Abstract
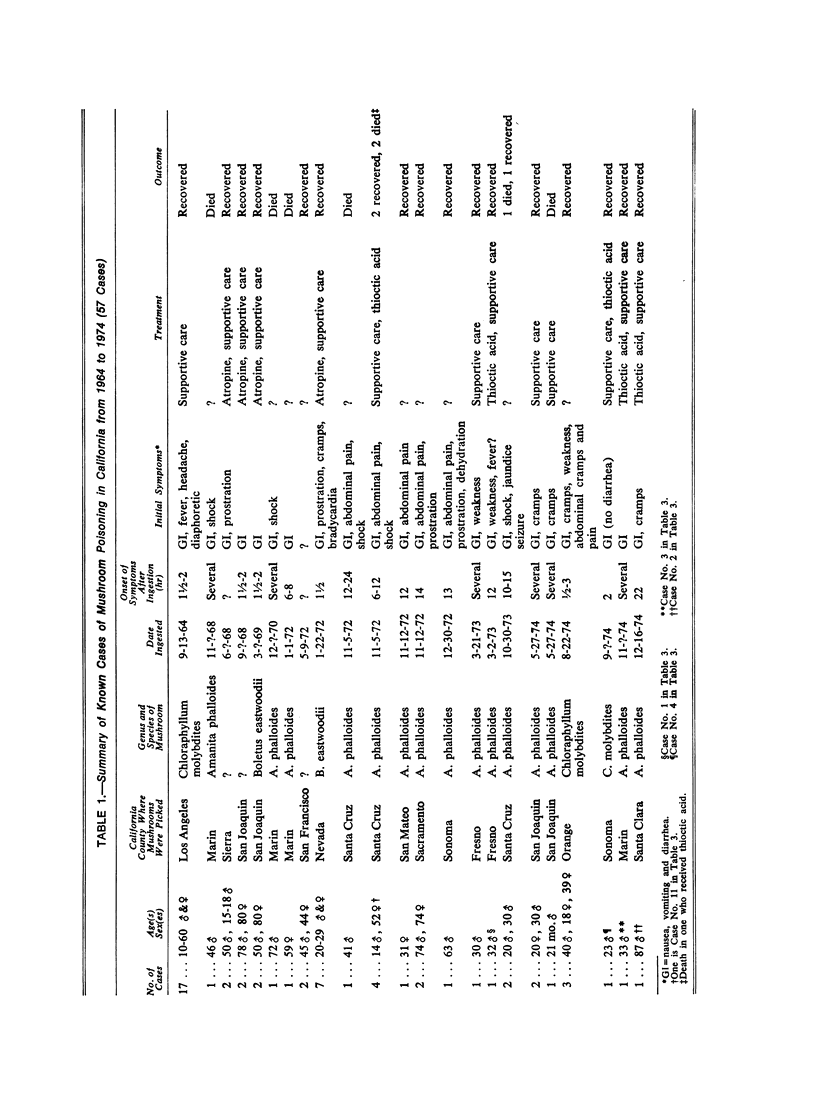
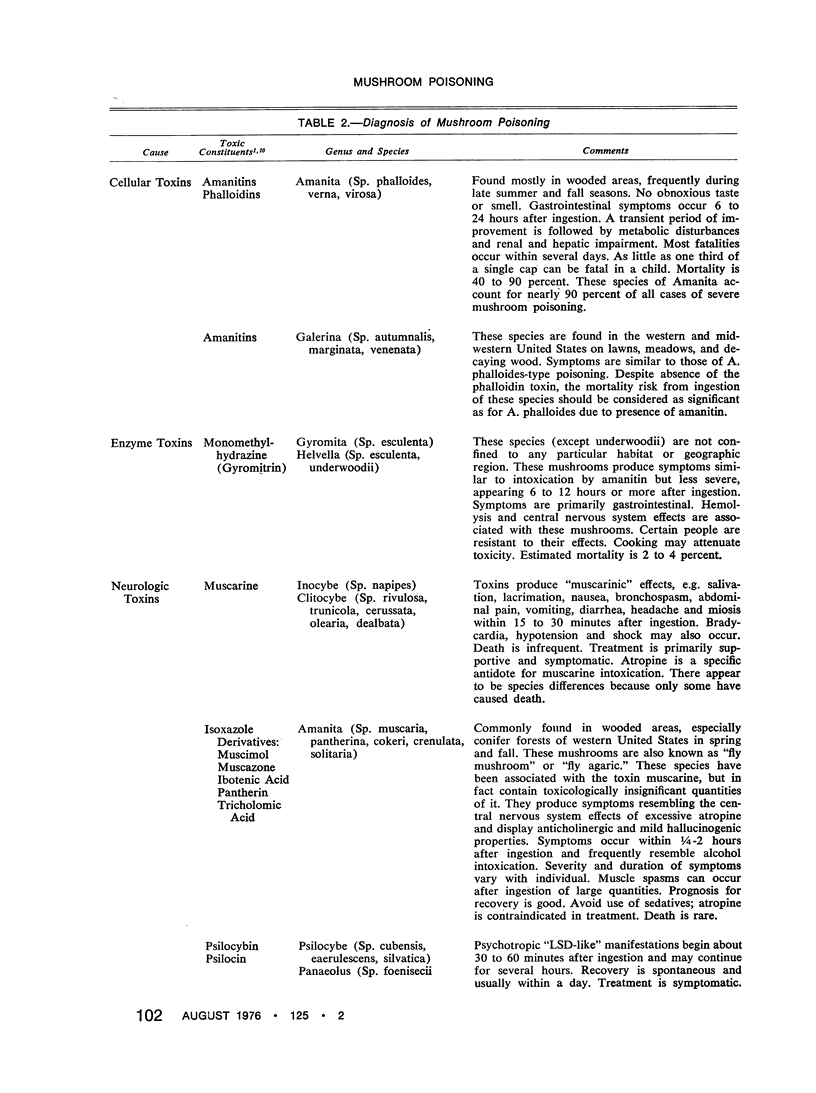
The number of cases of mushroom poisoning is increasing as a result of the increasing popularity of “wild” mushroom consumption. Amanitin and phalloidin cytotoxins found in some Amanita and Galerina species produce the most severe and frequent life-threatening symptoms of Amanita phalloidestype poisoning. Delay in onset of symptoms, individual susceptibility variation and lack of rapid and reliable identification have contributed to the significant morbidity and mortality of this type of poisoning.
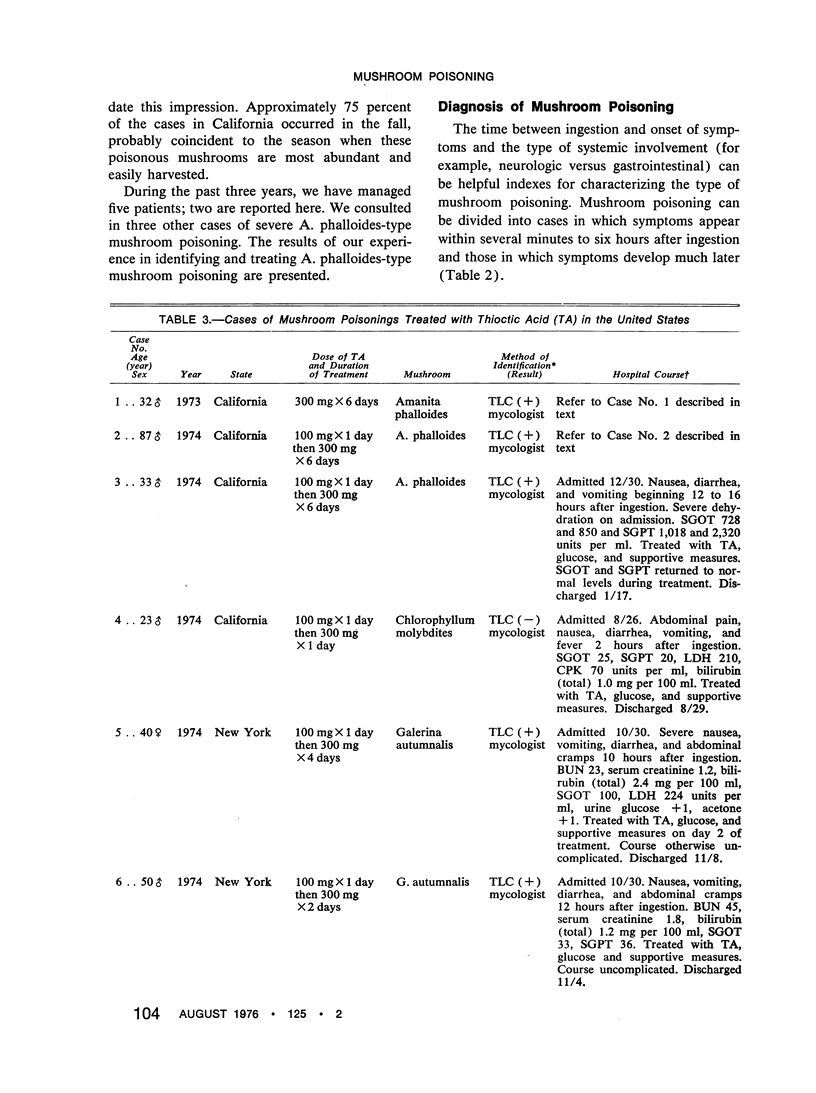
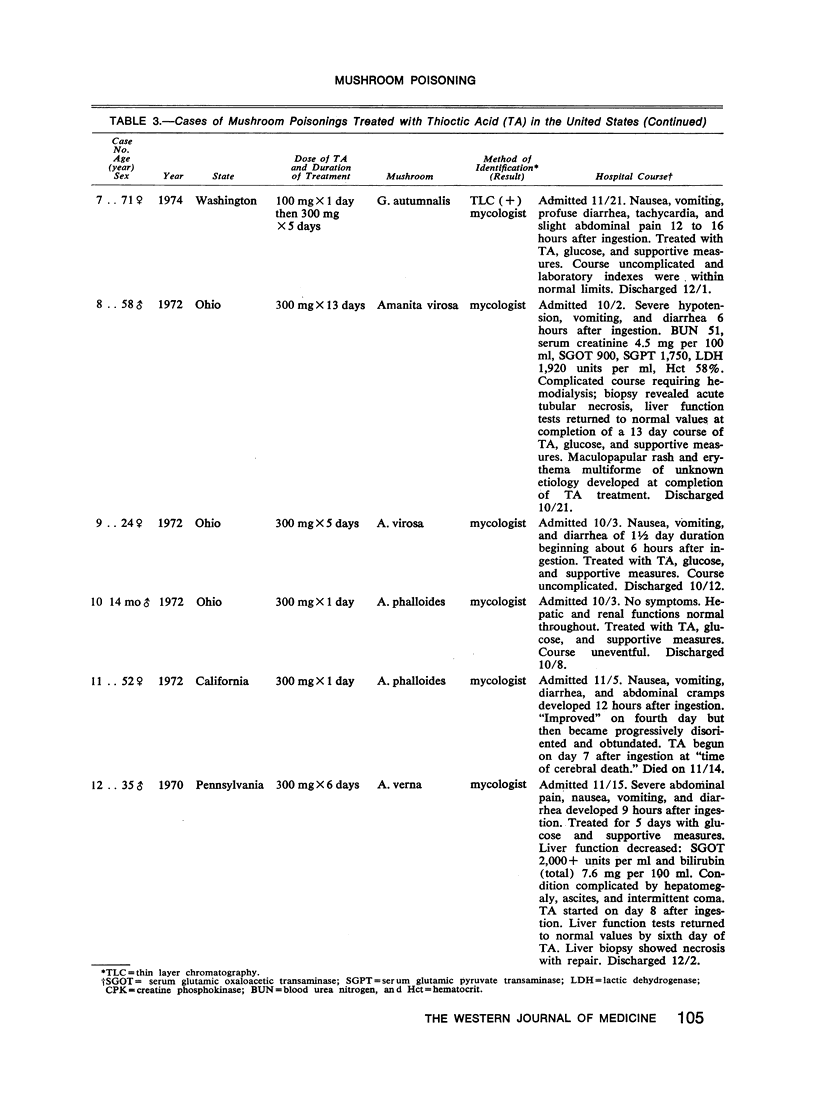
A rapid chromatographic assay for identifying the potent cytotoxins and apparently successful management using thioctic acid of two cases of A. phalloides-type mushroom poisoning are reported. All known cases of A. phalloides-type mushroom poisoning treated with thioctic acid in the United States are summarized.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABUL-HAJ S. K., EWALD R. A., KAZYAK L. Fatal mushroom poisoning. Report of a case confirmed by toxicologic analysis of tissue. N Engl J Med. 1963 Aug 1;269:223–227. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196308012690501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alleva F. R. Thioctic Acid and mushroom poisoning. Science. 1975 Jan 24;187(4173):216–216. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4173.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCK R. W. POISONING BY WILD MUSHROOMS. Clin Med (Northfield) 1964 Aug;71:1353–1363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartter F. C. Letters to the editor. Science. 