Abstract
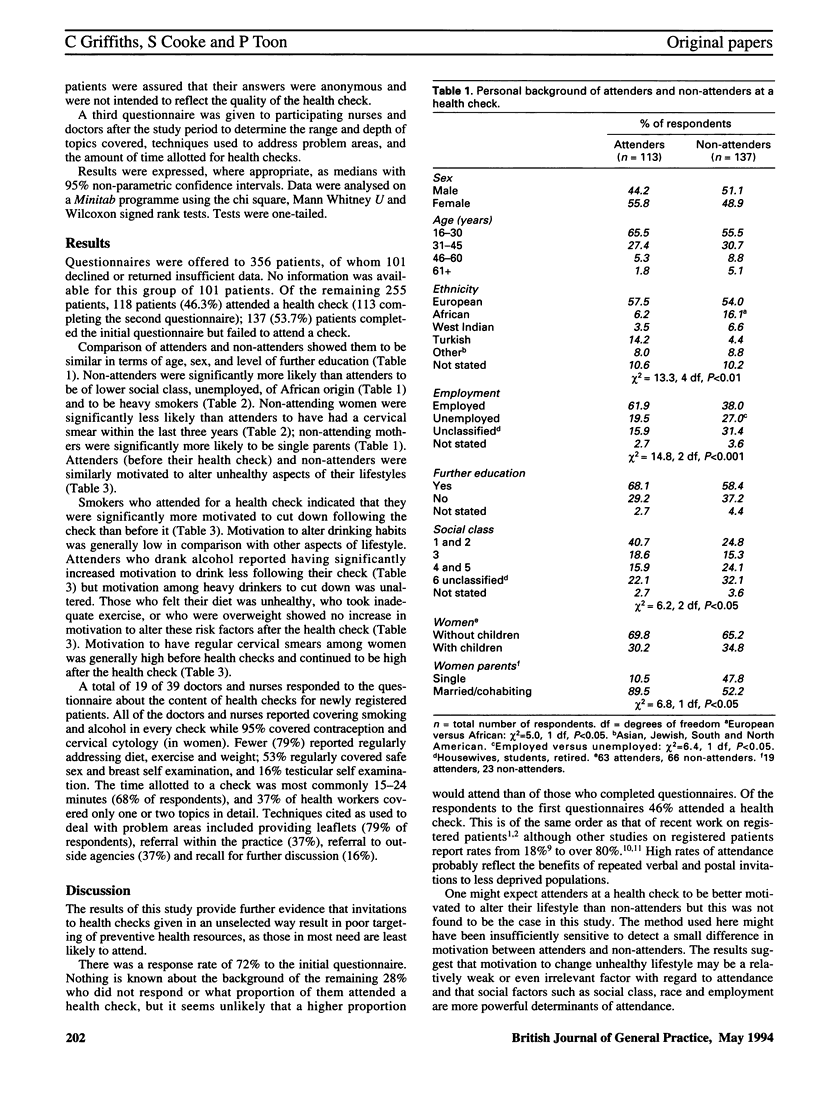
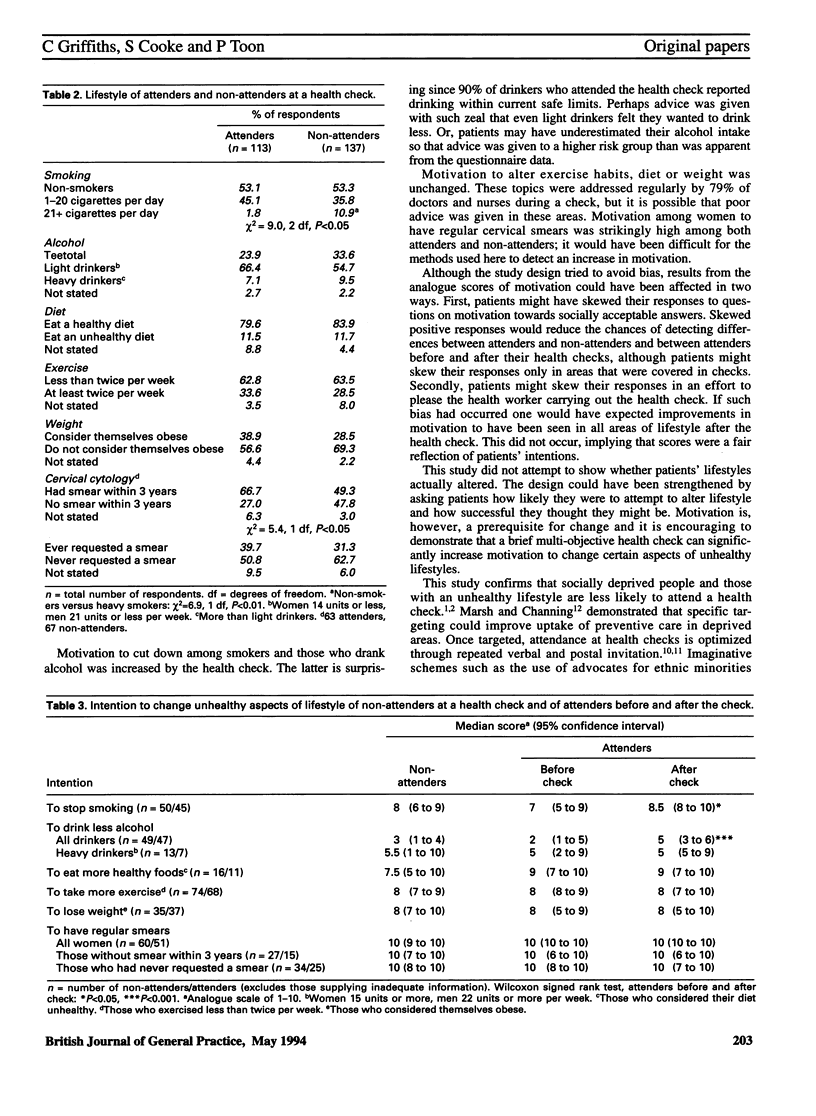
BACKGROUND. Attendance at health checks of patients already registered with a general practitioner is known to be poor, with those in need least likely to attend. Little is known of the efficacy of such checks for newly registered patients. AIM. This study set out to determine the characteristics of attenders and non-attenders at health checks for patients registering with a general practitioner in east London, and the effect of health checks on motivation to change unhealthy lifestyles. METHOD. A questionnaire analysis was carried out of patients aged 16 years and over at registration and after a health check in seven east London training practices. Questionnaires asked about personal background and lifestyle including smoking status, alcohol intake, diet, weight, exercise, cervical smear uptake, and motivation to change unhealthy aspects of lifestyle. RESULTS. Questionnaires were offered to 356 patients registering with the practices, of whom 101 declined or returned inadequate data. Of the remaining 255 patients, 118 (46%) attended a health check with 113 completing a second questionnaire after the check. Non-attenders were significantly more likely than attenders to be of lower social class, unemployed, of African origin and to be heavy smokers. Women who did not attend were significantly less likely than attenders to have had a cervical smear within the last three years. Non-attending mothers were significantly more likely than attending mothers to be single parents. Motivation among attenders to stop smoking and drink less alcohol was increased significantly after the health check. CONCLUSION. Attendance at registration health checks at these practices was poor and non-attenders tended to be more socially deprived than attenders and had relatively unhealthy lifestyles. Although the health checks increased the attenders' motivation to alter smoking and drinking habits, inviting all new patients to a health check would appear to result in poor targeting of health promotion resources and may widen inequalities in health.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron J. A., Gleason R., Crowe B., Mann J. I. Preliminary trial of the effect of general practice based nutritional advice. Br J Gen Pract. 1990 Apr;40(333):137–141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards G., Orford J., Egert S., Guthrie S., Hawker A., Hensman C., Mitcheson M., Oppenheimer E., Taylor C. Alcoholism: a controlled trial of "treatment" and "advice". J Stud Alcohol. 1977 May;38(5):1004–1031. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1977.38.