Abstract
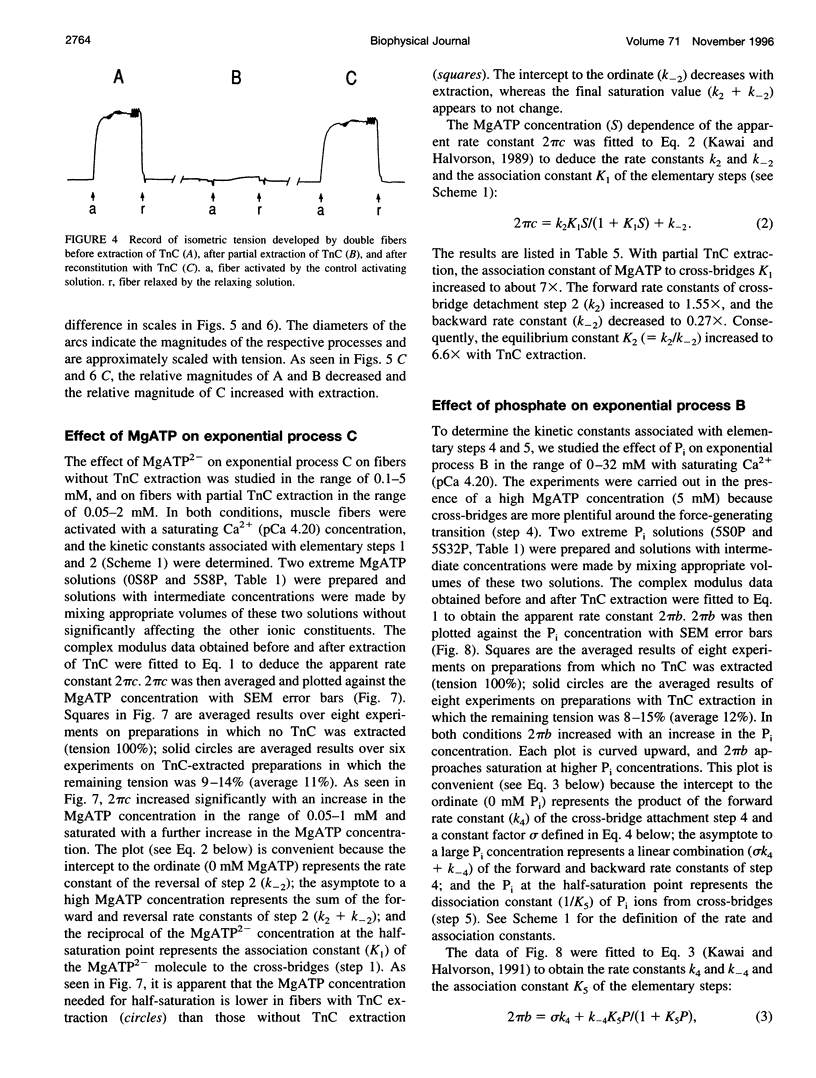
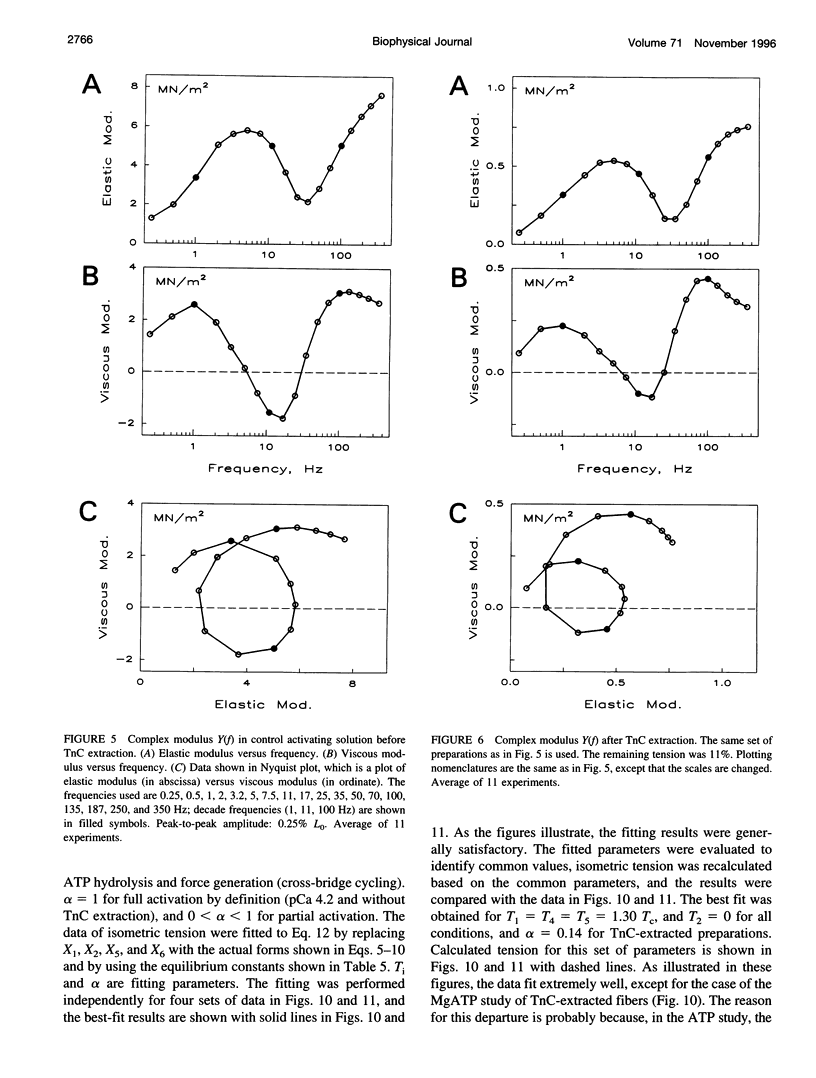
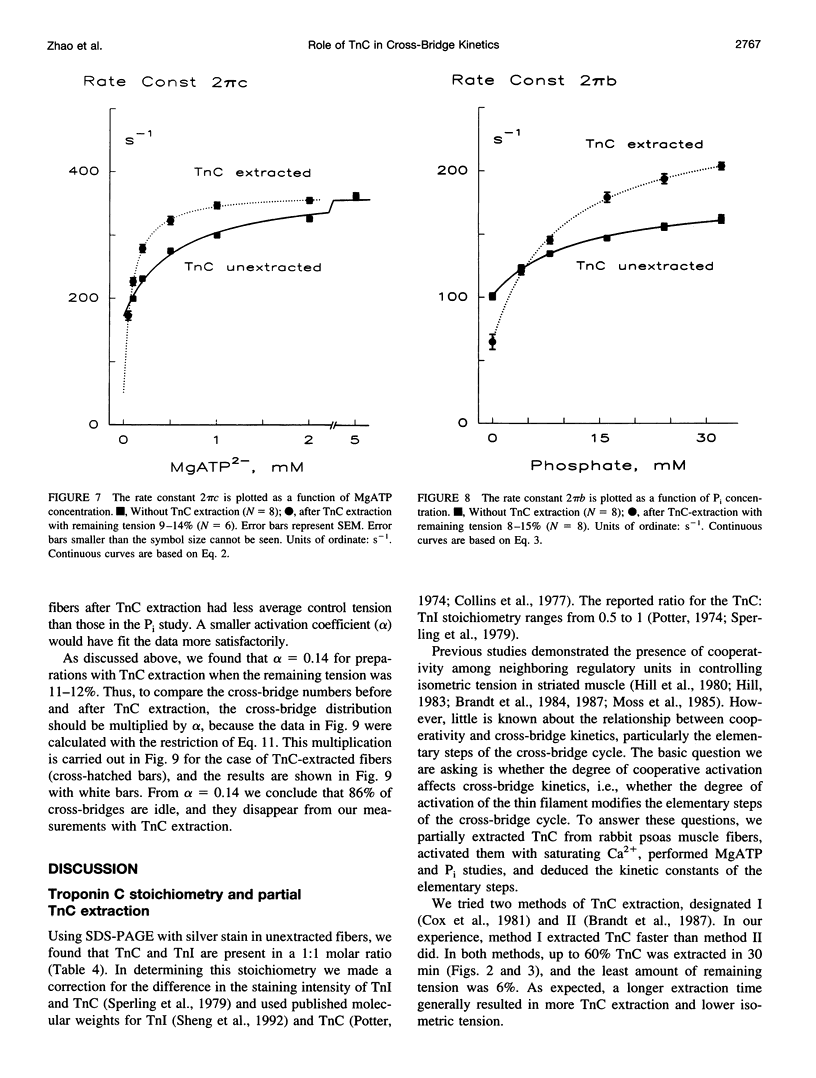
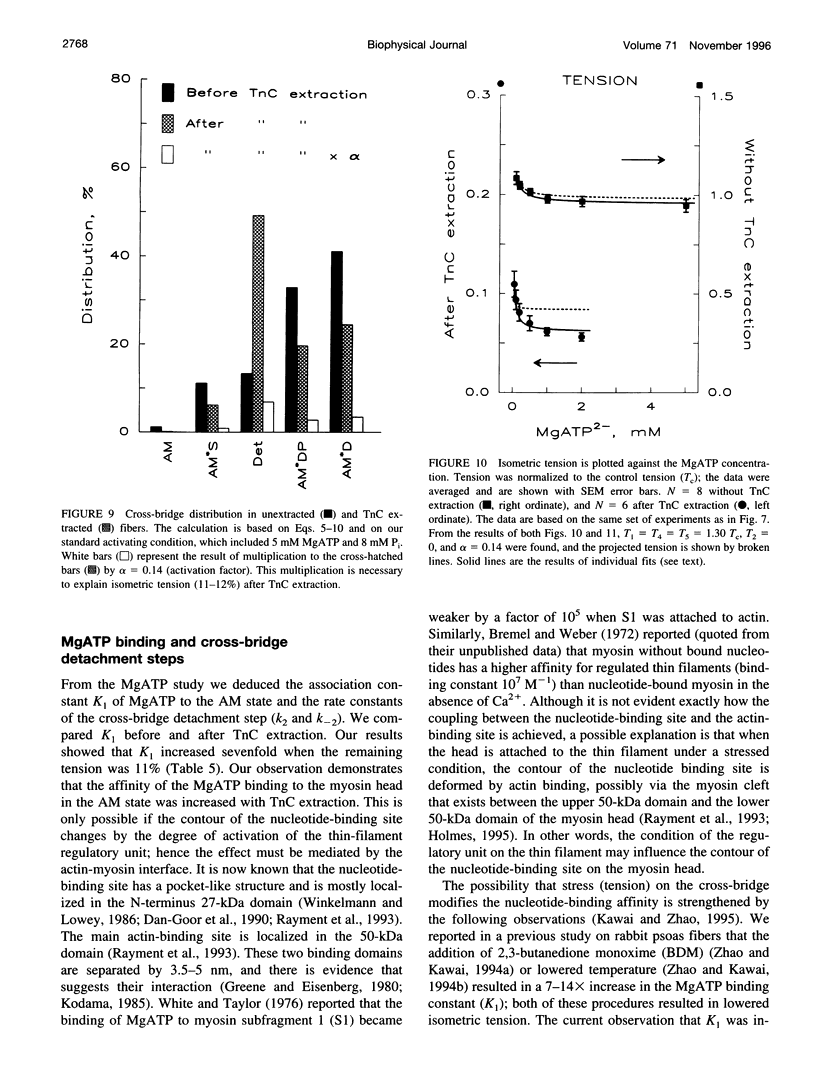
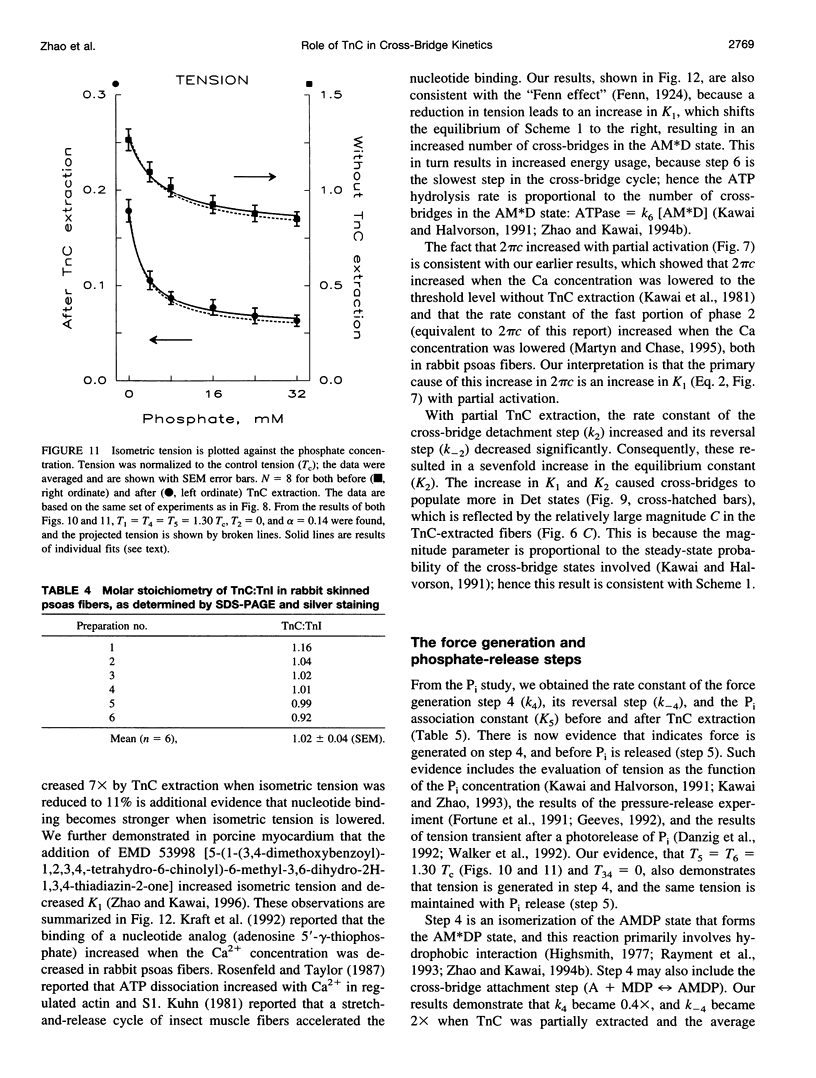
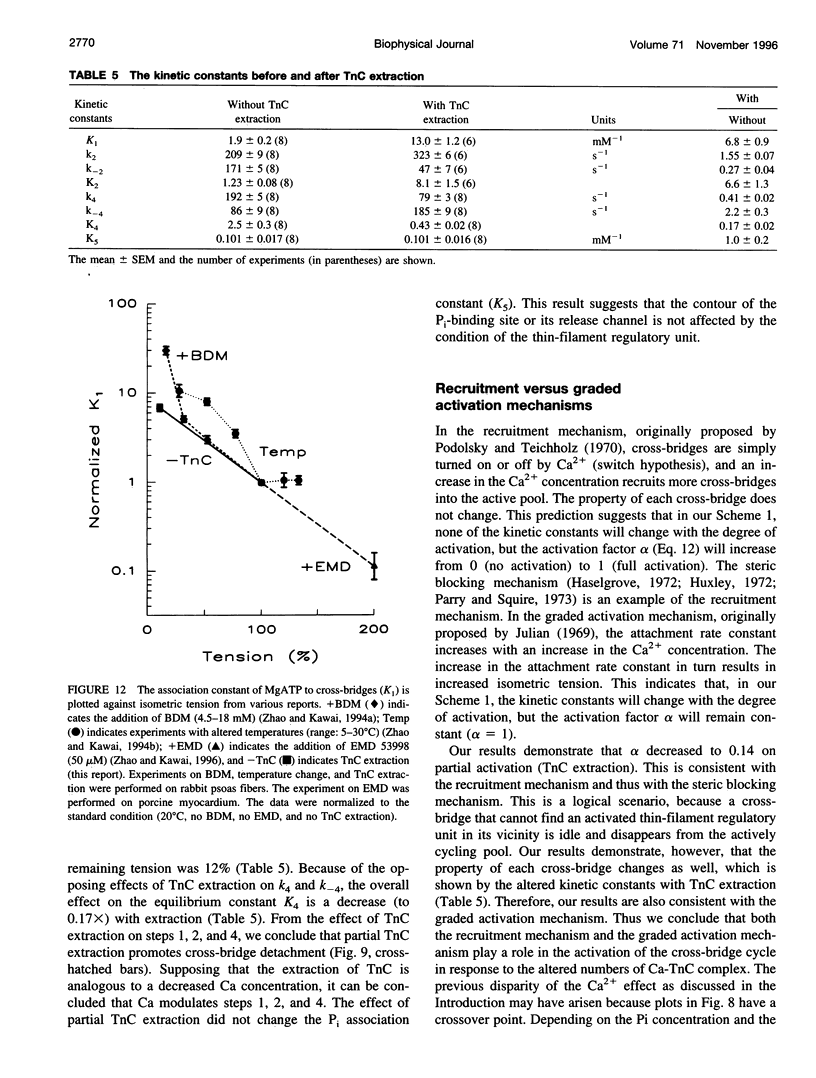
The elementary steps of the cross-bridge cycle in which troponin C (TnC) was partially extracted were investigated by sinusoidal analysis in rabbit psoas muscle fibers. The effects of MgATP and phosphate on the rate constants of exponential processes were studied at 200 mM ionic strength, pCa 4.20, pH 7.00, and at 20 degrees C. The results were analyzed with the following cross-bridge scheme: [formula: see text] where A is actin, M is myosin, S is MgATP, D is MgADP, and P is phosphate (Pi). When TnC was extracted so that the average remaining tension was 11% (range 8-15%), K1 (MgATP association constant) increased to 7x, k2 (rate constant of cross-bridge detachment) increased to 1.55x, k-2 (reversal of detachment) decreased to 0.27x, and K2 (= k2/k-2: equilibrium constant of cross-bridge detachment) increased to 6.6x, k4 (rate constant of force generation) decreased to 0.4x, k-4 (reversal of force generation) increased to 2x, K4 (= k4/k-4) decreased to 0.17x, and K5 (Pi association constant) did not change. The activation factor alpha, which represents the fraction of cross-bridges participating in the cycling, decreased from 1 to 0.14 with TnC extraction. The fact that K1 increased with TnC extraction implies that the condition of the thin filament modifies the contour of the substrate binding site on the myosin head and is consistent with the Fenn effect. The fact that alpha decreased to 0.14 is consistent with the steric blocking mechanism (recruitment hypothesis) and indicates that some of the cross-bridges disappear from the active cycling pool. The fact that the equilibrium constants changed is consistent with the cooperative activation mechanism (graded activation hypothesis) among thin-filament regulatory units that consist of troponin (TnC, Tnl, TnT), tropomyosin, and seven actin molecules, and possibly include cross-bridges.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandt P. W., Cox R. N., Kawai M. Can the binding of Ca2+ to two regulatory sites on troponin C determine the steep pCa/tension relationship of skeletal muscle? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4717–4720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt P. W., Cox R. N., Kawai M., Robinson T. Effect of cross-bridge kinetics on apparent Ca2+ sensitivity. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jun;79(6):997–1016. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.6.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt P. W., Diamond M. S., Rutchik J. S., Schachat F. H. Co-operative interactions between troponin-tropomyosin units extend the length of the thin filament in skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):885–896. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90492-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremel R. D., Weber A. Cooperation within actin filament in vertebrate skeletal muscle. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):97–101. doi: 10.1038/newbio238097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. A., Comte M., Stein E. A. Calmodulin-free skeletal-muscle troponin C prepared in the absence of urea. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):205–211. doi: 10.1042/bj1950205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dan-Goor M., Silberstein L., Kessel M., Muhlrad A. Localization of epitopes and functional effects of two novel monoclonal antibodies against skeletal muscle myosin. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1990 Jun;11(3):216–226. doi: 10.1007/BF01843575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzig J. A., Goldman Y. E., Millar N. C., Lacktis J., Homsher E. Reversal of the cross-bridge force-generating transition by photogeneration of phosphate in rabbit psoas muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1992;451:247–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M. Calcium ion and muscle contraction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1968;18:123–183. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(68)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenn W. O. The relation between the work performed and the energy liberated in muscular contraction. J Physiol. 1924 May 23;58(6):373–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1924.sp002141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortune N. S., Geeves M. A., Ranatunga K. W. Contractile activation and force generation in skinned rabbit muscle fibres: effects of hydrostatic pressure. J Physiol. 1994 Jan 15;474(2):283–290. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortune N. S., Geeves M. A., Ranatunga K. W. Tension responses to rapid pressure release in glycerinated rabbit muscle fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7323–7327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geeves M. A. The actomyosin ATPase: a two-state system. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1992 Apr 29;336(1276):63–71. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1992.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian G. G., Moss R. L., Greaser M. Improved methodology for analysis and quantitation of proteins on one-dimensional silver-stained slab gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Mar;129(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90551-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabarek Z., Grabarek J., Leavis P. C., Gergely J. Cooperative binding to the Ca2+-specific sites of troponin C in regulated actin and actomyosin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14098–14102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaser M. L., Gergely J. Purification and properties of the components from troponin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2125–2133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Cooperative binding of myosin subfragment-1 to the actin-troponin-tropomyosin complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulati J., Podolsky R. J. Contraction transients of skinned muscle fibers: effects of calcium and ionic strength. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Nov;72(5):701–715. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.5.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
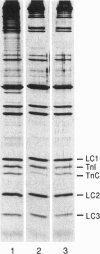
- Güth K., Potter J. D. Effect of rigor and cycling cross-bridges on the structure of troponin C and on the Ca2+ affinity of the Ca2+-specific regulatory sites in skinned rabbit psoas fibers. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13627–13635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F., NIEDERGERKE R. Structural changes in muscle during contraction; interference microscopy of living muscle fibres. Nature. 1954 May 22;173(4412):971–973. doi: 10.1038/173971a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY H., HANSON J. Changes in the cross-striations of muscle during contraction and stretch and their structural interpretation. Nature. 