Abstract
Quantal release, incremental detection, and oscillations are three types of Ca2+ responses that can be obtained in different conditions, after stimulation of the intracellular Ca2+ stores by submaximum concentrations of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (InsP3). All three phenomena are thought to occur through the regulatory properties of the InsP3 receptor/Ca2+ channel. In the present study, we perform further analysis of the model (Swillens et al., 1994, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 91:10074-10078) previously proposed for transient InsP3-induced Ca2+ release, based on the bell-shaped dependence of the InsP3 receptor activity on the Ca2+ level and on the existence of an intermediate Ca2+ domain located around the mouth of the channel. We show that Ca2+ oscillations also arise in the latter model. Conditions for the occurrence of the various behaviors are investigated. Numerical simulations also show that the existence of an intermediate Ca2+ domain can markedly increase the period of oscillations. Periods on the order of 1 min can indeed be accounted for by the model when one assigns realistic values to the kinetic constants of the InsP3 receptor, which, in the absence of a domain, lead to oscillations with periods of a few seconds. Finally, theoretical support in favor of a positive cooperativity in the regulation of the InsP3 receptor by Ca2+ is presented.
Full text
PDF

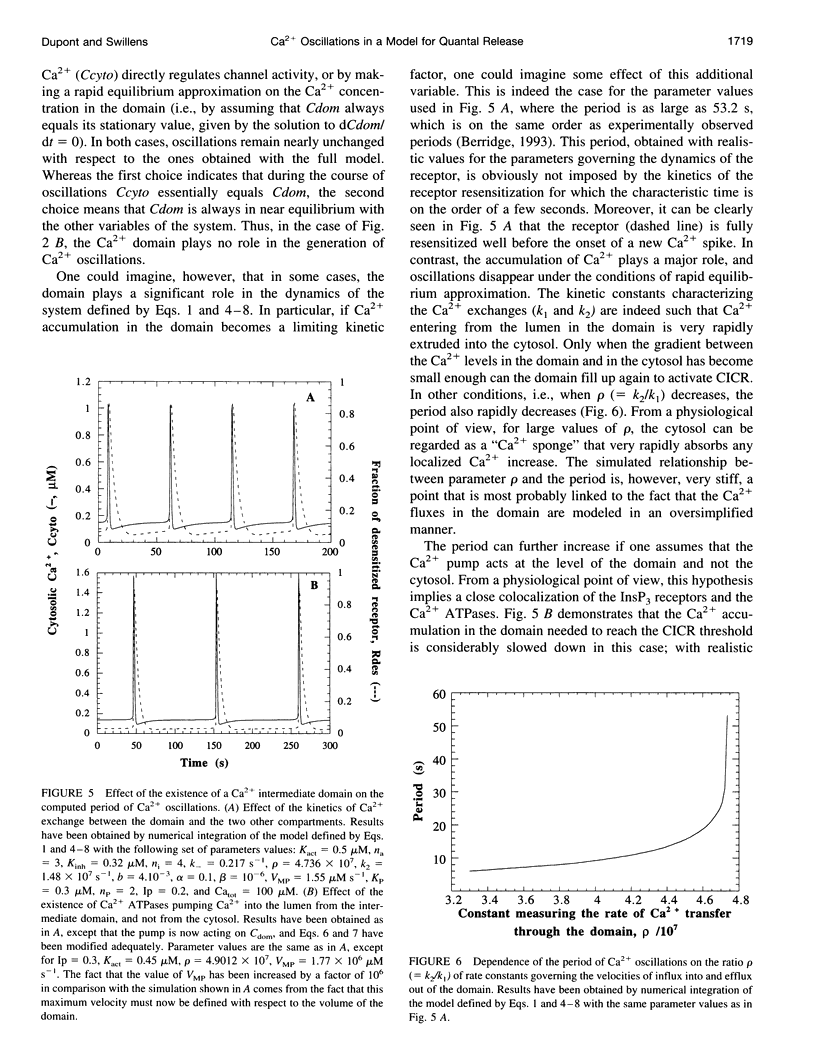
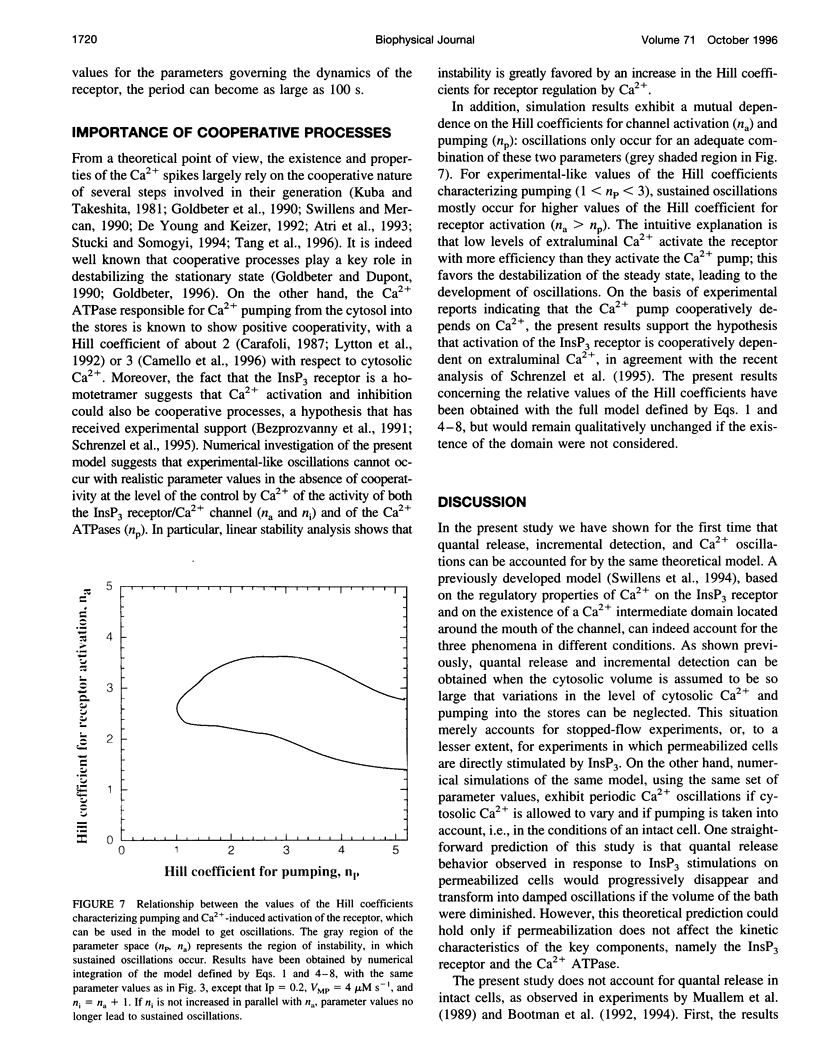


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atri A., Amundson J., Clapham D., Sneyd J. A single-pool model for intracellular calcium oscillations and waves in the Xenopus laevis oocyte. Biophys J. 1993 Oct;65(4):1727–1739. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81191-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dupont G. Spatial and temporal signalling by calcium. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;6(2):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Galione A. Cytosolic calcium oscillators. FASEB J. 1988 Dec;2(15):3074–3082. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.15.2847949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezprozvanny I., Watras J., Ehrlich B. E. Bell-shaped calcium-response curves of Ins(1,4,5)P3- and calcium-gated channels from endoplasmic reticulum of cerebellum. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):751–754. doi: 10.1038/351751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bootman M. D., Berridge M. J., Taylor C. W. All-or-nothing Ca2+ mobilization from the intracellular stores of single histamine-stimulated HeLa cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:163–178. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bootman M. D., Berridge M. J. The elemental principles of calcium signaling. Cell. 1995 Dec 1;83(5):675–678. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bootman M. D., Cheek T. R., Moreton R. B., Bennett D. L., Berridge M. J. Smoothly graded Ca2+ release from inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ stores. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24783–24791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camello P., Gardner J., Petersen O. H., Tepikin A. V. Calcium dependence of calcium extrusion and calcium uptake in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. J Physiol. 1996 Feb 1;490(Pt 3):585–593. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. Intracellular calcium homeostasis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:395–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combettes L., Claret M., Champeil P. Calcium control on InsP3-induced discharge of calcium from permeabilised hepatocyte pools. Cell Calcium. 