Abstract
Ionic ligands can bind to polyelectrolytes such as DNA or charged polysaccharides. We develop a Poisson-Boltzmann treatment to compute binding constants as a function of ligand charge and salt concentration in the limit of low ligand concentration. For flexible chain ligands, such as oligopeptides, we treat their conformations using lattice statistics. The theory predicts the salt dependence and binding free energies, of Mg(2+) ions to polynucleotides, of hexamine cobalt(III) to calf thymus DNA, of polyamines to T7 DNA, of oligolysines to poly(U) and poly(a), and of tripeptides to heparin, a charged polysaccharide. One parameter is required to obtain absolute binding constants, the distance of closest separation of the ligand to the polyion. Some, but not all, of the binding entropies and enthalpies are also predicted accurately by the model.
Full text
PDF


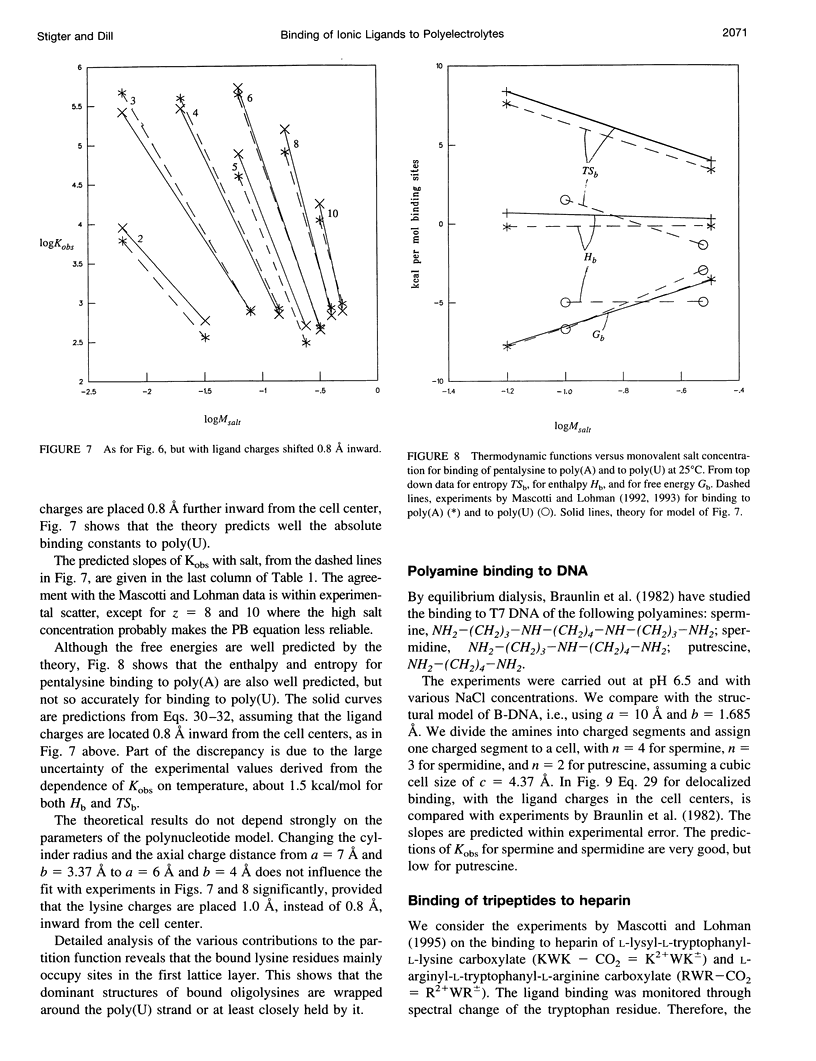
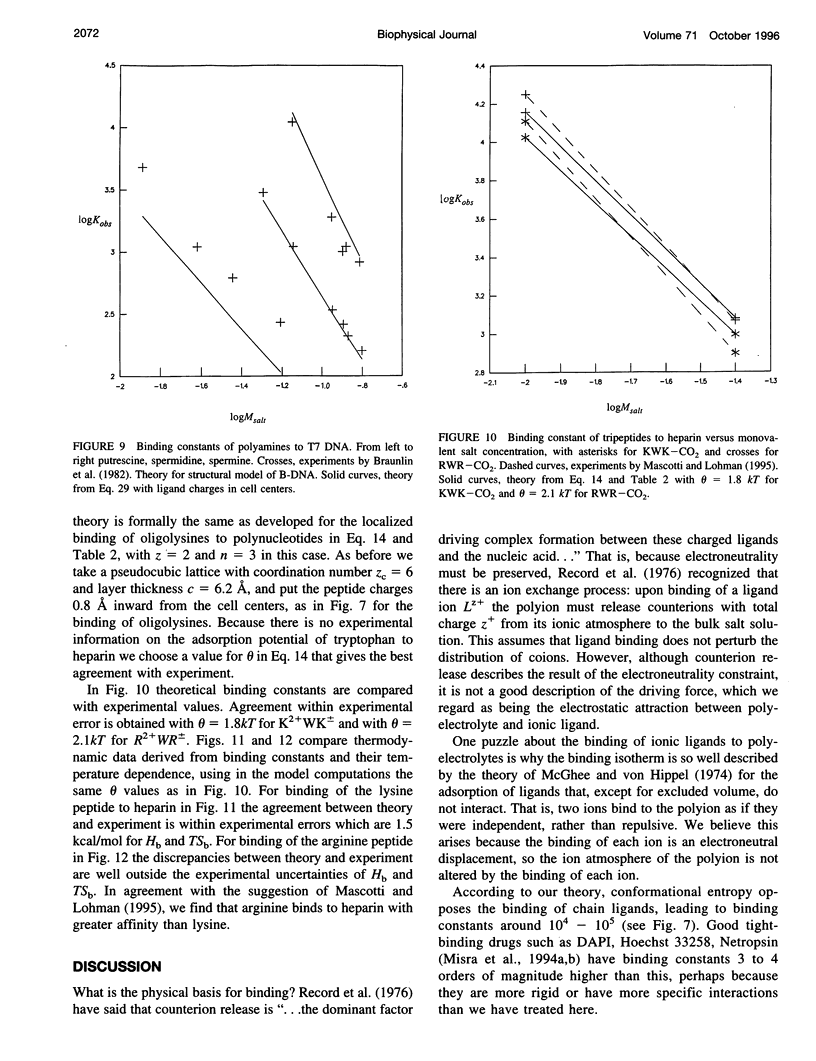
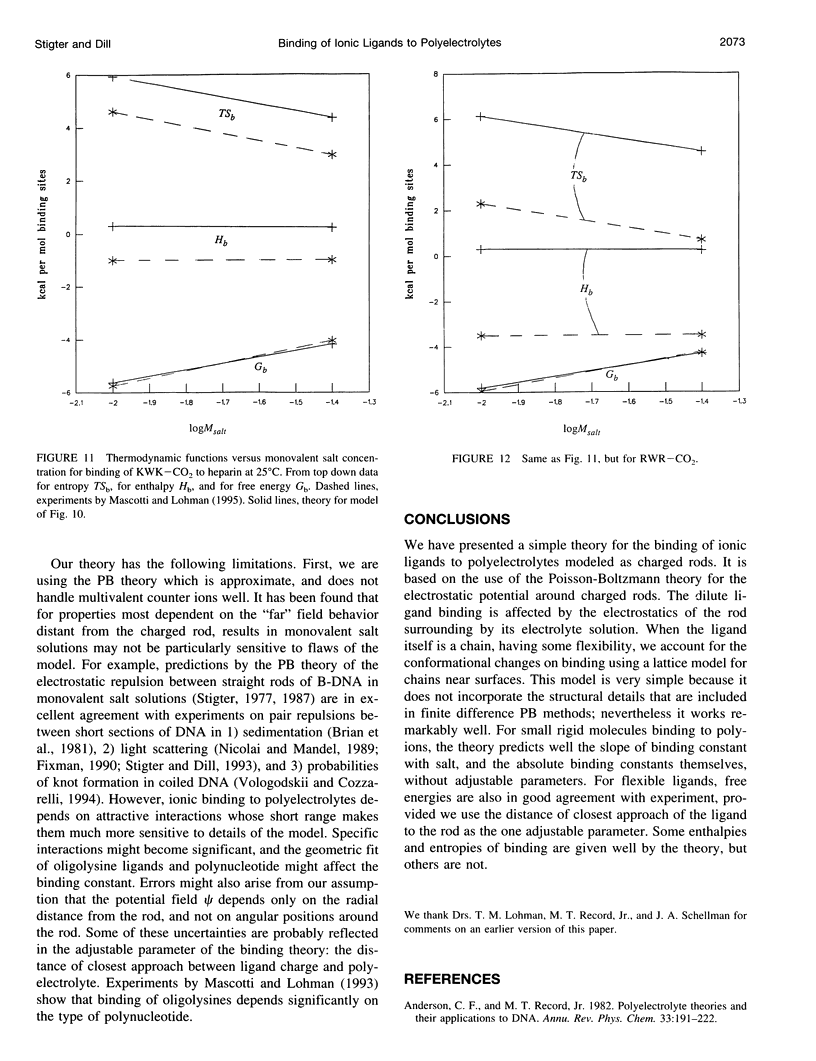

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braunlin W. H., Strick T. J., Record M. T., Jr Equilibrium dialysis studies of polyamine binding to DNA. Biopolymers. 1982 Jul;21(7):1301–1314. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brian A. A., Frisch H. L., Lerman L. S. Thermodynamics and equilibrium sedimentation analysis of the close approach of DNA molecules and a molecular ordering transition. Biopolymers. 1981 Jun;20(6):1305–1328. doi: 10.1002/bip.1981.360200615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dill K. A., Naghizadeh J., Marqusee J. A. Chain molecules at high densities at interfaces. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 1988;39:425–461. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pc.39.100188.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. A., Manning G. S. Polyelectrolyte effects on site-binding equilibria with application to the intercalation of drugs into DNA. Biopolymers. 1984 Dec;23(12):2671–2714. doi: 10.1002/bip.360231202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakauer H. A thermodynamic analysis of the influence of simple mono-and divalent cations on the conformational transitions of polynucleotide complexes. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2579–2589. