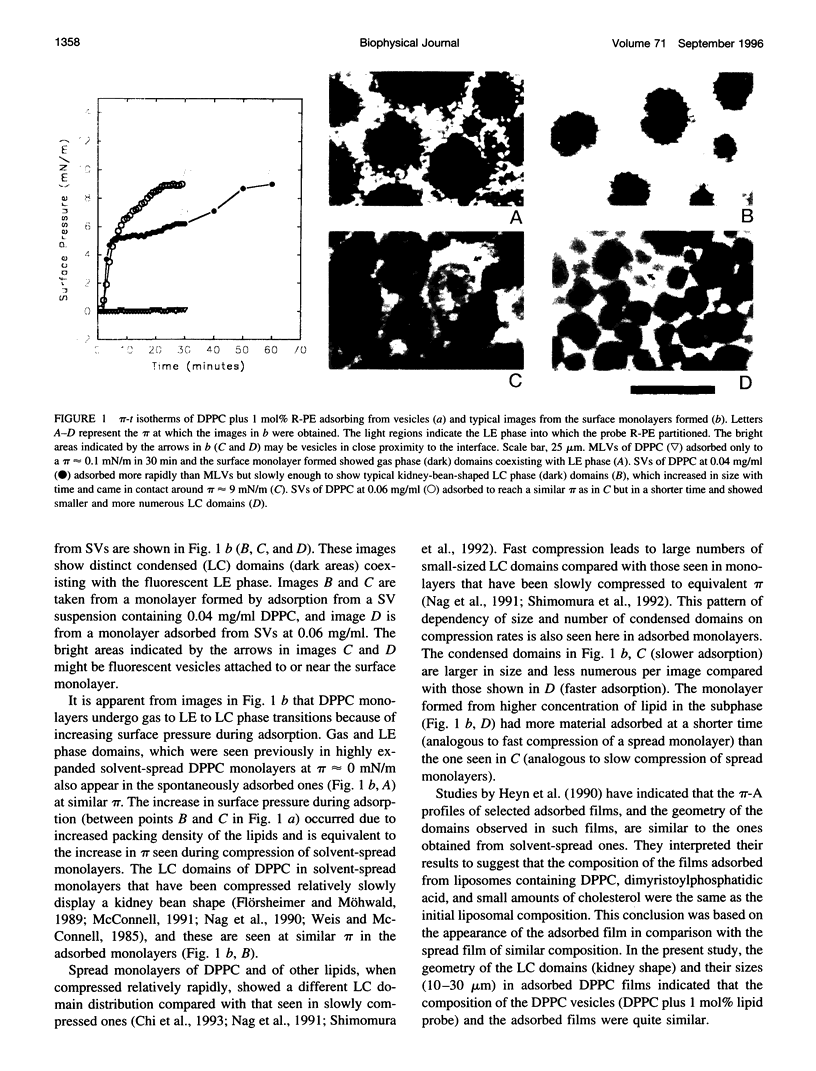
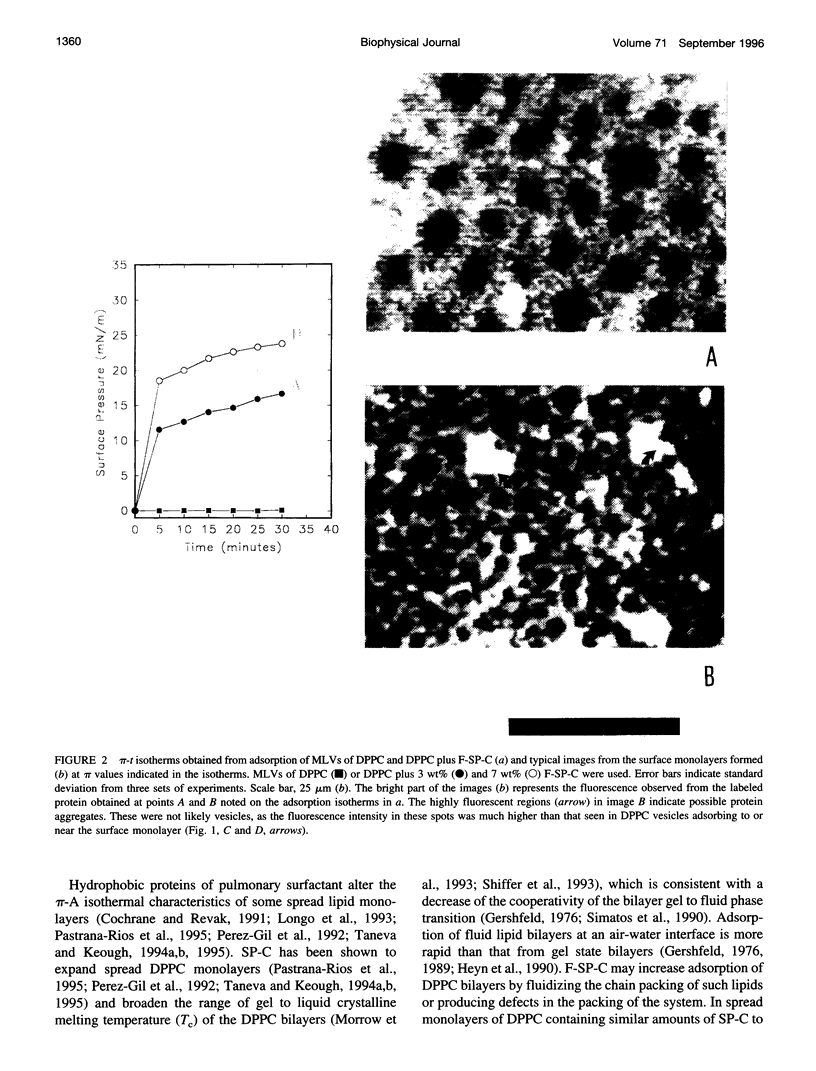
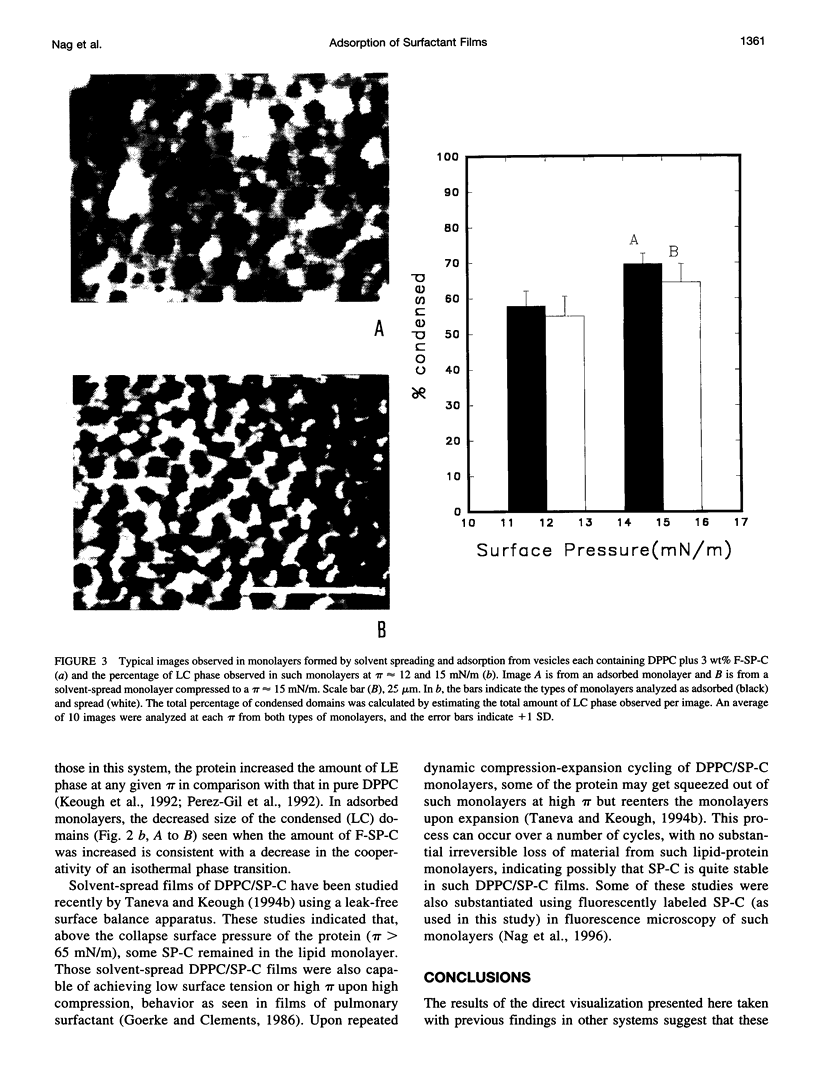
Spread and adsorbed monolayers of lipid-protein mixtures have served as models for biomembranes and pulmonary surfactant, but their similarity was unclear. Epifluorescence microscopy of monolayers spontaneously adsorbed from vesicles of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine or dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine plus surfactant protein C (SP-C) showed gas, liquid expanded, and liquid condensed (LC) domains. The shapes and distribution of LC domains in the adsorbed and solvent-spread monolayers were quite similar. Labeled SP-C adsorbed into the air-water interface in the company of the lipids. In both forms of monolayers, SP-C occupied the fluid phase and reduced the size and amount of the LC domains. The properties suggest that these adsorbed and spread monolayers are analogous to one another.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chi L. F., Anders M., Fuchs H., Johnston R. R., Ringsdorf H. Domain structures in langmuir-blodgett films investigated by atomic force microscopy. Science. 1993 Jan 8;259(5092):213–216. doi: 10.1126/science.259.5092.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Revak S. D. Pulmonary surfactant protein B (SP-B): structure-function relationships. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):566–568. doi: 10.1126/science.1948032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey T. R., Huang E. C., Henion J. D. Structural characterization of protein tryptic peptides via liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry and collision-induced dissociation of their doubly charged molecular ions. Anal Chem. 1991 Jul 1;63(13):1193–1200. doi: 10.1021/ac00013a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curstedt T., Johansson J., Persson P., Eklund A., Robertson B., Löwenadler B., Jörnvall H. Hydrophobic surfactant-associated polypeptides: SP-C is a lipopeptide with two palmitoylated cysteine residues, whereas SP-B lacks covalently linked fatty acyl groups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2985–2989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curstedt T., Jörnvall H., Robertson B., Bergman T., Berggren P. Two hydrophobic low-molecular-mass protein fractions of pulmonary surfactant. Characterization and biophysical activity. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Oct 15;168(2):255–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flörsheimer M., Möhwald H. Development of equilibrium domain shapes in phospholipid monolayers. Chem Phys Lipids. 