Abstract
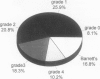
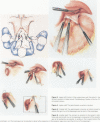
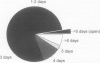
OBJECTIVE: The open Nissen fundoplication is effective therapy for gastroesophageal reflux disease. In this study, the outcomes in 198 patients treated with the laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication was evaluated for up to 32 months after surgery to ascertain whether similar positive results could be obtained. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: To ensure surgical success, patients were required to have mechanically defective sphincters on manometry and increased esophageal acid exposure on 24-hour pH monitoring. The patients either had severe complications of gastroesophageal reflux disease or had failed medical therapy. These requirements have been found to be necessary to ensure a successful surgical outcome. METHODS: The disease was complicated by ulceration (46), stricture (25) and Barrett's esophagus (33). Patients underwent standard Nissen fundoplications identical in every detail to open procedures except that the procedures were carried out by the laparoscopic route. RESULTS: Perioperative complications included gastric or esophageal perforation (3), pneumothorax (2), bleeding (2), breakdown of crural repair (2) and periesophageal abscess (1). The only mortality occurred from a duodenal perforation. Six patients required conversion to the open procedure. The median hospital stay was 3 days. One hundred patients were observed for follow-up for 6 to 32 months (median 12 months), with outcomes similar to the open Nissen fundoplication. Further surgery was required for two patients who had recurrent gastroesophageal reflux and one who developed an esophageal stricture. Ninety-seven percent are satisfied with their decision to have the operation. CONCLUSIONS: The laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication can be carried out safely and effectively with similar positive results to the open procedure and with all of the advantages of the minimally invasive approach.
Full text
PDF