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakauer H. The binding of Mg++ ions to polyadenylate, polyuridylate, and their complexes. Biopolymers. 1971;10(12):2459–2490. doi: 10.1002/bip.360101209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latt S. A., Sober H. A. Protein-nucleic acid interactions. 3. Cation effect on binding strength and specificity. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3307–3314. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latt S. A., Sober H. A. Protein-nucleic acid interactions. II. Oligopeptide-polyribonucleotide binding studies. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3293–3306. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascotti D. P., Lohman T. M. Thermodynamic extent of counterion release upon binding oligolysines to single-stranded nucleic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3142–3146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascotti D. P., Lohman T. M. Thermodynamics of charged oligopeptide-heparin interactions. Biochemistry. 1995 Mar 7;34(9):2908–2915. doi: 10.1021/bi00009a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascotti D. P., Lohman T. M. Thermodynamics of single-stranded RNA and DNA interactions with oligolysines containing tryptophan. Effects of base composition. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 12;32(40):10568–10579. doi: 10.1021/bi00091a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascotti D. P., Lohman T. M. Thermodynamics of single-stranded RNA binding to oligolysines containing tryptophan. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 22;31(37):8932–8946. doi: 10.1021/bi00152a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., von Hippel P. H. Theoretical aspects of DNA-protein interactions: co-operative and non-co-operative binding of large ligands to a one-dimensional homogeneous lattice. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):469–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V. K., Hecht J. L., Sharp K. A., Friedman R. A., Honig B. Salt effects on protein-DNA interactions. The lambda cI repressor and EcoRI endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 29;238(2):264–280. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V. K., Sharp K. A., Friedman R. A., Honig B. Salt effects on ligand-DNA binding. Minor groove binding antibiotics. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 29;238(2):245–263. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plum G. E., Bloomfield V. A. Equilibrium dialysis study of binding of hexammine cobalt(III) to DNA. Biopolymers. 1988 Jun;27(6):1045–1051. doi: 10.1002/bip.360270611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Lohman M. L., De Haseth P. Ion effects on ligand-nucleic acid interactions. J Mol Biol. 1976 Oct 25;107(2):145–158. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Bourgeois S., Cohn M. The lac repressor-operator interaction. 3. Kinetic studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 14;53(3):401–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Suzuki H., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. I. Equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellman J. A. Electrical double layer, zeta potential, and electrophoretic charge of double-stranded DNA. Biopolymers. 1977 Jul;16(7):1415–1434. doi: 10.1002/bip.1977.360160704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stigter D. Donnan membrane equilibrium, sedimentation equilibrium, and coil expansion of DNA in salt solutions. Cell Biophys. 1987 Dec;11:139–158. doi: 10.1007/BF02797120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stigter D. Evaluation of the counterion condensation theory of polyelectrolytes. Biophys J. 1995 Aug;69(2):380–388. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)79910-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stigter D. Interactions of highly charged colloidal cylinders with applications to double-stranded. Biopolymers. 1977 Jul;16(7):1435–1448. doi: 10.1002/bip.1977.360160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vologodskii A. V., Cozzarelli N. R. Conformational and thermodynamic properties of supercoiled DNA. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1994;23:609–643. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.003141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. W., Rau D. C., Bloomfield V. A. Comparison of polyelectrolyte theories of the binding of cations to DNA. Biophys J. 1980 May;30(2):317–325. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85097-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


