Abstract
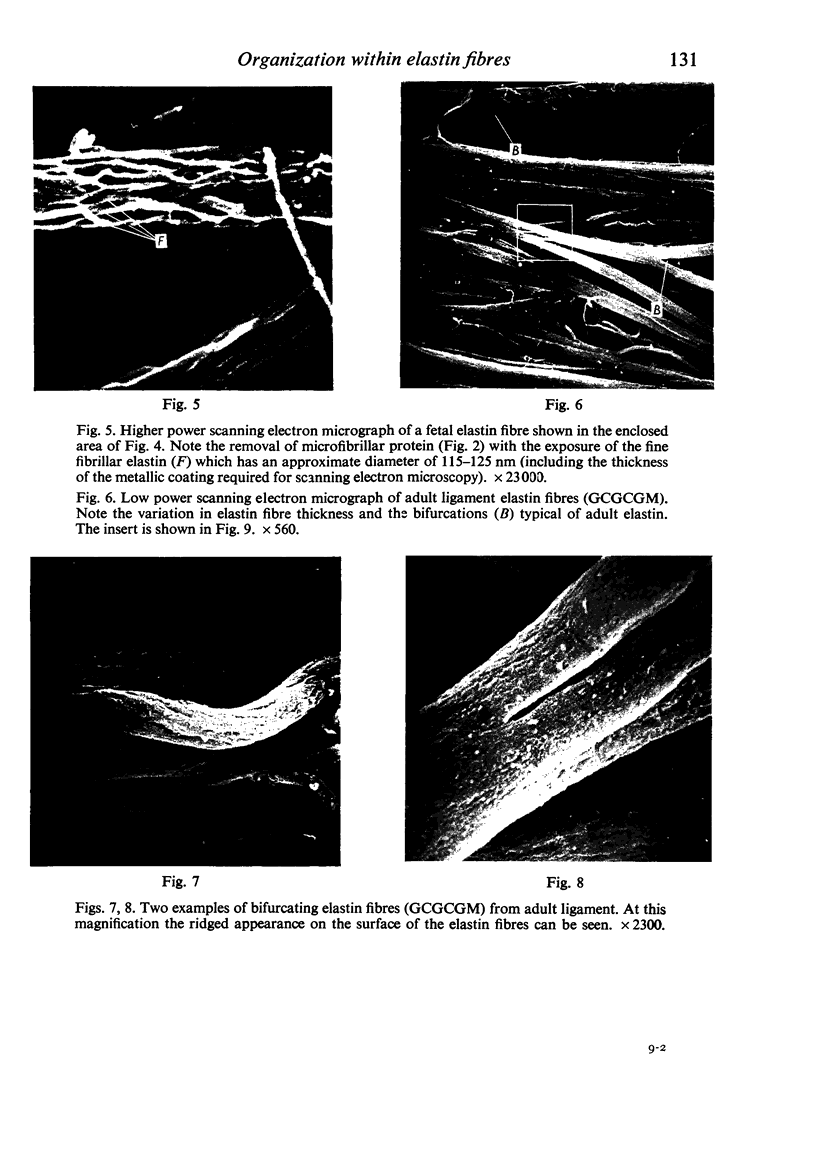
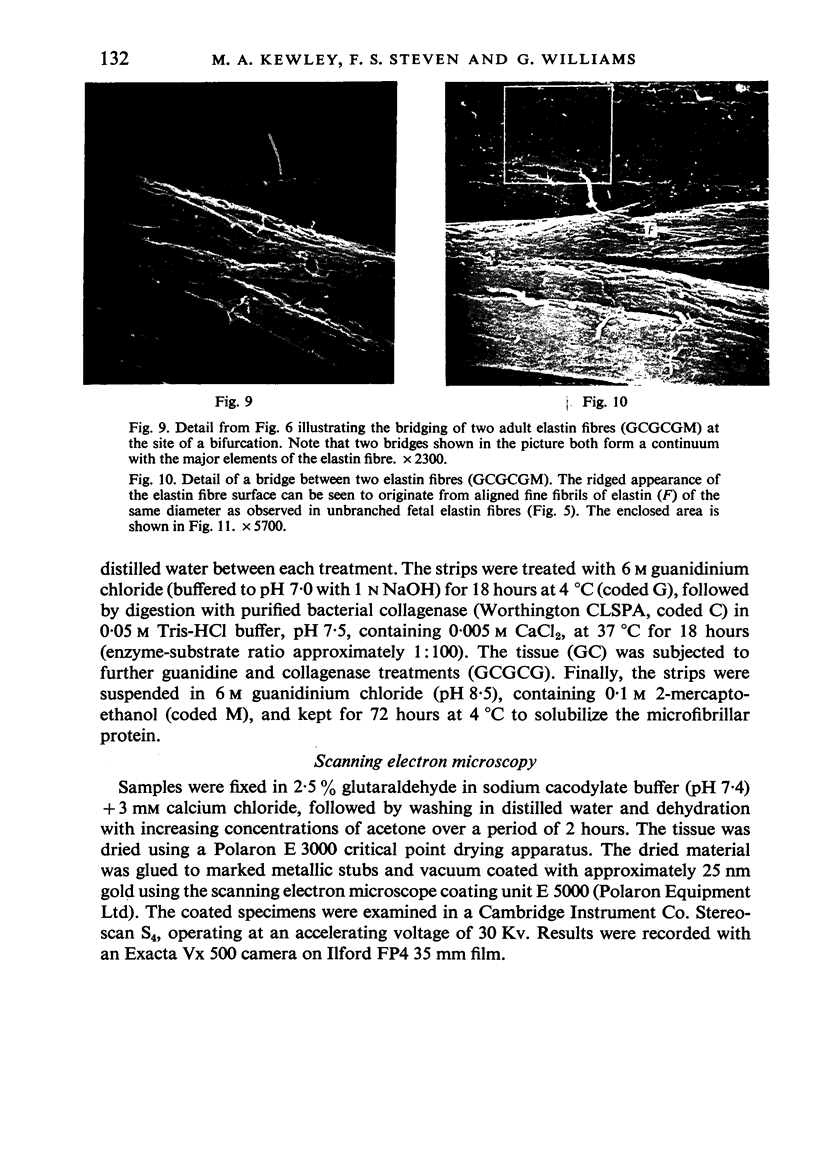
Scanning electron microscopy of critical point dried, enzymically and chemically purified fetal and adult elastin fibres from bovine ligamentum nuchae has shown that the fibres are composed of fine elastin fibrils (110-130nm diameter). In the fetal tissue the elastin fibres were of relatively uniform thickness and did not bifurcate, but in the adult, much thicker, branching fibres were present. It would appear that, during maturation of the elastin fibre, thickening is the result of the aggregation of many fine fibrils, and bifurcations result form bundles of such fibrils crossing over from one fibre to another.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Finlay J. B., Steven F. S. The fibrous components of bovine ligamentum nuchae observed in the scanning electron microscope. J Microsc. 1973 Sep;99(1):57–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1973.tb03852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotte L., Giro M. G., Volpin D., Horne R. W. The ultrastructural organization of elastin. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 Jan;46(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)80019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARRER H. E. An electron microscope study of the aorta in young and in aging mice. J Ultrastruct Res. 1961 Mar;5:1–27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(61)80002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintarelli G., Bellocci M., Zito R. Structural features of insoluble elastin. Histochemie. 1973 Oct 3;37(1):49–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00306859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Bornstein P. The elastic fiber. I. The separation and partial characterization of its macromolecular components. J Cell Biol. 1969 Feb;40(2):366–381. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]