Abstract
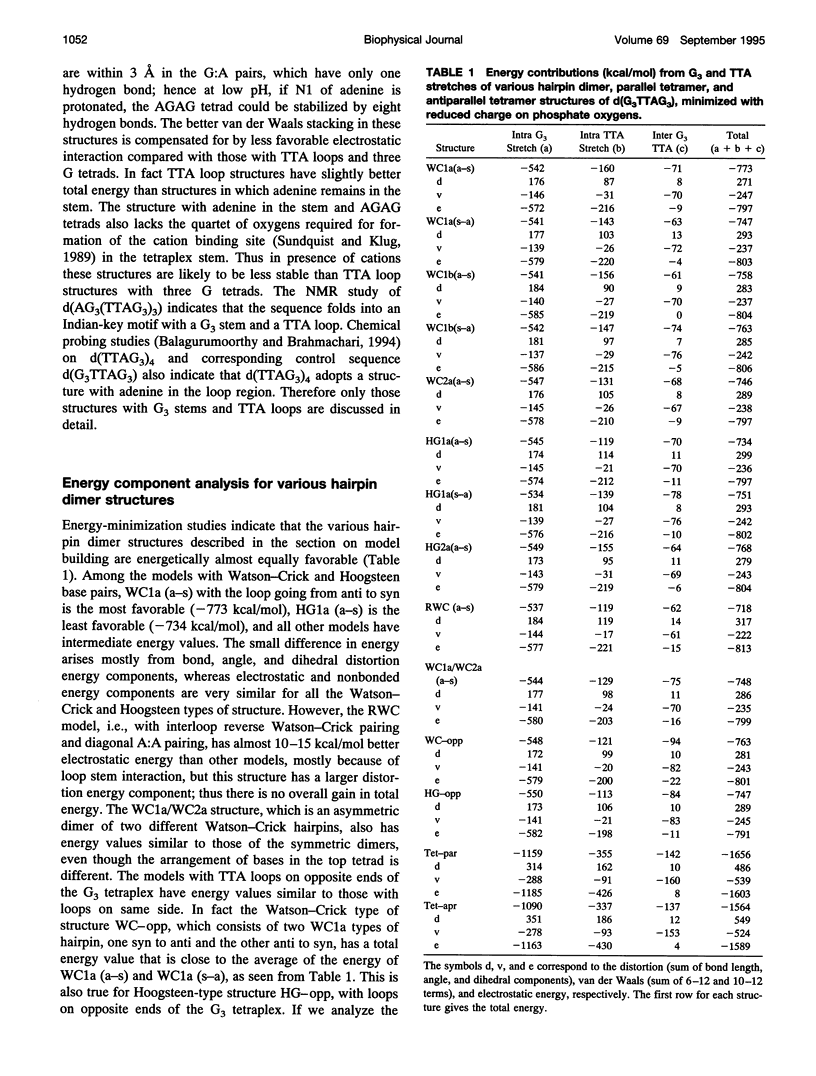
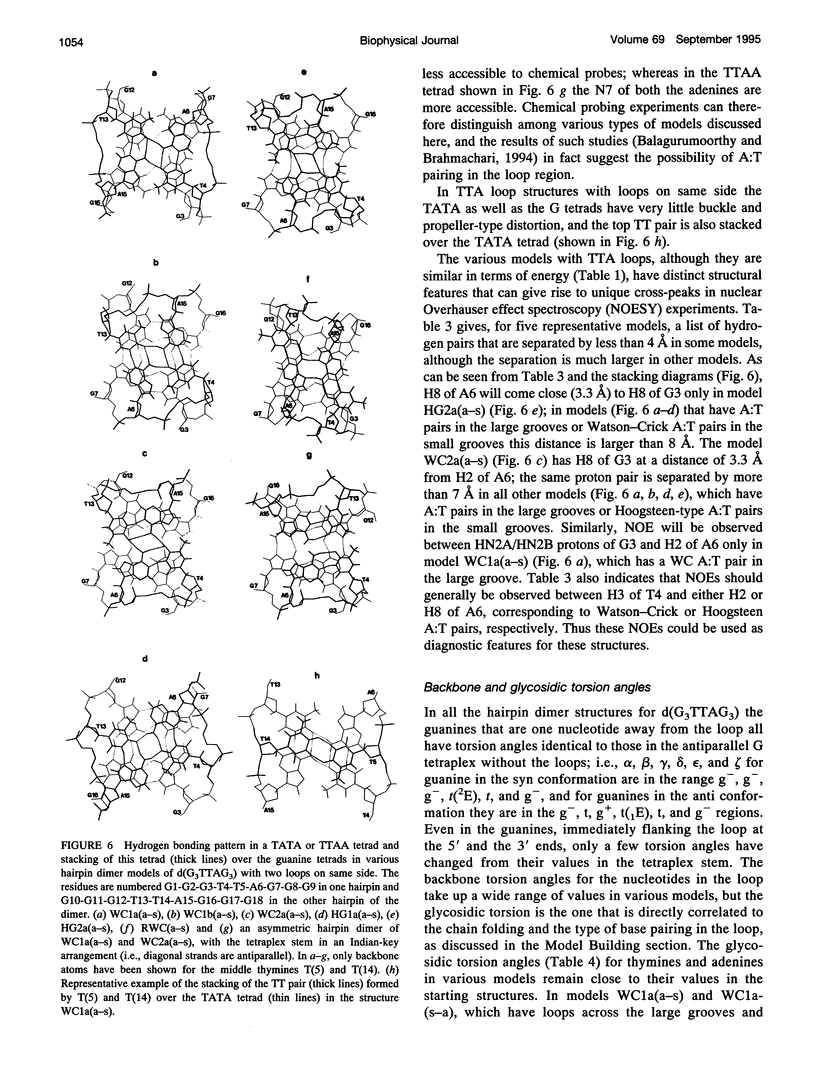
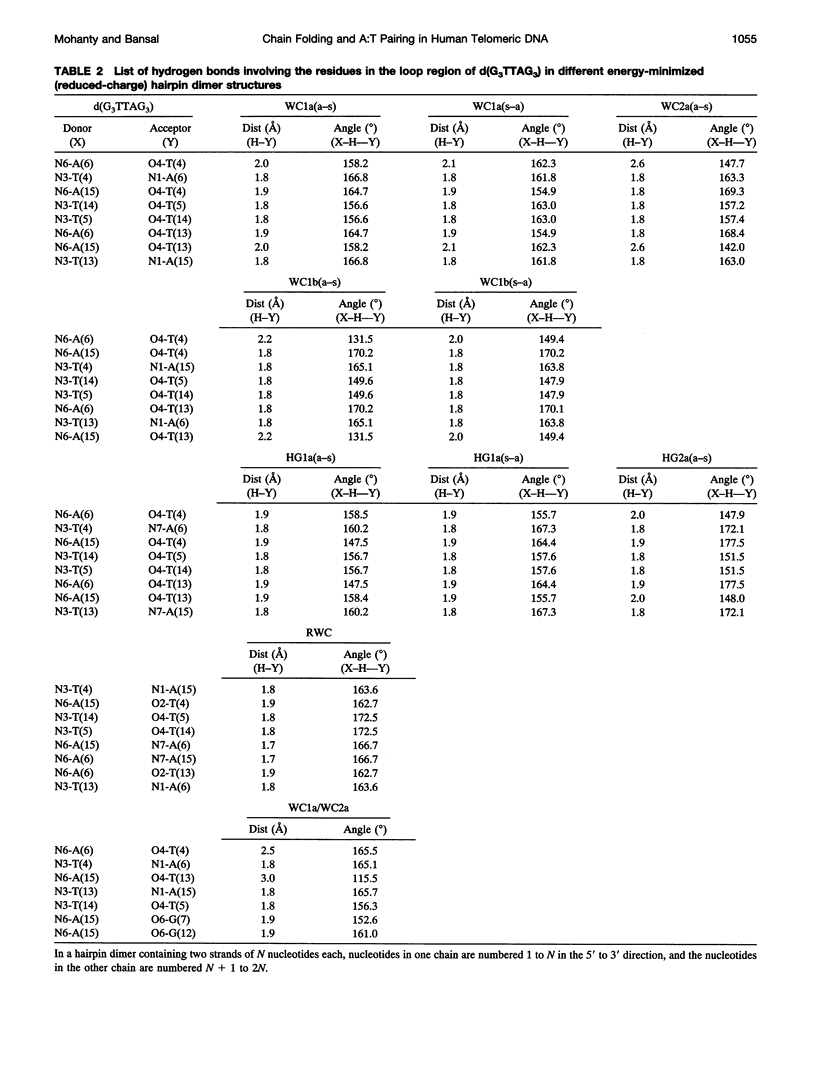
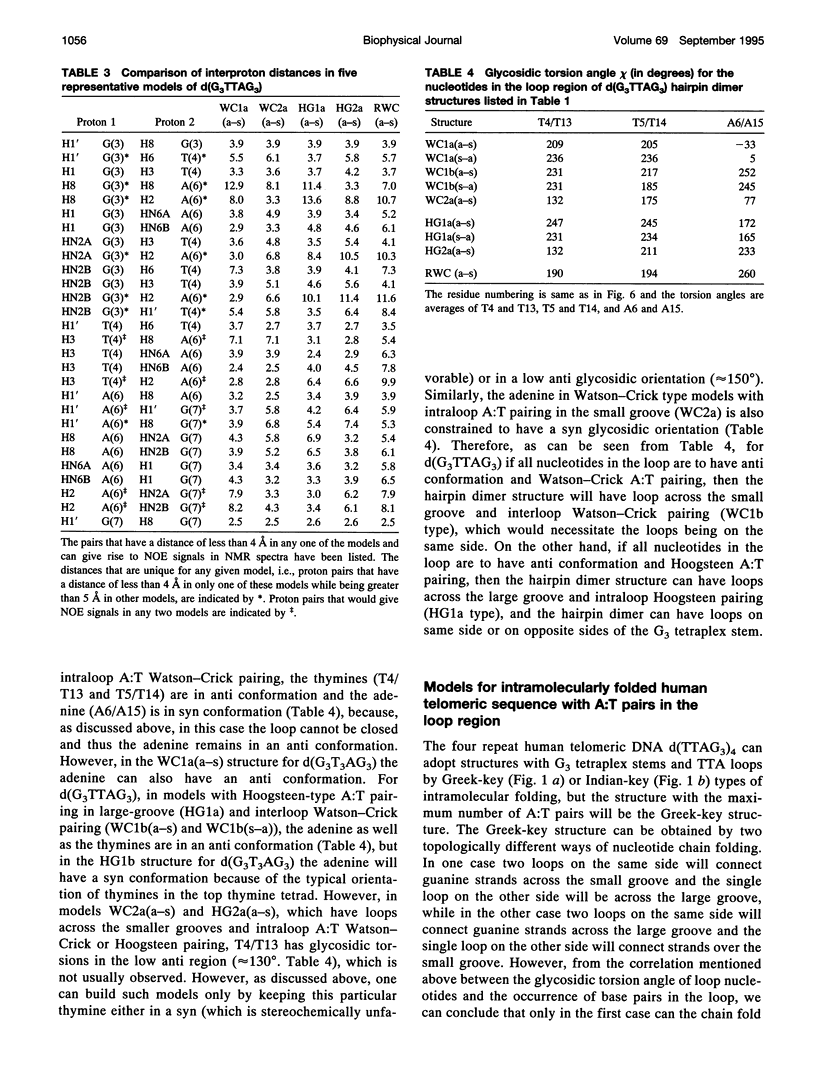
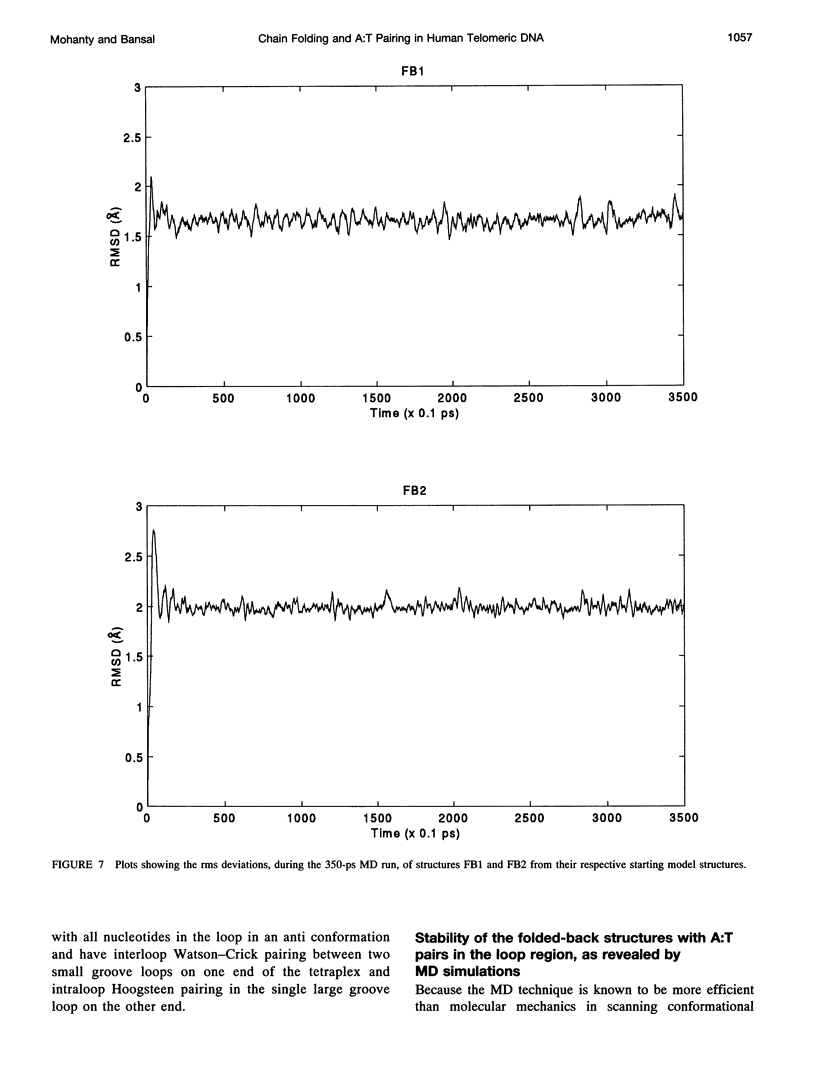
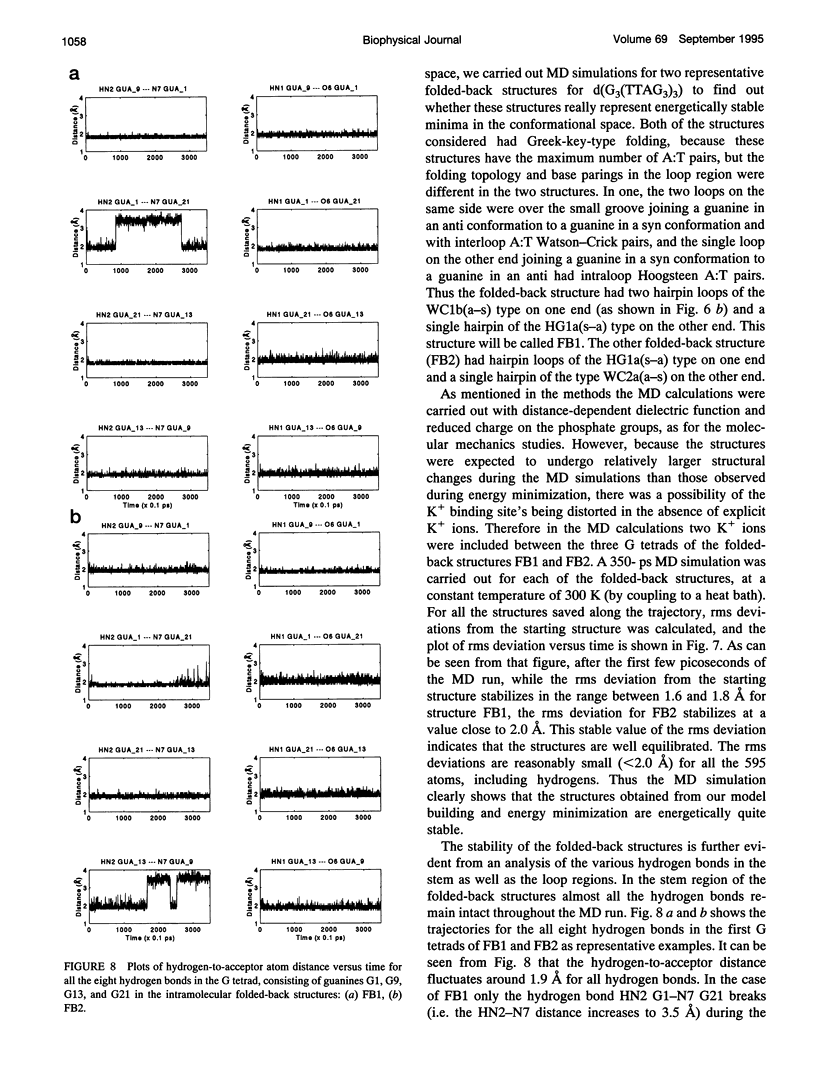
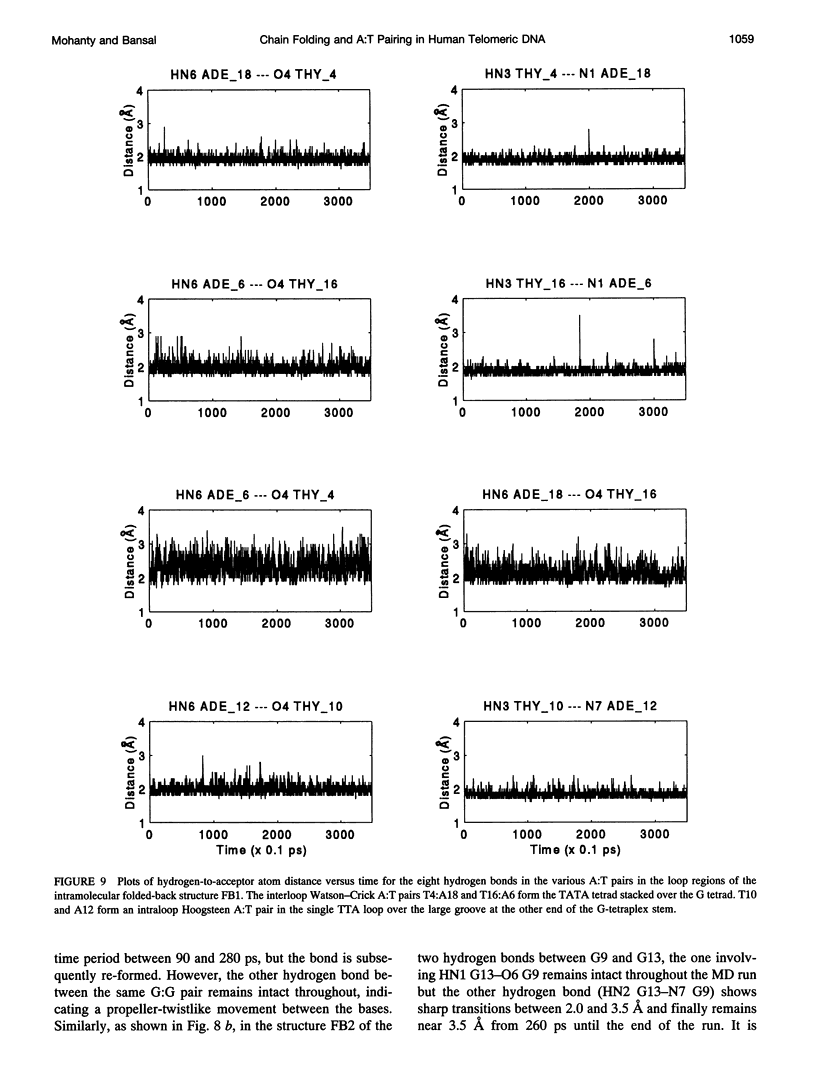
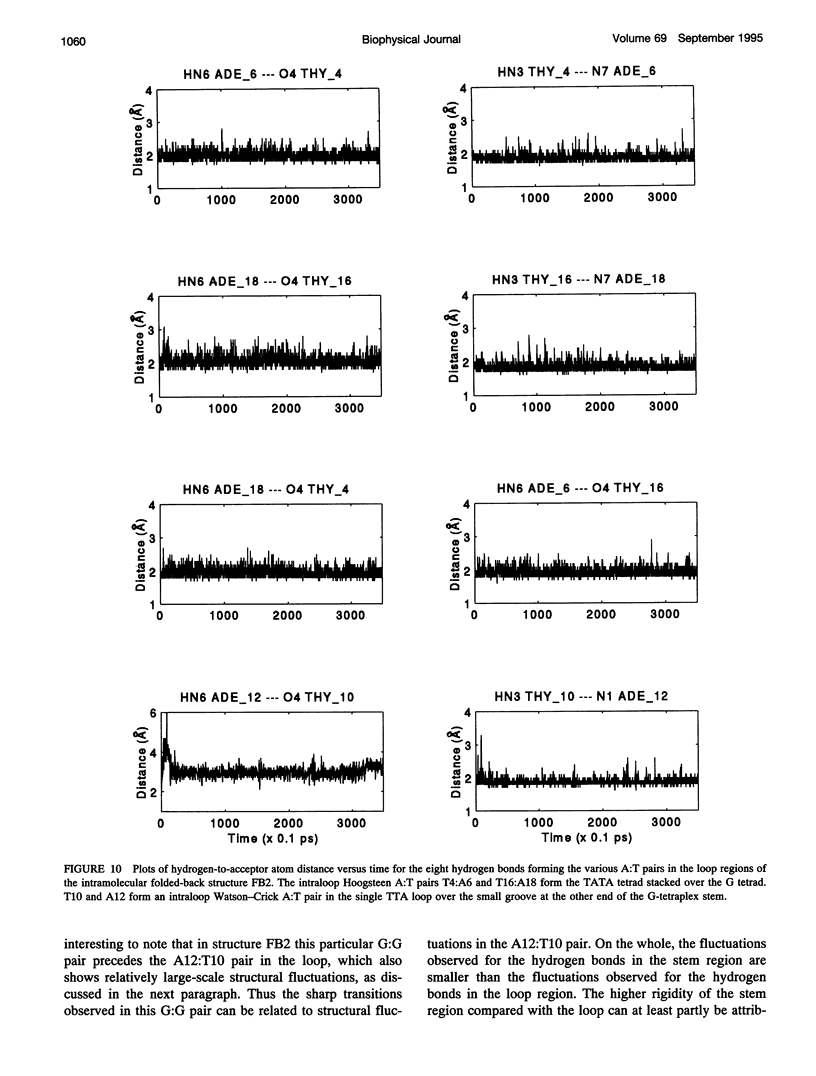
The various types of chain folding and possible intraloop as well as interloop base pairing in human telomeric DNA containing d(TTAG3) repeats have been investigated by model-building, molecular mechanics, and molecular dynamics techniques. Model-building and molecular mechanics studies indicate that it is possible to build a variety of energetically favorable folded-back structures with the two TTA loops on same side and the 5' end thymines in the two loops forming TATA tetrads involving a number of different intraloop as well as interloop A:T pairing schemes. In these folded-back structures, although both intraloop and interloop Watson-Crick pairing is feasible, no structure is possible with interloop Hoogsteen pairing. MD studies of representative structures indicate that the guanine-tetraplex stem is very rigid and, while the loop regions are relatively much more flexible, most of the hydrogen bonds remain intact throughout the 350-ps in vacuo simulation. The various possible TTA loop structures, although they are energetically similar, have characteristic inter proton distances, which could give rise to unique cross-peaks in two-dimensional nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY) experiments. These folded-back structures with A:T pairings in the loop region help in rationalizing the data from chemical probing and other biochemical studies on human telomeric DNA.