Abstract
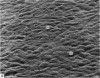
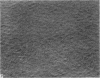
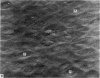
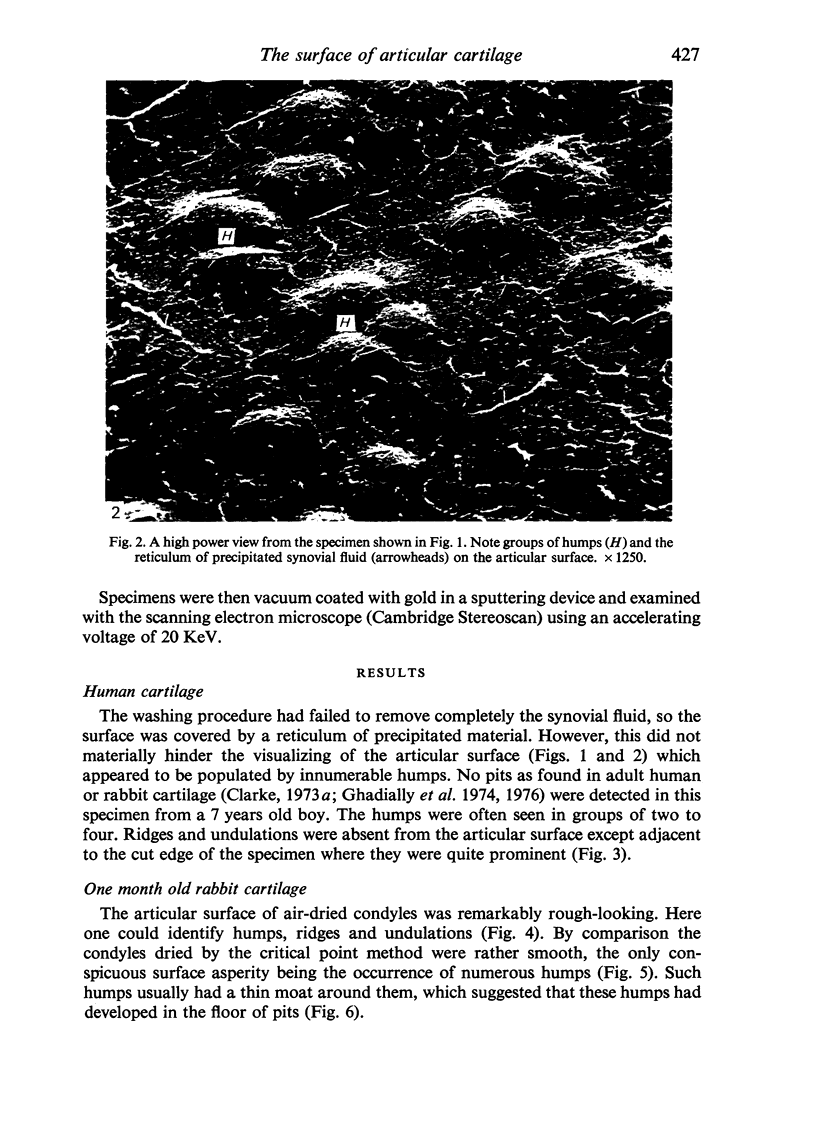
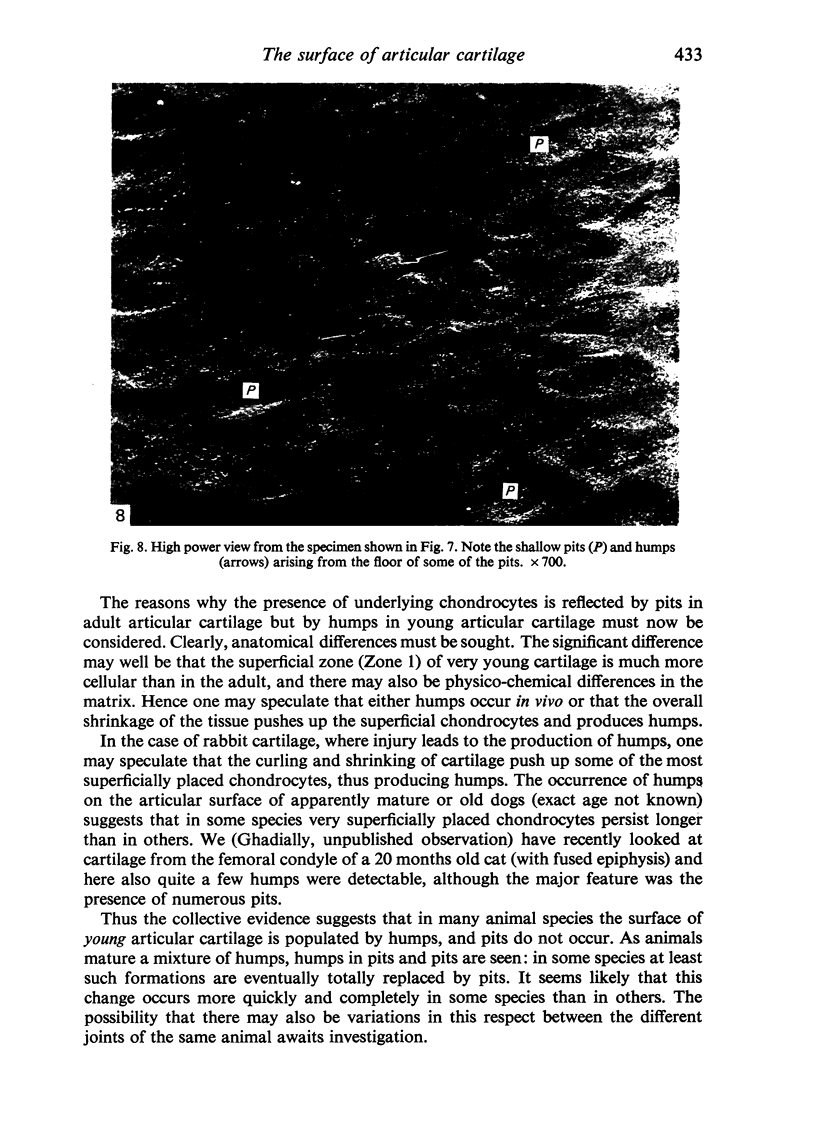
Scanning electron microscopic studies revealed numerous humps on the surface or articular cartilage from a 7 years old boy and from 1 month old rabbits. This shows that the surface topography of articular cartilage in young individuals is different from that of older individuals (human and rabbit) where the surface is beset by numerous pits. In 2 months old rabbits an intermediate situation was witnessed, for both shallow pits and occasional humps were present. Ridges and undulations were not seen on the articular surface of the 7 years old boy, except near the cut edge of the specimen. They were, however, found on air-dried specimens of 1 month old rabbit cartilage, but were absent from specimens dried by the critical-point method. The collective evidence supports the idea that ridges and undulations are not a constant feature of the normal articular surface, but that such features are artefactual, a typical or pathological.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarke I. C. A method for the replication of articular cartilage surfaces suitable for the scanning electron microscope. J Microsc. 1971 Feb;93(1):67–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1971.tb02266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke I. C. Human articular surface contours and related surface depression frequency studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 Jan;30(1):15–23. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke I. C. Quantitative measurement of human articular surface topography in vitro by profile recorder and stereomicroscopy techniques. J Microsc. 1973 Apr;97(3):309–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1973.tb03785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke I. C. Surface characteristics of human articular cartilage--a scanning electron microscope study. J Anat. 1971 Jan;108(Pt 1):23–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D. L. The influence of microscopic technology on knowledge of cartilage surface structure. Ann Rheum Dis. 1972 Jul;31(4):235–258. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.4.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D. L., Woodward D. Scanning electron microscopy and replica studies of articular surfaces of guinea-pig synovial joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 1969 Jul;28(4):379–391. doi: 10.1136/ard.28.4.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadially F. N., Ailsby R. L., Oryschak A. F. Scanning electron microscopy of superficial defects in articular cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 Jul;33(4):327–332. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.4.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadially F. N., Ghadially J. A., Oryschak A. F., Yong N. K. Experimental production of ridges on rabbit articular cartilage: a scanning electron microscope study. J Anat. 1976 Feb;121(Pt 1):119–132. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadially F. N., Ghadially J. A., Oryschak A. F., Yong N. K. The surface of dog articular cartilage: a scanning electron microscope study. J Anat. 1977 Apr;123(Pt 2):527–536. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadially J. A., Ghadially F. N. Evidence of cartilage flow in deep defects in articular cartilage. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1975 Jul 18;18(3):193–204. doi: 10.1007/BF02889247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longmore R. B., Gardner D. L. Development with age of human articular cartilage surface structure. A survey by interference microscopy of the lateral femoral condyle. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Feb;34(1):26–37. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall J. G. Scanning electron microscopy of articular surfaces. Lancet. 1968 Nov 30;2(7579):1194–1194. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91680-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meachim G. Light microscopy of Indian ink preparations of fibrillated cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 1972 Nov;31(6):457–464. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.6.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mow V. C., Lai W. M. Some surface characteristics of articular cartilage. I. A scanning electron microscopy study and a theoretical model for the dynamic interaction of synovial fluid and articular cartilage. J Biomech. 1974 Sep;7(5):449–456. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(74)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redler I. A scanning electron microscopic study of human normal and osteoarthritic articular cartilage. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974;(103):262–268. doi: 10.1097/00003086-197409000-00087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redler I., Zimny M. L. Scanning electron microscopy of normal and abnormal articular cartilage and synovium. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970 Oct;52(7):1395–1404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. S., Sikorski J., Dowson D., Longfield M. D., Wright V., Buckley T. Behaviour of synovial fluid on surfaces of articular cartilage. A scanning electron microscope study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1969 Jan;28(1):1–14. doi: 10.1136/ard.28.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]