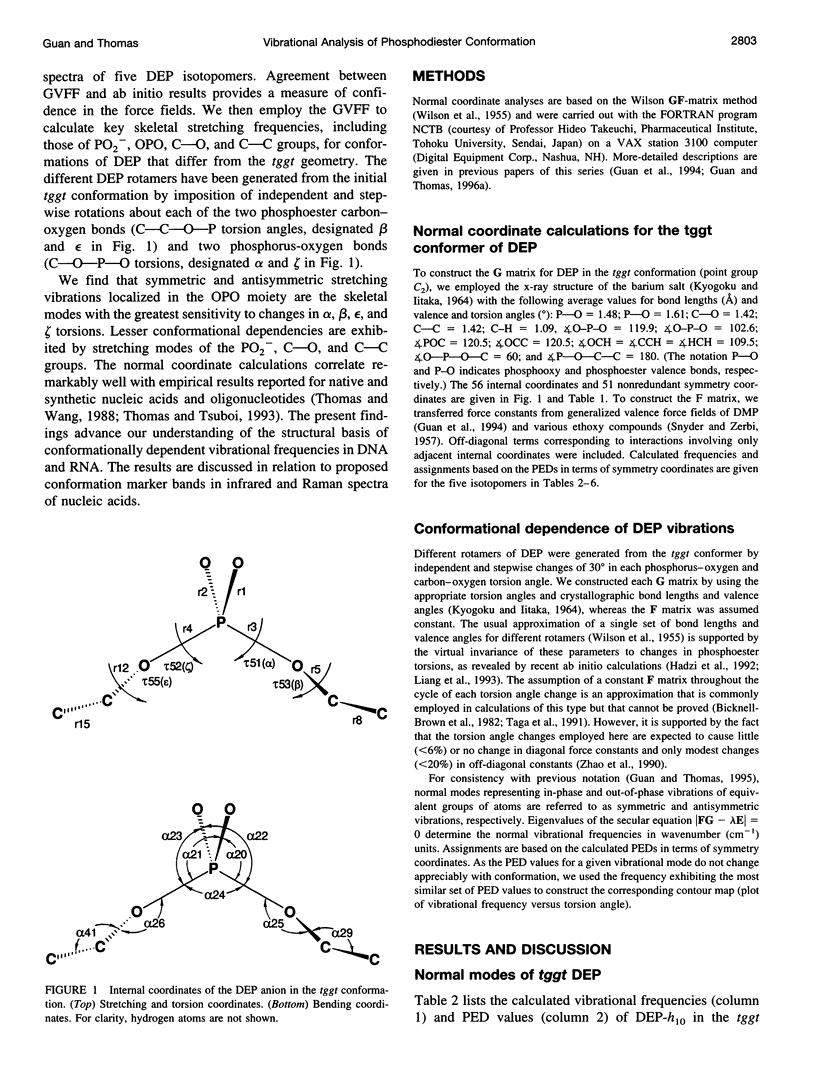
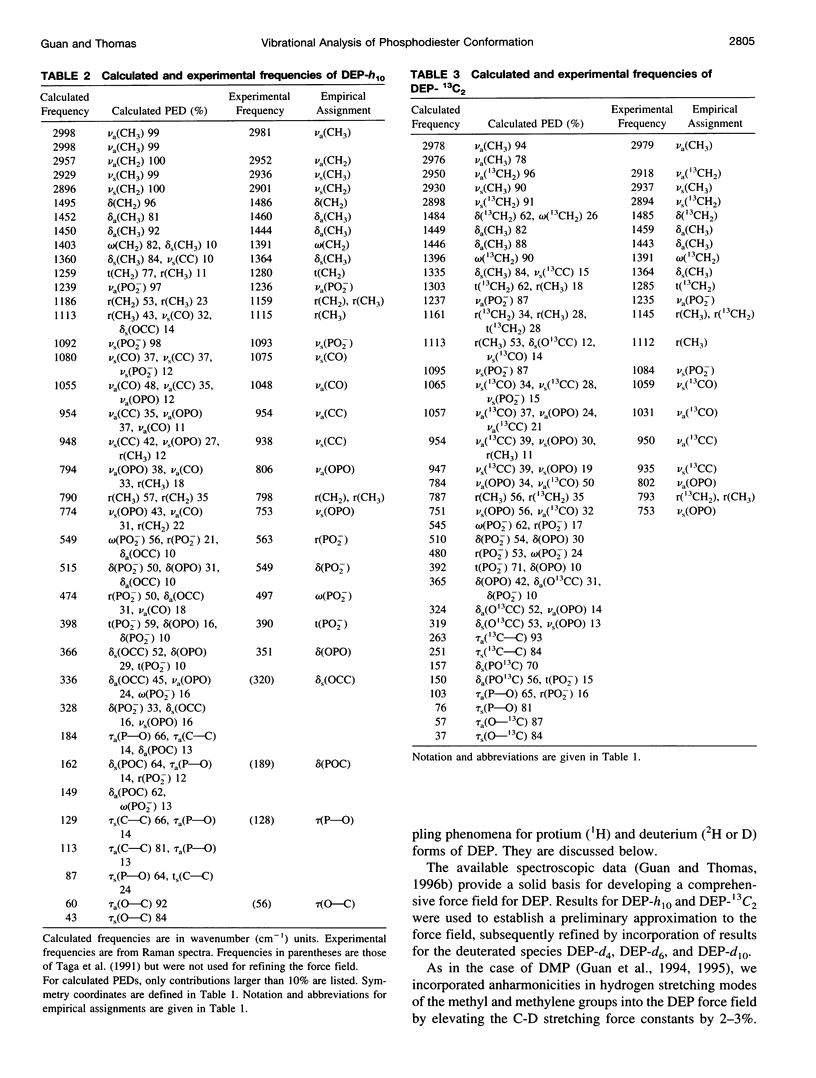
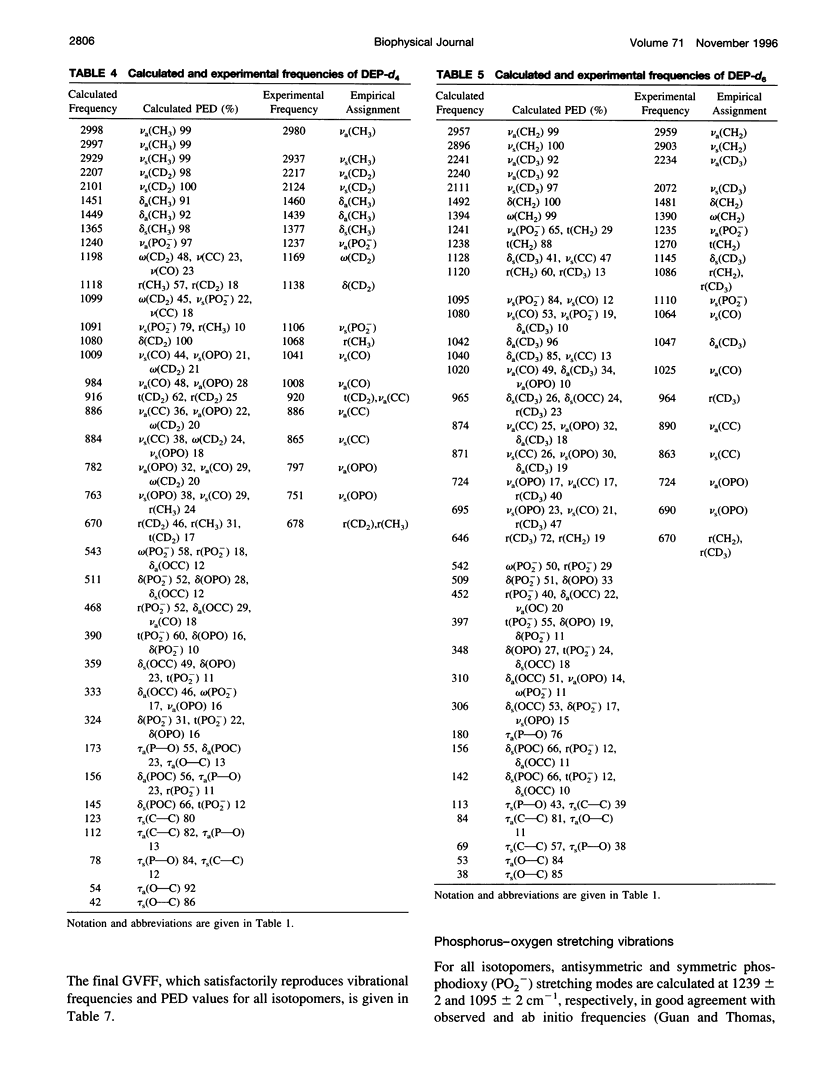
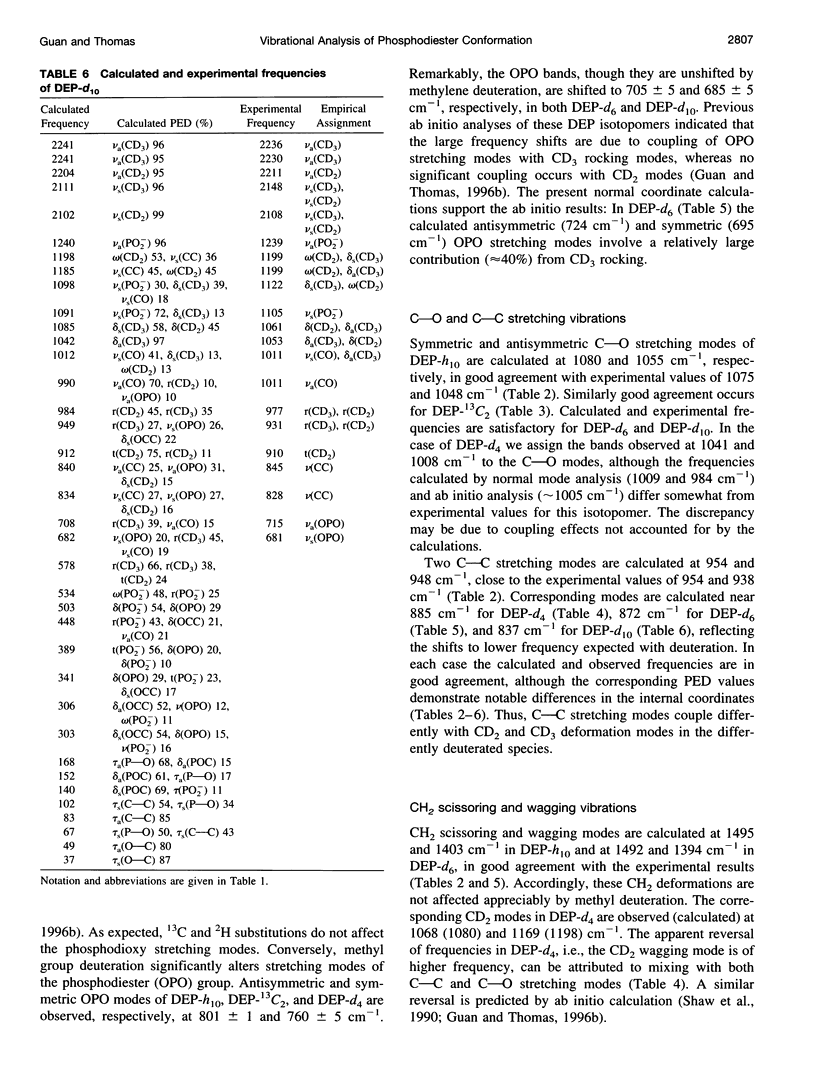
Abstract
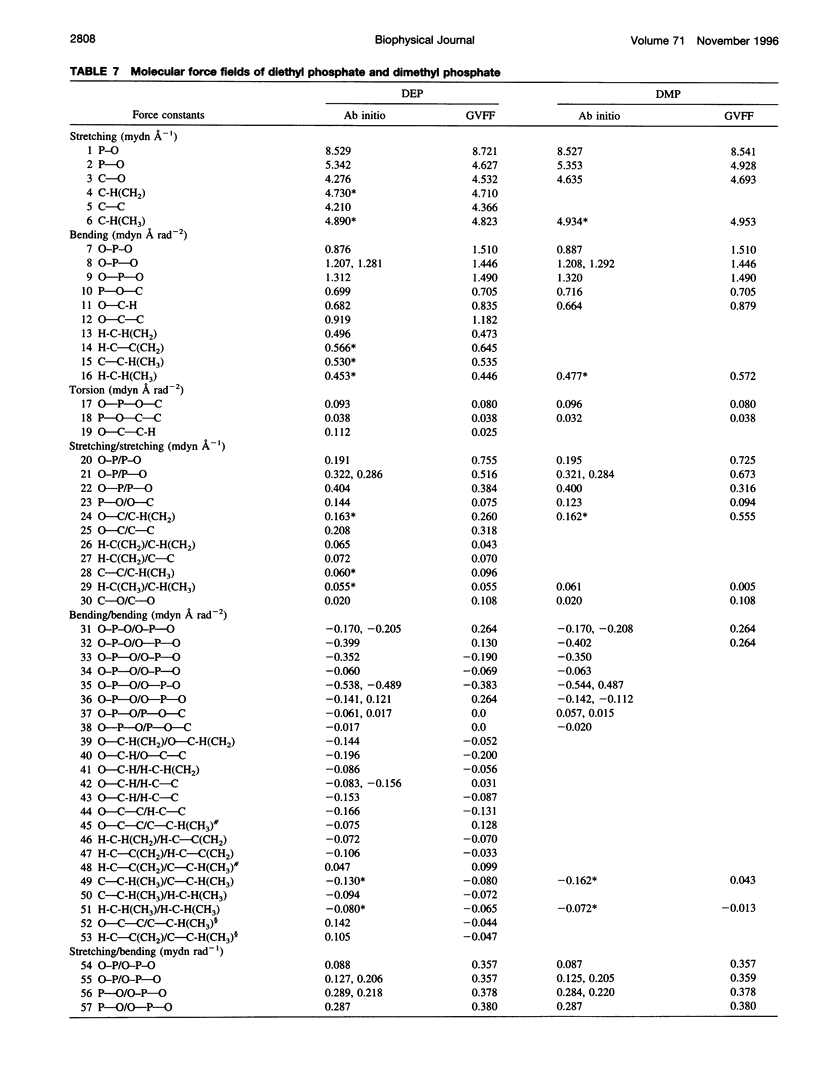
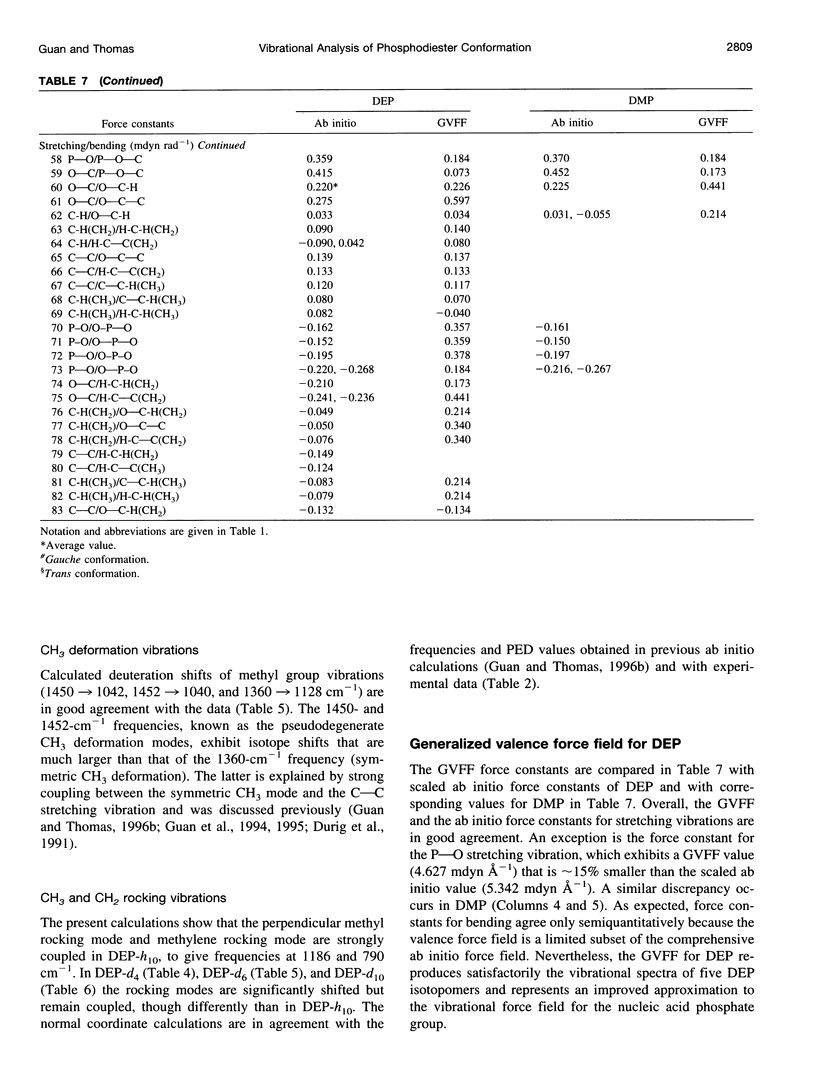
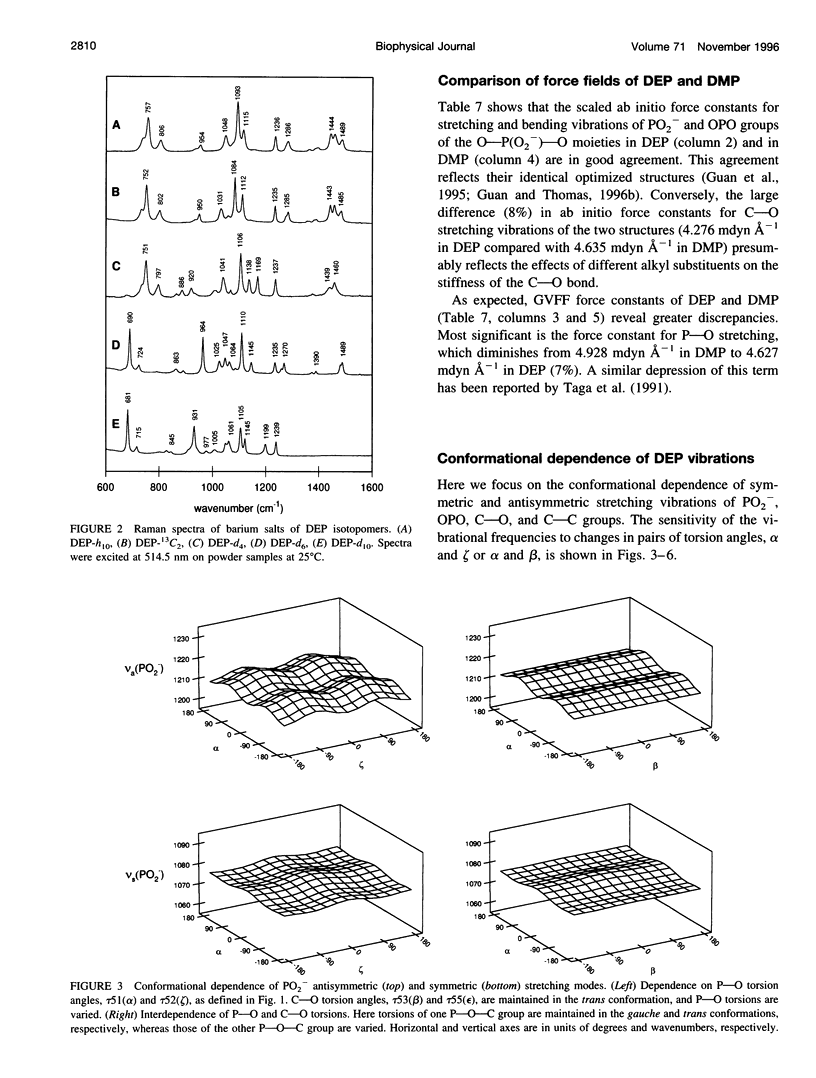
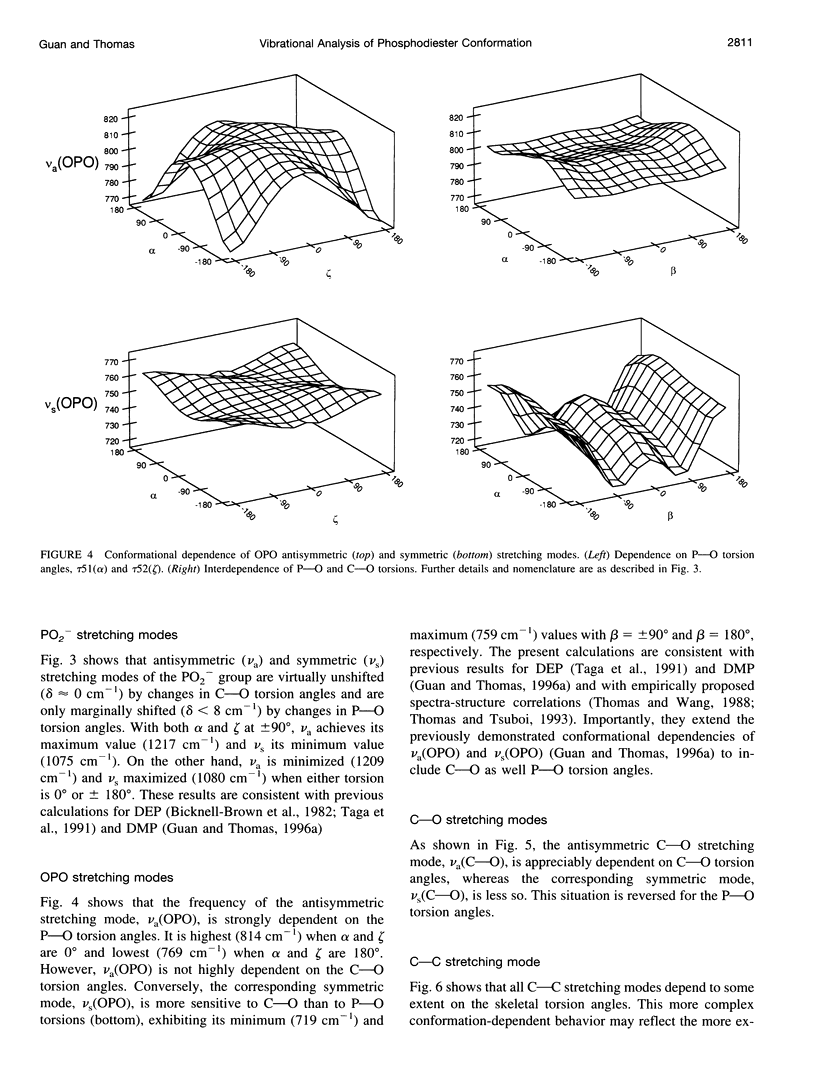
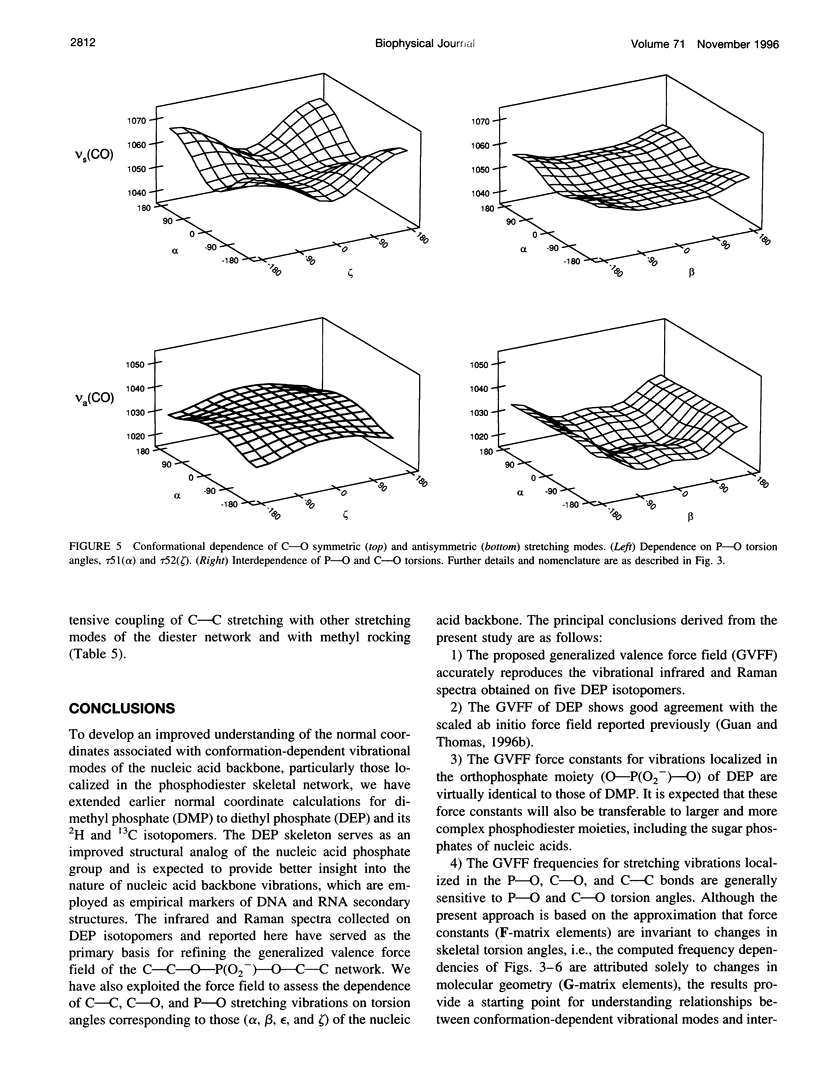
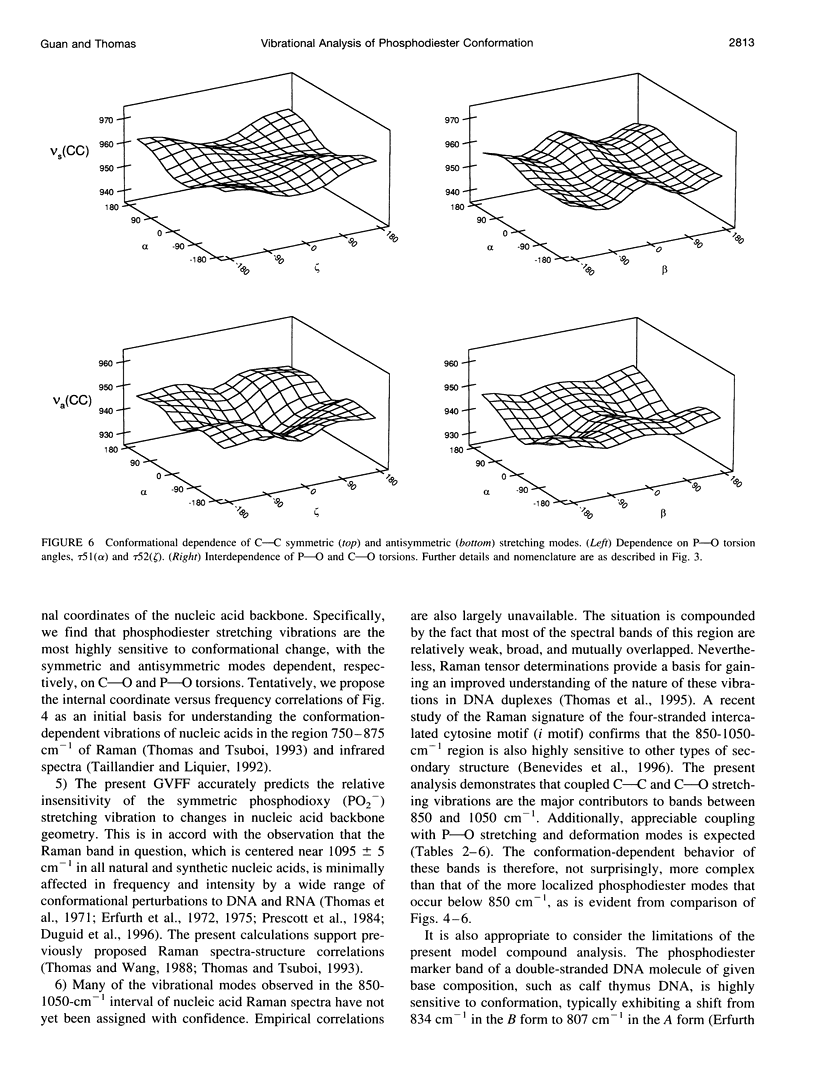
A generalized valence force field is derived for the diethyl phosphate anion [(CH3CH2O)2PO2-] and its deuterium [(CH3CD2O)2PO2-, (CD3CH2O)2PO2- and (CD3CD2O)2PO2-] and