1975 Jan 24;187(4173):216–216. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4173.216-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady L. R. Toxins of higher fungi. Lloydia. 1975 Jan-Feb;38(1):36–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culliton B. J. The destroying angel: a story of a search for an antidote. Science. 1974 Aug 16;185(4151):600–601. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4151.600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derenzini M., Fiume L., Marinozzi V., Mattioli A., Montanaro L., Sperti S. Pathogenesis of liver necrosis produced by amanitin-albumin conjugates. Lab Invest. 1973 Aug;29(2):150–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT W., HALL M., KERR D. N., ROLLAND C. F., SMART G. A., SWINNEY J. Mushroom poisoning. Lancet. 1961 Sep 16;2(7203):630–633. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)90309-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulstich H., Fauser U. Untersuchungen zur Frage der Hämodialyse bei der Knollenblätterpilzvergiftung. Serumspiegel und Ausscheidung von Amanitin. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1973 Nov 23;98(47):2258–2259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finestone A. J., Berman R., Widmer B., Markowitz J., Laquer U. J. Thioctic acid treatment of acute mushroom poisoning. Pa Med. 1972 Jul;75(7):49–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floersheim G. L. Antidotes to experimental -amanitin poisoning. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 29;236(65):115–117. doi: 10.1038/newbio236115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floersheim G. L. Curative potencies against -amanitin poisoning by cytochrome c. Science. 