Abstract
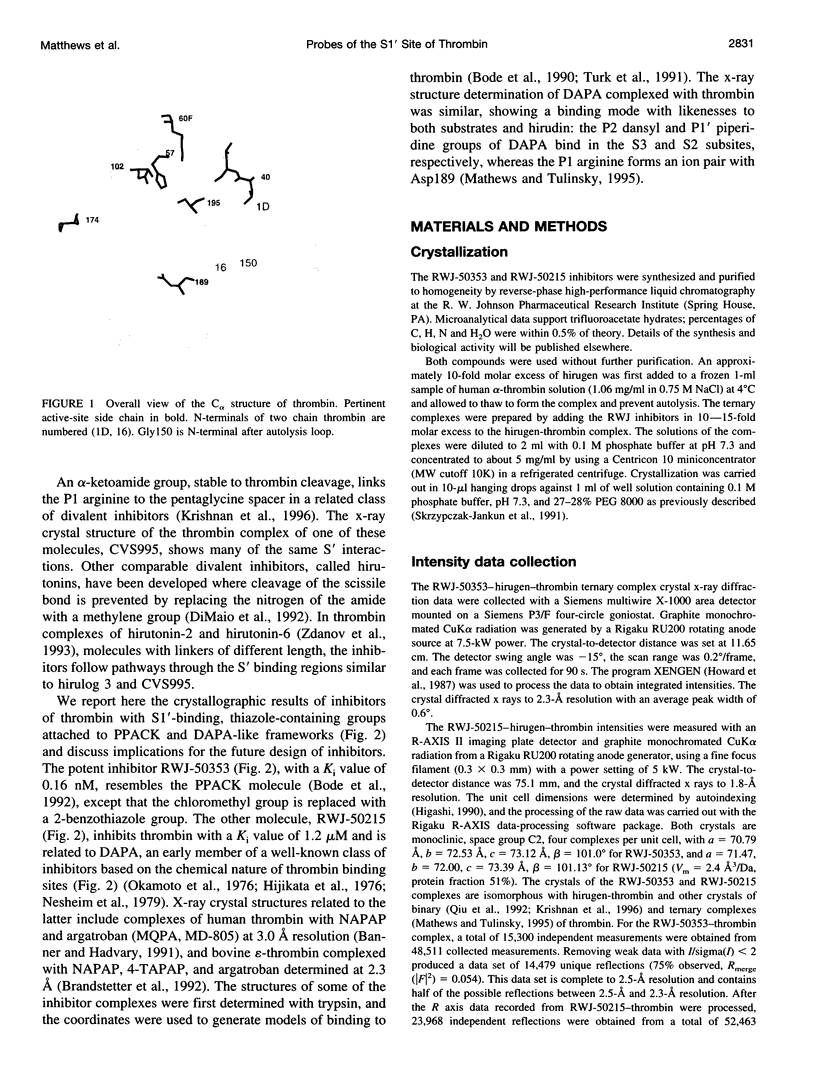
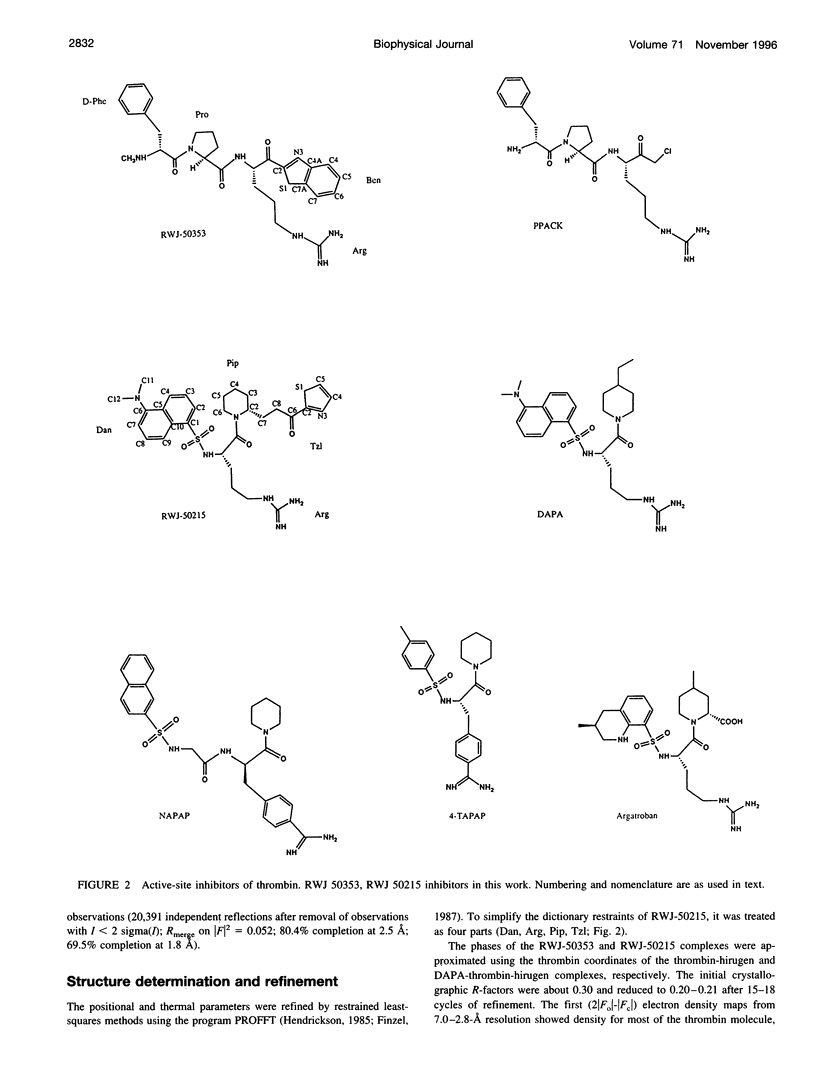
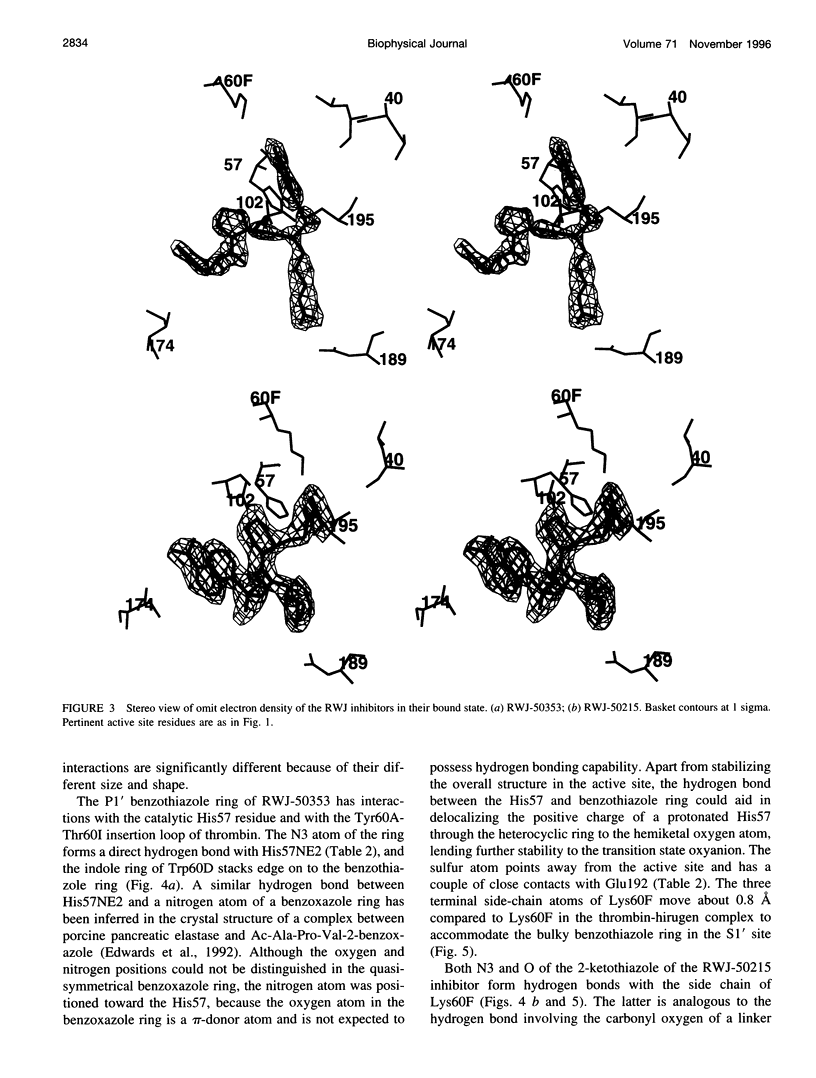
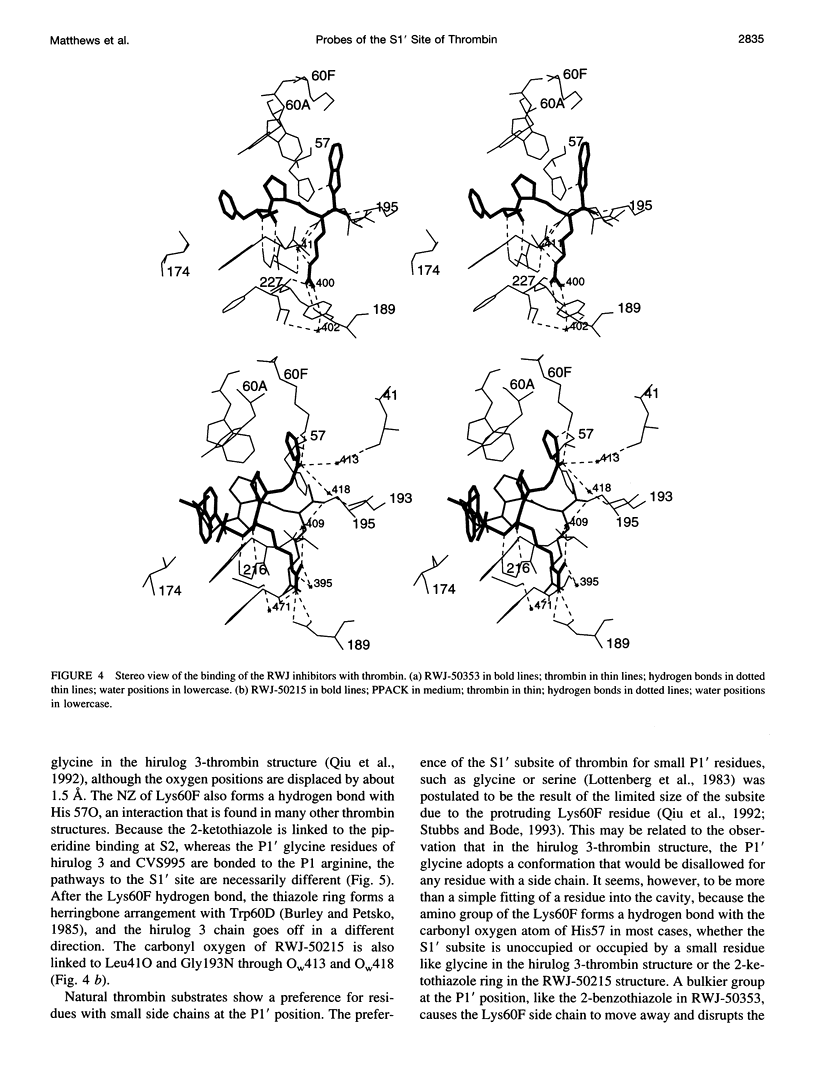
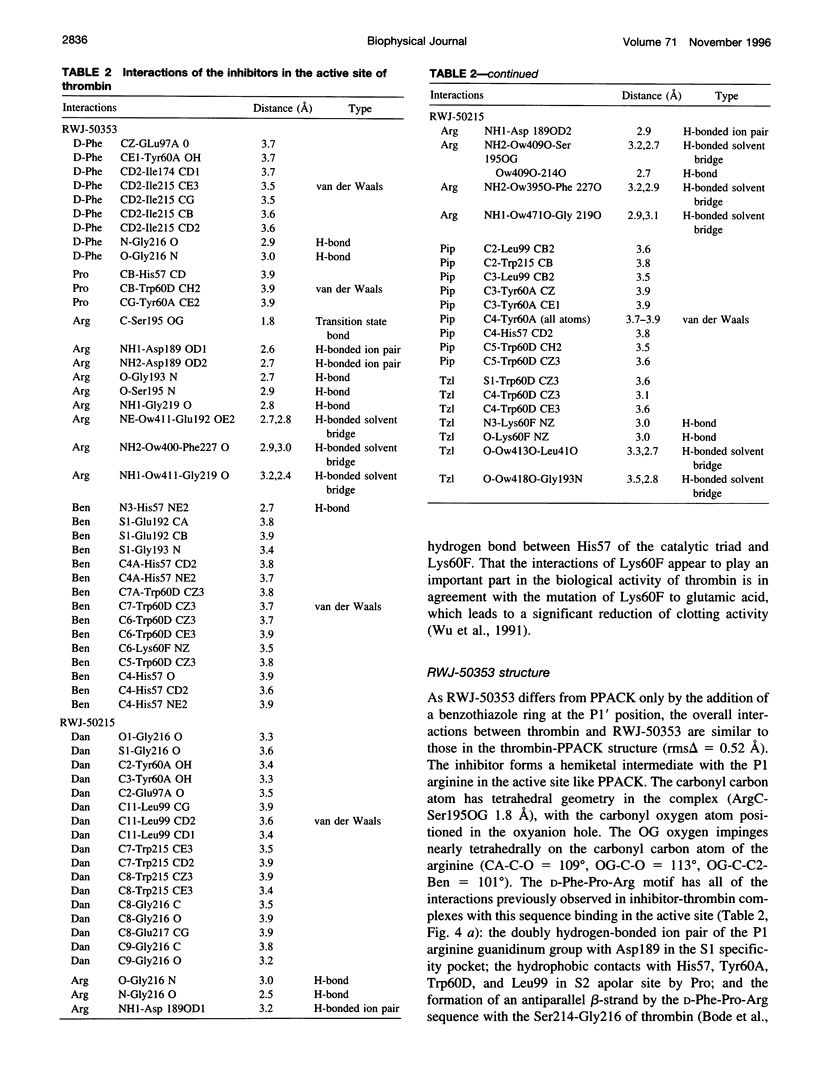
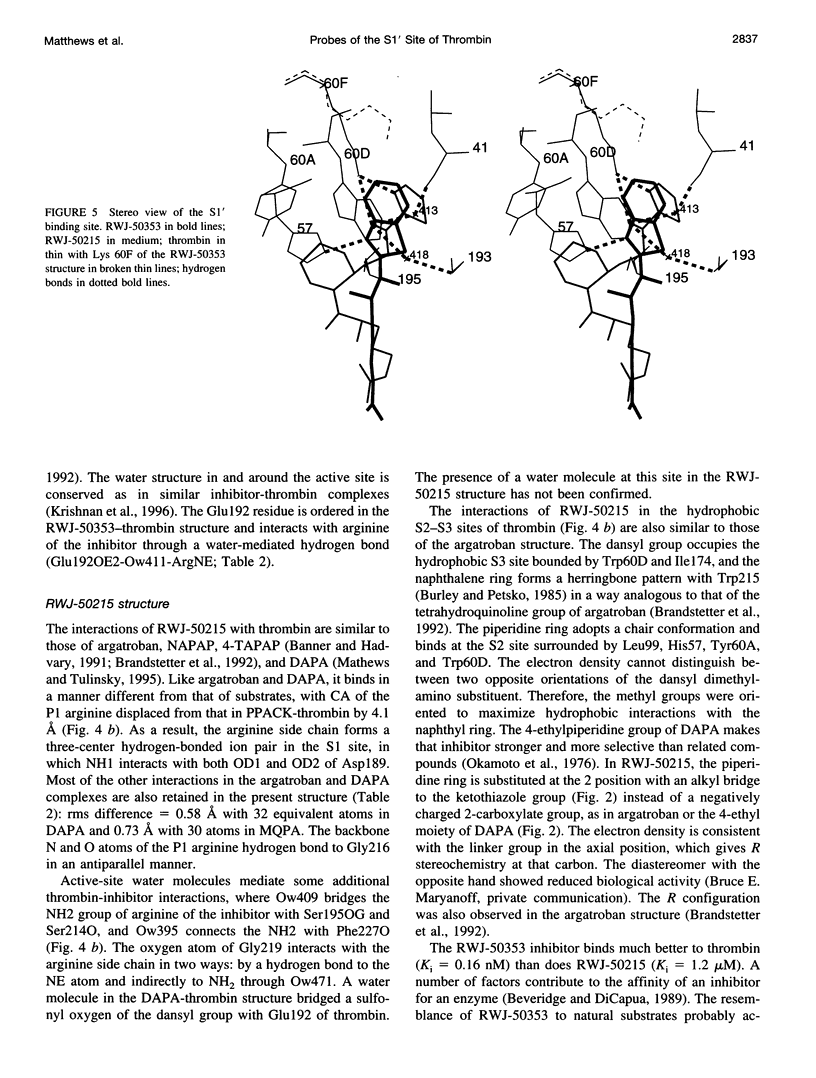
Structures of the blood clotting enzyme thrombin complexed with hirugen and two active site inhibitors, RWJ-50353 10080(N-methyl-D-phenylalanyl-N-[5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-1- [[(2-benzothiazolyl)carbonyl]butyl]-L-prolinamide trifluoroacetate hydrate) and RWJ-50215 (N-[4-(aminoiminomethyl)amino-1-[2- (thiazol-2-ylcarbonylethyl)piperidin- 1-ylcarbonyl]butyl]-5-(dimethylamino)naphthalenesulfonamide trifluoroacetate hydrate), were determined by x-ray crystallography. The refinements converged at R values of 0.158 in the 7.0-2.3-A range for RWJ-50353 and 0.155 in the 7.0-1.8-A range for RWJ-50215. Interactions between the protein and the thiazole rings of the two inhibitors provide new valuable information about the S1' binding site of thrombin. The RWJ-50353 inhibitor consists of an S1'-binding benzothiazole group linked to the D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethyl ketone motif. Interactions with the S1-S3 sites are similar to the D-phenylalanyl-prolyl-arginyl chloromethylketone structure. In RWJ-50215, a S1'-binding 2-ketothiazole group was added to the thrombin inhibitor-like framework of dansylarginine N-(3-ethyl-1,5-pentanediyl)amide. The geometry at the S1-S3 sites here is also similar to that of the parent compound. The benzothiazole and 2-ketothiazole groups bind in a cavity surrounded by His57, Tyr60A, Trp60D, and Lys60F. This location of the S1' binding site is consistent with previous structures of thrombin complexes with hirulog-3, CVS-995, and hirutonin-2 and -6. The ring nitrogen of the RWJ-50353 benzothiazole forms a hydrogen bond with His57, and Lys60F reorients because of close contacts. The oxygen and nitrogen of the ketothiazole of RWJ-50215 hydrogen bond with the NZ atom of Lys60F.