Abstract
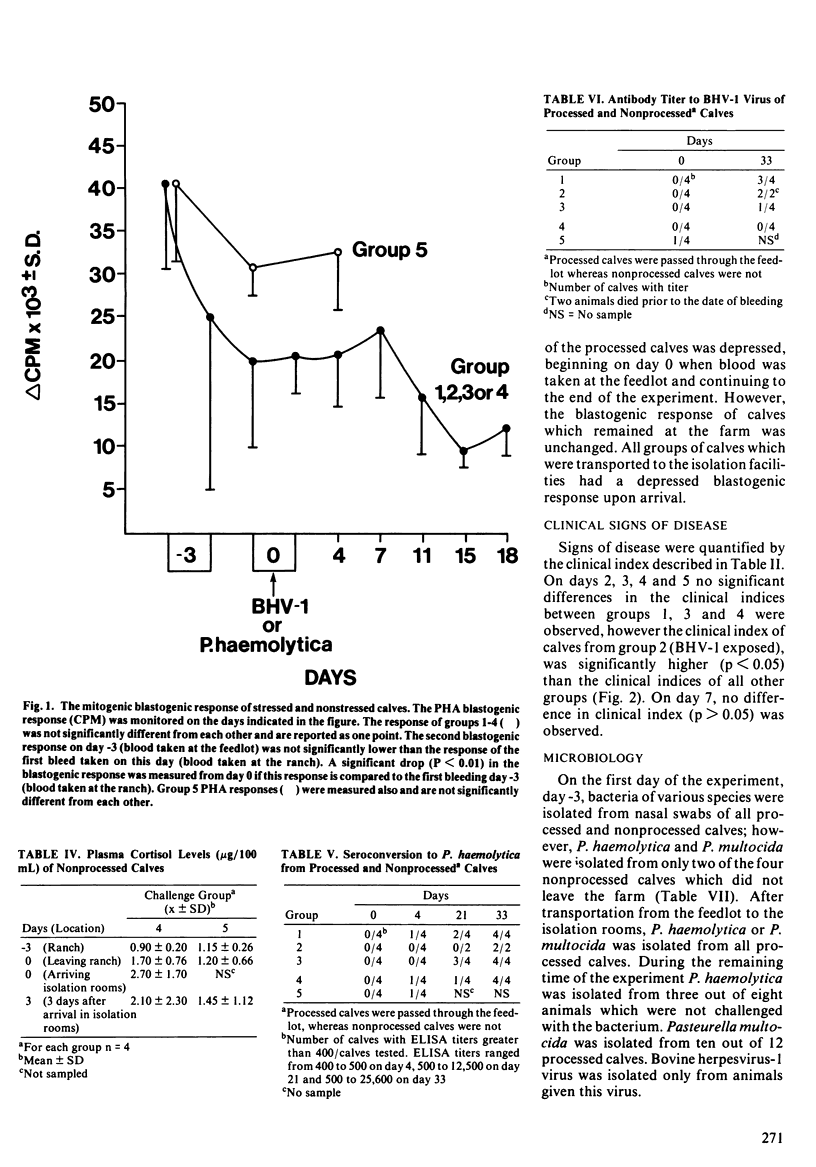
Five groups of range bred calves (four calves per group) were used to investigate the effect of stress on susceptibility to aerosol exposures with bovine herpesvirus-1 or Pasteurella haemolytica. Twelve calves were weaned, transported, processed at a commercial feedlot and transported to isolation facilities three days later. An aerosol challenge of either 10 colony forming units of P. haemolytica or 10 plaque forming units of bovine herpesvirus-1 virus was given to two groups of calves and the third group was not challenged. The fourth group was transported directly to the isolation facilities after weaning and aerosol challenged with P. haemolytica. The fifth group remained at the farm after weaning and was not challenged. All transported animals had elevated plasma cortisol levels which remained above normal for at least three days postchallenge. The blastogenic response of all calves was depressed after leaving the farm and remained depressed throughout the experiment. The suppression correlated well with elevated serum cortisol levels. Calves processed through the feedlot encountered bovine herpesvirus-1 because eight out of 12 animals seroconverted to this antigen. Most calves seroconverted to P. haemolytica whether they were experimentally challenged or not. Where the unchallenged calves encountered P. haemolytica is unknown. Calves challenged with bovine herpesvirus-1 but not with P. haemolytica, had significant clinical signs of pneumonia and two animals died due to bovine herpesvirus-1 infection.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arave C. W., Walters J. L., Lamb R. C. Effect of exercise on glucocorticoids and other cellular components of blood. J Dairy Sci. 1978 Nov;61(11):1567–1572. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(78)83766-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabello G. Plasma cortisol and aldosterone levels in healthy and diarrhoeic calves. Br Vet J. 1980 Mar-Apr;136(2):160–167. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)32339-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crookshank H. R., Elissalde M. H., White R. G., Clanton D. C., Smalley H. E. Effect of transportation and handling of calves upon blood serum composition. J Anim Sci. 1979 Mar;48(3):430–435. doi: 10.2527/jas1979.483430x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degré M. Synergistic effect in viral-bacterial infection. 5. Functional studies on the role of the ciliary activity in the mouse trachea. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(2):137–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorák M. Plasma 17-hydroxycorticosteroid levels in healthy and diarrhoeic calves. Br Vet J. 1971 Aug;127(8):372–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filion L. G., McGuire R. L., Babiuk L. A. Nonspecific suppressive effect of bovine herpesvirus type 1 on bovine leukocyte functions. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):106–112. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.106-112.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. C., Wilkie B. N., Thomson R. G., Barnum D. A. Bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis: experimental induction in vaccinated and nonvaccinated calves. Can J Comp Med. 1977 Jan;41(1):77–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidry A. J., Paape M. J., Pearson R. E. Effects of parturition and lactation on blood and milk cell concentrations, corticosteroids, and neutrophil phagocytosis in the cow. Am J Vet Res. 1976 Oct;37(10):1195–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwazdauskas F. C., Gross W. B., Bibb T. L., McGilliard M. L. Antibody titers and plasma glucocorticoid concentrations near weaning in steer and heifer calves. Can Vet J. 1978 Jun;19(6):150–154. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOERLEIN A. B., MARSH C. L. Studies on the epizootiology of shipping fever in calves. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1957 Aug 1;131(3):123–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson S., Mullford M., Whittlestone W. G., Payne E. Bovine plasma corticoids during parturition. J Dairy Sci. 1976 Apr;59(4):744–746. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(76)84267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Pierson R. E., Braddy P. M., Saari D. A., Lauerman L. H., England J. J., Keyvanfar H., Collier J. R., Horton D. P., McChesney A. E. Shipping fever pneumonia in yearling feedlot cattle. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1976 Sep 1;169(5):500–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jericho K. W., Darcel C. L., Langford E. V. Respiratory disease in calves produced with aerosols of parainfluenza-3 virus and Pasteurella haemolytica. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jul;46(3):293–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jericho K. W., Darcel C. Q. Response of the respiratory tract of calves kept at controlled climatic conditions to bovine Herpesvirus 1 in aerosol. Can J Comp Med. 1978 Apr;42(2):156–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jericho K. W., Langford E. V. Pneumonia in calves produced with aerosols of bovine herpesvirus 1 and Pasteurella haemolytica. Can J Comp Med. 1978 Jul;42(3):269–277. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller S. E., Weiss J. M., Schleifer S. J., Miller N. E., Stein M. Suppression of immunity by stress: effect of a graded series of stressors on lymphocyte stimulation in the rat. Science. 1981 Sep 18;213(4514):1397–1400. doi: 10.1126/science.6973822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley K. W., Greenfield R. E., Evermann J. F., Parish S. M., Perryman L. E. Delayed-type hypersensitivity, contact sensitivity, and phytohemagglutinin skin-test responses of heat- and cold-stressed calves. Am J Vet Res. 1982 May;43(5):775–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landi M. S., Kreider J. W., Lang C. M., Bullock L. P. Effects of shipping on the immune function in mice. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Sep;43(9):1654–1657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massip A. Haematocrit, biochemical and plasma cortisol changes associated with diarrhoea in the calf. Br Vet J. 1979 Nov-Dec;135(6):600–605. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)30014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman P. R., Corstvet R. E., Panciera R. J. Distribution of Pasteurella haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida in the bovine lung following vaccination and challenge exposure as an indicator of lung resistance. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Mar;43(3):417–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent K. M., Pesanti E. L. Chronic glucocorticosteroid therapy impairs staphylococcal clearance from murine lungs. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1033–1036. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1033-1036.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paape M. J., Schultze W. D., Desjardins C., Miller R. H. Plasma corticosteroid, circulating leukocyte and milk somatic cell responses to Escherichia coli endotoxin-induced mastitis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Feb;145(2):553–559. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-37850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. A., Kaeberle M. L. Effect of glucocorticoids on the bovine immune system. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1982 Apr 15;180(8):894–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. A., Kaeberle M. L. Effects of in vivo dexamethasone administration on in vitro bovine polymorphonuclear leukocyte function. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):434–441. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.434-441.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. A., Kaeberle M. L., Hsu W. H. Effects of ACTH administration on bovine polymorphonuclear leukocyte function and lymphocyte blastogenesis. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Mar;43(3):412–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW K. E., NICHOLS R. E. PLASMA 17-HYDROXYCORTICOSTEROIDS IN CALVES--THE EFFECTS OF SHIPPING. Am J Vet Res. 1964 Jan;25:252–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffy B. E., Davies D. H. Reactivation of a bovine herpesvirus after corticosteroid treatment. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jul;140(3):974–976. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens D. B. Stress and its measurement in domestic animals: a review of behavioral and physiological studies under field and laboratory situations. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1980;24:179–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L. H., Stott E. J., Collins A. P., Jebbett N. J., Stark A. J. Evaluation of respiratory disease in calves: comparison of disease response to different viruses. Res Vet Sci. 1977 Sep;23(2):157–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson R. G., Chander S., Savan M., Fox M. L. Investigation of factors of probable significance in the pathogenesis of pneumonic pasteurellosis in cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1975 Apr;39(2):194–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates W. D. A review of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, shipping fever pneumonia and viral-bacterial synergism in respiratory disease of cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jul;46(3):225–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates W. D., Jericho K. W., Doige C. E. Effect of bacterial dose on pneumonia induced by aerosol exposure of calves to bovine herpesvirus-1 and Pasteurella haemolytica. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Feb;44(2):238–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