1954 May 22;173(4412):973–976. doi: 10.1038/173973a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon J. D., Martyn D. A., Gordon A. M. Effects of cycling and rigor crossbridges on the conformation of cardiac troponin C. Circ Res. 1992 Oct;71(4):984–991. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.4.984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinl P., Kuhn H. J., Rüegg J. C. Tension responses to quick length changes of glycerinated skeletal muscle fibres from the frog and tortoise. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):243–258. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith S. The effects of temperature and salts on myosin subfragment-1 and F-actin association. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Apr 30;180(2):404–408. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., Eisenberg E., Greene L. Theoretical model for the cooperative equilibrium binding of myosin subfragment 1 to the actin-troponin-tropomyosin complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3186–3190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L. Two elementary models for the regulation of skeletal muscle contraction by calcium. Biophys J. 1983 Dec;44(3):383–396. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84312-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. C. The actomyosin interaction and its control by tropomyosin. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):2S–7S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holroyde M. J., Robertson S. P., Johnson J. D., Solaro R. J., Potter J. D. The calcium and magnesium binding sites on cardiac troponin and their role in the regulation of myofibrillar adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11688–11693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Proposed mechanism of force generation in striated muscle. Nature. 1971 Oct 22;233(5321):533–538. doi: 10.1038/233533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T., Wakabayashi T. Calcium induced change in three-dimensional structure of thin filaments of rabbit skeletal muscle as revealed by cryo-electron microscopy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Sep 15;203(2):951–958. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J. Activation in a skeletal muscle contraction model with a modification for insect fibrillar muscle. Biophys J. 1969 Apr;9(4):547–570. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86403-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J., Moss R. L. Effects of calcium and ionic strength on shortening velocity and tension development in frog skinned muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:179–199. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J. The effect of calcium on the force-velocity relation of briefly glycerinated frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(1):117–145. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Brandt P. W., Cox R. N. The role of Ca2+ in cross-bridge kinetics in chemically skinned rabbit psoas fibers. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;170:657–672. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4703-3_61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Brandt P. W. Sinusoidal analysis: a high resolution method for correlating biochemical reactions with physiological processes in activated skeletal muscles of rabbit, frog and crayfish. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1980 Sep;1(3):279–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00711932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Cox R. N., Brandt P. W. Effect of Ca ion concentration on cross-bridge kinetics in rabbit psoas fibers. Evidence for the presence of two Ca-activated states of thin filament. Biophys J. 1981 Aug;35(2):375–384. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84796-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Halvorson H. R. Role of MgATP and MgADP in the cross-bridge kinetics in chemically skinned rabbit psoas fibers. Study of a fast exponential process (C) Biophys J. 1989 Apr;55(4):595–603. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82857-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Halvorson H. R. Two step mechanism of phosphate release and the mechanism of force generation in chemically skinned fibers of rabbit psoas muscle. Biophys J. 1991 Feb;59(2):329–342. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82227-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Zhao Y. Cross-bridge scheme and force per cross-bridge state in skinned rabbit psoas muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1993 Aug;65(2):638–651. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81109-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Zhao Y. Nucleotide-binding site of the myosin head is under the influence of thin filament proteins. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):216S–216S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T. Thermodynamic analysis of muscle ATPase mechanisms. Physiol Rev. 1985 Apr;65(2):467–551. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1985.65.2.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft T., Yu L. C., Kuhn H. J., Brenner B. Effect of Ca2+ on weak cross-bridge interaction with actin in the presence of adenosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11362–11366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn H. J. The mechanochemistry of force production in muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1981 Mar;2(1):7–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00712060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman W., Craig R., Vibert P. Ca(2+)-induced tropomyosin movement in Limulus thin filaments revealed by three-dimensional reconstruction. Nature. 1994 Mar 3;368(6466):65–67. doi: 10.1038/368065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martyn D. A., Chase P. B. Faster force transient kinetics at submaximal Ca2+ activation of skinned psoas fibers from rabbit. Biophys J. 1995 Jan;68(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80179-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKillop D. F., Geeves M. A. Regulation of the interaction between actin and myosin subfragment 1: evidence for three states of the thin filament. Biophys J. 1993 Aug;65(2):693–701. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81110-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger J. M., Moss R. L. Kinetics of a Ca(2+)-sensitive cross-bridge state transition in skeletal muscle fibers. Effects due to variations in thin filament activation by extraction of troponin C. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Aug;98(2):233–248. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.2.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. A., Brown T. R., Kushmerick M. J. Phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance of fast- and slow-twitch muscle. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):C279–C287. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.3.C279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar N. C., Homsher E. The effect of phosphate and calcium on force generation in glycerinated rabbit skeletal muscle fibers. A steady-state and transient kinetic study. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20234–20240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. L., Giulian G. G., Greaser M. L. The effects of partial extraction of TnC upon the tension-pCa relationship in rabbit skinned skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Oct;86(4):585–600. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. L., Swinford A. E., Greaser M. L. Alterations in the Ca2+ sensitivity of tension development by single skeletal muscle fibers at stretched lengths. Biophys J. 1983 Jul;43(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84329-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. M., Weber A. Cooperativity of the calcium switch of regulated rabbit actomyosin system. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Feb 26;35(1):11–15. doi: 10.1007/BF02358183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A., Squire J. M. Structural role of tropomyosin in muscle regulation: analysis of the x-ray diffraction patterns from relaxed and contracting muscles. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 25;75(1):33–55. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90527-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolsky R. J., Teichholz L. E. The relation between calcium and contraction kinetics in skinned muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Nov;211(1):19–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. D., Gergely J. The calcium and magnesium binding sites on troponin and their role in the regulation of myofibrillar adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4628–4633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
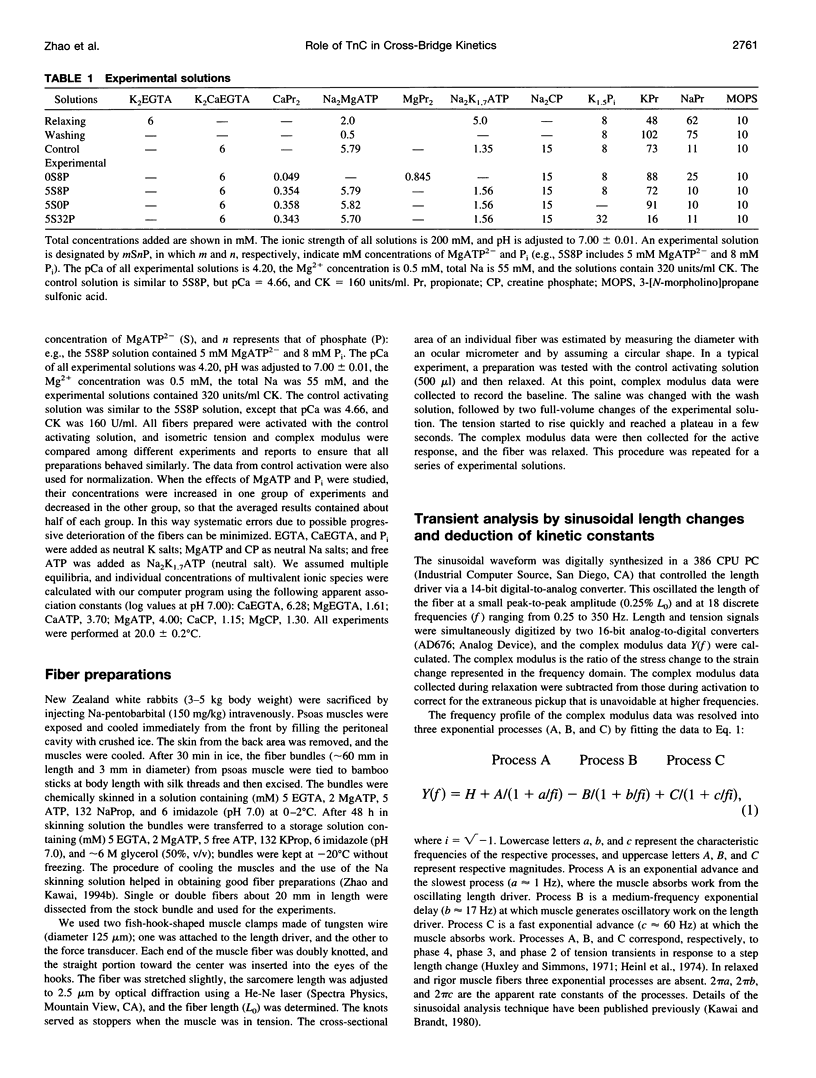
- Potter J. D. Preparation of troponin and its subunits. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):241–263. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. D. The content of troponin, tropomyosin, actin, and myosin in rabbit skeletal muscle myofibrils. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jun;162(2):436–441. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Rypniewski W. R., Schmidt-Bäse K., Smith R., Tomchick D. R., Benning M. M., Winkelmann D. A., Wesenberg G., Holden H. M. Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):50–58. doi: 10.1126/science.8316857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
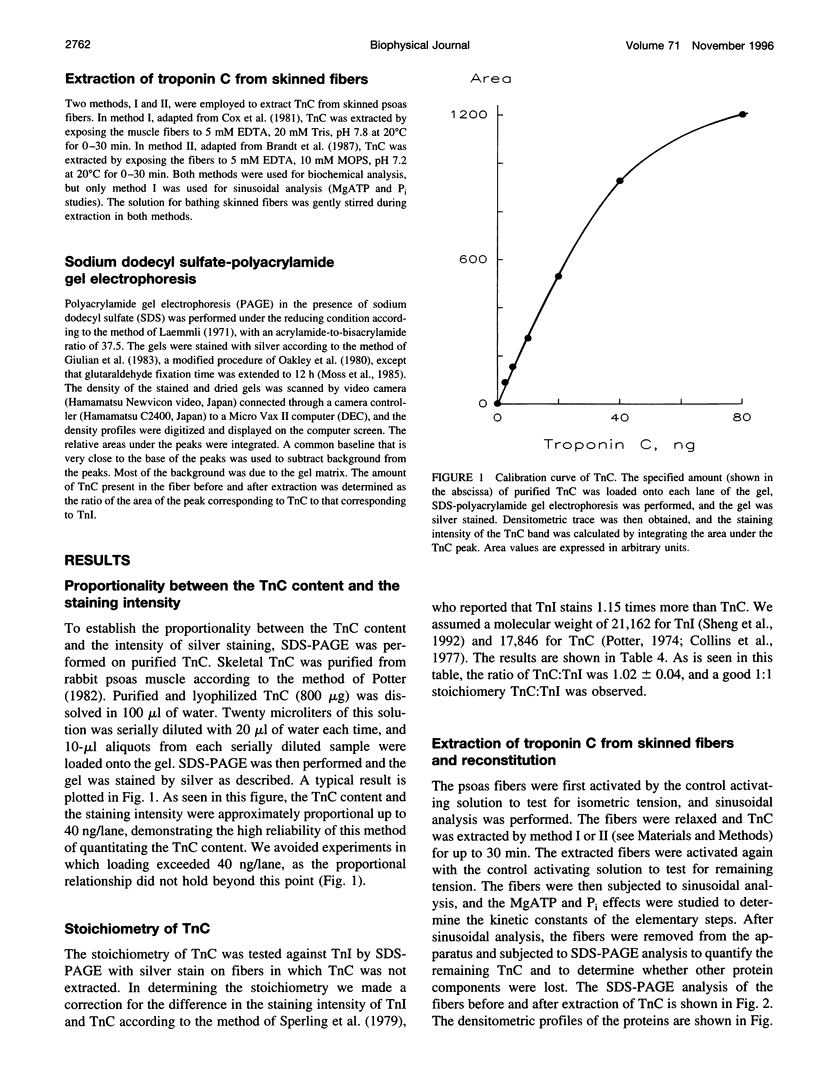
