Abstract
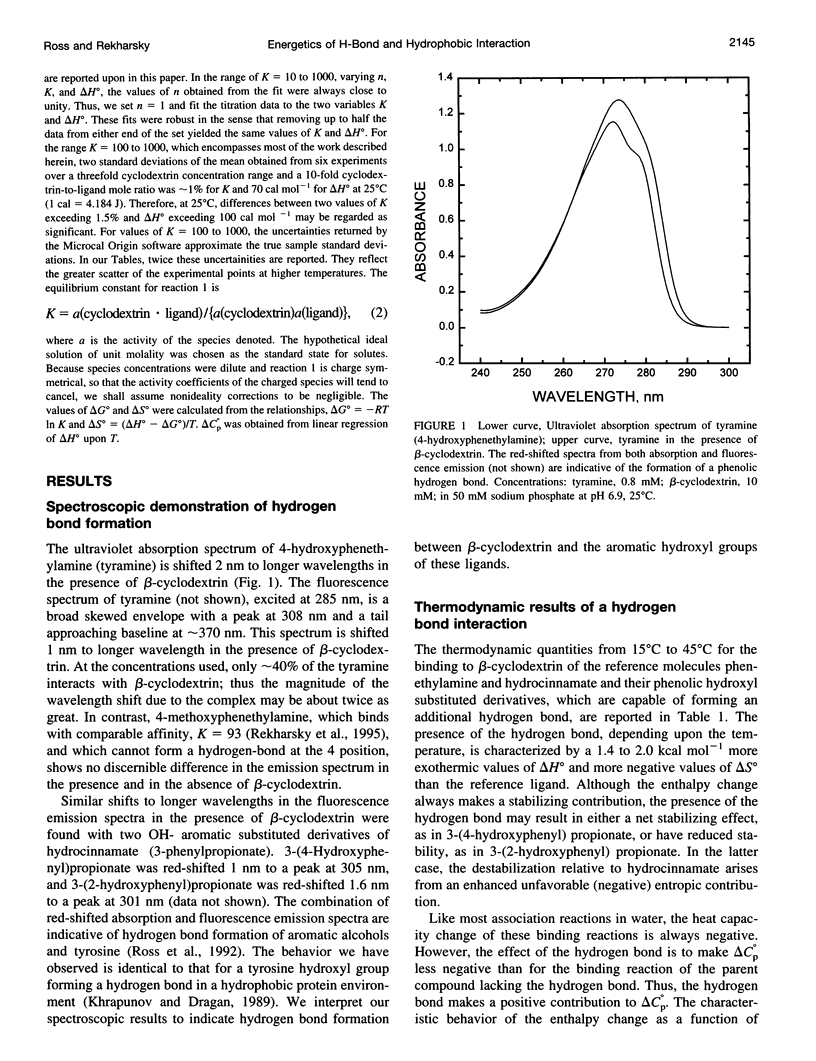
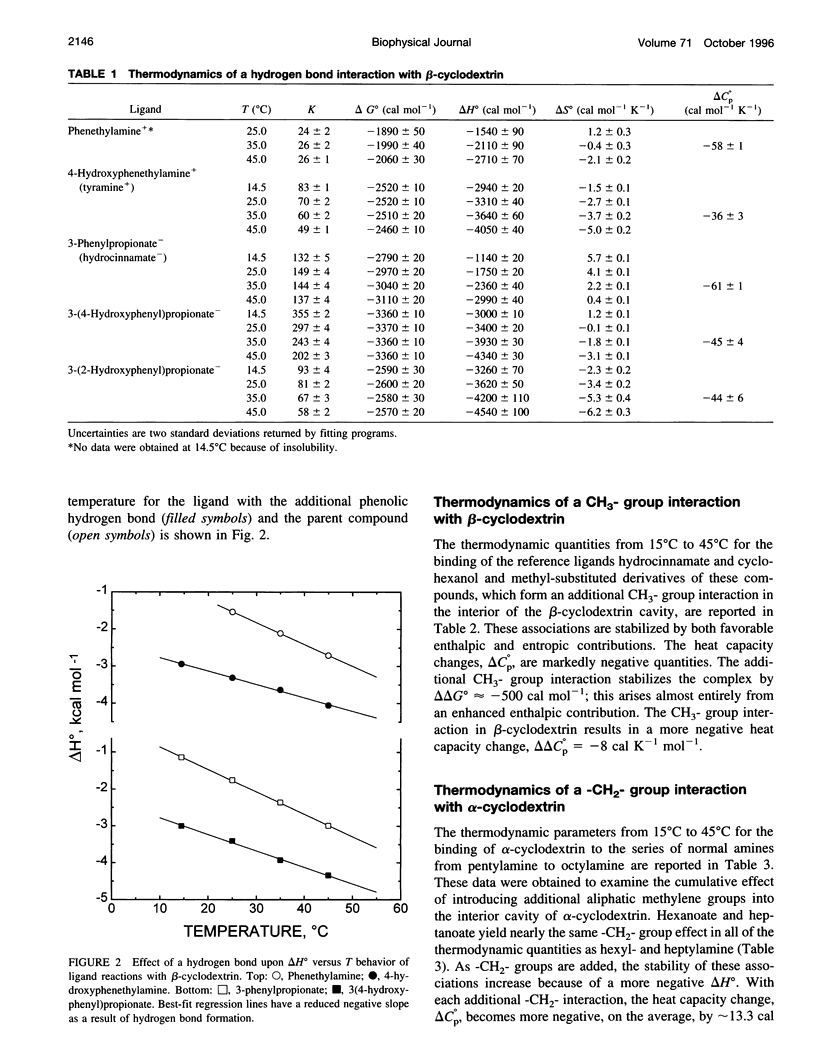
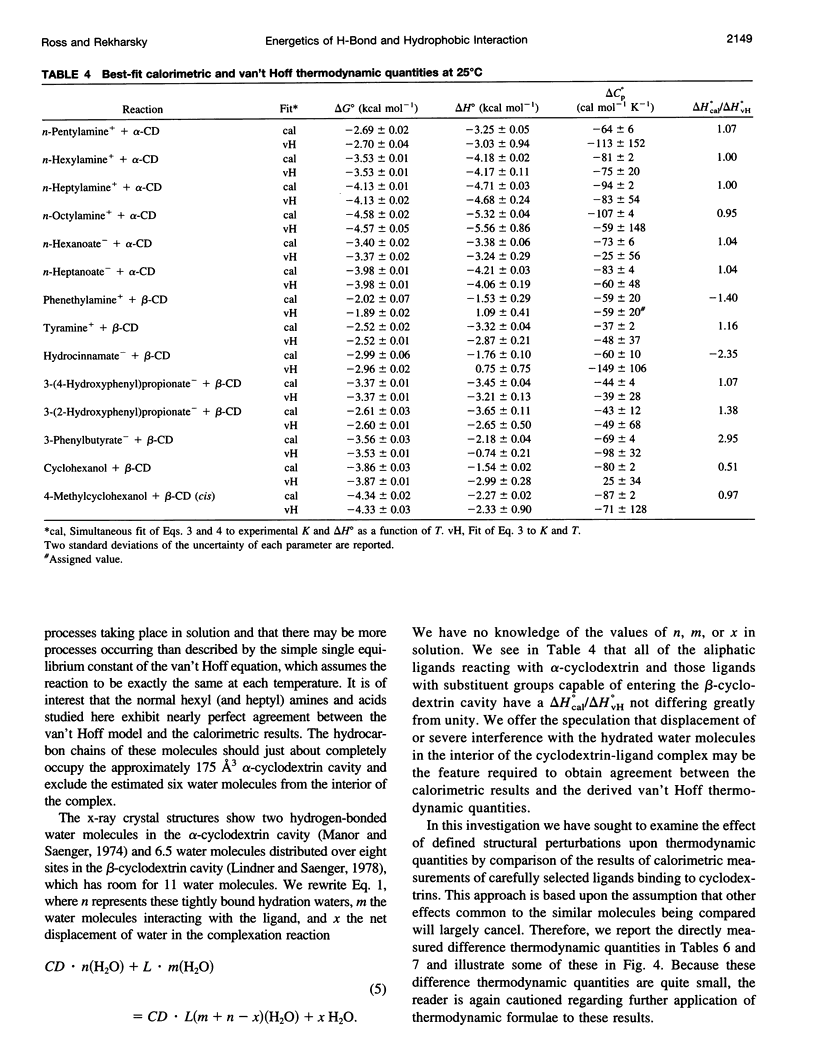
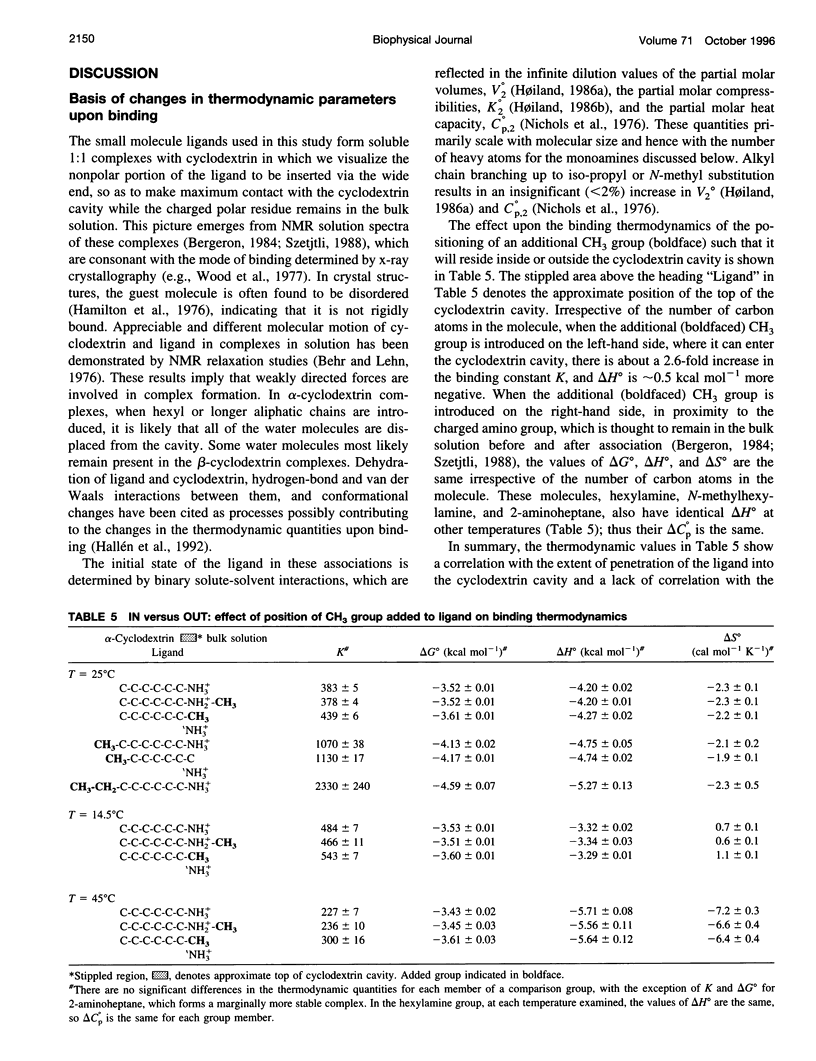
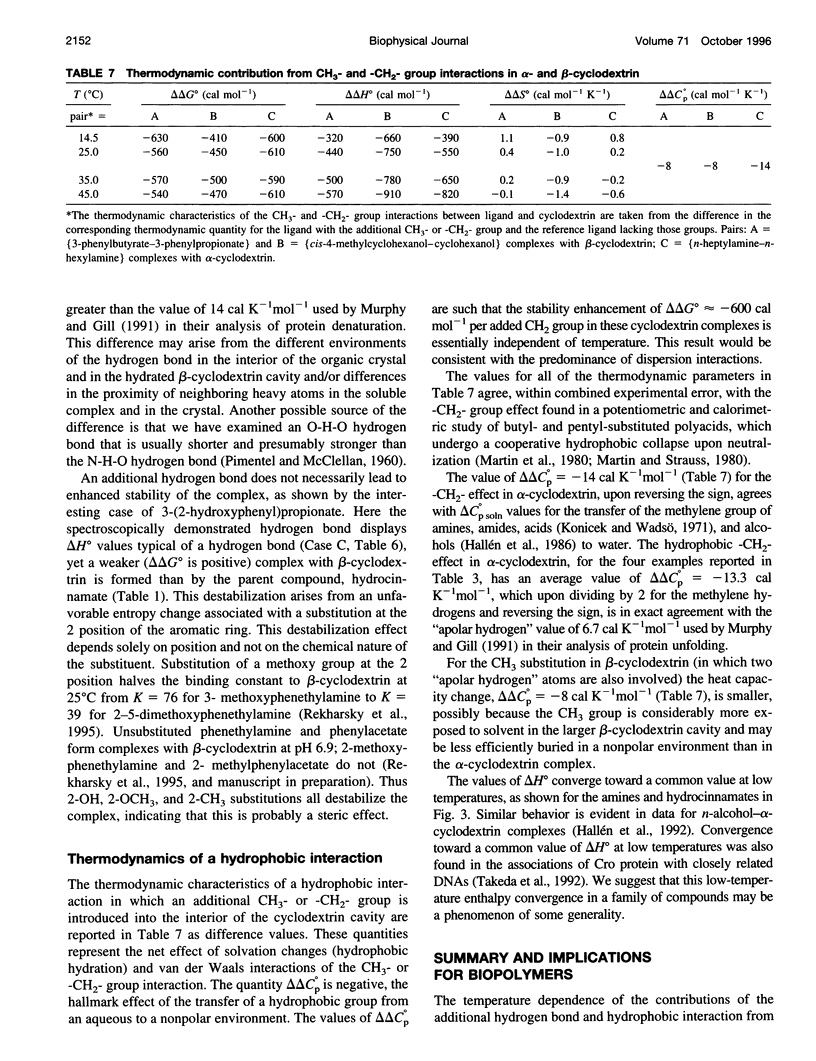
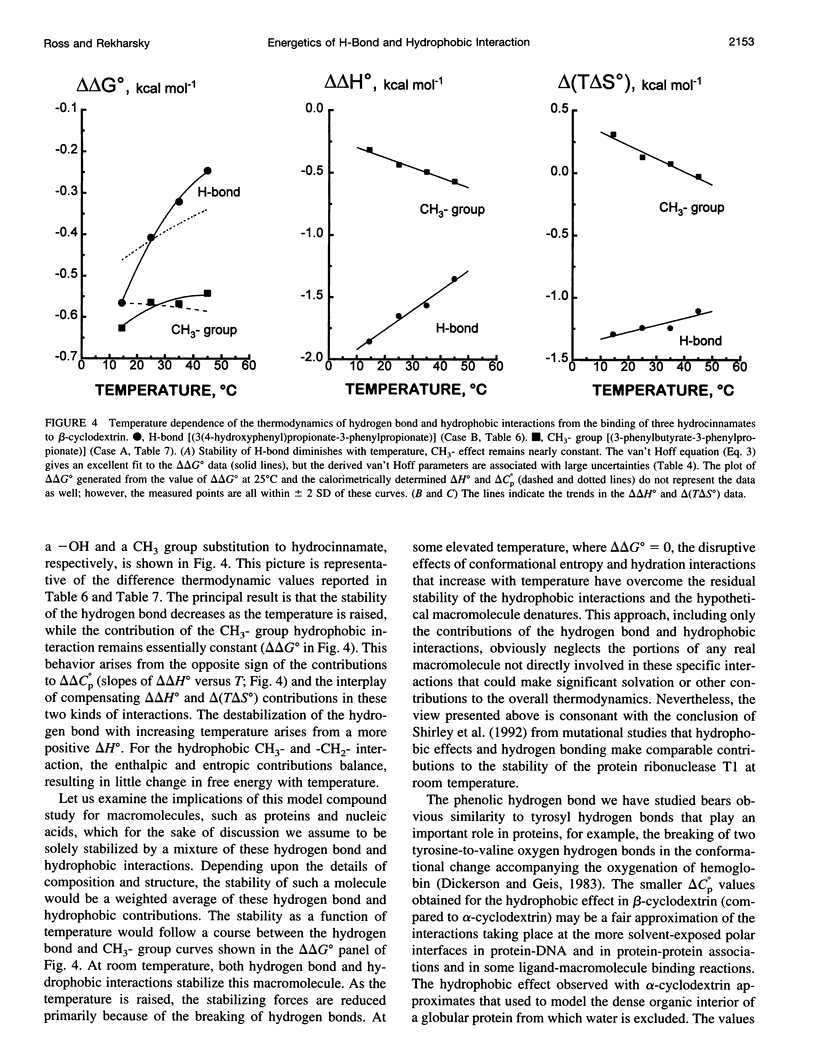
Values of K, delta G(o), delta H(o), delta S(o) and delta C(po) for the binding reaction of small organic ligands forming 1:1 complexes with either alpha- or beta-cyclodextrin were obtained by titration calorimetry from 15 degrees C to 45 degrees C. A hydrogen bond or hydrophobic interaction was introduced by adding a single functional group to the ligand. The thermodynamics of binding with and without the added group are compared to estimate the contribution of the hydrogen bond or hydrophobic interaction. A change in the environment of a functional group is required to influence the binding thermodynamics, but molecular size-dependent solute-solvent interactions have no effect. For phenolic O-H-O hydrogen bond formation, delta