Abstract
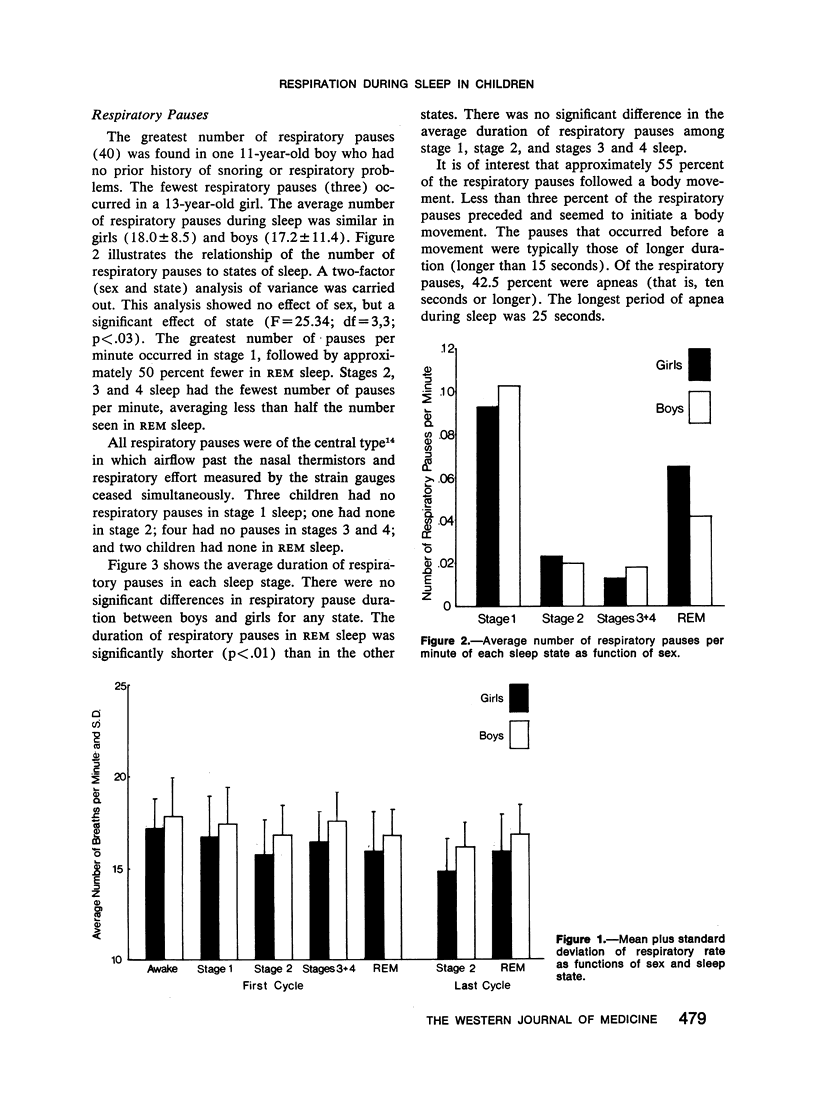
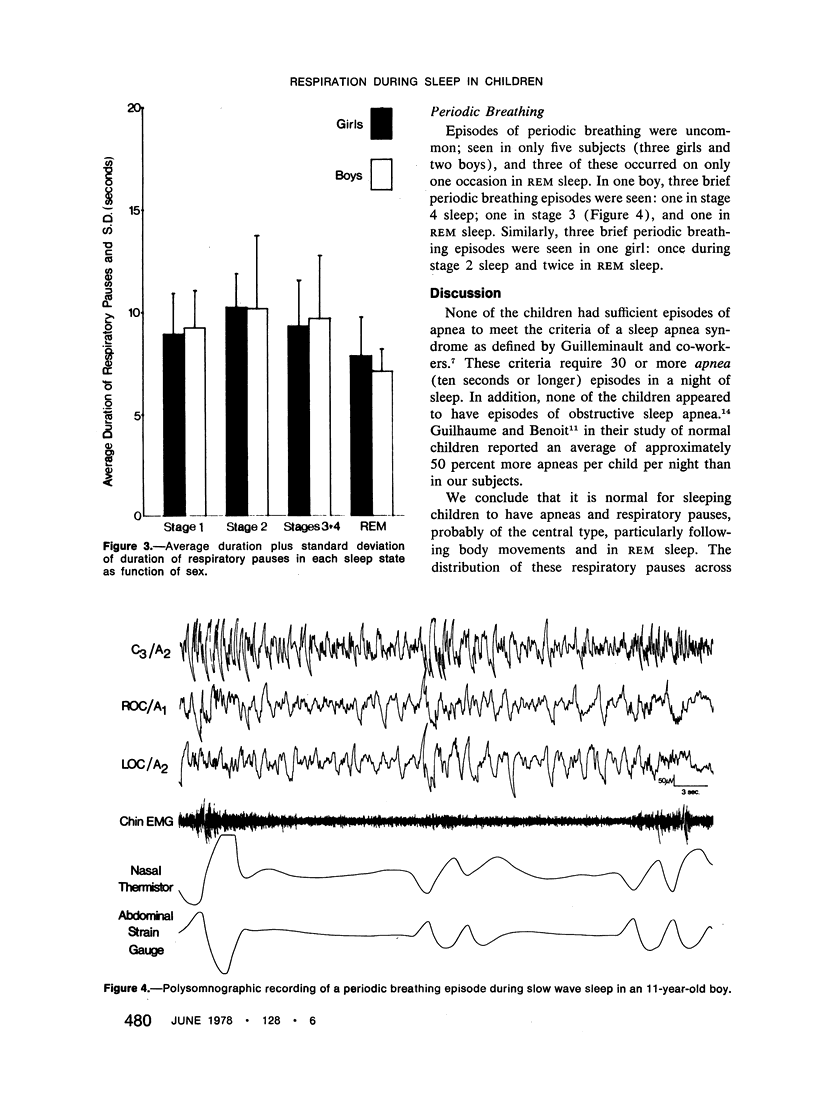
In 22 children (11 boys and 11 girls), aged 9 to 13 years, respiration was monitored during one night of sleep. No child had a significant history of breathing problems during sleep. Sleep was recorded using standard techniques (electroencephalography, electrooculography, electromyography), and respiration was measured with nasal thermistors and abdominal or thoracic strain gauges. Respiratory pauses (five seconds or longer) were determined for all sleep stages. Respiratory rate was scored only in the first and last sleep cycles and during ten waking minutes before sleep onset. Respiratory rate was significantly affected by wakefulness or stage of sleep: highest in wakefulness and stage 1, lowest in stage 2 of the last sleep cycle. Regularity of respiratory rate showed a similar effect. Variance of respiratory rate was significantly lower in girls than boys. Respiratory pauses during sleep were seen in every child, ranging from 3 to 40 pauses per night (average, 17.2 for boys and 18.0 for girls). Significantly greater numbers of pauses per minute were seen in stage 1 and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep than in stages 2, 3 and 4. The longest respiratory pause was 25 seconds. The conclusion is made that a small number of respiratory pauses during sleep are normal in children of this age.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gastaut H., Tassinari C. A., Duron B. Polygraphic study of the episodic diurnal and nocturnal (hypnic and respiratory) manifestations of the Pickwick syndrome. Brain Res. 1966 Feb;1(2):167–186. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(66)90117-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilhaume A., Benoit O. Pauses respiratoires au cours du sommeil chez l'enfant normal. Observation de 3 cas pathologiques. Rev Electroencephalogr Neurophysiol Clin. 1976 Jan-Mar;6(1):116–123. doi: 10.1016/s0370-4475(76)80070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Ariagno R., Souquet M., Dement W. C. Abnormal polygraphic findings in near-miss sudden infant death. Lancet. 1976 Jun 19;1(7973):1326–1327. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92656-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Dement W. C., Monod N. Syndrome "mort subite du nourrisson": apnées au cours du sommeil. Nouvelle hypothése. Nouv Presse Med. 1973 May 19;2(20):1355–1358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Eldridge F. L., Simmon F. B., Dement W. C. Sleep apnea syndrome. Can it induce hemodynamic changes? West J Med. 1975 Jul;123(1):7–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Eldridge F. L., Simmons F. B., Dement W. C. Sleep apnea in eight children. Pediatrics. 1976 Jul;58(1):23–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Peraita R., Souquet M., Dement W. C. Apneas during sleep in infants: possible relationship with sudden infant death syndrome. Science. 1975 Nov 14;190(4215):677–679. doi: 10.1126/science.1188364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Tilkian A. G., Dement W. C. Sommeil et respiration dans le syndrome "apnée au cours du sommeil" chez l'enfant. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1976 Oct;41(4):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(76)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Tilkian A., Dement W. C. The sleep apnea syndromes. Annu Rev Med. 1976;27:465–484. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.27.020176.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monod N., Curzi-Dascalova L., Guidasci S., Valenzuela S. Pauses respiratoires et sommeil chez le nouveau-né et le nourrisson. Rev Electroencephalogr Neurophysiol Clin. 1976 Jan-Mar;6(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/s0370-4475(76)80068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmelee A. H., Stern E., Harris M. A. Maturation of respiration in prematures and young infants. Neuropadiatrie. 1972 Mar;3(3):294–304. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1091768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER F., HOBSON J. A., MORRISON D. F., GOLDFRANK F. CHANGES IN RESPIRATION, HEART RATE, AND SYSTOLIC BLOOD PRESSURE IN HUMAN SLEEP. J Appl Physiol. 1964 May;19:417–422. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.3.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinschneider A. Prolonged apnea and the sudden infant death syndrome: clinical and laboratory observations. Pediatrics. 1972 Oct;50(4):646–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


