Abstract
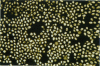
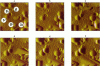
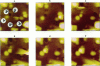
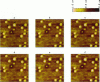
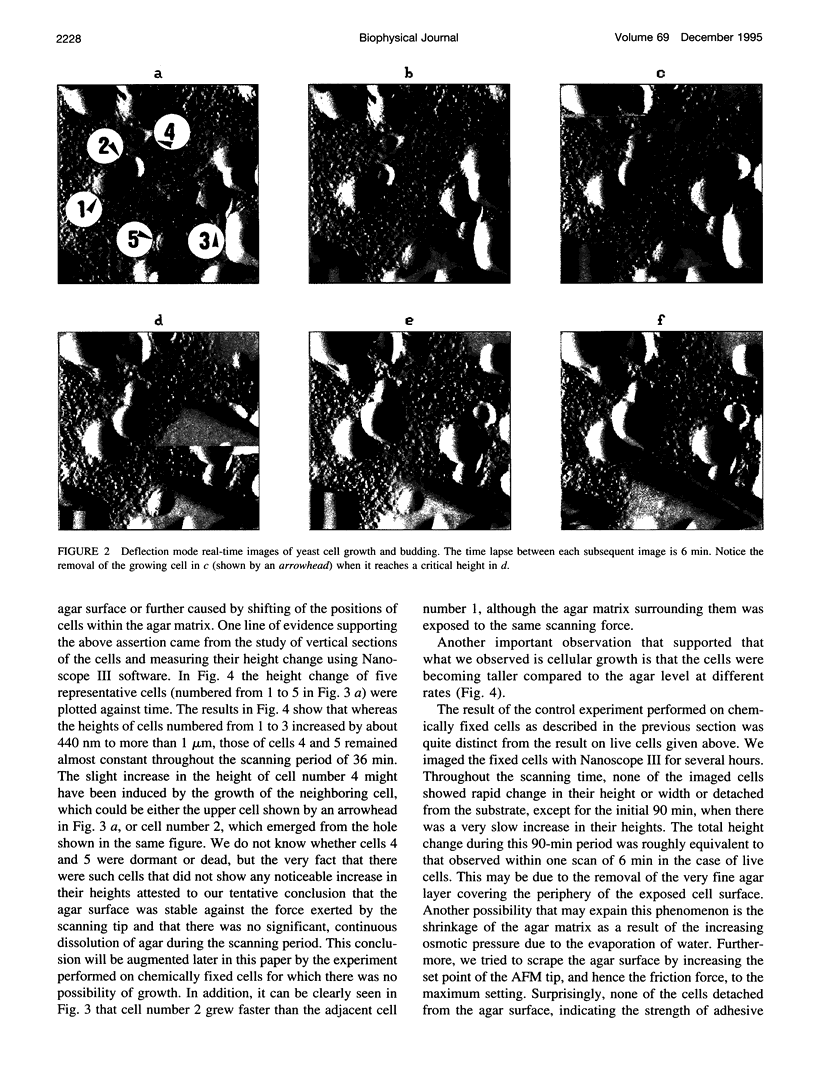
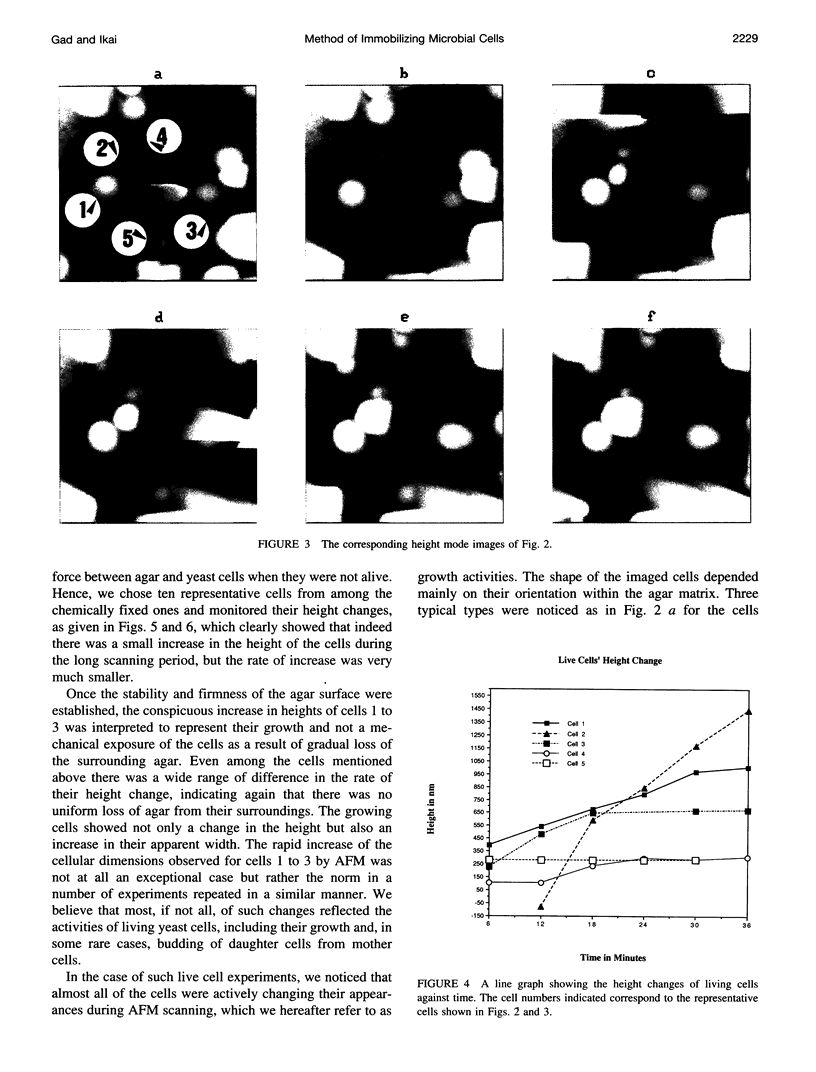
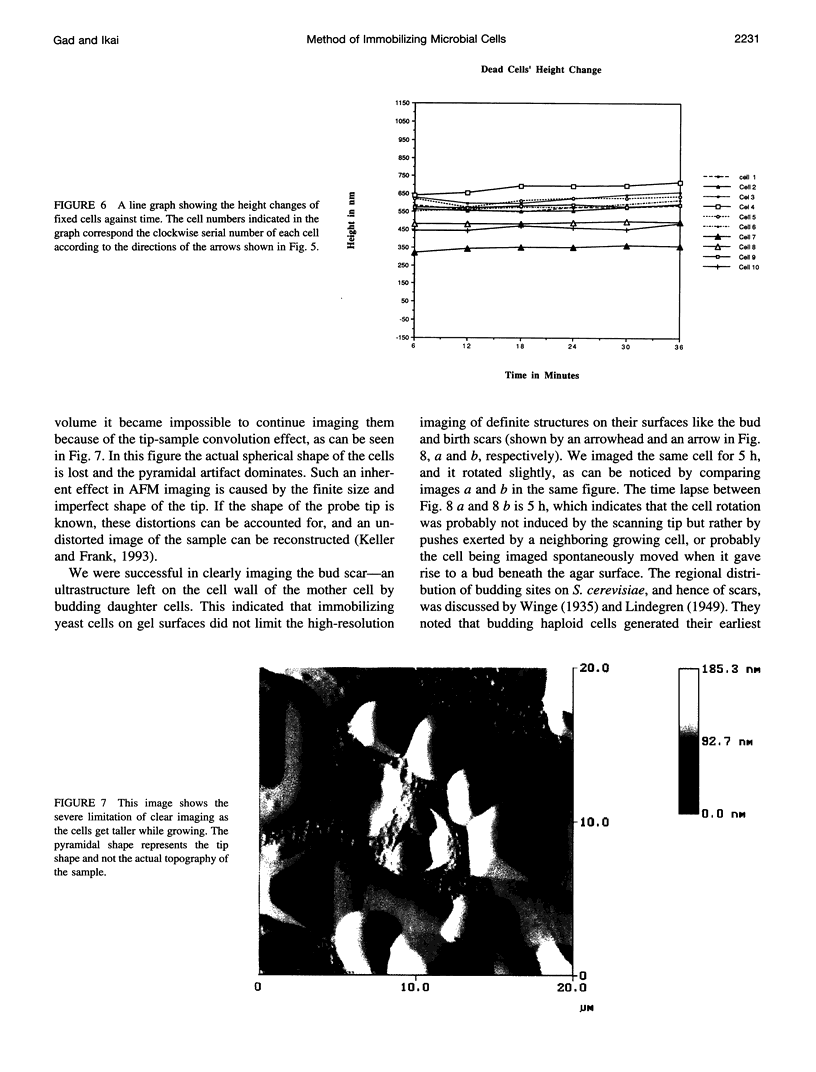
The processes of cell growth and budding of the yeast cells Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which were gently immobilized on 3% agar and submerged in culture medium, were successfully imaged with an atomic force microscope for 6-7 h. Similar experiments on chemically fixed cells did not detect any appreciable change in their appearance except in a few scannings at the very beginning, indicating that the dissolution of agar and/or scraping of its surface by the scanning tip, if any, did not significantly interfere with the images taken thereafter. The increment in the height of many of the untreated cells, accompanied by their lateral enlargement, was taken as an indication of successful imaging of the growth process of yeast cells, together with an image of a growing daughter cell attached to its mother cell.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison D. P., Bottomley L. A., Thundat T., Brown G. M., Woychik R. P., Schrick J. J., Jacobson K. B., Warmack R. J. Immobilization of DNA for scanning probe microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10129–10133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biely P., Kovarík J., Bauer S. Cell wall formation in yeast. An electron microscopic autoradiographic study. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Dec 31;94(4):356–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binnig G, Quate CF, Gerber C. Atomic force microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 1986 Mar 3;56(9):930–933. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.56.930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnham NA, Dominguez DD, Mowery RL, Colton RJ. Probing the surface forces of monolayer films with an atomic-force microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 1990 Apr 16;64(16):1931–1934. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.64.1931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt H. J., Downing K. H., Hansma P. K. Imaging the membrane protein bacteriorhodopsin with the atomic force microscope. Biophys J. 1990 Dec;58(6):1473–1480. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82492-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt H. J., Wolff E. K., Gould S. A., Dixon Northern B., Peterson C. M., Hansma P. K. Imaging cells with the atomic force microscope. J Struct Biol. 1990 Oct-Dec;105(1-3):54–61. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(90)90098-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake B., Prater C. B., Weisenhorn A. L., Gould S. A., Albrecht T. R., Quate C. F., Cannell D. S., Hansma H. G., Hansma P. K. Imaging crystals, polymers, and processes in water with the atomic force microscope. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1586–1589. doi: 10.1126/science.2928794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREIFELDER D. Bud position in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1960 Oct;80:567–568. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.4.567-568.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas V., Kovarík J., Kosinová A., Bauer S. Autoradiographic study of mannan incorporation into the growing cell walls of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):265–269. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.265-269.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz M., Radmacher M., Gaub H. E. Granula motion and membrane spreading during activation of human platelets imaged by atomic force microscopy. Biophys J. 1994 May;66(5):1328–1334. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80963-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay J. L., Martin M. An electron microscopic study of bud development in Saccharomycodes ludwigii and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;78(2):145–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00424871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma H. G., Bezanilla M., Zenhausern F., Adrian M., Sinsheimer R. L. Atomic force microscopy of DNA in aqueous solutions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):505–512. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma H. G., Vesenka J., Siegerist C., Kelderman G., Morrett H., Sinsheimer R. L., Elings V., Bustamante C., Hansma P. K. Reproducible imaging and dissection of plasmid DNA under liquid with the atomic force microscope. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1180–1184. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegner M., Wagner P., Semenza G. Immobilizing DNA on gold via thiol modification for atomic force microscopy imaging in buffer solutions. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 28;336(3):452–456. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80854-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Haydon P. G., Sakaguchi D. S. Actin filament dynamics in living glial cells imaged by atomic force microscopy. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1944–1946. doi: 10.1126/science.1411511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häberle W., Hörber J. K., Ohnesorge F., Smith D. P., Binnig G. In situ investigations of single living cells infected by viruses. Ultramicroscopy. 1992 Jul;42-44(Pt B):1161–1167. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90418-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörber J. K., Häberle W., Ohnesorge F., Binnig G., Liebich H. G., Czerny C. P., Mahnel H., Mayr A. Investigation of living cells in the nanometer regime with the scanning force microscope. Scanning Microsc. 1992 Dec;6(4):919–930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasas S., Gotzos V., Celio M. R. Observation of living cells using the atomic force microscope. Biophys J. 1993 Feb;64(2):539–544. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81396-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasas S., Ikai A. A method for anchoring round shaped cells for atomic force microscope imaging. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1678–1680. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80344-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mate CM, McClelland GM, Erlandsson R, Chiang S. Atomic-scale friction of a tungsten tip on a graphite surface. Phys Rev Lett. 1987 Oct 26;59(17):1942–1945. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.59.1942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neagu C., van der Werf K. O., Putman C. A., Kraan Y. M., de Grooth B. G., van Hulst N. F., Greve J. Analysis of immunolabeled cells by atomic force microscopy, optical microscopy, and flow cytometry. J Struct Biol. 1994 Jan-Feb;112(1):32–40. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1994.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao N. J., Lindsay S. M., Lees S. Measuring the microelastic properties of biological material. Biophys J. 1992 Oct;63(4):1165–1169. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81692-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thundat T., Allison D. P., Warmack R. J., Brown G. M., Jacobson K. B., Schrick J. J., Ferrell T. L. Atomic force microscopy of DNA on mica and chemically modified mica. Scanning Microsc. 1992 Dec;6(4):911–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkacz J. S., Lampen J. O. Wall replication in saccharomyces species: use of fluorescein-conjugated concanavalin A to reveal the site of mannan insertion. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Sep;72(2):243–247. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenhorn A. L., Drake B., Prater C. B., Gould S. A., Hansma P. K., Ohnesorge F., Egger M., Heyn S. P., Gaub H. E. Immobilized proteins in buffer imaged at molecular resolution by atomic force microscopy. Biophys J. 1990 Nov;58(5):1251–1258. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82465-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Mou J., Shao Z. Molecular resolution atomic force microscopy of soluble proteins in solution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Mar 2;1199(2):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(94)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]