Abstract
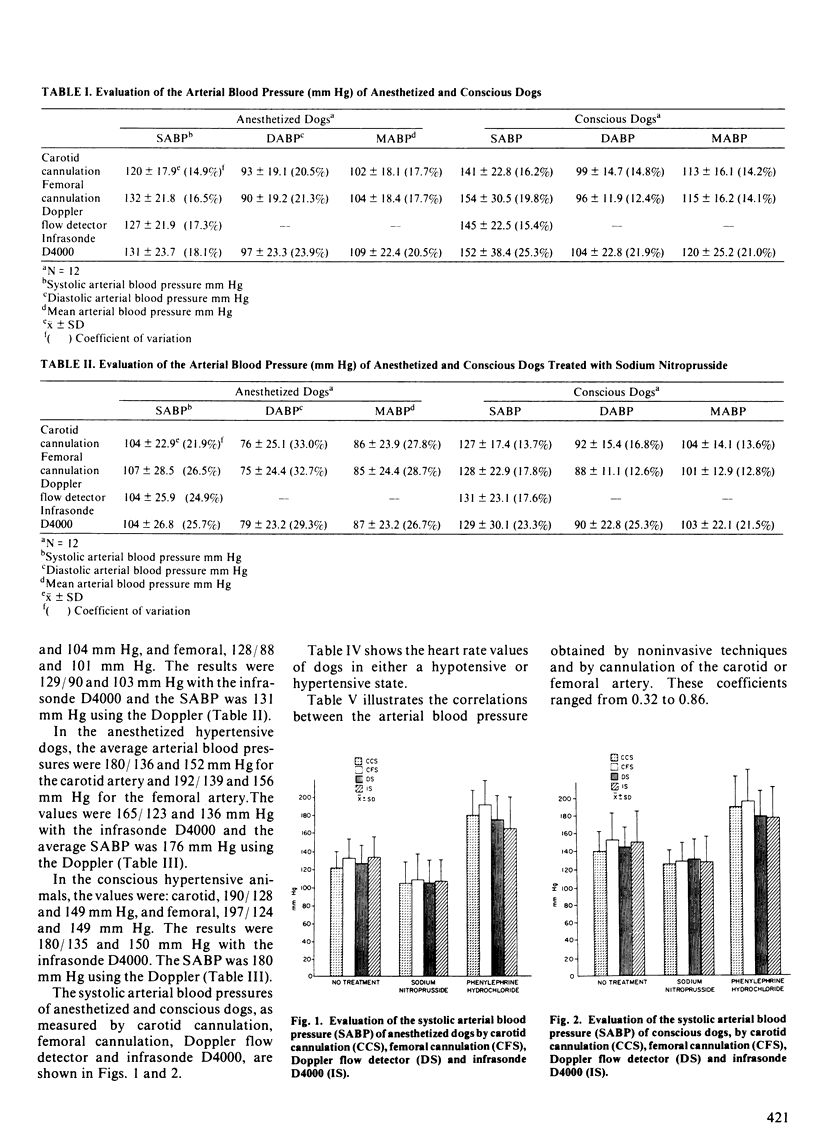
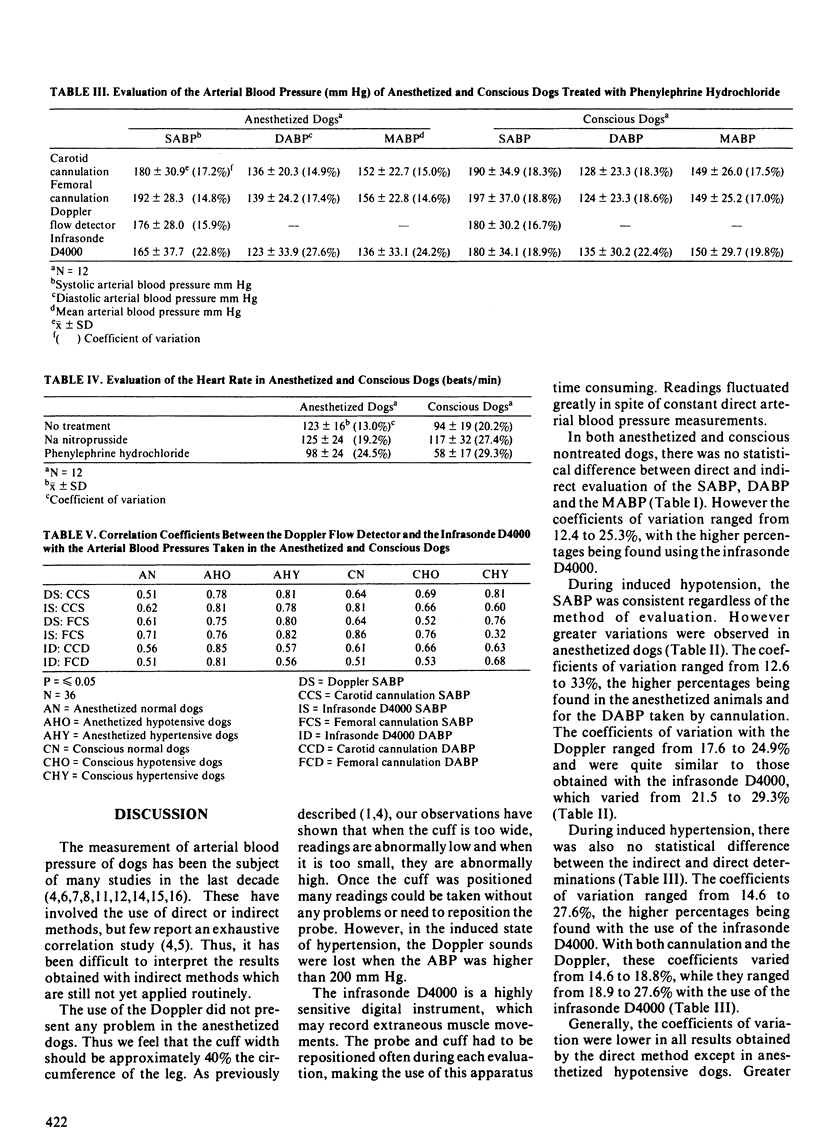
The determination of the arterial blood pressure was done on 12 healthy mixed breed dogs in both the anesthetized and the conscious state, to evaluate two instruments (Doppler flow detector and infrasonde D4000), in their ability to indirectly determine arterial blood pressure. The coefficients of variation were higher with indirect methods when compared with the results obtained by cannulation. These coefficients were lower with the Doppler flow detector. The correlation study showed that both apparatuses were reliable in most situations. The infrasonde D4000 was more accurate than the Doppler in the conscious animals. However the results showed a lack of precision in hypertensive conscious dogs. The diastolic arterial blood pressure was particularly precise in the case of the anesthetized hypotensive dogs. Its sensitivity allowed it to register muscle movement artifacts. The Doppler flow detector showed less variation and was particularly accurate in both anesthetized and conscious hypertensive dogs. Its sensitivity allowed artifact movement sounds to be detected. The Doppler should be used in quiet surroundings or earphones should be worn by the evaluator. Some form of restraint is needed with the use of both instruments. Even if the correlations with the direct arterial blood pressure values were better with the infrasonde D4000, greater variations were found in the individual readings. The Doppler instrument represents in the hands of the investigators a better instrument for routine monitoring of blood pressure in the dog.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergel D. H., Peveler R. C., Robinson J. L., Sleight P. The measurement of arterial pressure, carotid sinus radius and baroreflex sensitivity in the conscious greyhound [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:65P–66P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter D. B., Whelan S. C., Wilson R. C., Goetsch D. D. Determination of blood pressure by indirect methods in dogs given acetylpromazine maleate. Cornell Vet. 1981 Jan;71(1):75–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich J. J., Detweiler D. K., Hance H. E. Indirect blood pressure determination by the ultrasonic doppler technique in dogs. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1972 Feb;14(2):73–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner H. E., Hahn A. W., Hartley J. W., Hutcheson D. P., Coffman J. R. Indirect blood pressure measurement in the dog. Lab Anim Sci. 1975 Apr;25(2):197–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes L. A., Combs W., Denton W., Whistler S. J., Bourland J. D. Indirect mean arterial pressure in the anesthetized dog. Am J Physiol. 1980 May;238(5):H664–H666. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1980.238.5.H664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlin R. L., Kittleson M. D., Rice D., Knowlen G., Seyffert R. Noninvasive measurement of systemic arterial pressure in dogs by automatic sphygmomanometry. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Jul;43(7):1271–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeish I. Doppler ultrasonic arterial pressure measurement in the cat. Vet Rec. 1977 Apr 2;100(14):290–291. doi: 10.1136/vr.100.14.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. S., Peel H. H., Wigodsky H. S., Morris M. D. Noninvasive oscillometric measurement of blood pressure in baboons (Papio cynocephalus). Lab Anim Sci. 1980 Aug;30(4 Pt 1):666–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON R. B., CLARKE T. J. INDIRECT MEASUREMENT OF SYSTOLIC BLOOD PRESSURE IN DOGS BY THE USE OF A XYLOL PULSE INDICATOR. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1964 May 1;144:981–984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. G., Spangler W. L., Gribble D. H. Blood pressure measurement in the dog. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1977 Aug 15;171(4):364–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. B., Schapiro H., Yeiser P. E. Noninvasive blood pressure determination in the rabbit with a Doppler ultrasound probe. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Jul;161(3):417–420. doi: 10.3181/00379727-161-40564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamakoshi K. I., Shimazu H., Togawa T. Indirect measurement of instantaneous arterial blood pressure in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1979 Nov;237(5):H632–H637. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.237.5.H632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