1989 Mar;49(4):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(89)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershfeld N. L. The critical unilamellar lipid state: a perspective for membrane bilayer assembly. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 6;988(3):335–350. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F. Lipid exchange between membranes. Biophys J. 1984 Dec;46(6):687–694. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84067-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo M. L., Bisagno A. M., Zasadzinski J. A., Bruni R., Waring A. J. A function of lung surfactant protein SP-B. Science. 1993 Jul 23;261(5120):453–456. doi: 10.1126/science.8332910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow M. R., Taneva S., Simatos G. A., Allwood L. A., Keough K. M. 2H NMR studies of the effect of pulmonary surfactant SP-C on the 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine headgroup: a model for transbilayer peptides in surfactant and biological membranes. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 26;32(42):11338–11344. doi: 10.1021/bi00093a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhwald H. Phospholipid and phospholipid-protein monolayers at the air/water interface. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 1990;41:441–476. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pc.41.100190.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag K., Boland C., Rich N., Keough K. M. Epifluorescence microscopic observation of monolayers of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine: dependence of domain size on compression rates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Sep 30;1068(2):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90204-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag K., Keough K. M. Epifluorescence microscopic studies of monolayers containing mixtures of dioleoyl- and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholines. Biophys J. 1993 Sep;65(3):1019–1026. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81155-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastrana-Rios B., Taneva S., Keough K. M., Mautone A. J., Mendelsohn R. External reflection absorption infrared spectroscopy study of lung surfactant proteins SP-B and SP-C in phospholipid monolayers at the air/water interface. Biophys J. 1995 Dec;69(6):2531–2540. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80124-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattus F., Rothen C., Streit M., Zahler P. Structure, composition, enzymatic activities of human erythrocyte and sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane films. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 21;647(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Gil J., Cruz A., Casals C. Solubility of hydrophobic surfactant proteins in organic solvent/water mixtures. Structural studies on SP-B and SP-C in aqueous organic solvents and lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jul 1;1168(3):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(93)90181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Gil J., Nag K., Taneva S., Keough K. M. Pulmonary surfactant protein SP-C causes packing rearrangements of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine in spread monolayers. Biophys J. 1992 Jul;63(1):197–204. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81582-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salesse C., Ducharme D., Leblanc R. M. Direct evidence for the formation of a monolayer from a bilayer. An ellipsometric study at the nitrogen-water interface. Biophys J. 1987 Aug;52(2):351–352. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83223-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H. Exchange and interactions between lipid layers at the surface of a liposome solution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 7;555(2):316–336. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90171-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H. Planar lipid-protein membranes: strategies of formation and of detecting dependencies of ion transport functions on membrane conditions. Methods Enzymol. 1989;171:225–253. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)71014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schürholz T., Schindler H. Lipid-protein surface films generated from membrane vesicles: selfassembly, composition, and film structure. Eur Biophys J. 1991;20(2):71–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00186255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiffer K., Hawgood S., Düzgünes N., Goerke J. Interactions of the low molecular weight group of surfactant-associated proteins (SP 5-18) with pulmonary surfactant lipids. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2689–2695. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiffer K., Hawgood S., Haagsman H. P., Benson B., Clements J. A., Goerke J. Lung surfactant proteins, SP-B and SP-C, alter the thermodynamic properties of phospholipid membranes: a differential calorimetry study. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 19;32(2):590–597. doi: 10.1021/bi00053a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simatos G. A., Forward K. B., Morrow M. R., Keough K. M. Interaction between perdeuterated dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine and low molecular weight pulmonary surfactant protein SP-C. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5807–5814. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stine K. J. Investigations of monolayers by fluorescence microscopy. Microsc Res Tech. 1994 Apr 1;27(5):439–450. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1070270510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi A., Fujiwara T. Proteolipid in bovine lung surfactant: its role in surfactant function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):527–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taneva S. G., Keough K. M. Calcium ions and interactions of pulmonary surfactant proteins SP-B and SP-C with phospholipids in spread monolayers at the air/water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 May 24;1236(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(95)00046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taneva S. G., Keough K. M. Dynamic surface properties of pulmonary surfactant proteins SP-B and SP-C and their mixtures with dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry. 1994 Dec 13;33(49):14660–14670. doi: 10.1021/bi00253a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taneva S., Keough K. M. Pulmonary surfactant proteins SP-B and SP-C in spread monolayers at the air-water interface: II. Monolayers of pulmonary surfactant protein SP-C and phospholipids. Biophys J. 1994 Apr;66(4):1149–1157. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80896-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. C., Hawgood S., Hamilton R. L. Changes in lipid structure produced by surfactant proteins SP-A, SP-B, and SP-C. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Jul;5(1):41–50. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodle M. C., Papahadjopoulos D. Liposome preparation and size characterization. Methods Enzymol. 1989;171:193–217. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)71012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. H., Possmayer F. Role of bovine pulmonary surfactant-associated proteins in the surface-active property of phospholipid mixtures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Oct 1;1046(3):233–241. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90236-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]