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayala Y., Di Cera E. Molecular recognition by thrombin. Role of the slow-->fast transition, site-specific ion binding energetics and thermodynamic mapping of structural components. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 14;235(2):733–746. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banner D. W., Hadváry P. Crystallographic analysis at 3.0-A resolution of the binding to human thrombin of four active site-directed inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20085–20093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge D. L., DiCapua F. M. Free energy via molecular simulation: applications to chemical and biomolecular systems. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:431–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.002243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Blombäck M., Hessel B., Iwanaga S. Structure of N-terminal fragments of fibrinogen and specificity of thrombin. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1445–1448. doi: 10.1038/2151445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Turk D., Karshikov A. The refined 1.9-A X-ray crystal structure of D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethylketone-inhibited human alpha-thrombin: structure analysis, overall structure, electrostatic properties, detailed active-site geometry, and structure-function relationships. Protein Sci. 1992 Apr;1(4):426–471. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Turk D., Stürzebecher J. Geometry of binding of the benzamidine- and arginine-based inhibitors N alpha-(2-naphthyl-sulphonyl-glycyl)-DL-p-amidinophenylalanyl-pipe ridine (NAPAP) and (2R,4R)-4-methyl-1-[N alpha-(3-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-8- quinolinesulphonyl)-L-arginyl]-2-piperidine carboxylic acid (MQPA) to human alpha-thrombin. X-ray crystallographic determination of the NAPAP-trypsin complex and modeling of NAPAP-thrombin and MQPA-thrombin. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Oct 5;193(1):175–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandstetter H., Turk D., Hoeffken H. W., Grosse D., Stürzebecher J., Martin P. D., Edwards B. F., Bode W. Refined 2.3 A X-ray crystal structure of bovine thrombin complexes formed with the benzamidine and arginine-based thrombin inhibitors NAPAP, 4-TAPAP and MQPA. A starting point for improving antithrombotics. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 20;226(4):1085–1099. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91054-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burley S. K., Petsko G. A. Aromatic-aromatic interaction: a mechanism of protein structure stabilization. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):23–28. doi: 10.1126/science.3892686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo M. J., Maryanoff B. E., Hecker L. R., Schott M. R., Yabut S. C., Zhang H. C., Andrade-Gordon P., Kauffman J. A., Lewis J. M., Krishnan R. Potent thrombin inhibitors that probe the S1 subsite: tripeptide transition state analogues based on a heterocycle-activated carbonyl group. J Med Chem. 1996 Aug 2;39(16):3039–3043. doi: 10.1021/jm9603274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie E. W., Fujikawa K., Kisiel W. The coagulation cascade: initiation, maintenance, and regulation. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 29;30(43):10363–10370. doi: 10.1021/bi00107a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Cera E., Guinto E. R., Vindigni A., Dang Q. D., Ayala Y. M., Wuyi M., Tulinsky A. The Na+ binding site of thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 22;270(38):22089–22092. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.38.22089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio J., Gibbs B., Lefebvre J., Konishi Y., Munn D., Yue S. Y., Hornberger W. Synthesis of a homologous series of ketomethylene arginyl pseudodipeptides and application to low molecular weight hirudin-like thrombin inhibitors. J Med Chem. 1992 Sep 4;35(18):3331–3341. doi: 10.1021/jm00096a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The roles of protein C