1972 Sep 1;177(4051):808–809. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4051.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSSMAN C. M., MALBIN B. Mushroom poisoning: a review of the literature and report of two cases caused by a previously undescribed species. Ann Intern Med. 1954 Feb;40(2):249–259. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-40-2-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON D. C., COGGINS C. H., WELLAND F. H., NELSON S. MUSHROOM POISONING IN FIVE PATIENTS. Am J Med. 1965 May;38:787–792. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisilevsky R. Hepatic nuclear and nucleolar changes in Amanita poisoning. Arch Pathol. 1974 Apr;97(4):253–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubicka J., Alder A. E. Ueber eine neuere Behandlungsmethode der Vergiftung durch den Knollenblätterpilz. Praxis. 1968 Sep 24;57(38):1304–1306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe K. F. Current concepts of therapy in mushroom intoxication. Clin Toxicol. 1974;7(1):115–121. doi: 10.3109/15563657408987983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litten W. The most poisonous mushrooms. Sci Am. 1975 Mar;232(3):90–101. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0375-90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lough J., Kinnear D. G. Mushroom poisoning in Canada: report of a fatal case. Can Med Assoc J. 1970 Apr 25;102(8):858–860. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYLER R. K., LEE J. C., HOPPER J., Jr RENAL TUBULAR NECROSIS CAUSED BY MUSHROOM POISONING. RENAL BIOPSY FINDINGS BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY AND USE OF PERITONEAL DIALYSIS IN TREATMENT. Arch Intern Med. 1964 Aug;114:196–204. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1964.03860080046003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinozzi V., Fiume L. Effects of -amanitin on mouse and rat liver cell nuclei. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Aug;67(2):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paaso B., Harrison D. C. A new look at an old problem: mushroom poisoning. Clinical presentations and new therapeutic approaches. Am J Med. 1975 Apr;58(4):505–509. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panner B. J., Hanss R. J. Hepatic injury in mushroom poisoning. Arch Pathol. 1969 Jan;87(1):35–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skrabal F., Dittrich P. Death-cap poisoning. Lancet. 1973 Apr 7;1(7806):767–768. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steyn D. G. The treatment of cases of Amanita phalloides and Amanita capensis poisoning. S Afr Med J. 1966 May 14;40(18):405–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland T. Poisonous principles of mushrooms of the genus Amanita. Four-carbon amines acting on the central nervous system and cell-destroying cyclic peptides are produced. Science. 1968 Mar 1;159(3818):946–952. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3818.946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zulik R., Bakó F., Budavári J. Death-cap poisoning. Lancet. 1972 Jul 29;2(7770):228–228. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91659-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


