Abstract
We have analyzed the pH dependencies of published amide proton exchange rates (kex) in three proteins: bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI), bull seminal plasma proteinase inhibitor IIA (BUSI IIA), and calbindin D9K. The base-catalyzed exchange rate constants (kOH) of solvent exposed amides in BPTI are lower for residues with low peptide carbonyl exposure, showing that the environment around the carbonyl oxygen influences kOH. We also examined the possible importance of an exchange mechanism that involves formations of imidic acid intermediates along chains of hydrogen-bonded peptides in the three proteins. By invoking this "relayed imidic acid exchange mechanism," which should be essentially acid-catalyzed, we can explain the surprisingly high pHmin (the pH value at which kex reaches a minimum) found for the non-hydrogen-bonded amide protons in the beta-sheet in BPTI. The successive increase of pHmin along a chain of hydrogen-bonded peptides from the free amide to the free carbonyl, observed in BPTI, can be explained as an increasing contribution of the proposed mechanism in this direction of the chain. For BUSI IIA (pH 4-5) and calbindin D9K (pH 6-7) the majority of amide protons with negative pH dependence of kex are located in chains of hydrogen-bonded peptides; this situation is shown to be consistent with the proposed mechanism.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akke M., Forsén S., Chazin W. J. Molecular basis for co-operativity in Ca2+ binding to calbindin D9k. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance studies of (Cd2+)1-bovine calbindin D9k. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jul 5;220(1):173–189. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90389-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berendsen H. J., Van Gunsteren W. F., Zwinderman H. R., Geurtsen R. G. Simulations of proteins in water. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;482:269–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb20961.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berndt K. D., Güntert P., Orbons L. P., Wüthrich K. Determination of a high-quality nuclear magnetic resonance solution structure of the bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor and comparison with three crystal structures. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 5;227(3):757–775. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90222-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chazin W. J., Kördel J., Drakenberg T., Thulin E., Brodin P., Grundström T., Forsén S. Proline isomerism leads to multiple folded conformations of calbindin D9k: direct evidence from two-dimensional 1H NMR spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2195–2198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delepierre M., Dobson C. M., Karplus M., Poulsen F. M., States D. J., Wedin R. E. Electrostatic effects and hydrogen exchange behaviour in proteins. The pH dependence of exchange rates in lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1987 Sep 5;197(1):111–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90613-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L. M., Bloomfield V. A., Woodward C. K. Hydrogen-tritium exchange kinetics of soybean trypsin inhibitor (Kunitz). Solvent accessibility in the folded conformation. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 29;14(15):3413–3419. doi: 10.1021/bi00686a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englander J. J., Rogero J. R., Englander S. W. Identification of an allosterically sensitive unfolding unit in hemoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 5;169(1):325–344. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80186-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englander S. W., Englander J. J., McKinnie R. E., Ackers G. K., Turner G. J., Westrick J. A., Gill S. J. Hydrogen exchange measurement of the free energy of structural and allosteric change in hemoglobin. Science. 1992 Jun 19;256(5064):1684–1687. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5064.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fersht A. R. Acyl-transfer reactions of amides and esters with alcohols and thiols. A reference system for the serine and cysteine proteinases. Concerning the N protonation of amides and amide-imidate equilibria. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jul 14;93(14):3504–3515. doi: 10.1021/ja00743a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher W., Tao F., Woodward C. Comparison of hydrogen exchange rates for bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor in crystals and in solution. Biochemistry. 