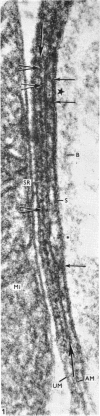
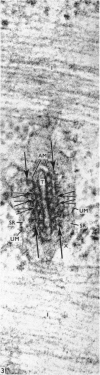
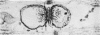Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAULFIELD J. B. Effects of varying the vehicle for OsO4 in tissue fixation. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 Sep 25;3(5):827–830. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.5.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edge M. B., Walker S. M. Evidence for a structural relationship between sarcoplasmic reticulum and Z lines in dog papillary muscle. Anat Rec. 1970 Jan;166(1):51–65. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091660105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANZINI-ARMSTRONG C., PORTER K. R. SARCOLEMMAL INVAGINATIONS CONSTITUTING THE T SYSTEM IN FISH MUSCLE FIBERS. J Cell Biol. 1964 Sep;22:675–696. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. W., McNutt N. S. The ultrastructure of the cat myocardium. I. Ventricular papillary muscle. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):1–45. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY H. E. EVIDENCE FOR CONTINUITY BETWEEN THE CENTRAL ELEMENTS OF THE TRIADS AND EXTRACELLULAR SPACE IN FROG SARTORIUS MUSCLE. Nature. 1964 Jun 13;202:1067–1071. doi: 10.1038/2021067b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. A., Sommer J. R. A strand of cardiac muscle. Its ultrastructure and the electrophysiological implications of its geometry. J Cell Biol. 1967 Apr;33(1):103–129. doi: 10.1083/jcb.33.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. E. The fine structure of skeletal muscle triad junctions. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Oct;29(1):37–49. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)80054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDNER E. Die submikroskopische Morphologie des Herzmuskels. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1957;45(6):702–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER K. R., PALADE G. E. Studies on the endoplasmic reticulum. III. Its form and distribution in striated muscle cells. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 Mar 25;3(2):269–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER K. R. The sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells of Amblystoma larvae. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Jul 25;2(4 Suppl):163–170. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.4.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peachey L. D. The sarcoplasmic reticulum and transverse tubules of the frog's sartorius. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3 Suppl):209–231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REGER J. F. The fine structure of neuromuscular junctions and the sarcoplasmic reticulum of extrinsic eye muscles of Fundulus heteroclitus. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Aug;10(4):111–121. doi: 10.1083/jcb.10.4.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REVEL J. P. The sarcoplasmic reticulum of the bat cricothroid muscle. J Cell Biol. 1962 Mar;12:571–588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiaffino S., Margreth A. Coordinated development of the sarcoplasmic reticulum and T system during postnatal differentiation of rat skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jun;41(3):855–875. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.3.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson F. O., Rayns D. G. The relationship between the transverse tubular system and other tubules at the Z disc levels of myocardial cells in the ferret. Am J Anat. 1968 Mar;122(2):193–207. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001220203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer J. R., Johnson E. A. Cardiac muscle. A comparative study of Purkinje fibers and ventricular fibers. J Cell Biol. 1968 Mar;36(3):497–526. doi: 10.1083/jcb.36.3.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. M., Schrodt G. R., Bingham M. Electron microscope study of the sarcoplasmic reticulum at the Z line level in skeletal muscle fibers of fetal and newborn rats. J Cell Biol. 1968 Nov;39(2):469–475. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. M., Schrodt G. R., Bingham M. Evidence for connections of the sarcoplasmic reticulum with the sarcolemma and with the Z line in skeletal muscle fibers of fetal and newborn rats. Am J Phys Med. 1969 Apr;48(2):63–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. M., Schrodt G. R. Membrane-like structures within the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1965 Apr 10;206(980):150–154. doi: 10.1038/206150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. M., Schrodt G. R. T system connexions with the sarcolemma and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1966 Aug 27;211(5052):935–938. doi: 10.1038/211935a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. M., Schrodt G. R. Triads in foetal skeletal muscle. Nature. 1967 Dec 9;216(5119):985–988. doi: 10.1038/216985a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. M., Schrodt G. R. Triads in skeletal muscle fibers of 19-day fetal rats. J Cell Biol. 1968 May;37(2):564–569. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.2.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]