Abstract
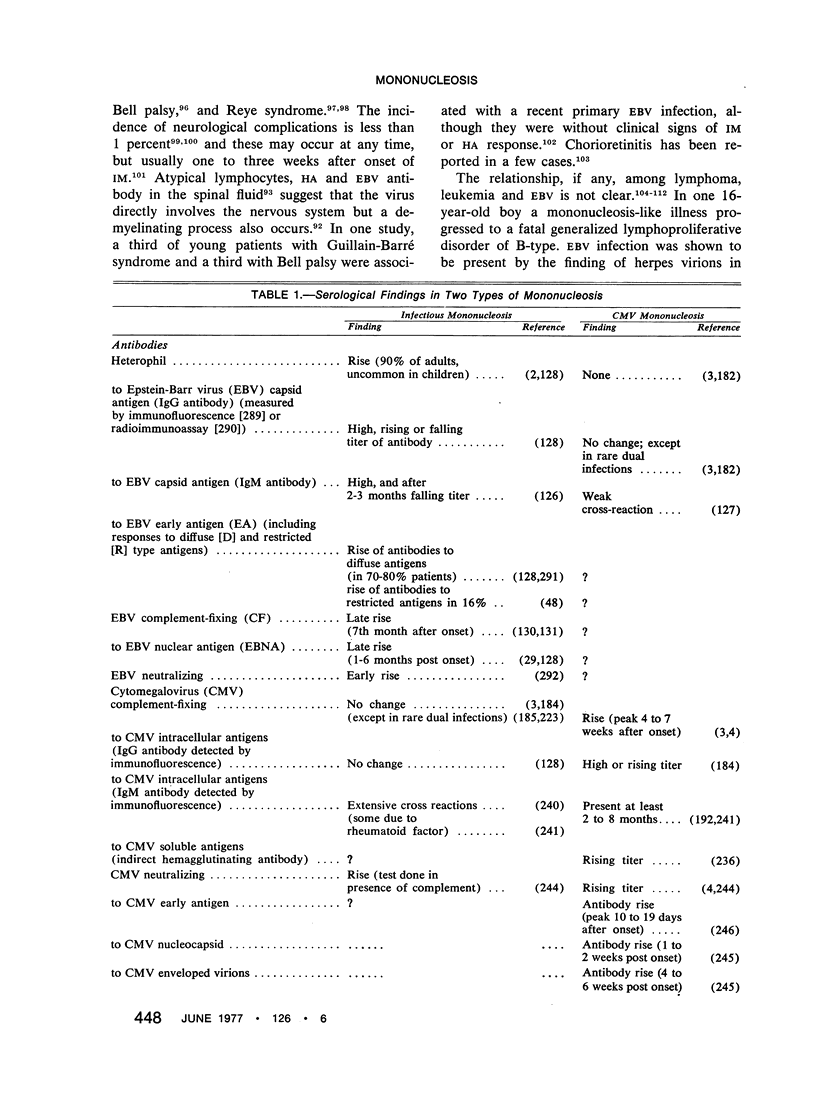
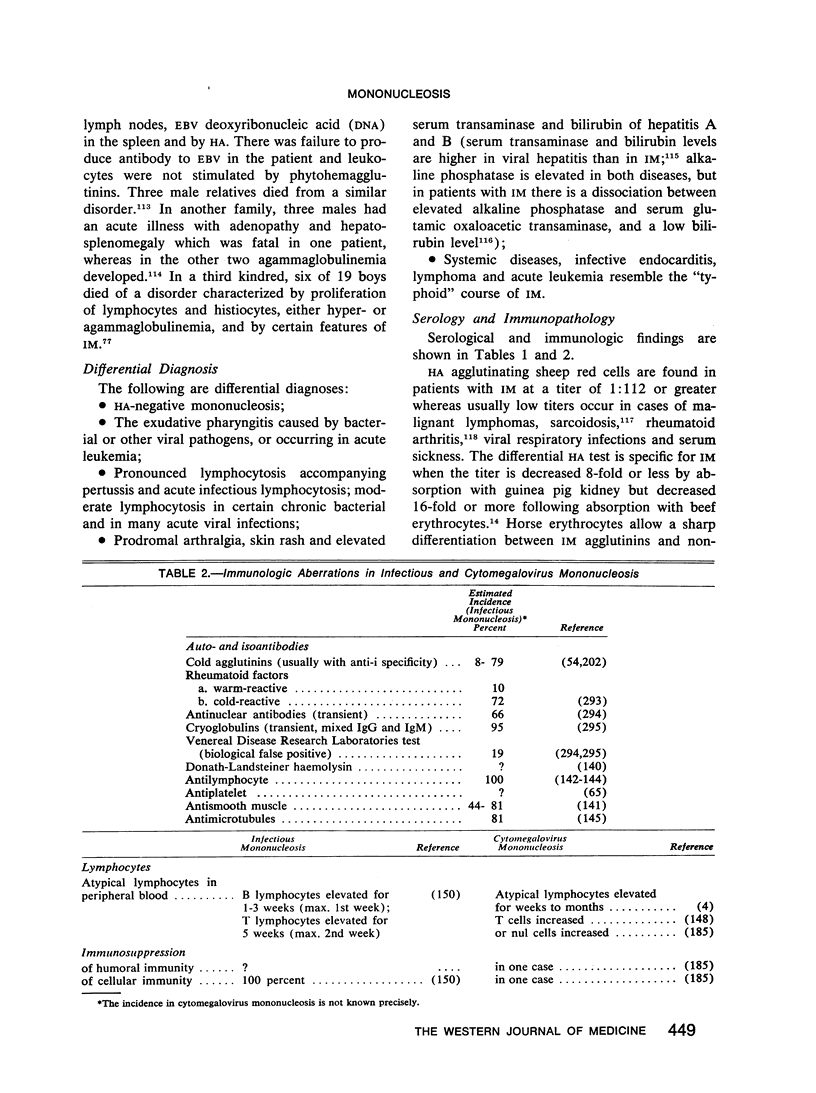
Infectious mononucleosis (IM) and cytomegalovirus (CMV) mononucleosis are caused by a primary infection with related viruses, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and CMV. Despite the similarity of clinical manifestations, basic differences exist: (1) The heterophil antibody (HA) response is absent in CMV mononucleosis, whereas it is present in IM. (2) In IM atypical lymphocytosis reflects proliferation of B cells early and of T cells later in the disease course; in CMV mononucleosis the situation appears complex. (3) In blood, EBV is restricted to B lymphocytes, whereas CMV is found in polymorphonuclear and mononuclear leukocytes. (4) Complications of CMV mononucleosis such as hepatitis and pneumonitis may be due to virus cytopathic effect in target organs. Prominent tonsillopharyngitis with adenopathy, and visceral complications of IM are related to lymphoproliferation which is self-limited except in males with a rare familial defect in defense against EBV. Immune complex-mediated pathology may occur in both diseases. (5) CMV is frequently transmitted to a fetus in utero or to an infant during or after birth, and this occasionally leads to severe cytomegalic inclusion disease; vertical transmission of EBV appears to be exceptional. (6) Secondary EBV infections are associated with certain malignancies whereas such an association has not been recognized in the case of CMV.
Toxoplasma gondii is another cause of HA-negative mononucleosis. Its complications in the heart, in skeletal muscle and in the central nervous system are related to direct invasion by the parasite. Cellular immunity plays an important role in defense against all three agents.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiuti F., Rocchi G., D'Amelio R., Giunta S., Fiorilli M. Lymphoid cells in infectious mononucleosis classified according to T and B cell markers. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;48(3):353–363. doi: 10.1159/000231320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht T., Rapp F. Malignant transformation of hamster embryo fibroblasts following exposure to ultraviolet-irradiated human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler M., Stoll J., Tzamaloukas A., Albala M. M. Focal encephalomyelitis in infectious mononucleosis. A report with pathological description. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Oct;75(4):579–583. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-4-579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen H. K., Godtfredsen A., Spencer E. S. Studies on the specificity of the complement fixation test in cytomegalovirus infections. With special reference to possible cross-reactions with other herpesvirus antigens. Scand J Infect Dis. 1971;3(3):183–187. doi: 10.3109/inf.1971.3.issue-3.01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen H. K., Gravesen J. J., Iversen T. Cytomegalovirus infection anong infants admitted to a paediatric department. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1972 Jul;61(4):445–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1972.tb15862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen H. K., Spencer E. S. Cytomegalovirus infection among renal allograft recipients. Acta Med Scand. 1969 Jul-Aug;186(1-2):7–19. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1969.tb01432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen H. K. Studies of human cytomegalovirus strain variations by kinetic neutralization tests. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;38(4):297–305. doi: 10.1007/BF01262820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Adlard J., Thomas F. B. Lymphopenic infectious mononucleosis. Arch Intern Med. 1975 Feb;135(2):334–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., DeLor C. J., Clausen K. P., Hurtubise P., Henle W., Hewetson J. F. Fatal infectious mononucleosis in a family. N Engl J Med. 1974 Feb 14;290(7):363–367. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197402142900704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett E. V., Bluestone R., Cracchiolo A., 3rd, Goldberg L. S., Kantor G. L., McIntosh R. M. Cryoglobulinemia and disease. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Jul;73(1):95–107. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender C. E. The value of corticosteroids in the treatment of infectious mononucleosis. JAMA. 1967 Feb 20;199(8):529–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein M. T., Stewart J. A. Indirect hemagglutination test for detection of antibodies to Cytomegalovirus. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jan;21(1):84–89. doi: 10.1128/am.21.1.84-89.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonamour G., Pommier M. L. Manifestations chorio-rétiniennes dans la mononucléose infectieuse. Bull Soc Ophtalmol Fr. 1968 Jan;68(1):52–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonkowsky H. L., Lee R. V., Klatskin G. Acute granulomatous hepatitis. Occurrence in cytomegalovirus mononucleosis. JAMA. 1975 Sep 22;233(12):1284–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman H. S., Marsh W. L., Schumacher H. R., Oyen R., Reihart J. Auto anti-N immunohemolytic anemia in infectious mononucleosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Apr;61(4):465–472. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/61.4.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd J. F., Reid D. Bone marrow in infectious mononucleosis. Br Med J. 1973 Apr 21;2(5859):176–176. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5859.176-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess J. A., Kirkpatrick K. L., Menser M. A. Fulminant onset of diabetes mellitus during an attack of infectious mononucleosis. Med J Aust. 1974 Nov 9;2(19):706–707. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1974.tb71105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkitt D. P. Etiology of Burkitt's lymphoma--an alternative hypothesis to a vectored virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Jan;42(1):19–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. L., Carlton L., DeGreen H. P., Teplick S. K., Metz J. R. Transient malabsorption in infectious mononucleosis. Case report. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1974 Oct;122(2):241–244. doi: 10.2214/ajr.122.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Dowling P., Cook S., Kunkel H. G. An incomplete cold-reactive gamma G antibody with i specificity in infectious mononucleosis. Vox Sang. 1969 Jan;16(1):10–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1969.tb04711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G. Cold-reactive rheumatoid factors in infectious mononucleosis and other diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1969 Apr;12(2):67–73. doi: 10.1002/art.1780120202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey R. M., Kimball A. C., Armstrong D., Lieberman P. H. Toxoplasmosis. Clinical experiences in a cancer hospital. Am J Med. 1973 Jan;54(1):30–38. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlström G., Aldén J., Belfrage S., Hedenström G., Holmberg L., Nordbring F., Sterner G. Acquired cytomegalovirus infection. Br Med J. 1968 Jun 1;2(5604):521–525. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5604.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. L. Granulocyte changes in infectious mononucleosis. J Clin Pathol. 1966 May;19(3):279–283. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.3.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. L. Infectious mononucleosis: model for self-limiting lymphoproliferation. Lancet. 1975 Apr 12;1(7911):846–849. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)93014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ch'ien L. T., Cannon N. J., Whitley R. J., Diethelm A. G., Dismukes W. E., Scott C. W., Buchanan R. A., Alford C. A., Jr Effect of adenine arabinoside on cytomegalovirus infections. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jul;130(1):32–39. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanarin I., Walford D. M. Thrombocytopenic purpura in cytomegalovirus mononucleosis. Lancet. 1973 Aug 4;2(7823):238–239. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93138-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandar K., Mair H. J., Mair N. S. Case of toxoplasma polymyositis. Br Med J. 1968 Jan 20;1(5585):158–159. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5585.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. Y., Campbell W. G., Jr Fatal infectious mononucleosis. Association with liver necrosis and herpes-like virus particles. Arch Pathol. 