and thrombomodulin in the regulation of blood coagulation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4743–4746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Isolation of a membrane-bound cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):859–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grütter M. G., Priestle J. P., Rahuel J., Grossenbacher H., Bode W., Hofsteenge J., Stone S. R. Crystal structure of the thrombin-hirudin complex: a novel mode of serine protease inhibition. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2361–2365. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W. A. Stereochemically restrained refinement of macromolecular structures. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:252–270. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijikata A., Okamoto S., Mori E., Kinjo K., Kikumoto R. In vitro and in vivo studies of a new series of synthetic thrombin-inhibitors (OM-inhibitors). Thromb Res. 1976 May;8(2 Suppl):83–89. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg D. H., Blombäck B. The mechanism of the fibrinogen-thrombin reaction. Thromb Res. 1978 Jun;12(6):953–964. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung D. T., Vu T. K., Wheaton V. I., Ishii K., Coughlin S. R. Cloned platelet thrombin receptor is necessary for thrombin-induced platelet activation. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1350–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI115721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M., Nemerson Y. Blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:765–811. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikumoto R., Tamao Y., Ohkubo K., Tezuka T., Tonomura S., Okamoto S., Funahara Y., Hijikata A. Thrombin inhibitors. 2. Amide derivatives of N alpha-substituted L-arginine. J Med Chem. 1980 Aug;23(8):830–836. doi: 10.1021/jm00182a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikumoto R., Tamao Y., Tezuka T., Tonomura S., Hara H., Ninomiya K., Hijikata A., Okamoto S. Selective inhibition of thrombin by (2R,4R)-4-methyl-1-[N2-[(3-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-8-quinolinyl++ +) sulfonyl]-l-arginyl)]-2-piperidinecarboxylic acid. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 3;23(1):85–90. doi: 10.1021/bi00296a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan R., Tulinsky A., Vlasuk G. P., Pearson D., Vallar P., Bergum P., Brunck T. K., Ripka W. C. Synthesis, structure, and structure-activity relationships of divalent thrombin inhibitors containing an alpha-keto-amide transition-state mimetic. Protein Sci. 1996 Mar;5(3):422–433. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560050303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lottenberg R., Hall J. A., Blinder M., Binder E. P., Jackson C. M. The action of thrombin on peptide p-nitroanilide substrates. Substrate selectivity and examination of hydrolysis under different reaction conditions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 15;742(3):539–557. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90272-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh H. C., Jr, Meinwald Y. C., Thannhauser T. W., Scheraga H. A. Mechanism of action of thrombin on fibrinogen. Kinetic evidence for involvement of aspartic acid at position P10. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 30;22(18):4170–4174. doi: 10.1021/bi00287a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews I. I., Padmanabhan K. P., Ganesh V., Tulinsky A., Ishii M., Chen J., Turck C. W., Coughlin S. R., Fenton J. W., 2nd Crystallographic structures of thrombin complexed with thrombin receptor peptides: existence of expected and novel binding modes. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 22;33(11):3266–3279. doi: 10.1021/bi00177a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews I. I., Tulinsky A. Active-site mimetic inhibition of thrombin. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1995 Jul 1;51(Pt 4):550–559. doi: 10.1107/S0907444994013132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Prendergast F. G., Mann K. G. Interactions of a fluorescent active-site-directed inhibitor of thrombin: dansylarginine N-(3-ethyl-1,5-pentanediyl)amide. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 20;18(6):996–1003. doi: 10.1021/bi00573a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto S., Hijikata A., Ikezawa K., Kinjo K., Kikumoto R. A new series of synthetic thrombin-inhibitors (OM-inhibitors) having extremely potent and selective action. Thromb Res. 1976 May;8(2 Suppl):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu X., Padmanabhan K. P., Carperos V. E., Tulinsky A., Kline T., Maraganore J. M., Fenton J. W., 2nd Structure of the hirulog 3-thrombin complex and nature of the S' subsites of substrates and inhibitors. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 1;31(47):11689–11697. doi: 10.1021/bi00162a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydel T. J., Ravichandran K. G., Tulinsky A., Bode W., Huber R., Roitsch C., Fenton J. W., 2nd The structure of a complex of recombinant hirudin and human alpha-thrombin. Science. 1990 Jul 20;249(4966):277–280. doi: 10.1126/science.2374926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydel T. J., Tulinsky A., Bode W., Huber R. Refined structure of the hirudin-thrombin complex. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 20;221(2):583–601. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh J., Thornton J. M., Snarey M., Campbell S. F. The geometries of interacting arginine-carboxyls in proteins. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):161–171. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80441-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skrzypczak-Jankun E., Carperos V. E., Ravichandran K. G., Tulinsky A., Westbrook M., Maraganore J. M. Structure of the hirugen and hirulog 1 complexes of alpha-thrombin. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1379–1393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs M. T., Bode W. A player of many parts: the spotlight falls on thrombin's structure. Thromb Res. 1993 Jan 1;69(1):1–58. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(93)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabernero L., Chang C. Y., Ohringer S. L., Lau W. F., Iwanowicz E. J., Han W. C., Wang T. C., Seiler S. M., Roberts D. G., Sack J. S. Structure of a retro-binding peptide inhibitor complexed with human alpha-thrombin. J Mol Biol. 1995 Feb 10;246(1):14–20. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulinsky A., Qiu X. Active site and exosite binding of alpha-thrombin. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1993 Apr;4(2):305–312. doi: 10.1097/00001721-199304000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk D., Stürzebecher J., Bode W. Geometry of binding of the N alpha-tosylated piperidides of m-amidino-, p-amidino- and p-guanidino phenylalanine to thrombin and trypsin. X-ray crystal structures of their trypsin complexes and modeling of their thrombin complexes. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 5;287(1-2):133–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80033-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayalakshmi J., Padmanabhan K. P., Mann K. G., Tulinsky A. The isomorphous structures of prethrombin2, hirugen-, and PPACK-thrombin: changes accompanying activation and exosite binding to thrombin. Protein Sci. 1994 Dec;3(12):2254–2271. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560031211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Q. Y., Sheehan J. P., Tsiang M., Lentz S. R., Birktoft J. J., Sadler J. E. Single amino acid substitutions dissociate fibrinogen-clotting and thrombomodulin-binding activities of human thrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6775–6779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zdanov A., Wu S., DiMaio J., Konishi Y., Li Y., Wu X., Edwards B. F., Martin P. D., Cygler M. Crystal structure of the complex of human alpha-thrombin and nonhydrolyzable bifunctional inhibitors, hirutonin-2 and hirutonin-6. Proteins. 1993 Nov;17(3):252–265. doi: 10.1002/prot.340170304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]