carbon-13 [(CH3 13CH2O)2PO2-] derivatives in the stable trans-gauche-gauche-trans conformation. Normal coordinate analysis of the trans-gauche-gauche-trans conformer, which serves as a structural analog of the nucleic acid phosphodiester group, is based on comprehensive infrared and Raman spectroscopic data and vibrational assignments obtained for the diethyl phosphate anion. The generalized valence force field is in good agreement with the scaled ab initio force field of diethyl phosphate and represents significant improvement over earlier modeling of the phosphodiester moiety with dimethyl phosphate. The conformational dependence of skeletal C-C-O-P(O2-)-O-C-C stretching vibrations is also explored. Starting with the trans-gauche-gauche-trans conformation, the frequency dependence of skeletal stretching modes has been obtained by stepwise rotation of the torsion angles of the P-O and C-O bonds corresponding to nucleic acid torsions alpha (P-O5'), beta (O5'-C5'), epsilon (C3'-O3'), and zeta (O3'-P). Both symmetric and antisymmetric phosphoester stretching modes are highly sensitive to P-O and C-O torsions, whereas symmetric and antisymmetric phosphodioxy (PO2-) stretching modes are less sensitive. The present results provide an improved structural basis for understanding previously developed empirical correlations between vibrational marker bands and nucleic acid backbone conformation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benevides J. M., Kang C., Thomas G. J., Jr Raman signature of the four-stranded intercalated cytosine motif in crystal and solution structures of DNA deoxycytidylates d(CCCT) and d(C8). Biochemistry. 1996 May 7;35(18):5747–5755. doi: 10.1021/bi9529420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erfurth