1975 Apr;99(4):185–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S., Golden H. D. Transformation of human leucocytes by throat washing from infectious mononucleosis patients. Nature. 1971 Dec 10;234(5328):359–360. doi: 10.1038/234359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin W., Magoffin R., Frierson J. G., Lennette E. H. Cytomegalovirus infection. A case with meningoencephalitis. JAMA. 1973 Aug 13;225(7):740–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly R. R., Christine B. W. A cohort study of cancer following infectious mononucleosis. Cancer Res. 1974 May;34(5):1172–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneshbod K., Liao K. T. Hyaline degeneration of splenic follicular arteries in infectious mononucleosis: histochemical and electron microscopic studies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Apr;59(4):473–479. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/59.4.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das R. K., Seidelin R. Blood dyscrasias and myocarditis in infectious mononucleosis. Br Med J. 1972 Jan 29;1(5795):289–289. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5795.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. E., Tweed G. V., Chin T. D., Miller G. L. Interuterine diagnosis of cytomegalovirus infection: viral recovery from amniocentesis fluid. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1971 Apr 15;109(8):1217–1219. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(71)90674-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. E., Tweed G. V., Stewart J. A., Bernstein M. T., Miller G. L., Gravelle C. R., Chin T. D. Cytomegalovirus mononucleosis in a first trimester pregnant female with transmission to the fetus. Pediatrics. 1971 Aug;48(2):200–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibel R., Smith R., Clarke L. M., Decher W., Jacobs J. Cytomegalovirus infections in New York State. N Y State J Med. 1974 May;74(5):785–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denman A. M., Pelton B. K. Control mechanisms in infectious mononucleosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):13–25. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmonts G., Couvreur J., Alison F., Baudelot J., Gerbeaux J., Lelong M. Etude épidémiologique sur la toxoplasmose: de l'influence de la cuisson des viandes de boucherie sur la fréquence de l'infection humaine. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1965 Nov;10(9):952–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmkrong-At A., Bloom G. E. Acquired hemolytic anemia associated with infectious mononucleosis in a patient with congenital pyruvate kinase deficiency. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1973 Feb;12(2):119–121. doi: 10.1177/000992287301200217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl V., Henle G., Henle W., Kohn G. Demonstration of a herpes group virus in cultures of peripheral leukocytes from patients with infectious mononucleosis. J Virol. 1968 Jul;2(7):663–669. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.7.663-669.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diosi P., Moldovan E., Tomescu N. Latent cytomegalovirus infection in blood donors. Br Med J. 1969 Dec 13;4(5684):660–662. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5684.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman R. F., Remington J. S. Value of lymph-node biopsy in the diagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Oct 25;289(17):878–881. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197310252891702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman J. M., Glick T. H., Shannon D. C., Galdabini J., Walker A. Complications of infectious mononucleosis. A fatal case in a 2-year-old child. Am J Dis Child. 1974 Aug;128(2):239–243. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110270113023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elek S. D., Stern H. Development of a vaccine against mental retardation caused by cytomegalovirus infection in utero. Lancet. 1974 Jan 5;1(7845):1–5. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92997-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellman L., Carvalho A., Jacobson B. M., Colman R. W. Platelet autoantibody in a case of infectious mononucleosis presenting as thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Med. 1973 Nov;55(5):723–726. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enberg R. N., Eberle B. J., Williams R. C., Jr T- and B-cells in peripheral blood during infectious mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1974 Aug;130(2):104–111. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.2.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. A., Achong B. G. Various forms of Epstein-Barr virus infection in man: established facts and a general concept. Lancet. 1973 Oct 13;2(7833):836–839. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90874-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. S. Commentary. EB virus, infectious mononucleosis, and cancer: the closing of the web. Yale J Biol Med. 1974;47(2):113–122. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. S., Niederman J. C., Cenabre L. C., West B., Richards V. A. A prospective evaluation of heterophile and Epstein-Barr virus-specific IgM antibody tests in clinical and subclinical infectious mononucleosis: Specificity and sensitivity of the tests and persistence of antibody. J Infect Dis. 1975 Nov;132(5):546–554. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.5.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. S., Niederman J. C., McCollum R. W. Seroepidemiologic studies of infectious mononucleosis with EB virus. N Engl J Med. 1968 Nov 21;279(21):1121–1127. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196811212792101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. S., Niederman J. C., Sawyer R. N. Prospective studies of a group of Yale University freshmen. II. Occurrence of acute respiratory infections and rubella. J Infect Dis. 1971 Mar;123(3):271–278. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.3.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. S. The spectrum of infections with Epstein-Barr virus: a hypothesis. J Infect Dis. 1971 Sep;124(3):330–337. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.3.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDMAN H. A., MILLER L. T. Serological study of toxoplasmosis prevalence. Am J Hyg. 1956 Nov;64(3):320–335. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRENKEL J. K., WEBER R. W., LUNDE M. N. Acute toxoplasmosis. Effective treatment with pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine, leucovorin calcium, and yeast. JAMA. 1960 Jul 30;173:1471–1476. doi: 10.1001/jama.1960.03020310059017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fermaglich D. R. Pulmonary involvement in infectious mononucleosis. J Pediatr. 1975 Jan;86(1):93–95. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80712-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiala M., Chow A. W., Miyasaki K., Guze L. B. Susceptibility of herpesviruses to three nucleoside analogues and their combinations and enhancement of the antiviral effect of acid pH. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jan;129(1):82–85. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiala M., Kattlove H. Letter: Cytomegalovirus mononucleosis with severe thrombocytopenia. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Sep;79(3):450–451. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-3-450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiala M., Payne J. E., Berne T. V., Moore T. C., Henle W., Montgomerie J. Z., Chatterjee S. N., Guze L. B. Epidemiology of cytomegalovirus infection after transplantation and immunosuppression. J Infect Dis. 1975 Oct;132(4):421–433. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.4.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K. Advances in the biology of sporozoa. Z Parasitenkd. 1974;45(2):125–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00348532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K. Pathology and pathogenesis of congenital toxoplasmosis. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1974 Feb;50(2):182–191. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELB D., WEST M., ZIMMERMAN H. J. Serum enzymes in disease. IX. Analysis of factors responsible for elevated values in infectious mononucleosis. Am J Med. 1962 Aug;33:249–261. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(62)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber P., Lucas S., Nonoyama M., Perlin E., Goldstein L. I. Oral excretion of Epstein-Barr virus by healthy subjects and patients with infectious mononucleosis. Lancet. 