Abstract
BACKGROUND. Concerns about laparoscopic antireflux surgery include the frequent appearance of troublesome postoperative dysphagia. This study reviews the frequency of early (less than 6 weeks) and persistent (greater than 6 weeks) solid food dysphagia in patients undergoing Toupet, Rosetti-Nissen, or Nissen fundoplications. METHODS. One hundred eighty-four consecutive patients with normal esophageal peristalsis undergoing laparoscopic antireflux surgery were prospectively studied. Before operation, all patients had endoscopy, 24-hour pH study, and an esophageal motility study. The choice of operation was dependent on anatomy and surgeon preference. Before discharge, all patients were given instructions on a soft diet. Postoperative symptoms were scored by the patients as absent, mild, moderate, or severe 4 weeks and 12 weeks after operation. The option of esophageal dilation was offered to patients with moderate to severe persistent solid food dysphagia. RESULTS. New onset moderate to severe dysphagia to solid foods was present in 30 (54%), 8 (17%), and 13 (16%) patients undergoing Rosetti-Nissen, Nissen, and Toupet fundoplications, respectively, in the first month after operation (p < 0.001). Moderate to severe dysphagia persisted at 3 months in six (11%), one (2%), and two (2%) patients undergoing laparoscopic Rosetti-Hell, Nissen, and Toupet fundoplications, respectively (p < 0.05). Esophageal dilatation was performed in five (4%), zero, and one (1%) patients undergoing laparoscopic Rosetti-Nissen, Nissen, and Toupet fundoplications, respectively (p < 0.05). There was no additional morbidity related to division of short gastric vessels in patients undergoing Nissen fundoplication. CONCLUSIONS. Laparoscopic Rosetti-Nissen fundoplication is associated with a higher rate of early and persistent postoperative dysphagia than either laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication or Toupet fundoplication. Consideration of complete fundus mobilization should be a part of all laparoscopic antireflux procedures.
Full text
PDF
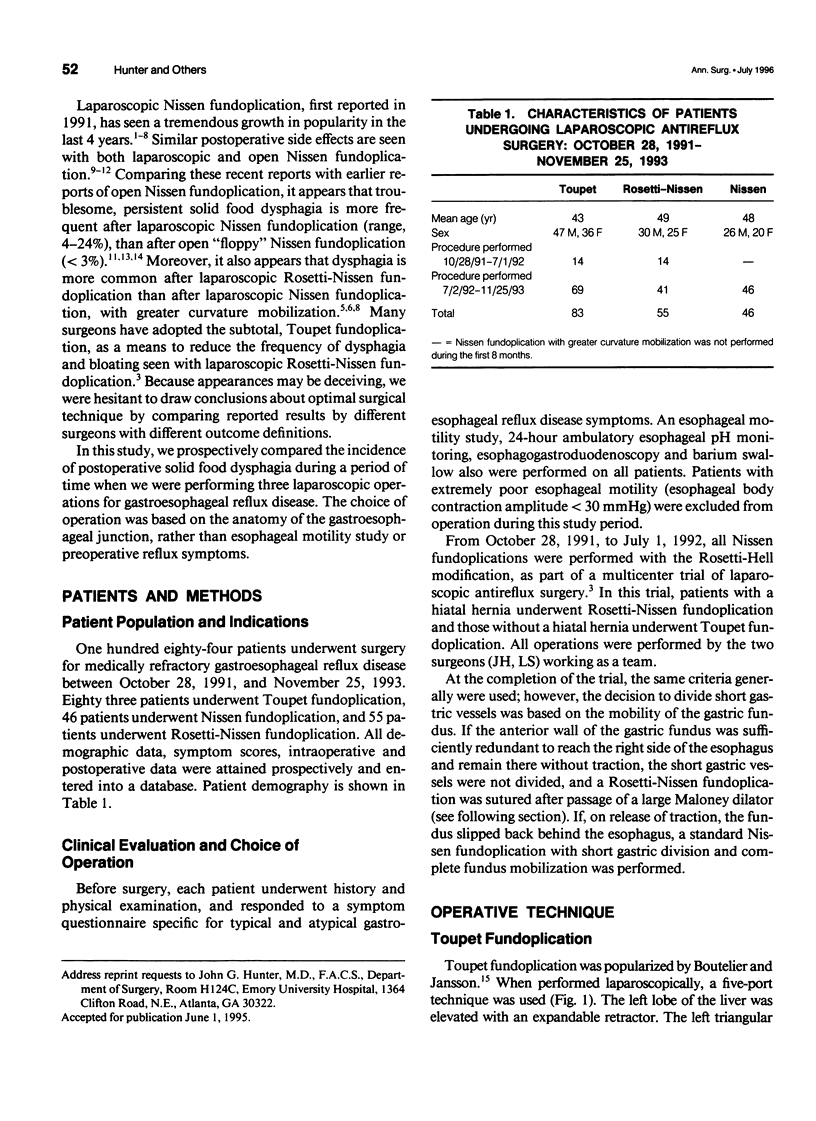
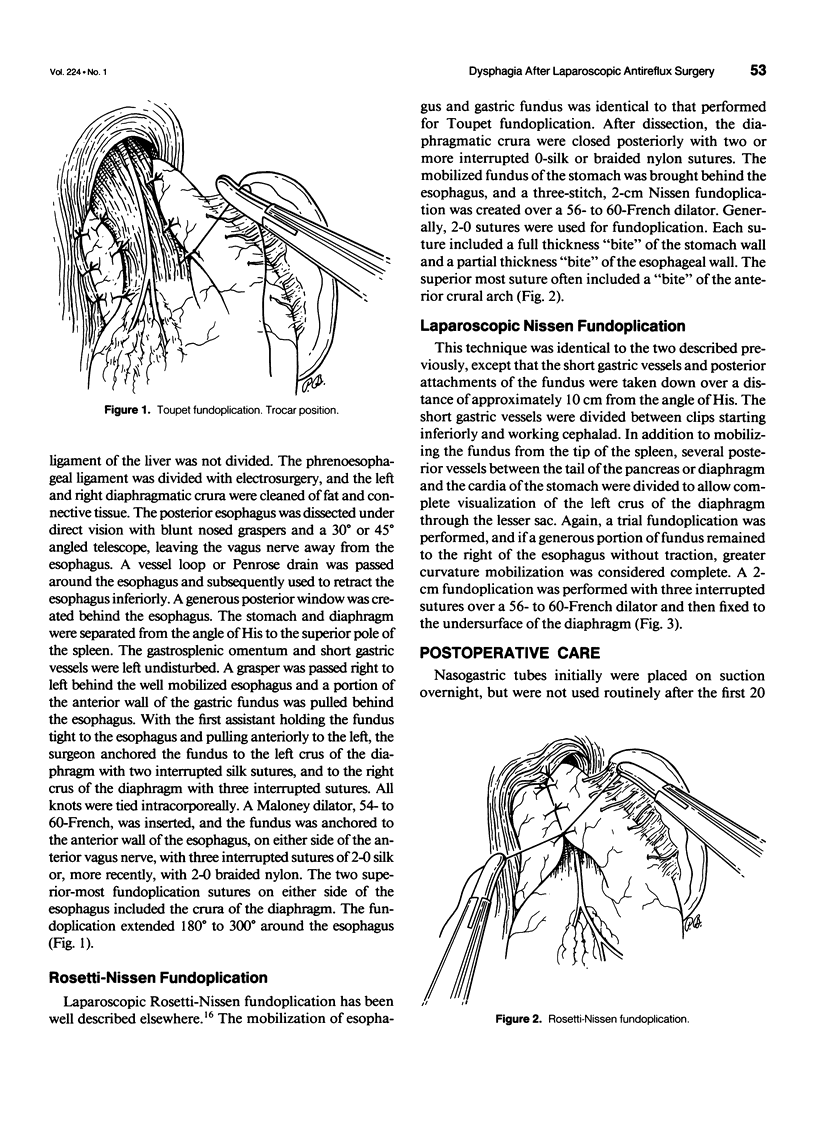
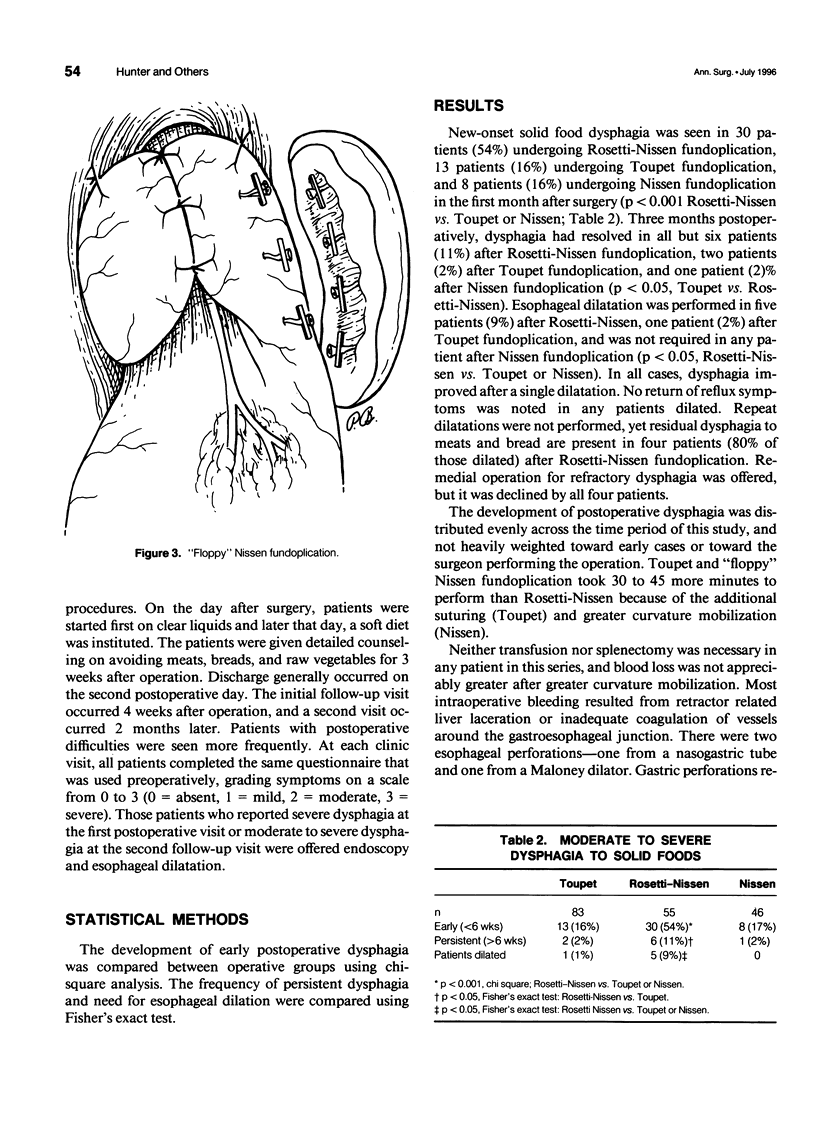



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bittner H. B., Meyers W. C., Brazer S. R., Pappas T. N. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: operative results and short-term follow-up. Am J Surg. 1994 Jan;167(1):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(94)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutelier P., Jonsell G. An alternative fundoplicative maneuver for gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Surg. 1982 Feb;143(2):260–264. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(82)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collard J. M., de Gheldere C. A., De Kock M., Otte J. B., Kestens P. J. Laparoscopic antireflux surgery. What is real progress? Ann Surg. 1994 Aug;220(2):146–154. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199408000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuschieri A., Hunter J., Wolfe B., Swanstrom L. L., Hutson W. Multicenter prospective evaluation of laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Preliminary report. Surg Endosc. 1993 Nov-Dec;7(6):505–510. doi: 10.1007/BF00316690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallemagne B., Weerts J. M., Jehaes C., Markiewicz S., Lombard R. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: preliminary report. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1991 Sep;1(3):138–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., Bonavina L., Albertucci M. Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Evaluation of primary repair in 100 consecutive patients. Ann Surg. 1986 Jul;204(1):9–20. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198607000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue P. E., Samelson S., Nyhus L. M., Bombeck C. T. The floppy Nissen fundoplication. Effective long-term control of pathologic reflux. Arch Surg. 1985 Jun;120(6):663–668. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1985.01390300013002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galmiche J. P., Ténière P., Ducrotte P., Denis P., Colin R., Testart J. Traitement du reflux gastro-cesophagien acide par hémifundoplicature postérieure. Résultats cliniques et pH-métriques. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1983 Apr;7(4):385–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geagea T. Laparoscopic Nissen's fundoplication: preliminary report on ten cases. Surg Endosc. 1991;5(4):170–173. doi: 10.1007/BF02653255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert C. A., O'Mara C. S. The Belsey operation for hiatal hernia: a twenty year experience. Am J Surg. 1979 Apr;137(4):532–535. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(79)90126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinder R. A., Filipi C. J., Wetscher G., Neary P., DeMeester T. R., Perdikis G. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication is an effective treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg. 1994 Oct;220(4):472–483. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199410000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson G. G., Watson D. I., Britten-Jones R., Mitchell P. C., Anvari M. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Ann Surg. 1994 Aug;220(2):137–145. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199408000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson W. R., Miyagishima R. T., Carr D. M., Stordy S. N., Sharp F. R. Surgical management of primary motor disorders of the esophagus. Am J Surg. 1984 Jul;148(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(84)90286-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luostarinen M. Nissen fundoplication for reflux esophagitis. Long-term clinical and endoscopic results in 109 of 127 consecutive patients. Ann Surg. 1993 Apr;217(4):329–337. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199304000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirazi S. S., Schulze K., Soper R. T. Long-term follow-up for treatment of complicated chronic reflux esophagitis. Arch Surg. 1987 May;122(5):548–552. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1987.01400170054008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J. Comparison of medical and surgical therapy for complicated gastroesophageal reflux disease in veterans. The Department of Veterans Affairs Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1992 Mar 19;326(12):786–792. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199203193261202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart R. C., Dawson K., Keeling P., Byrne P. J., Hennessy T. P. A prospective randomized trial of angelchik prosthesis versus Nissen fundoplication. Br J Surg. 1989 Jan;76(1):86–89. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800760127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom L., Wayne R. Spectrum of gastrointestinal symptoms after laparoscopic fundoplication. Am J Surg. 1994 May;167(5):538–541. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(94)90253-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thor K. B., Silander T. A long-term randomized prospective trial of the Nissen procedure versus a modified Toupet technique. Ann Surg. 1989 Dec;210(6):719–724. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198912000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerts J. M., Dallemagne B., Hamoir E., Demarche M., Markiewicz S., Jehaes C., Lombard R., Demoulin J. C., Etienne M., Ferron P. E. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: detailed analysis of 132 patients. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1993 Oct;3(5):359–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]