S. C., Bond P. J., Peticolas W. L. Characterization of the A in equilibrium B transition of DNA in fibers and gels by laser Raman spectroscopy. Biopolymers. 1975 Jun;14(6):1245–1257. doi: 10.1002/bip.1975.360140613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erfurth S. C., Kiser E. J., Peticolas W. L. Determination of the backbone structure of nucleic acids and nucleic acid oligomers by laser Raman scattering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):938–941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan Y., Wurrey C. J., Thomas G. J., Jr Vibrational analysis of nucleic acids. I. The phosphodiester group in dimethyl phosphate model compounds: (CH3O)2PO2-, (CD3O)2PO2-, and (13CH3O)2PO2-. Biophys J. 1994 Jan;66(1):225–235. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80767-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott B., Steinmetz W., Thomas G. J., Jr Characterization of DNA structures by laser Raman spectroscopy. Biopolymers. 1984 Feb;23(2):235–256. doi: 10.1002/bip.360230206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seggewiss H., Fassbender D., Terwesten H. P., Schmidt H. K., Greve H., Bogunovic N., Gleichmann U. Perkutane Mitralvalvulotomie mit dem Inoue-Ballon bei über 65jährigen Patienten--Akutergebnisse und kurzfristiger Verlauf im Vergleich zu jüngeren Patienten. Z Kardiol. 1995 Apr;84(4):255–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taillandier E., Liquier J. Infrared spectroscopy of DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1992;211:307–335. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)11018-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. J., Jr, Benevides J. M., Overman S. A., Ueda T., Ushizawa K., Saitoh M., Tsuboi M. Polarized Raman spectra of oriented fibers of A DNA and B DNA: anisotropic and isotropic local Raman tensors of base and backbone vibrations. Biophys J. 1995 Mar;68(3):1073–1088. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80282-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. J., Medeiros G. C., Hartman K. A. The dependence of raman scattering on the conformation of ribosomal RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 6;44(3):587–592. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80123-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


