Abstract
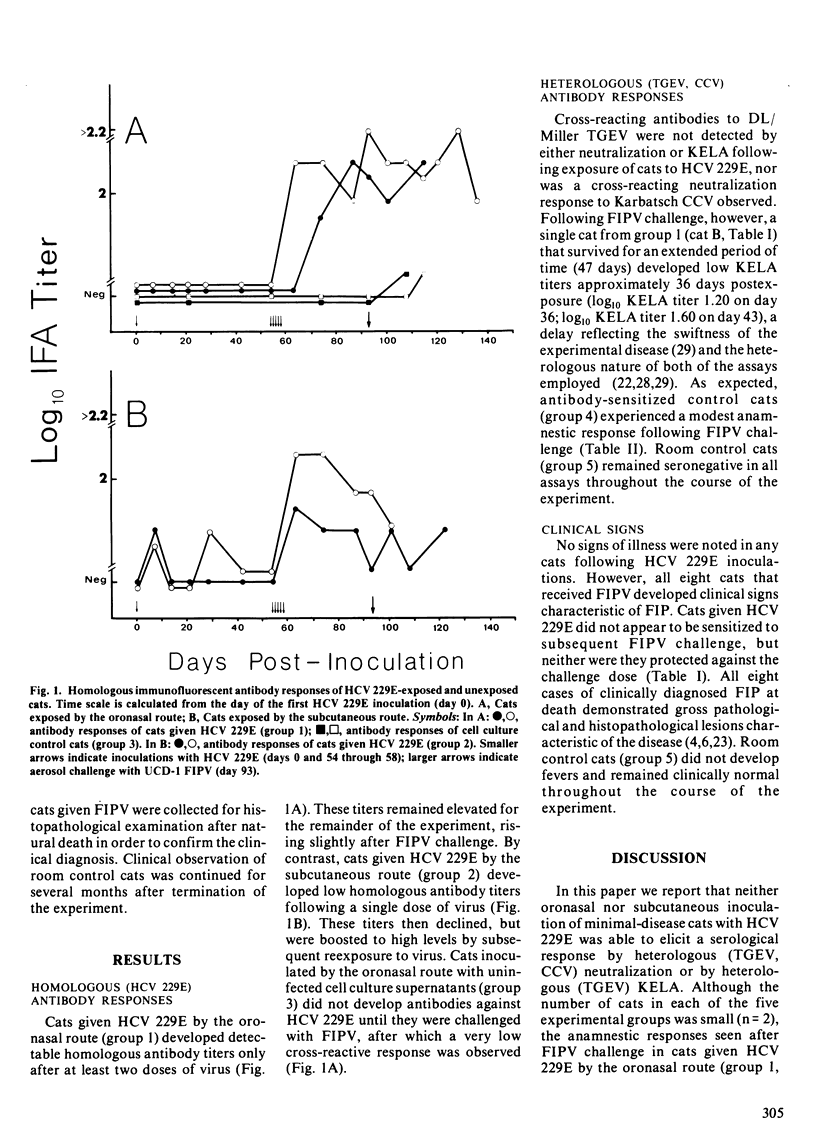
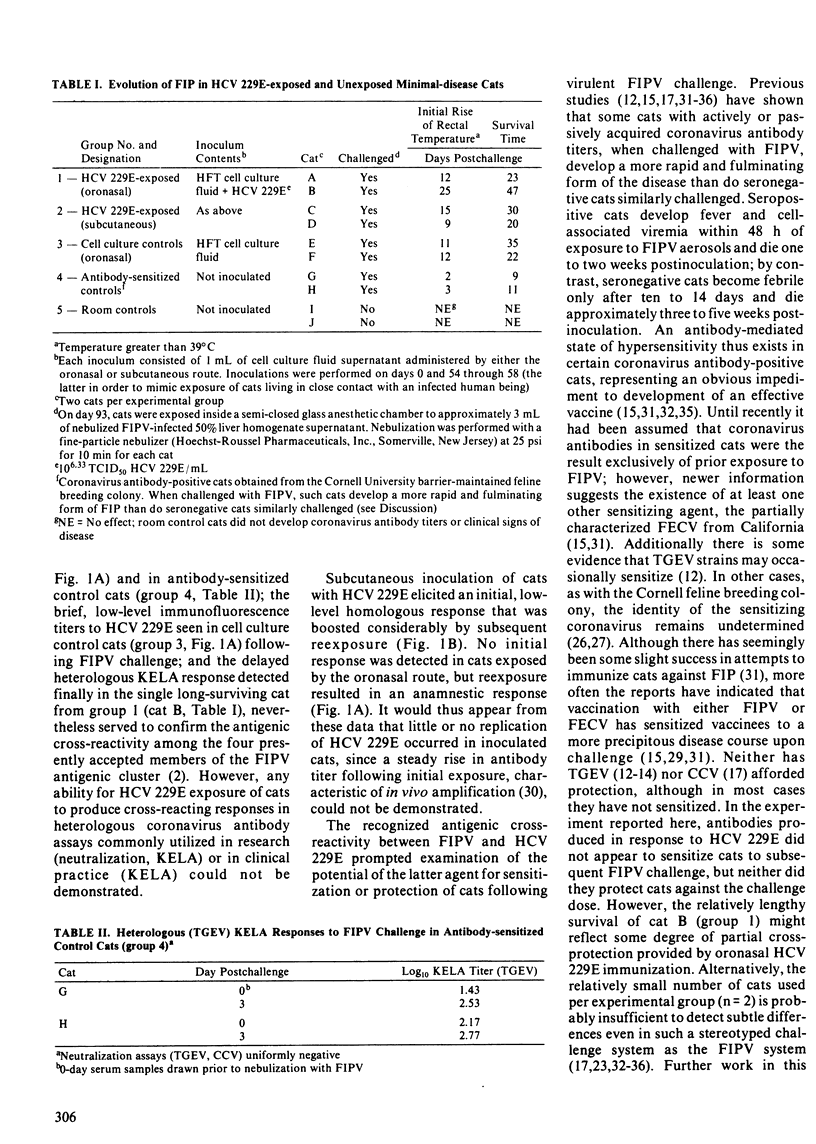
Minimal-disease cats exposed to live human coronavirus 229E developed homologous antibody responses that suggested little or no replication of the virus in inoculated animals. Oronasal and subcutaneous inoculation of coronavirus 229E did not elicit an antibody response by heterologous (transmissible gastroenteritis virus, canine coronavirus) neutralization or by heterologous (transmissible gastroenteritis virus) kinetics-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. No clinical signs attributable to coronavirus 229E were seen in inoculated cats. Although the number of animals in each of the five experimental groups was small (n = 2), antibodies produced in response to the virus did not appear to sensitize cats to subsequent feline infectious peritonitis virus challenge, but neither did they cross-protect cats against the challenge dose.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlough J. E., Jacobson R. H., Downing D. R., Marcella K. L., Lynch T. J., Scott F. W. Evaluation of a computer-assisted, kinetics-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of coronavirus antibodies in cats. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):202–217. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.202-217.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlough J. E., Jacobson R. H., Scott F. W. Macrotiter assay for coronavirus-neutralizing activity in cats using a canine continuous cell line (A-72). Lab Anim Sci. 1983 Dec;33(6):567–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlough J. E., Stoddart C. A., Sorresso G. P., Jacobson R. H., Scott F. W. Experimental inoculation of cats with canine coronavirus and subsequent challenge with feline infectious peritonitis virus. Lab Anim Sci. 1984 Dec;34(6):592–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binn L. N., Marchwicki R. H., Stephenson E. H. Establishment of a canine cell line: derivation, characterization, and viral spectrum. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Jun;41(6):855–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaloner Larsson G., Johnson-Lussenburg C. M. Establishment and maintenance of a persistent infection of L132 cells by human coronavirus strain 229E. Arch Virol. 1981;69(2):117–129. doi: 10.1007/BF01315155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horzinek M. C., Lutz H., Pedersen N. C. Antigenic relationships among homologous structural polypeptides of porcine, feline, and canine coronaviruses. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1148–1155. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1148-1155.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horzinek M. C., Osterhaus A. D. The virology and pathogenesis of feline infectious peritonitis. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1979;59(1-2):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01317889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterhaus A. D., Horzinek M. C., Reynolds D. J. Seroepidemiology of feline infectious peritonitis virus infections using transmissible gastroenteritis virus as antigen. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1977 Dec;24(10):835–841. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1977.tb00976.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. C., Black J. W. Attempted immunization of cats against feline infectious peritonitis, using avirulent live virus or sublethal amounts of virulent virus. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Feb;44(2):229–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. C., Boyle J. F., Floyd K., Fudge A., Barker J. An enteric coronavirus infection of cats and its relationship to feline infectious peritonitis. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Mar;42(3):368–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. C. Morphologic and physical characteristics of feline infectious peritonitis virus and its growth in autochthonous peritoneal cell cultures. Am J Vet Res. 1976 May;37(5):567–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. C. Serologic studies of naturally occurring feline infectious peritonitis. Am J Vet Res. 1976 Dec;37(12):1449–1453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. C., Ward J., Mengeling W. L. Antigenic relationship of the feline infectious peritonitis virus to coronaviruses of other species. Arch Virol. 1978;58(1):45–53. doi: 10.1007/BF01315534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen N. C., Boyle J. F. Immunologic phenomena in the effusive form of feline infectious peritonitis. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Jun;41(6):868–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. J., Garwes D. J. Virus isolation and serum antibody responses after infection of cats with transmissible gastroenteritis virus. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1979;60(2):161–166. doi: 10.1007/BF01348032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt O. W., Cooney M. K., Kenny G. E. Plaque assay and improved yield of human coronaviruses in a human rhabdomyosarcoma cell line. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jun;9(6):722–728. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.6.722-728.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt O. W., Kenny G. E. Immunogenicity and antigenicity of human coronaviruses 229E and OC43. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1000–1006. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1000-1006.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S. G., Anderson R., Cavanagh D., Fujiwara K., Klenk H. D., Macnaughton M. R., Pensaert M., Stohlman S. A., Sturman L., van der Zeijst B. A. Coronaviridae. Intervirology. 1983;20(4):181–189. doi: 10.1159/000149390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoddart C. A., Barlough J. E., Scott F. W. Experimental studies of a coronavirus and coronavirus-like agent in a barrier-maintained feline breeding colony. Arch Virol. 1984;79(1-2):85–94. doi: 10.1007/BF01314306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. C., Dodds W. J., Scott F. W. Disseminated intravascular coagulation in experimentally induced feline infectious peritonitis. Am J Vet Res. 1980 May;41(5):663–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. C., Scott F. W. Antibody-mediated enhancement of disease in feline infectious peritonitis: comparisons with dengue hemorrhagic fever. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1981;4(2):175–189. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(81)90003-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. C., Scott F. W. Pathogenesis of feline infectious peritonitis: nature and development of viremia. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Mar;42(3):382–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. C., Scott F. W. Pathogenesis of feline infetious peritonitis: pathologic changes and immunofluorescence. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Dec;42(12):2036–2048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte K. H., Tuch K., Dubenkropp H., Walther C. Untersuchungen über die Antigenverwandtschaft der Viren der Felinen Infektiösen Peritonitis (FIP) und der Transmissiblen Gastroenteritis (TGE) des Schweines. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1977 Oct 15;90(20):396–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


