Abstract
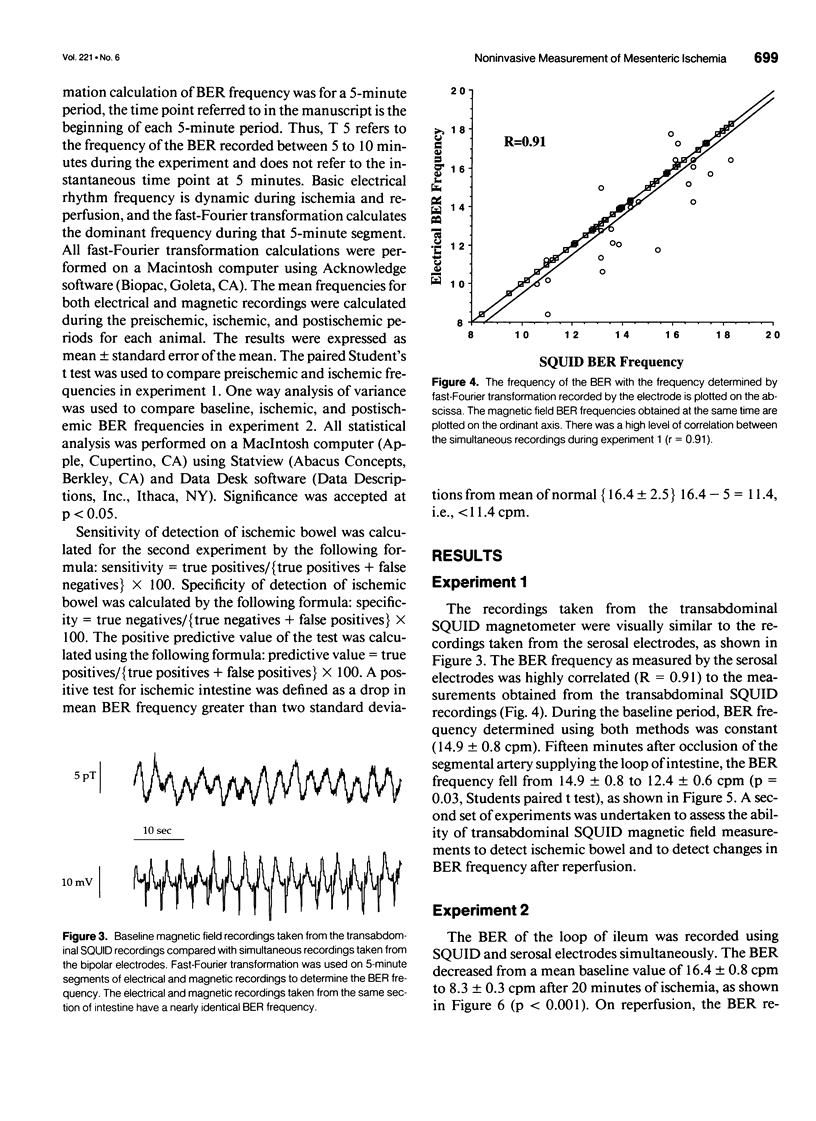
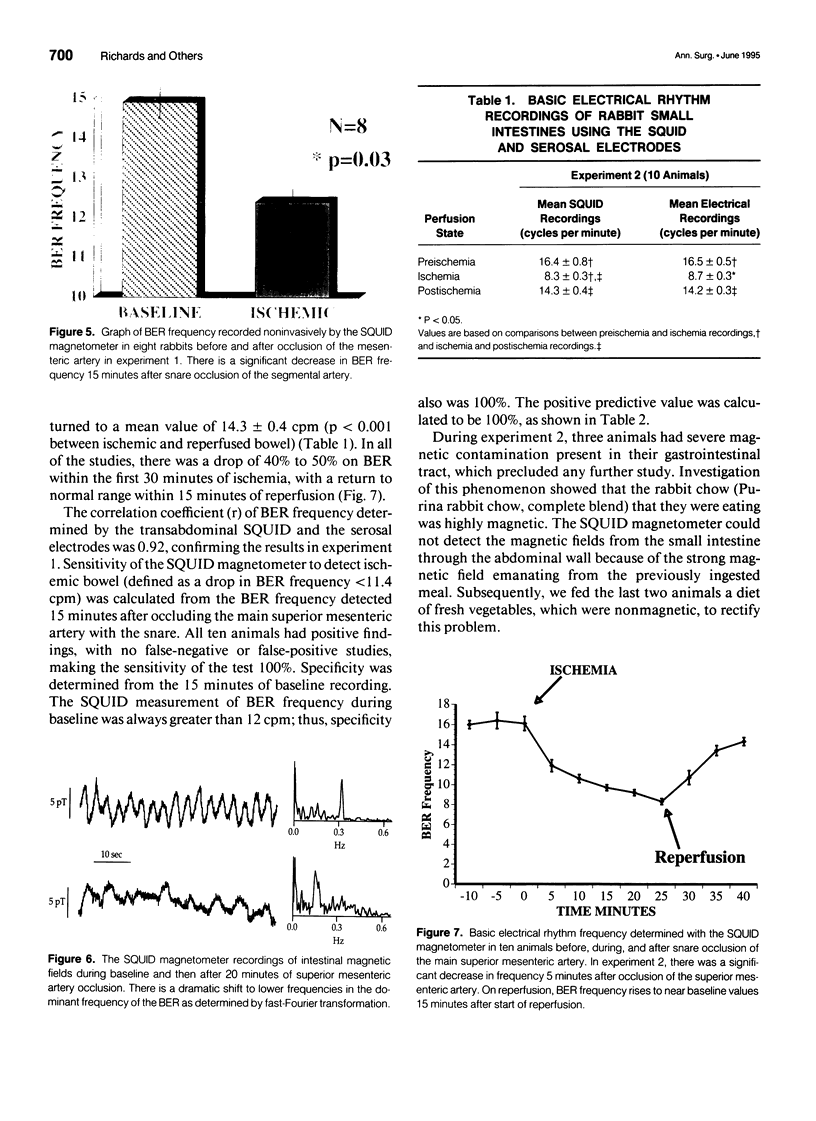
OBJECTIVE: The authors assessed the ability of a Superconducting Quantum Interference Device (SQUID) magnetometer to noninvasively detect mesenteric ischemia in a rabbit model. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Superconducting Quantum Interference Device magnetometers have been used to detect magnetic fields created by the basic electrical rhythm (BER) and to detect changes in BER of exteriorized bowel of anesthetized rabbits during mesenteric ischemia. METHODS: The BER of rabbit ileum was noninvasively measured transabdominally using a SQUID magnetometer and compared with the electrical activity recorded with surgically implanted serosal electrodes before, during, and after snare occlusion of the superior mesenteric artery. RESULTS: Transabdominal SQUID recording of BER frequency was highly correlated to the measurements obtained with electrodes (R = 0.91). Basic electrical rhythm frequency decreased from 16.4 +/- 0.8 to 8.3 +/- 0.3 cpm (p < 0.001) after 25 minutes of ischemia. Reperfusion of ischemic bowel resulted in recovery of BER frequency to 14.3 +/- 0.4 cpm 10 minutes after blood flow was restored. CONCLUSIONS: A SQUID magnetometer is capable of noninvasively detecting mesenteric ischemia reliably and at an early stage by detecting a significant drop in BER frequency. These positive findings have encouraged the authors to continue development of clinically useful, noninvasive, detection of intestinal magnetic fields using SQUID magnetometers.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boley S. J., Feinstein F. R., Sammartano R., Brandt L. J., Sprayregen S. New concepts in the management of emboli of the superior mesenteric artery. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1981 Oct;153(4):561–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brolin R. E., Semmlow J. L., Koch R. A., Reddell M. T., Mast B. A., Mackenzie J. W. Myoelectric assessment of bowel viability. Surgery. 1987 Jul;102(1):32–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brolin R. E., Semmlow J. L., Sehonanda A., Koch R. A., Reddell M. T., Mast B. A., Mackenzie J. W. Comparison of five methods of assessment of intestinal viability. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1989 Jan;168(1):6–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulkley G. B., Zuidema G. D., Hamilton S. R., O'Mara C. S., Klacsmann P. G., Horn S. D. Intraoperative determination of small intestinal viability following ischemic injury: a prospective, controlled trial of two adjuvant methods (Doppler and fluorescein) compared with standard clinical judgment. Ann Surg. 1981 May;193(5):628–637. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198105000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabot R. M., Kohatsu S. The effects of ischemia on the electrical and contractile activities of the canine small intestine. Am J Surg. 1978 Aug;136(2):242–246. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(78)90237-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIEL E. E., WACHTER B. T., HONOUR A. J., BOGOCH A. The relationship between electrical and mechanical activity of the small intestine of dog and man. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1960 Jul;38:777–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duret R. L., Bastenie P. A. Intestinal disorders in hypothyroidism. Clinical and manometric study. Am J Dig Dis. 1971 Aug;16(8):723–727. doi: 10.1007/BF02239597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flinn W. R., Rizzo R. J., Park J. S., Sandager G. P. Duplex scanning for assessment of mesenteric ischemia. Surg Clin North Am. 1990 Feb;70(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)45036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharagozloo F., Bulkley G. B., Zuidema G. D., O'Mara C. S., Alderson P. O. The use of intraperitoneal xenon for early diagnosis of acute mesenteric ischemia. Surgery. 1984 Apr;95(4):404–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golzarian J., Staton D. J., Wikswo J. P., Jr, Friedman R. N., Richards W. O. Diagnosing intestinal ischemia using a noncontact superconducting quantum interference device. Am J Surg. 1994 Jun;167(6):586–592. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(94)90103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaleya R. N., Boley S. J. Acute mesenteric ischemia: an aggressive diagnostic and therapeutic approach. 1991 Roussel Lecture. Can J Surg. 1992 Dec;35(6):613–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schamaun M. Electromyography to determine viability of injured small bowel segments: an experimental study with preliminary clinical observations. Surgery. 1967 Nov;62(5):899–909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smout A. J., van der Schee E. J., Grashuis J. L. What is measured in electrogastrography? Dig Dis Sci. 1980 Mar;25(3):179–187. doi: 10.1007/BF01308136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szurszewski J., Steggerda F. R. The effect of hypoxia on the electrical slow wave of the canine small intestine. Am J Dig Dis. 1968 Feb;13(2):168–177. doi: 10.1007/BF02232959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkerson D. K., Mezrich R., Drake C., Sebok D., Zatina M. A. Magnetic resonance imaging of acute occlusive intestinal ischemia. J Vasc Surg. 1990 Apr;11(4):567–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