- Reedy M. K., Reedy M. C., Schachat F. Tropomyosin. Does resolution lead to reconciliation? Curr Biol. 1994 Jul 1;4(7):624–626. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00137-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. S., Taylor E. W. The mechanism of regulation of actomyosin subfragment 1 ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):9984–9993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng Z., Pan B. S., Miller T. E., Potter J. D. Isolation, expression, and mutation of a rabbit skeletal muscle cDNA clone for troponin I. The role of the NH2 terminus of fast skeletal muscle troponin I in its biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25407–25413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling J. E., Feldmann K., Meyer H., Jahnke U., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Isolation, characterization and phosphorylation pattern of the troponin complexes TI2C and I2C. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Nov;101(2):581–592. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb19753.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobacman L. S. Thin filament-mediated regulation of cardiac contraction. Annu Rev Physiol. 1996;58:447–481. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.58.030196.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
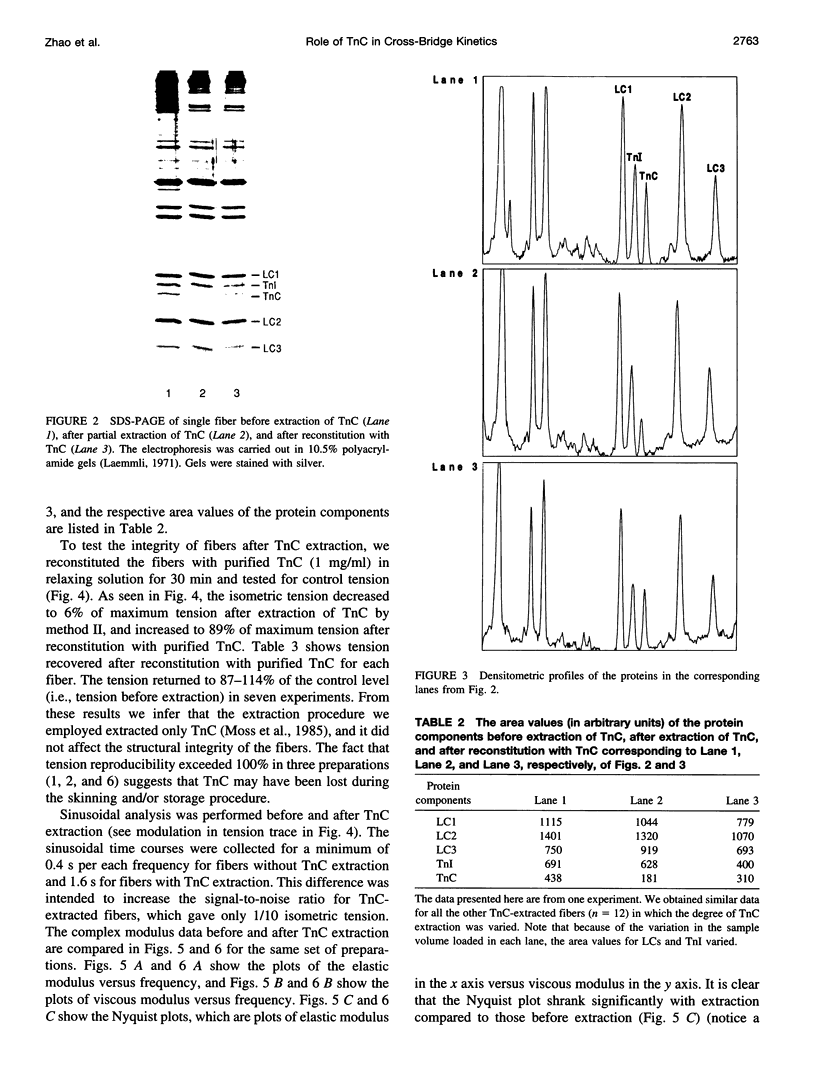
- Walker J. W., Lu Z., Moss R. L. Effects of Ca2+ on the kinetics of phosphate release in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2459–2466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. D., Taylor E. W. Energetics and mechanism of actomyosin adenosine triphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 28;15(26):5818–5826. doi: 10.1021/bi00671a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelmann D. A., Lowey S. Probing myosin head structure with monoclonal antibodies. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):595–612. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y., Kawai M. BDM affects nucleotide binding and force generation steps of the cross-bridge cycle in rabbit psoas muscle fibers. Am J Physiol. 1994 Feb;266(2 Pt 1):C437–C447. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.266.2.C437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y., Kawai M. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of the cross-bridge cycle in rabbit psoas muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1994 Oct;67(4):1655–1668. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80638-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]