H(o) varies from -2 to -1.4 kcal mol(-1) from 15 degrees C to 45 degrees C, and delta C(p) is increased by 18 cal K(-1) mol(-1). The hydrophobic interaction has an opposite effect: in alpha-cyclodextrin, delta C(po) = -13.3 cal K(-1) mol(-1) per ligand -CH(2)-, identical to values found for the transfer of a -CH(2)-group from water to a nonpolar environment. At room temperature, the hydrogen bond and the -CH(2)-interaction each contribute about -600 cal mol(-1) to the stability (delta G(o)) of the complex. With increased temperature, the hydrogen bond stability decreases (i.e., hydrogen bonds "melt"), but the stability of the hydrophobic interaction remains essentially constant.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hamilton J. A., Sabesan M. N., Steinrauf K. L., Geddes A. The crystal structure of a complex of cycloheptaamylose with 2,5-diiodobenzoic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 6;73(3):659–664. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90861-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapunov S. N., Dragan A. I. Spektroskopiia mezhmolekuliarnykh vzaimodeistvii tirozinovogo khromofora. III. Klassifikatsiia sostoianiia ostatkov tirozina v belkakh po ikh élektronnym spektram. Biofizika. 1989 May-Jun;34(3):357–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makhatadze G. I., Privalov P. L. Contribution of hydration to protein folding thermodynamics. I. The enthalpy of hydration. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jul 20;232(2):639–659. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. J., Strauss U. P. Thermodynamics of hydrophobic polyacids. Biophys Chem. 1980 Jun;11(3-4):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(80)87013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy K. P., Freire E. Thermodynamics of structural stability and cooperative folding behavior in proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1992;43:313–361. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60556-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy K. P., Gill S. J. Solid model compounds and the thermodynamics of protein unfolding. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 5;222(3):699–709. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90506-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naghibi H., Tamura A., Sturtevant J. M. Significant discrepancies between van't Hoff and calorimetric enthalpies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5597–5599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalov P. L., Makhatadze G. I. Contribution of hydration to protein folding thermodynamics. II. The entropy and Gibbs energy of hydration. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jul 20;232(2):660–679. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHELLMAN J. A. The thermodynamics of urea solutions and the heat of formation of the peptide hydrogen bond. C R Trav Lab Carlsberg Chim. 1955;29(14-15):223–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUSI H., TIMASHEFF S. N., ARD J. S. NEAR INFRARED INVESTIGATION OF INTERAMIDE HYDROGEN BONDING IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:3051–3054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirley B. A., Stanssens P., Hahn U., Pace C. N. Contribution of hydrogen bonding to the conformational stability of ribonuclease T1. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 28;31(3):725–732. doi: 10.1021/bi00118a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Ross P. D., Mudd C. P. Thermodynamics of Cro protein-DNA interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8180–8184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman T., Williston S., Brandts J. F., Lin L. N. Rapid measurement of binding constants and heats of binding using a new titration calorimeter. Anal Biochem. 1989 May 15;179(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90213-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