1992 May 19;31(19):4673–4680. doi: 10.1021/bi00134a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory R. B., Crabo L., Percy A. J., Rosenberg A. Water catalysis of peptide hydrogen isotope exchange. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 15;22(4):910–917. doi: 10.1021/bi00273a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton B. D., Trudeau K., Woodward C. K. Hydrogen exchange rates in pancreatic trypsin inhibitor are not correlated to thermal stability in urea. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 4;20(16):4697–4703. doi: 10.1021/bi00519a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton B. D., Woodward C. K. On the mechanism of isotope exchange kinetics of single protons in bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1979 Dec 25;18(26):5834–5841. doi: 10.1021/bi00593a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hvidt A., Nielsen S. O. Hydrogen exchange in proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1966;21:287–386. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60129-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwajima K., Baldwin R. L. Exchange behavior of the H-bonded amide protons in the 3 to 13 helix of ribonuclease S. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 5;169(1):299–323. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
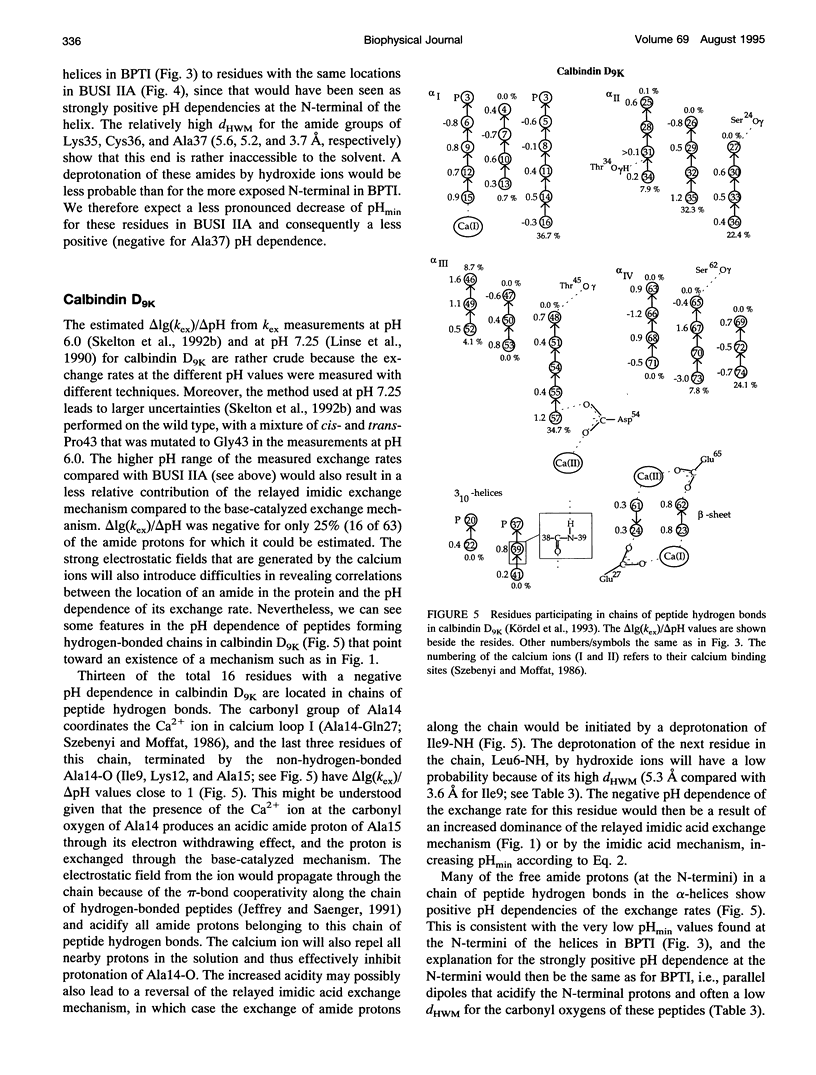
- Kördel J., Skelton N. J., Akke M., Chazin W. J. High-resolution structure of calcium-loaded calbindin D9k. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jun 5;231(3):711–734. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Richards F. M. The interpretation of protein structures: estimation of static accessibility. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):379–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linse S., Teleman O., Drakenberg T. Ca2+ binding to calbindin D9k strongly affects backbone dynamics: measurements of exchange rates of individual amide protons using 1H NMR. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 26;29(25):5925–5934. doi: 10.1021/bi00477a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molday R. S., Englander S. W., Kallen R. G. Primary structure effects on peptide group hydrogen exchange. Biochemistry. 1972 Jan 18;11(2):150–158. doi: 10.1021/bi00752a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen T. G., Sigurskjold B. W., Andersen K. V., Kjaer M., Poulsen F. M., Dobson C. M., Redfield C. A nuclear magnetic resonance study of the hydrogen-exchange behaviour of lysozyme in crystals and solution. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 20;218(2):413–426. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90722-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen T. G., Thomsen N. K., Andersen K. V., Madsen J. C., Poulsen F. M. Determination of the rate constants k1 and k2 of the Linderström-Lang model for protein amide hydrogen exchange. A study of the individual amides in hen egg-white lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 20;230(2):651–660. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richarz R., Sehr P., Wagner G., Wüthrich K. Kinetics of the exchange of individual amide protons in the basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1979 May 5;130(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90549-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skelton N. J., Akke M., Kördel J., Thulin E., Forsén S., Chazin W. J. 15N NMR assignments and chemical shift analysis of uniformly labeled 15N calbindin D9k in the apo, (Cd2+)1 and (Ca2+)2 states. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 1;303(2-3):136–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80505-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skelton N. J., Kördel J., Akke M., Chazin W. J. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the internal dynamics in Apo, (Cd2+)1 and (Ca2+)2 calbindin D9k. The rates of amide proton exchange with solvent. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):1100–1117. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90524-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson L. A., Thulin E., Forsén S. Proline cis-trans isomers in calbindin D9k observed by X-ray crystallography. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 5;223(3):601–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90976-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szebenyi D. M., Moffat K. The refined structure of vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein from bovine intestine. Molecular details, ion binding, and implications for the structure of other calcium-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8761–8777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen N. K., Poulsen F. M. Low energy of activation for amide hydrogen exchange reactions in proteins supports a local unfolding model. J Mol Biol. 1993 Nov 5;234(1):234–241. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tüchsen E., Hayes J. M., Ramaprasad S., Copie V., Woodward C. Solvent exchange of buried water and hydrogen exchange of peptide NH groups hydrogen bonded to buried waters in bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 11;26(16):5163–5172. doi: 10.1021/bi00390a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tüchsen E., Woodward C. Hydrogen exchange kinetics of surface peptide amides in bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 20;193(4):793–802. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tüchsen E., Woodward C. Hydrogen kinetics of peptide amide protons at the bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor protein-solvent interface. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):405–419. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90412-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tüchsen E., Woodward C. Mechanism of surface peptide proton exchange in bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Salt effects and O-protonation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):421–430. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90413-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G., Wüthrich K. Amide protein exchange and surface conformation of the basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor in solution. Studies with two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):343–361. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90180-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G., Wüthrich K. Structural interpretation of the amide proton exchange in the basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor and related proteins. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 15;134(1):75–94. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90414-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wand A. J., Roder H., Englander S. W. Two-dimensional 1H NMR studies of cytochrome c: hydrogen exchange in the N-terminal helix. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 11;25(5):1107–1114. doi: 10.1021/bi00353a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson M. P., Havel T. F., Wüthrich K. Solution conformation of proteinase inhibitor IIA from bull seminal plasma by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance and distance geometry. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 20;182(2):295–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90347-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward C. K. Dynamic solvent accessibility in the soybean trypsin inhibitor--trypsin complex. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr 25;111(4):509–515. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward C. K., Hilton B. D. Hydrogen isotope exchange kinetics of single protons in bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Biophys J. 1980 Oct;32(1):561–575. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)84990-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward C. K., Rosenberg A. Studies of hydrogen exchange in proteins. V. The correlation of ribonuclease exchange kinetics with the temperature-induced transition. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4105–4113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K., Eugster A., Wagner G. p2H dependence of the exchange with the solvent of interior amide protons in basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor modified by reduction of the disulfide bone 14--38. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 25;144(4):601–604. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90342-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K., Strop P., Ebina S., Williamson M. P. A globular protein with slower amide proton exchange from an alpha helix than from antiparallel beta sheets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1174–1178. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91215-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K., Wagner G. Nuclear magnetic resonance of labile protons in the basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1979 May 5;130(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90548-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