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aboul-ela F., Murchie A. I., Lilley D. M. NMR study of parallel-stranded tetraplex formation by the hexadeoxynucleotide d(TG4T). Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):280–282. doi: 10.1038/360280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aboul-ela F., Murchie A. I., Norman D. G., Lilley D. M. Solution structure of a parallel-stranded tetraplex formed by d(TG4T) in the presence of sodium ions by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mol Biol. 1994 Oct 28;243(3):458–471. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Marttila C. M. Structures for polyinosinic acid and polyguanylic acid. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;141(2):537–543. doi: 10.1042/bj1410537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balagurumoorthy P., Brahmachari S. K., Mohanty D., Bansal M., Sasisekharan V. Hairpin and parallel quartet structures for telomeric sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):4061–4067. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balagurumoorthy P., Brahmachari S. K. Structure and stability of human telomeric sequence. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 26;269(34):21858–21869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bansal M., Pattabiraman N. Molecular mechanics studies on poly(purine).poly(pyrimidine) sequences in DNA: polymorphism and local variability. Biopolymers. 1989 Feb;28(2):531–548. doi: 10.1002/bip.360280202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):569–573. doi: 10.1038/350569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Telomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:113–129. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. The molecular structure of centromeres and telomeres. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:163–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruskov V. I., Bushuev V. N., Okon M. S., Shulyupina N. V., Poltev V. I. C-H ... O hydrogen bonding in solutions of methylated nucleic acid base analogs as revealed by NMR. Biopolymers. 1989 Feb;28(2):589–604. doi: 10.1002/bip.360280205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheong C., Moore P. B. Solution structure of an unusually stable RNA tetraplex containing G- and U-quartet structures. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 15;31(36):8406–8414. doi: 10.1021/bi00151a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernyi A. A., Lysov YuP, Il'ychova I. A., Zibrov A. S., Shchyolkina A. K., Borisova O. F., Mamaeva O. K., Florentiev V. L. Four-stranded DNA helices: conformational analysis of regular poly(dT).poly(dA).poly(dA).poly(dT) helices with various types of base binding. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1990 Dec;8(3):513–527. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1990.10507826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Q., Lu M., Kallenbach N. R. Adenine affects the structure and stability of telomeric sequences. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15293–15300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Q., Lu M., Kallenbach N. R. Effect of thymine tract length on the structure and stability of model telomeric sequences. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 13;32(14):3596–3603. doi: 10.1021/bi00065a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta G., Garcia A. E., Guo Q., Lu M., Kallenbach N. R. Structure of a parallel-stranded tetramer of the Oxytricha telomeric DNA sequence dT4G4. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 20;32(28):7098–7103. doi: 10.1021/bi00079a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guschlbauer W., Chantot J. F., Thiele D. Four-stranded nucleic acid structures 25 years later: from guanosine gels to telomer DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1990 Dec;8(3):491–511. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1990.10507825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E. R., Blackburn E. H. An overhanging 3' terminus is a conserved feature of telomeres. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):345–348. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Hardin C. C., Walk S. K., Tinoco I., Jr, Blackburn E. H. Telomeric DNA oligonucleotides form novel intramolecular structures containing guanine-guanine base pairs. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):899–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90577-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin R. Z., Breslauer K. J., Jones R. A., Gaffney B. L. Tetraplex formation of a guanine-containing nonameric DNA fragment. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):543–546. doi: 10.1126/science.2237404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C., Zhang X., Ratliff R., Moyzis R., Rich A. Crystal structure of four-stranded Oxytricha telomeric DNA. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):126–131. doi: 10.1038/356126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughlan G., Murchie A. I., Norman D. G., Moore M. H., Moody P. C., Lilley D. M., Luisi B. The high-resolution crystal structure of a parallel-stranded guanine tetraplex. Science. 1994 Jul 22;265(5171):520–524. doi: 10.1126/science.8036494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macaya R. F., Schultze P., Smith F. W., Roe J. A., Feigon J. Thrombin-binding DNA aptamer forms a unimolecular quadruplex structure in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3745–3749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura T., Thomas G. J., Jr Structural polymorphism of telomere DNA: interquadruplex and duplex-quadruplex conversions probed by Raman spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1994 Jun 28;33(25):7848–7856. doi: 10.1021/bi00191a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty D., Bansal M. Conformational polymorphism in G-tetraplex structures: strand reversal by base flipover or sugar flipover. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1767–1774. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty D., Bansal M. Conformational polymorphism in telomeric structures: loop orientation and interloop pairing in d(G4TnG4). Biopolymers. 1994 Sep;34(9):1187–1211. doi: 10.1002/bip.360340908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Buckingham J. M., Cram L. S., Dani M., Deaven L. L., Jones M. D., Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Wu J. R. A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG)n, present at the telomeres of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan K., Padmanabhan K. P., Ferrara J. D., Sadler J. E., Tulinsky A. The structure of alpha-thrombin inhibited by a 15-mer single-stranded DNA aptamer. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17651–17654. doi: 10.2210/pdb1hut/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyutin I. G., Kovalsky O. I., Budowsky E. I., Dickerson R. E., Rikhirev M. E., Lipanov A. A. G-DNA: a twice-folded DNA structure adopted by single-stranded oligo(dG) and its implications for telomeres. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):867–870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson A. M., Rich A., Krieger M. Polynucleotide binding to macrophage scavenger receptors depends on the formation of base-quartet-stabilized four-stranded helices. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3546–3554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinnavaia T. J., Miles H. T., Becker E. D. Letter: Self-assembled 5'-guanosine monophosphate. Nuclear magnetic resonance evidence for a regular, ordered structure and slow chemical exchange. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Nov 26;97(24):7198–7200. doi: 10.1021/ja00857a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose I. A., Hanson K. R., Wilkinson K. D., Wimmer M. J. A suggestion for naming faces of ring compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2439–2441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasisekharan V., Zimmerman S., Davies D. R. The structure of helical 5'-guanosine monophosphate. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 25;92(2):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90221-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaria P. V., Shire S. J., Shafer R. H. Quadruplex structure of d(G3T4G3) stabilized by K+ or Na+ is an asymmetric hairpin dimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10336–10340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultze P., Macaya R. F., Feigon J. Three-dimensional solution structure of the thrombin-binding DNA aptamer d(GGTTGGTGTGGTTGG). J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 4;235(5):1532–1547. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. A sodium-potassium switch in the formation of four-stranded G4-DNA. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):410–414. doi: 10.1038/344410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):364–366. doi: 10.1038/334364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. W., Feigon J. Quadruplex structure of Oxytricha telomeric DNA oligonucleotides. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):164–168. doi: 10.1038/356164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. W., Feigon J. Strand orientation in the DNA quadruplex formed from the Oxytricha telomere repeat oligonucleotide d(G4T4G4) in solution. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 24;32(33):8682–8692. doi: 10.1021/bi00084a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist W. I., Heaphy S. Evidence for interstrand quadruplex formation in the dimerization of human immunodeficiency virus 1 genomic RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3393–3397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist W. I., Klug A. Telomeric DNA dimerizes by formation of guanine tetrads between hairpin loops. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):825–829. doi: 10.1038/342825a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tidor B., Irikura K. K., Brooks B. R., Karplus M. Dynamics of DNA oligomers. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(1):231–252. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K., Gualberto A. MyoD binds to the guanine tetrad nucleic acid structure. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13714–13718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K. Y., McCurdy S., Shea R. G., Swaminathan S., Bolton P. H. A DNA aptamer which binds to and inhibits thrombin exhibits a new structural motif for DNA. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 2;32(8):1899–1904. doi: 10.1021/bi00059a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K. Y., Swaminathan S., Bolton P. H. Tertiary structure motif of Oxytricha telomere DNA. Biochemistry. 1994 Jun 21;33(24):7517–7527. doi: 10.1021/bi00190a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Patel D. J. Guanine residues in d(T2AG3) and d(T2G4) form parallel-stranded potassium cation stabilized G-quadruplexes with anti glycosidic torsion angles in solution. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 8;31(35):8112–8119. doi: 10.1021/bi00150a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Patel D. J. Solution structure of the human telomeric repeat d[AG3(T2AG3)3] G-tetraplex. Structure. 1993 Dec 15;1(4):263–282. doi: 10.1016/0969-2126(93)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R. G-quartet structures in telomeric DNA. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1994;23:703–730. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.003415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Raghuraman M. K., Cech T. R. Monovalent cation-induced structure of telomeric DNA: the G-quartet model. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. R., Vickers T. A., Roberson J. L., Buckheit R. W., Jr, Klimkait T., DeBaets E., Davis P. W., Rayner B., Imbach J. L., Ecker D. J. Combinatorially selected guanosine-quartet structure is a potent inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus envelope-mediated cell fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1356–1360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhurkin V. B., Raghunathan G., Ulyanov N. B., Camerini-Otero R. D., Jernigan R. L. A parallel DNA triplex as a model for the intermediate in homologous recombination. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jun 3;239(2):181–200. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. B., Cohen G. H., Davies D. R. X-ray fiber diffraction and model-building study of polyguanylic acid and polyinosinic acid. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 25;92(2):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90222-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