1972 Nov 11;2(7785):988–989. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92402-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon R. K. T cell control of antibody production. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1974;3:1–40. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3045-5_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg B. E., Wasserman J., Huldt G., Bergstrand A. Case of glomerulonephritis associated with acute toxoplasmosis. Br Med J. 1974 Sep 14;3(5932):664–665. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5932.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg C. M., Henle G., Henle W. An outbreak of infectious mononucleosis among the personnel of an outpatient clinic. Am J Epidemiol. 1976 Nov;104(5):571–575. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuliano V. J., Jasin H. E., Ziff M. The nature of the atypical lymphocyte in infectious mononucleosis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974 Sep;3(1):90–98. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg L. S., Barnett E. V. Mixed gamma G-gamma M cold agglutinin. J Immunol. 1967 Oct;99(4):803–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Brown G. Epstein-Barr virus binding sites on lymphocyte subpopulations and the origin of lymphoblasts in cultured lymphoic cell lines and in the blood of patients with infectious mononucleosis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Mar;3(4):514–524. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee J. E., Johnson W. D., Jr, campa J. F., Adelman L. S., Sande M. A. Adult toxoplasmosis presenting as polymyositis and cerebellar ataxia. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Mar;82(3):367–371. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-3-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Feorino P. M., Dye L. A., Rand J. Bell's palsy and infectious mononucleosis. Lancet. 1973 Aug 4;2(7823):231–232. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Feorino P. M. Epstein-Barr virus and Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet. 1972 Dec 16;2(7790):1285–1287. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92654-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Henle W., Henle G., Feorino P. M. Primary Epstein-Barr-virus infections in acute neurologic diseases. N Engl J Med. 1975 Feb 20;292(8):392–395. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197502202920804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guignard J. P., Torrado A. Interstital nephritis and toxoplasmosis in a 10-year-old child. J Pediatr. 1974 Sep;85(3):381–382. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutgesell H. P., Jr Acute airway obstruction in infectious mononucleosis. Pediatrics. 1971 Jan;47(1):141–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOAGLAND R. J. MONONUCLEOSIS AND HEART DISEASE. Am J Med Sci. 1964 Jul;248:1–6. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196407000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOAGLAND R. J. The transmission of infectious mononucleosis. Am J Med Sci. 1955 Mar;229(3):262–272. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195503000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallee T. J., Evans A. S., Niederman J. C., Brooks C. M., Voegtly j. H. Infectious mononucleosis at the United States Military Academy. A prospective study of a single class over four years. Yale J Biol Med. 1974 Sep;47(3):182–195. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamblin T. J. Mononucleosis and the miniskirt: an incompatible combination. Br Med J. 1972 Dec 23;4(5842):708–709. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5842.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampar B., Hsu K. C., Martos L. M., Walker J. L. Serologic evidence that a herpes-type virus is the etiologic agent of heterophile-positive infectious mononucleosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1407–1411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanshaw J. B. A cytomegalovirus vaccine? Am J Dis Child. 1974 Aug;128(2):141–142. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110270015002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanshaw J. B., Niederman J. C., Chessin L. N. Cytomegalovirus macroglobulin in cell-associated herpesvirus infections. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):304–306. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harries J. T., Ferguson A. W. Fatal infectious mononucleosis with liver failure in two sisters. Arch Dis Child. 1968 Aug;43(230):480–485. doi: 10.1136/adc.43.230.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henie G., Henle W., Horwitz C. A. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen in infectious mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):231–239. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W., Diehl V. Relation of Burkitt's tumor-associated herpes-ytpe virus to infectious mononucleosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):94–101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Immunofluorescence in cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1248-1256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G. E., Horwitz C. A. Epstein-Barr virus specific diagnostic tests in infectious mononucleosis. Hum Pathol. 1974 Sep;5(5):551–565. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(74)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G. Evidence for an oncogenic potential of the Epstein-Barr virus. Cancer Res. 1973 Jun;33(6):1419–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G., Hewetson J., Rocchi G., Leikola J. Failure to detect heterophile antigens in Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells and to demonstrate interaction of heterophile antibodies with Epstein-Barr virus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jun;17(2):281–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G., Niederman J. C., Klemola E., Haltia K. Antibodies to early antigens induced by Epstein-Barr virus in infectious mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jul;124(1):58–67. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson D. E., Grimley P. M., Strano A. J. Postnatal cytomegalovirus hepatitis. An autopsy and liver biopsy study. Hum Pathol. 1974 Jan;5(1):93–103. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(74)80103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlong W. B., Esham R. H. Letter: Asymptomatic cytomegalovirus mononucleosis. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Nov;79(5):756–756. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-5-756_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewetson J. F., Rocchi G., Henle W., Henle G. Neutralizing antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in healthy populations and patients with infectious mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):283–289. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holborow E. J., Hemsted E. H., Mead S. V. Smooth muscle autoantibodies in infectious mononucleosis. Br Med J. 1973 Aug 11;3(5875):323–325. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5875.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz C. A., Henle W., Henle G., Polesky H., Wexler H., Ward P. The specificity of heterophil antibodies in patients and healthy donors with no or minimal signs of infectious mononucleosis. Blood. 1976 Jan;47(1):91–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz C. A., Henle W., Henle G., Schmitz H. Clinical evaluation of patients with infectious mononucleosis and development of antibodies to the R component of the Epstein-Barr virus-induced early antigen complex. Am J Med. 1975 Mar;58(3):330–338. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90599-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz C. A., Henle W., Henle G., Segal M., Arnold T., Lewis F. B., Zanick D., Ward P. C. Clinical and laboratory evaluation of elderly patients with heterophil-antibody positive infectious mononucleosis. Report of seven patients, ages 40 to 78. Am J Med. 1976 Sep;61(3):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90369-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz C. A., Polesky H., Stillman T., Ward P. C., Henle G., Henle W. Persistent haemagglutination for infectious mononucleosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J. 1973 Mar 10;1(5853):591–592. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5853.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossaini A. A. Anti-i in infectious mononucleosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Feb;53(2):198–203. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/53.2.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Pagano J. S. Replication of cytomegalovirus DNA in human lymphoblastoid cells. IARC Sci Publ. 1975;(11 Pt 1):475–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultquist G., Nordvall S., Sundström C. Insulitis in cytomegalovirus infection in a newborn infant. Ups J Med Sci. 1973;78(2):139–144. doi: 10.3109/03009737309178618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson H. D., Ziegler D. W., Feorino P. M. Radioimmunoassay for detection of antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in human infectious mononucleosis serum specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 May;1(5):429–433. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.5.429-433.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutt L. M., Huang Y. T., Dascomb H. E., Pagano J. S. Enhanced destruction of lymphoid cell lines by peripheral blood leukocytes taken from patients with acute infectious mononucleosis. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):243–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBS L., REMINGTON J. S., MELTON M. L. A survey of meat samples from swine, cattle, and sheep for the presence of encysted Toxoplasma. J Parasitol. 1960 Feb;46:23–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANDL J. H., JACOB H. S., DALAND G. A. Hypersplenism due to infection. A study of five cases manifesting hemolytic anemia. N Engl J Med. 1961 May 25;264:1063–1071. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196105252642101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES T. C., KEAN B. H., KIMBALL A. C. PERICARDITIS ASSOCIATED WITH TOXOPLASMOSIS: REPORT OF A CASE AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Apr;62:786–790. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-62-4-786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeor S. C., Albrecht T. B., Funk F. D., Rapp F. Stimulation of cellular DNA synthesis by human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):353–362. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.353-362.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Klein G. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. II. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus receptors on B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1365–1378. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Kean B. H., Kimball A. C. Acquired toxoplasmosis. N Y State J Med. 1969 Aug 15;69(16):2237–2242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. C., Rousseau W. E., Noble G. R., Steward J. A., Chin T. D. Association of cervical cytomegaloviruses with venereal disease. N Engl J Med. 1973 May 3;288(18):932–934. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197305032881803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. C., Rousseau W., Stewart J. A., Noble G. R., Chin T. D. Spontaneous cytomegalovirus mononucleosis. Clinical and laboratory observations in nine cases. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Aug;79(2):153–160. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-2-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagen L. J., Kimball A. C., Christian C. L. Serologic evidence of toxoplasmosis among patients with polymyositis. Am J Med. 1974 Feb;56(2):186–191. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90596-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane R. C., Rousseau W. E., Noble G. R., Tegtmeier G. E., Wulff H., Herndon H. B., Chin T. D., Bayer W. L. Cytomegalovirus infection in a volunteer blood donor population. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):719–723. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.719-723.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor F. S. Infection, anergy and cell-mediated immunity. N Engl J Med. 1975 Mar 20;292(12):629–634. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197503202921210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor G. L., Goldberg L. S., Johnson B. L., Jr, Derechin M. M., Barnett E. V. Immunologic abnormalities induced by postperfusion cytomegalovirus infection. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Oct;73(4):553–558. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-4-553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor G. L., Johnson B. L., Jr Cytomegalovirus infection associated with cardiopulmonary bypass. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Mar;125(3):488–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. E. Cryoglobulinemia in infectious mononucleosis: quantitation and characterization of the cryoproeins. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 May;71(5):754–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. E., Tan E. M. Antinuclear antibodies in infectious mononucleosis. Lancet. 1968 Mar 16;1(7542):561–563. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92831-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean B. H., Kimball A. C., Christenson W. N. An epidemic of acute toxoplasmosis. JAMA. 1969 May 12;208(6):1002–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerns D., Shira J. E., Go S., Summers R. J., Schwab J. A., Plunket D. C. Ampicillin rash in children. Relationship to penicillin allergy and infectious mononucleosis. Am J Dis Child. 1973 Feb;125(2):187–190. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1973.04160020023004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick Z. M. Structural and functional abnormalities of liver in infectious mononucleosis. Arch Intern Med. 1966 Jan;117(1):47–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Sugden B., Leibold W., Menezes J. Infection of EBV-genome-negative and -positive human lymphoblastoid cell lines with biologically different preparations of EBV. Intervirology. 1974;3(4):232–244. doi: 10.1159/000149760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. The Epstein-Barr virus and neoplasia. N Engl J Med. 1975 Dec 25;293(26):1353–1357. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197512252932607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemola E. Hypersensitivity reactions to ampicillin in cytomegalovirus mononucleosis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1970;2(1):29–31. doi: 10.3109/inf.1970.2.issue-1.05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemola E., Käriäinen L. Cytomegalovirus as a possible cause of a disease resembling infectious mononucleosis. Br Med J. 1965 Nov 6;2(5470):1099–1102. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5470.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemola E., Käriäinen L., von Essen R., Haltia K., Koivuniemi A., von Bonsdorff C. H. Further studies on cytomegalovirus mononucleosis in previously healthy individuals. Acta Med Scand. 1967 Sep;182(3):311–322. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1967.tb11529.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemola E., Salmi I., Käriäinen L., Koivuniemi A. Hepatosplenomegaly after "cytomegalovirus mononucleosis" in a child. Ann Paediatr Fenn. 1966;12(1):39–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemola E., Stenström R., von Essen R. Pneumonia as a clinical manifestation of cytomegalovirus infection in previously healthy adults. Scand J Infect Dis. 1972;4(1):7–10. doi: 10.3109/inf.1972.4.issue-1.02. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemola E., Von Essen R., Henle G., Henle W. Infectious-mononucleosis-like disease with negative heterophil agglutination test. Clinical features in relation to Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1970 Jun;121(6):608–614. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.6.608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemola E., Weckman N., Haltia K., Käriäinen L. The Guillain-Barré syndrome associated with acquired cytomegalovirus infection. Acta Med Scand. 1967 May;181(5):603–607. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1967.tb07283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemola E., von Essen R., Wager O., Haltia K., Koivuniemi A., Salmi I. Cytomegalovirus mononucleosis in previously healthy individuals. Five new cases and follow-up of 13 previously published cases. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Jul;71(1):11–19. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-71-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostinas J. E., Cantow E. F. Studies on infectious mononucleosis. II. Autohemolysis. Am J Med Sci. 1966 Sep;252(3):296–300. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196609000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koziner B., Hadler N., Parrillo J., Ellman L. Agranulocytosis following infectious mononucleosis. JAMA. 1973 Sep 3;225(10):1235–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kufe D., Hehlmann R., Spiegelman S. RNA related to that of a murine leukemia virus in Burkitt's tumors and nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):5–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Klemola E., Paloheimo J. Rise of cytomegalovirus antibodies in an infectious-mononucleosis-like syndrome after transfusion. Br Med J. 1966 May 21;1(5498):1270–1272. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5498.1270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb S. G., Stern H. Cytomegalovirus mononucleosis with jaundice as presenting sign. Lancet. 1966 Nov 5;2(7471):1003–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92929-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. J., Hanshaw J. B. Cytomegalovirus infection and the postperfusion syndrome. Recognition of primary infections in four patients. N Engl J Med. 1969 May 22;280(21):1145–1149. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196905222802103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. J., Kummer J. F. Demonstration of cytomegalovirus in semen. N Engl J Med. 1972 Oct 12;287(15):756–758. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197210122871508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. J., Kummer J. F., Hartley D. P. Cytomegalovirus in semen. Persistence and demonstration in extracellular fluids. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jul 18;291(3):121–123. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197407182910303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange B. J., Berman P. H., Bender J., Henle W., Hewetson J. F. Encephalitis in infectious mononucleosis: diagnostic considerations. Pediatrics. 1976 Dec;58(6):877–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langenhuysen M. M., The T. H., Nieweg H. O., Kapsenberg J. G. Demonstration of IgM cytomegalovirus-antibodies as an aid to early diagnosis in adults. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Mar;6(3):387–393. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lascelles R. G., Longson M., Johnson P. J., Chiang A. Infectious mononucleosis presenting as acute cerebellar syndrome. Lancet. 1973 Sep 29;2(7831):707–709. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92540-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. L., Davidsohn I., Panczyszyn O. Horse agglutinins in infectious mononucleosis. II. The spot test. Am J Clin Pathol. 1968 Jan;49(1):12–18. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/49.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. L., Davidsohn I., Slaby R. Horse agglutinins in infectious mononucleosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1968 Jan;49(1):3–11. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/49.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine P. H., Stevens D. A., Coccia P. F., Dabich L., Roland A. Infectious mononucleosis prior to acute leukemia: a possible role for the Epstein-Barr virus. Cancer. 1972 Oct;30(4):875–880. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197210)30:4<875::aid-cncr2820300402>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li F., Hanshaw J. B. Cytomegalovirus infection among migrant children. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 Jul;86(1):137–141. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman M., Andrews L., Niederman J., Miller G. Direct visualization of enveloped Epstein-Barr Herpesvirus in throat washing with leukocyte-transforming activity. J Infect Dis. 1975 Nov;132(5):520–523. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.5.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liveson J. A., Goodgold J. Mononeuritis multiplex associated with infectious mononucleosis. Can J Neurol Sci. 1974 Aug;1(3):203–205. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100119262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luby J. P., Burnett W., Hull A. R., Ware A. J., Shorey J. W., Peters P. C. Relationship between cytomegalovirus and hepatic function abnormalities in the period after renal transplant. J Infect Dis. 1974 May;129(5):511–518. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.5.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunde M. N. Laboratory methods in the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis. Health Lab Sci. 1973 Oct;10(4):319–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madigan N. P., Newcomer A. D., Campbell D. C., Taswell H. F. Intense jaundice in infectious mononucleosis. Mayo Clin Proc. 1973 Dec;48(12):857–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangi R. J., Niederman J. C., Kelleher J. E., Jr, Dwyer J. M., Evans A. S., Kantor F. S. Depression of cell-mediated immunity during acute infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1974 Nov 28;291(22):1149–1153. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197411282912202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken A. W., D'Agostino A. N., Brucks A. B., Kingsley W. B. Acquired cytomegalovirus infection presenting as viral endometritis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Apr;61(4):556–560. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/61.4.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. Epstein-Barr herpesvirus and infectious mononucleosis. Prog Med Virol. 1975;20:84–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Niederman J. C., Andrews L. L. Prolonged oropharyngeal excretion of Epstein-Barr virus after infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Feb 1;288(5):229–232. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197302012880503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Robinson J., Heston L., Lipman M. Differences between laboratory strains of Epstein-Barr virus based on immortalization, abortive infection, and interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4006–4010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Shope T., Heston L., O'Brien R., Schwartz A., Pearson H. Prospective study of Epstein-Barr virus infections in acute lymphoblastic leukemia of childhood. J Pediatr. 1972 Jun;80(6):932–937. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. The oncogenicity of Epstein-Barr virus. J Infect Dis. 1974 Aug;130(2):187–205. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. W., Beebe G. W. Infectious mononucleosis and the empirical risk of cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Feb;50(2):315–321. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.2.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R., Ward C., Amsterdam E., Mason D. T., Zelis R. Focal mononucleosis myocarditis simulating myocardial infarction. Chest. 1973 Jan;63(1):102–105. doi: 10.1378/chest.63.1.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mir M. A., Delamore I. W. Aplastic anaemia complicating infectious mononucleosis. Scand J Haematol. 1973;11(4):314–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1973.tb00134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovic R., Werch J., South M. A., Benyesh-Melnick M. Incidence of cytomegaloviremia in blood-bank donors and in infants with congenital cytomegalic inclusion disease. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):45–50. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.45-50.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monif G. R., Egan E. A., 2nd, Held B., Eitzman D. V. The correlation of maternal cytomegalovirus infection during varying stages in gestation with neonatal involvement. J Pediatr. 1972 Jan;80(1):17–20. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80446-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundy G. R. Infectious mononucleosis with pulmonary parenchymal involvement. Br Med J. 1972 Jan 22;1(5794):219–220. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5794.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Stamou A., Senn H. J., Emödy G. Epidermolysis in a case of severe cytomegalovirus infection. Br Med J. 1974 Sep 7;3(5931):609–610. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5931.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaratnam N., Stephen S. J. Chronic constrictive pericarditis associated with toxoplasmosis. Br Heart J. 1973 Aug;35(8):868–870. doi: 10.1136/hrt.35.8.868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederman J. C., Miller G., Pearson H. A., Pagano J. S., Dowaliby J. M. Infectious mononucleosis. Epstein-Barr-virus shedding in saliva and the oropharynx. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jun 17;294(25):1355–1359. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197606172942501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikoskelainen J., Hänninen P. Antibody response to Epstein-Barr virus in infectious mononucleosis. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):42–51. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.42-51.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikoskelainen J., Leikola J., Klemola E. IgM antibodies specific for Epstein-Barr virus in infectious mononucleosis without heterophil antibodies. Br Med J. 1974 Oct 12;4(5936):72–75. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5936.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama M., Huang C. H., Pagano J. S., Klein G., Singh S. DNA of Epstein-Barr virus detected in tissue of Burkitt's lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3265–3268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordbring F., Johansson S. G., Espmark A. Raised serum levels of IgE in infectious mononucleosis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1972;4(2):119–124. doi: 10.3109/inf.1972.4.issue-2.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numazaki Y., Yano N., Morizuka T., Takai S., Ishida N. Primary infection with human cytomegalovirus: virus isolation from healthy infants and pregnant women. Am J Epidemiol. 1970 Apr;91(4):410–417. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oill P. A., Fiala M., Schofferman J., Byfield P. E., Guze L. B. Cytomegalovirus mononucleosis in a healthy adult: association with hepatitis, secondary Epstein-Barr Virus antibody response and immunosuppression. Am J Med. 1977 Mar;62(3):413–417. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90840-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olding L. B., Jensen F. C., Oldstone M. B. Pathogenesis of of cytomegalovirus infection. I. Activation of virus from bone marrow-derived lymphocytes by in vitro allogenic reaction. J Exp Med. 1975 Mar 1;141(3):561–572. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano J. S., Huang C. H., Klein G., de-Thé G., Shanmugaratnam K., Yang C. S. Homology of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in nasopharyngeal carcinomas from Kenya, Taiwan, Singapore and Tunisia. IARC Sci Publ. 1975;(11 Pt 2):179–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paloheimo J. A., von Essen R., Klemola E., Käriäinen L., Siltanen P. Subclinical cytomegalovirus infections and cytomegalovirus mononculeosis after open heart surgery. Am J Cardiol. 1968 Nov;22(5):624–630. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(68)90198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papamichail M., Sheldon P. J., Holborow E. J. T- and B-cell subpopulations in infectious mononucleosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):1–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattengale P. K., Smith R. W., Gerber P. B-cell characteristics of human peripheral and cord blood lymphocytes transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Apr;52(4):1081–1086. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.4.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattengale P. K., Smith R. W., Perlin E. Atypical lymphocytes in acute infectious mononucleosis. Identification by multiple T and B lymphocyte markers. N Engl J Med. 1974 Nov 28;291(22):1145–1148. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197411282912201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen P. R., Gerber P., Sweeney G., Blom J. Infectious mononucleosis preceding acute myelomonocytic leukemia. Am J Med Sci. 1975 Jan-Feb;269(1):131–135. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197501000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman H. G. Extreme neutropenia in glandular fever. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Jan;21(1):48–49. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman H. G. Fatal infectious mononucleosis: a critical review. J Clin Pathol. 1970 Dec;23(9):765–771. doi: 10.1136/jcp.23.9.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Szmuness W., Millian S. J., David D. S. A serologic study of cytomegalovirus infections associated with blood transfusions. N Engl J Med. 1971 May 20;284(20):1125–1131. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197105202842004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provisor A. J., Iacuone J. J., Chilcote R. R., Neiburger R. G., Crussi F. G. Acquired agammaglobulinemia after a life-threatening illness with clinical and laboratory features of infectious mononucleosis in three related male children. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jul 10;293(2):62–65. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197507102930202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen H., Wright N., Murdoch J. M. Hypersensitivity reactions to antibacterial drugs in infectious mononucleosis. Lancet. 1967 Dec 2;2(7527):1176–1178. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91893-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., Cassel C. K., Yang J. P., Harper R. X-linked recessive progressive combined variable immunodeficiency (Duncan's disease). Lancet. 1975 Apr 26;1(7913):935–940. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAWAL B. D. Laboratory infection with Toxoplasma. J Clin Pathol. 1959 Jan;12(1):59–61. doi: 10.1136/jcp.12.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REMINGTON J. S., BARNETT C. G., MEIKEL M., LUNDE M. N. Toxoplasmosis and infectious mononucleosis. Arch Intern Med. 1962 Nov;110:744–753. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1962.03620230190026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWE W. P., HARTLEY J. W., WATERMAN S., TURNER H. C., HUEBNER R. J. Cytopathogenic agent resembling human salivary gland virus recovered from tissue cultures of human adenoids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Jun;92(2):418–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahal J. J., Jr, Henle G. Infectious mononucleosis and Reye's syndrome: a fatal case with studies for Epstein-Barr virus. Pediatrics. 1970 Nov;46(5):776–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller L. B. Granulomatous hepatitis associated with acute cytomegalovirus infection. Lancet. 1973 Jan 6;1(7793):20–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Anderson S. E., Jr Diagnosis and treatment of pneumocystosis and toxoplasmosis in the immunosuppressed host. Transplant Proc. 1973 Sep;5(3):1263–1270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Miller M. J., Brownlee I. IgM antibodies in acute toxoplasmosis. II. Prevalence and significance in acquired cases. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 May;71(5):855–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds E. S., Walls K. W., Pfeiffer R. I. Generalized toxoplasmosis following renal transplantation. Report of a case. Arch Intern Med. 1966 Oct;118(4):401–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Jarvis J. E., Crawford D. H., Epstein M. A. Observations on the type of infection by Epstein-Barr virus in peripheral lymphoid cells of patients with infectious mononucleosis. Int J Cancer. 1974 Dec 15;14(6):704–715. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910140603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosdahl N., Larsen S. O., Clemmesen J. Hodgkin's disease in patients with previous infectious mononucleosis: 30 years' experience. Br Med J. 1974 May 4;2(5913):253–256. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5913.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royston I., Sullivan J. L., Periman P. O., Perlin E. Cell-mediated immunity to Epstein-Barr-virus-transformed lymphoblastoid cells in acute infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1975 Dec 4;293(23):1159–1163. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197512042932301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUMACHER H. R., JACOBSON W. A., BEMILLER C. R. Treatment of infectious mononucleosis. Ann Intern Med. 1963 Feb;58:217–228. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-58-2-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERN H., ELEK S. D. THE INCIDENCE OF INFECTION WITH CYTOMEGALOVIRUS IN A NORMAL POPULATION. A SEROLOGICAL STUDY IN GREATER LONDON. J Hyg (Lond) 1965 Mar;63:79–87. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400044983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B., Feldman H. A. Dyes as Microchemical Indicators of a New Immunity Phenomenon Affecting a Protozoon Parasite (Toxoplasma). Science. 1948 Dec 10;108(2815):660–663. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2815.