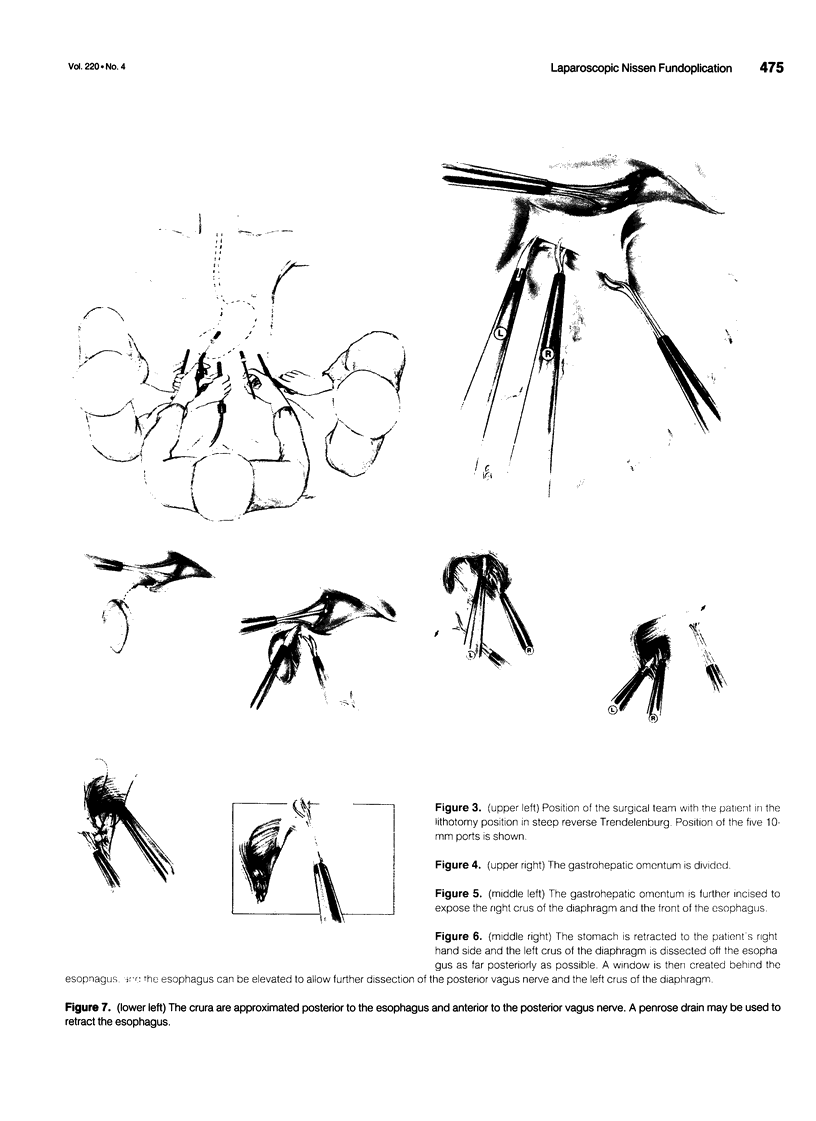



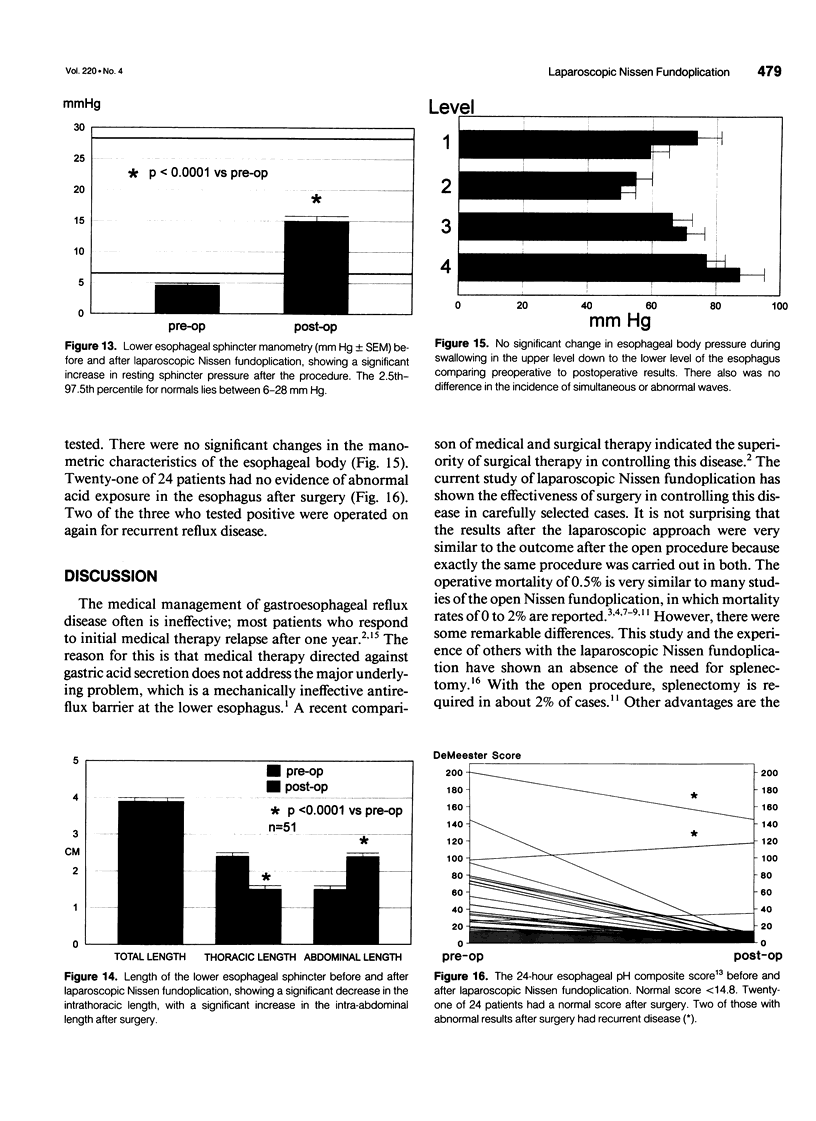


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anselmino M., Hinder R. A., Filipi C. J., Wilson P. Laparoscopic Heller cardiomyotomy and thoracoscopic esophageal long myotomy for the treatment of primary esophageal motor disorders. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1993 Oct;3(5):437–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonavina L., Evander A., DeMeester T. R., Walther B., Cheng S. C., Palazzo L., Concannon J. L. Length of the distal esophageal sphincter and competency of the cardia. Am J Surg. 1986 Jan;151(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(86)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., Bonavina L., Albertucci M. Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Evaluation of primary repair in 100 consecutive patients. Ann Surg. 1986 Jul;204(1):9–20. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198607000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demeester T. R., Johnson L. F., Kent A. H. Evaluation of current operations for the prevention of gastroesophageal reflux. Ann Surg. 1974 Oct;180(4):511–525. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197410000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue P. E., Samelson S., Nyhus L. M., Bombeck C. T. The floppy Nissen fundoplication. Effective long-term control of pathologic reflux. Arch Surg. 1985 Jun;120(6):663–668. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1985.01390300013002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetzel D. J., Dent J., Reed W. D., Narielvala F. M., Mackinnon M., McCarthy J. H., Mitchell B., Beveridge B. R., Laurence B. H., Gibson G. G. Healing and relapse of severe peptic esophagitis after treatment with omeprazole. Gastroenterology. 1988 Oct;95(4):903–912. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill L. D. An effective operation for hiatal hernia: an eight year appraisal. Ann Surg. 1967 Oct;166(4):681–692. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196710000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinder R. A., Filipi C. J. The technique of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1992 Sep;2(3):265–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Demeester T. R. Twenty-four-hour pH monitoring of the distal esophagus. A quantitative measure of gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Gastroenterol. 1974 Oct;62(4):325–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman D. A. Medical therapy for chronic reflux esophagitis. Long-term follow-up. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Oct;147(10):1717–1720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner D. B., Belsey R. H. Surgical management of esophageal reflux and hiatus hernia. Long-term results with 1,030 patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1967 Jan;53(1):33–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J. Comparison of medical and surgical therapy for complicated gastroesophageal reflux disease in veterans. The Department of Veterans Affairs Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1992 Mar 19;326(12):786–792. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199203193261202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stipa S., Fegiz G., Iascone C., Paolini A., Moraldi A., de Marchi C., Chieco P. A. Belsey and Nissen operations for gastroesophageal reflux. Ann Surg. 1989 Nov;210(5):583–589. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198911000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thor K. B., Silander T. A long-term randomized prospective trial of the Nissen procedure versus a modified Toupet technique. Ann Surg. 1989 Dec;210(6):719–724. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198912000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urschel J. D. Complications of antireflux surgery. Am J Surg. 1993 Jul;166(1):68–70. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(05)80587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerts J. M., Dallemagne B., Hamoir E., Demarche M., Markiewicz S., Jehaes C., Lombard R., Demoulin J. C., Etienne M., Ferron P. E. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: detailed analysis of 132 patients. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1993 Oct;3(5):359–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winans C. S., Harris L. D. Quantitation of lower esophageal sphincter competence. Gastroenterology. 1967 May;52(5):773–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]