1993 Apr;14(4):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(93)90049-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combettes L., Claret M., Champeil P. Do submaximal InsP3 concentrations only induce the partial discharge of permeabilized hepatocyte calcium pools because of the concomitant reduction of intraluminal Ca2+ concentration? FEBS Lett. 1992 Apr 27;301(3):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80258-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combettes L., Hannaert-Merah Z., Coquil J. F., Rousseau C., Claret M., Swillens S., Champeil P. Rapid filtration studies of the effect of cytosolic Ca2+ on inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced 45Ca2+ release from cerebellar microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 1;269(26):17561–17571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Young G. W., Keizer J. A single-pool inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-receptor-based model for agonist-stimulated oscillations in Ca2+ concentration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9895–9899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont G., Goldbeter A. Oscillations and waves of cytosolic calcium: insights from theoretical models. Bioessays. 1992 Jul;14(7):485–493. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont G., Goldbeter A. Properties of intracellular Ca2+ waves generated by a model based on Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release. Biophys J. 1994 Dec;67(6):2191–2204. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80705-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M., Iino M. Properties of calcium release channels of the intracellular calcium store in muscle cells. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1990;24:122–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Contractions induced by a calcium-triggered release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of single skinned cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;249(3):469–495. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favre C. J., Jerström P., Foti M., Stendhal O., Huggler E., Lew D. P., Krause K. H. Organization of Ca2+ stores in myeloid cells: association of SERCA2b and the type-1 inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. Biochem J. 1996 May 15;316(Pt 1):137–142. doi: 10.1042/bj3160137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch E. A., Turner T. J., Goldin S. M. Calcium as a coagonist of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):443–446. doi: 10.1126/science.2017683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbeter A., Dupont G. Allosteric regulation, cooperativity, and biochemical oscillations. Biophys Chem. 1990 Aug 31;37(1-3):341–353. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(90)88033-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbeter A., Dupont G., Berridge M. J. Minimal model for signal-induced Ca2+ oscillations and for their frequency encoding through protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1461–1465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne J. H., Meyer T. Luminal calcium regulates the inositol trisphosphate receptor of rat basophilic leukemia cells at a cytosolic site. Biochemistry. 1995 Oct 3;34(39):12738–12746. doi: 10.1021/bi00039a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. 'Quantal' Ca2+ release and the control of Ca2+ entry by inositol phosphates--a possible mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80692-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindman L. A., Meyer T. Use of intracellular Ca2+ stores from rat basophilic leukemia cells to study the molecular mechanism leading to quantal Ca2+ release by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 9;32(5):1270–1277. doi: 10.1021/bi00056a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Takeshita S. Simulation of intracellular Ca2+ oscillation in a sympathetic neurone. J Theor Biol. 1981 Dec 21;93(4):1009–1031. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(81)90352-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytton J., Westlin M., Burk S. E., Shull G. E., MacLennan D. H. Functional comparisons between isoforms of the sarcoplasmic or endoplasmic reticulum family of calcium pumps. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14483–14489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Stryer L. Calcium spiking. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:153–174. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Stryer L. Transient calcium release induced by successive increments of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3841–3845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muallem S., Pandol S. J., Beeker T. G. Hormone-evoked calcium release from intracellular stores is a quantal process. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):205–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier M. F., Bird G. S., Putney J. W., Jr Subcellular distribution of the calcium-storing inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive organelle in rat liver. Possible linkage to the plasma membrane through the actin microfilaments. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 15;274(Pt 3):643–650. doi: 10.1042/bj2740643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrenzel J., Demaurex N., Foti M., Van Delden C., Jacquet J., Mayr G., Lew D. P., Krause K. H. Highly cooperative Ca2+ elevations in response to Ins(1,4,5)P3 microperfusion through a patch-clamp pipette. Biophys J. 1995 Dec;69(6):2378–2391. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80107-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. D., Wagner J., Keizer J. Validity of the rapid buffering approximation near a point source of calcium ions. Biophys J. 1996 Jun;70(6):2527–2539. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79824-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneyd J., Keizer J., Sanderson M. J. Mechanisms of calcium oscillations and waves: a quantitative analysis. FASEB J. 1995 Nov;9(14):1463–1472. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.9.14.7589988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenbergen J. M., Fay F. S. The quantal nature of calcium release to caffeine in single smooth muscle cells results from activation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 26;271(4):1821–1824. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.4.1821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stucki J. W., Somogyi R. A dialogue on Ca2+ oscillations: an attempt to understand the essentials of mechanisms leading to hormone-induced intracellular Ca2+ oscillations in various kinds of cell on a theoretical level. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Jan 4;1183(3):453–472. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(94)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swillens S., Combettes L., Champeil P. Transient inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release: a model based on regulatory Ca(2+)-binding sites along the permeation pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):10074–10078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.10074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swillens S. Dynamic control of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release: a theoretical explanation for the quantal release of Ca2+. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;41(1):110–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swillens S., Mercan D. Computer simulation of a cytosolic calcium oscillator. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 1;271(3):835–838. doi: 10.1042/bj2710835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang Y., Stephenson J. L., Othmer H. G. Simplification and analysis of models of calcium dynamics based on IP3-sensitive calcium channel kinetics. Biophys J. 1996 Jan;70(1):246–263. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79567-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Potter B. V. The size of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ stores depends on inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate concentration. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):189–194. doi: 10.1042/bj2660189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathy A., Meissner G. Sarcoplasmic reticulum lumenal Ca2+ has access to cytosolic activation and inactivation sites of skeletal muscle Ca2+ release channel. Biophys J. 1996 Jun;70(6):2600–2615. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79831-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Calcium channels, stores, and oscillations. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:715–760. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]