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvador A. H., Harrison E. G., Jr, Kyle R. A. Lymphadenopathy due to infectious mononucleosis: its confusion with malignant lymphoma. Cancer. 1971 May;27(5):1029–1040. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197105)27:5<1029::aid-cncr2820270505>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J., Davey F. R. Human leukocyte locus A (HL-A) antigens and infectious mononucleosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Sep;62(3):325–328. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/62.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H. Bedeutung des Envelope bei CMV-Infektionen. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1974;227(1-4):416–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Doerr H. W., Obrig M. Envelope and nucleocapsid antigens of Cytomegalovirus (CMV). Med Microbiol Immunol. 1975 Jul 2;161(3):155–162. doi: 10.1007/BF02121005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Haas R. Determination of different cytomegalovirus immunoglobulins (IgG, IgA, IgM) by immunofluorescence. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;37(1):131–140. doi: 10.1007/BF01241158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Scherer M. IgM antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in infectious mononucleosis. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;37(4):332–339. doi: 10.1007/BF01241456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider U., zur Hausen H. Epstein-Barr virus-induced transformation of human leukocytes after cell fractionation. Int J Cancer. 1975 Jan 15;15(1):59–66. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell R. G., Dyck P. J., Bowie E. J., Klass D. W., Taswell H. F. Infectious mononucleosis: neurologic and EEG findings. Medicine (Baltimore) 1966 Jan;45(1):51–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. N., Daniels C. A., Klintworth G. K. Lymphoid cell necrosis, thymic atrophy, and growth retardation in newborn mice inoculated with murine cytomegalovirus. Am J Pathol. 1975 Jun;79(3):509–522. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selroos O. Infectious mononucleosis with thrombocytopenic purpura. Acta Med Scand. 1972 Nov;192(5):471–474. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1972.tb04848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shashaty G. G., Atamer M. A. Hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with infectious mononucleosis. Am J Dis Child. 1974 May;127(5):720–722. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110240106016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield H. G., Melton M. L. The fine structure and reproduction of Toxoplasma gondii. J Parasitol. 1968 Apr;54(2):209–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon P. J., Hemsted E. H., Papamichail M., Holborow E. J. Thymic origin of atypical lymphoid cells in infectious mononucleosis. Lancet. 1973 May 26;1(7813):1153–1155. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodaria P. V., Fraser K. B., Stanford F. Secondary fluorescent staining of virus antigens by rheumatoid factor and fluorescein-conjugated anti-IgM. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Jan;32(1):53–57. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shope T., Dechairo D., Miller G. Malignant lymphoma in cottontop marmosets after inoculation with Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2487–2491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shope T., Miller G. Epstein-Barr virus. Heterophile responses in squirrel monkeys inoculated with virus-transformed autologous leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):140–147. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster F., Ognibene A. J. Dissociation of serum bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase in infectious mononucleosis. JAMA. 1969 Jul 14;209(2):267–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein A., Steinberg G., Nathanson M. Nervous system involvement in infectious mononucleosis. The heralding and-or major manifestation. Arch Neurol. 1972 Apr;26(4):353–358. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490100083009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons R. L., Lopez C., Balfour H., Jr, Kalis J., Rattazzi L. C., Najarian J. S. Cytomegalovirus: Clinical virological correlations in renal transplant recipients. Ann Surg. 1974 Oct;180(4):623–634. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197410000-00028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons M. J., Wee G. B., Chan S. H., Shanmugaratnam K. Probable identification of an HL-A second-locus antigen associated with a high risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 1975 Jan 18;1(7899):142–143. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91433-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Reynolds D. W., Lakeman A., Charamella L. J., Alford C. A. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: consecutive occurrence due to viruses with similar antigenic compositions. Pediatrics. 1973 Dec;52(6):788–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Reynolds D., Tsiantos A., Fuccillo D. A., Smith R., Tiller M., Alford C. A., Jr Cervical cytomegalovirus excretion in pregnant and nonpregnant women: suppression in early gestation. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131(5):522–527. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.5.522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stell C. M., Ling N. R. Letter: Immunopathology of infectious mononucleosis. Lancet. 1973 Oct 13;2(7833):861–862. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90924-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern H. Isolation of cytomegalovirus and clinical manifestations of infection at different ages. Br Med J. 1968 Mar 16;1(5593):665–669. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5593.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. A., Levine P. H., Lee S. K., Sonley M. J., Waggoner D. E. Concurrent infectious mononucleosisand acute leukemia. Case reports. Review of theliterature and serologic studies with the herpes-type virus (EB virus). Am J Med. 1971 Feb;50(2):208–217. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90150-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R. N., Marston S. D., Almond E. J., Emond R. T. Aspects of Epstein-Barr virus infection in childhood. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Feb;49(2):102–106. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.2.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R. N., Marston S. D., Pullen H. J., Darby C. W., Emond R. T., Evans D. I. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr and other viruses in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Jul;49(7):540–544. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.7.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedmyr E., Jondal M. Cytotoxic effector cells specific for B Cell lines transformed by Epstein-Barr virus are present in patients with infectious mononucleosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1622–1626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TENHUNEN A. GLANDULAR TOXOPLASMOSIS. OCCURRENCE OF THE DISEASE IN FINLAND. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1964;172:SUPPL 172–17372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamir D., Benderly A., Levy J., Ben-Porath E., Vonsover A. Infectious mononucleosis and Epstein-Barr virus in childhood. Pediatrics. 1974 Mar;53(3):330–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennant F. S., Jr The glomerulonephritis of infectious mononucleosis. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1968 Winter;26(4):603–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The T. H., Klein G., Langenhuysen M. M. Antibody reactions to virus-specific early antigens (EA) in patients with cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jan;16(1):1-7,9-12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theologides A., Kennedy B. J. Toxoplasmic myocarditis and pericarditis. Am J Med. 1969 Aug;47(2):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90144-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. B. Antibodies to membrane antigen(s) common to thymocytes and a subpopulation of lymphocytes in infectious-mononucleosis sera. Lancet. 1972 Feb 19;1(7747):399–403. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90854-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. B., Phillips B. Evidence for membrane antigen(s) specific for human B lymphoblasts. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 May;14(1):91–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tindle B. H., Parker J. W., Lukes R. J. "Reed-Sternberg cells" in infectious mononucleosis? Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Dec;58(6):607–617. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/58.6.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiula E., Leinikki P. Fatal cytomegalovirus infection in a previously healthy boy with myocarditis and consumption coagulopathy as presenting signs. Scand J Infect Dis. 1972;4(1):57–60. doi: 10.3109/inf.1972.4.issue-1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toghill P. J., Bailey M. E., Williams R., Zeegen R., Bown R. Cytomegalovirus hepatitis in the adult. Lancet. 1967 Jun 24;1(7504):1351–1354. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91762-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxel D. B., Innella F., Cohen R. J. Infectious mononucleosis complicated by hemolytic anemia due to anti-i. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Dec;46(6):625–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vietzke W. M., Gelderman A. H., Grimley P. M., Valsamis M. P. Toxoplasmosis complicating malignancy. Experience at the National Cancer Institute. Cancer. 1968 May;21(5):816–827. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196805)21:5<816::aid-cncr2820210506>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virolainen M., Andersson L. C., Lalla M., von Essen R. T-lymphocyte proliferation in mononucleosis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1973 Nov;2(1):114–120. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(73)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vischer T. L., Bernheim C., Engelbrecht E. Two cases of hepatitis due to Toxoplasma gondii. Lancet. 1967 Oct 28;2(7522):919–921. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodopick H., Chaskes S. J., Solomon A., Stewart J. A. Transient monoclonal gammopathy associated with cytomegalovirus infection. Blood. 1974 Aug;44(2):189–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonka V., Vlcková I., Závadová H., Kouba K., Lazovská J., Duben J. Antibodies to EB virus capsid antigen and to soluble antigen of lymphoblastoid cells in infectious mononucleosis patients. Int J Cancer. 1972 May 15;9(3):529–535. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910090309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLER T. H., HANSHAW J. B., SCOTT D. E. Serologic differentiation of viruses responsible for cytomegalic inclusion disease. Virology. 1960 Sep;12:130–132. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wager O., Räsänen J. A., Hagman A., Klemola E. Mixed cryoimmunoglobulinaemia in infectious mononucleois and Cytomegalovirus mononucleosis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;34(4):345–361. doi: 10.1159/000230129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren B., Carlens E., Espmark A., Lundbeck H., Löfgren S., Madar E., Henle G., Henle W. Antibodies to various herpesviruses in sera from patients with sarcoidosis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Oct;47(4):747–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren B., Espmark A., Walldén G. Serological studies on cytomegalovirus infection in relation to infectious mononucleosis and similar conditions. Scand J Infect Dis. 1969;1(3):145–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren B., Lantorp K., Sterner G., Espmark A. EBV antibodies in family contacts of patients with infectious mononucleosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Mar;133(3):934–939. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace G. D. The role of the cat in the natural history of Toxoplasma gondii. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1973 May;22(3):313–322. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1973.22.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace G. D., Zigas V., Gajdusek D. C. Toxoplasmosis and cats in New Guinea. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1974 Jan;23(1):8–14. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1974.23.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Perrotto J. L., Isselbacher K. J. Circulating immune complexes and complement sequence activation in infectious mononucleosis. Am J Med. 1976 Feb;60(2):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90436-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waner J. L., Weller T. H., Kevy S. V. Patterns of cytomegaloviral complement-fixing antibody activity: a longitudinal study of blood donors. J Infect Dis. 1973 May;127(5):538–543. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.5.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waris E., Räsänen O., Kreus K. E., Kreus R. Fatal cytomegalovirus disease in a previously healthy adult. Scand J Infect Dis. 1972;4(1):61–67. doi: 10.3109/inf.1972.4.issue-1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weary P. E., Cole J. W., 3rd, Hickam L. H. Eruptions from ampicillin in patients with infectious mononucleosis. Arch Dermatol. 1970 Jan;101(1):86–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller T. H. The cytomegaloviruses: ubiquitous agents with protean clinical manifestations. I. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 22;285(4):203–214. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107222850406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner J., Pinto C. A., Haff R. F., Henle W., Henle G. Responses of gibbons to inoculation of Epstein-Barr virus. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):678–681. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse J. M., Ferguson N., Currie G. A. Autoantibody to microtubules in infectious mononucleosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jun;17(2):227–235. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson L. S., Petz L. D., Garratty G. Reappraisal of the role of anti-i in haemolytic anaemia in infectious mononucleosis. Br J Haematol. 1973 Dec;25(6):715–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb01784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills E. J. Electron microscopy of the liver in infectious mononucleosis hepatitis and cytomegalovirus hepatitis. Am J Dis Child. 1972 Apr;123(4):301–303. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110100033012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishart M. M., Davey M. G. Infectious mononucleosis complicated by acute haemolytic anaemia with a positive Donath-Landsteiner reaction. J Clin Pathol. 1973 May;26(5):332–334. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.5.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Werner J., zur Hausen H. EBV DNA in nonlymphoid cells of nasopharyngeal carcinomas and in a malignant lymphoma obtained after inoculation of EBV into cottontop marmosets. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):791–796. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim F. A. Immunoglobulin changes in the course of infectious mononucleosis. Scand J Haematol. 1968;5(2):97–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1968.tb01724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim F. A., Williams R. C., Jr Studies on the macroglobulins of human serum. I. Polyclonal immunoglobulin class M (IgM) increase in infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jan 13;274(2):61–67. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196601132740202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood T. A., Frenkel E. P. The atypical lymphocyte. Am J Med. 1967 Jun;42(6):923–936. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroffe A. J., Row P. G., Meadows R., Lawrence J. R. Nephritis in infectious mononucleosis. Q J Med. 1974 Jul;43(171):451–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorbala-Mallios H., Sutton R. N., Emond R. T. EB-virus-specific IgM and IgG antibodies in first-degree relatives of children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Arch Dis Child. 1975 Feb;50(2):137–141. doi: 10.1136/adc.50.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuelzer W. W., Stulberg C. S., Page R. H., Teruya J., Brough A. J. Etiology and pathogenesis of acquired hemolytic anemia. Transfusion. 1966 Sep-Oct;6(5):438–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1966.tb04759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de-The G. Is Burkitt's lymphoma related to perinatal infection by Epstein-Barr virus? Lancet. 1977 Feb 12;1(8007):335–338. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de-Thé G., Day N. E., Geser A., Lavoué M. F., Ho J. H., Simons M. J., Sohier R., Tukei P., Vonka V., Zavadova H. Sero-epidemiology of the Epstein-Barr virus: preliminary analysis of an international study - a review. IARC Sci Publ. 1975;(11 Pt 2):3–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