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman G. D., Collen M. F., Fireman B. H. Multiphasic Health Checkup Evaluation: a 16-year follow-up. J Chronic Dis. 1986;39(6):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(86)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart J. T. The inverse care law. Lancet. 1971 Feb 27;1(7696):405–412. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92410-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart J. T., Thomas C., Gibbons B., Edwards C., Hart M., Jones J., Jones M., Walton P. Twenty five years of case finding and audit in a socially deprived community. BMJ. 1991 Jun 22;302(6791):1509–1513. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6791.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh G. N., Channing D. M. Narrowing the health gap between a deprived and an endowed community. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 Jan 16;296(6616):173–176. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6616.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pill R., French J., Harding K., Stott N. Invitation to attend a health check in a general practice setting: comparison of attenders and non-attenders. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1988 Feb;38(307):53–56. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson J., Boomla K., Fitzpatrick S., Jewell A. J., Taylor J., Self J., Colyer M. Using nurses for preventive activities with computer assisted follow up: a randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 1989 Feb 18;298(6671):433–436. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6671.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks G., Marsden R. Evaluation of a practice-based programme of health checks: financial cost and success at risk detection. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1989 Sep;39(326):369–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders D., Fowler G., Mant D., Fuller A., Jones L., Marzillier J. Randomized controlled trial of anti-smoking advice by nurses in general practice. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1989 Jul;39(324):273–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. F. Inviting infrequent attenders to attend for a health check: costs and benefits. Br J Gen Pract. 1990 Jan;40(330):16–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller D., Agass M., Mant D., Coulter A., Fuller A., Jones L. Health checks in general practice: another example of inverse care? BMJ. 1990 Apr 28;300(6732):1115–1118. doi: 10.1136/bmj.300.6732.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


