Abstract
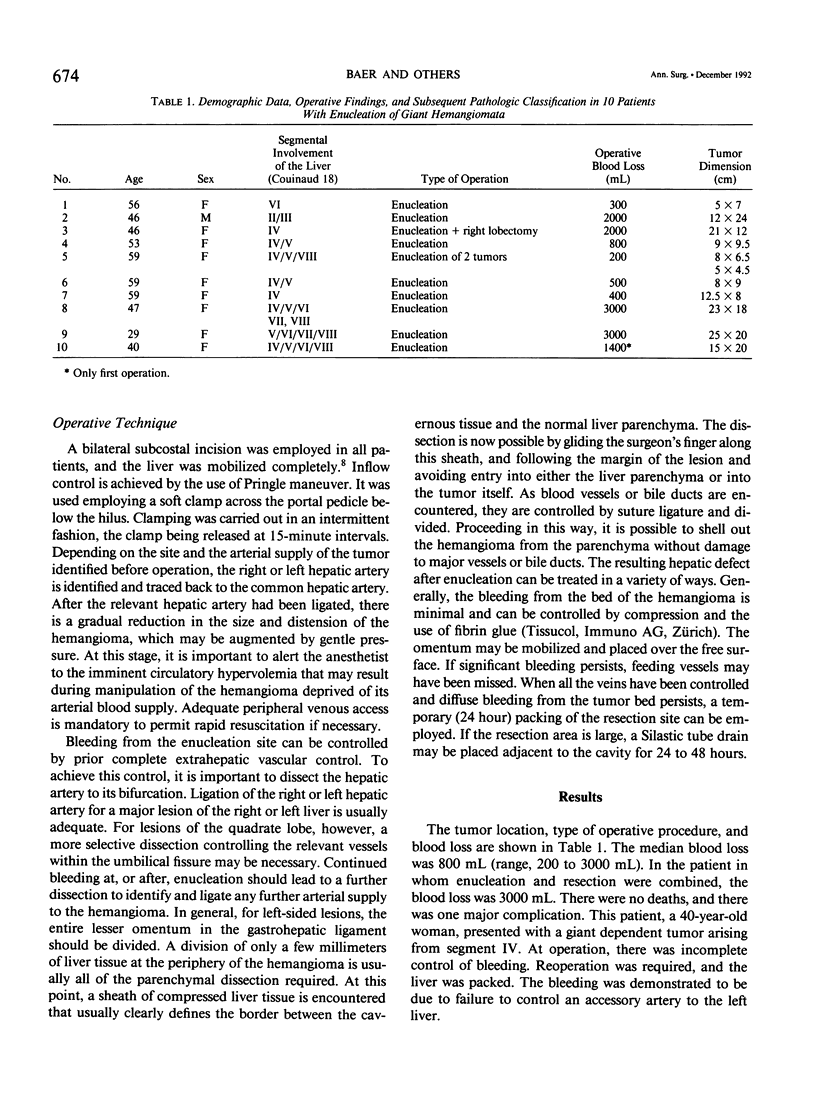
Cavernous hemangiomas are the most common benign tumors of the liver. Giant cavernous hemangiomas, defined as those larger than 4 cm in diameter, can reach enormous proportions. Newer imaging modalities, although often demonstrating characteristic features that strongly suggest the diagnosis, should not be augmented by biopsy because of the risk of hemorrhage. Elective surgical resection may be indicated for symptomatic giant lesions and for those with an atypical appearance where the diagnosis is in doubt. Between October 1986 and May 1991, we treated 10 patients with giant hemangiomas by enucleation or enucleation plus resection. Median operative blood loss was 800 mL (range, 200 to 3000 mL). One patient required reoperation for control of postoperative hemorrhage. Detailed pathologic examination has demonstrated an interface between hemangiomas and the normal liver tissue that allows enucleation. Enucleation is an underused procedure that if carefully performed allows resection of giant hemangiomas with a reduced blood loss and the preservation of virtually all normal hepatic parenchyma.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam Y. G., Huvos A. G., Fortner J. G. Giant hemangiomas of the liver. Ann Surg. 1970 Aug;172(2):239–245. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197008000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer H. U., Maddern G. J., Blumgart L. H. New water-jet dissector: initial experience in hepatic surgery. Br J Surg. 1991 Apr;78(4):502–503. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer H. U., Schweizer W., Gertsch P., Blumgart L. H. Klinik, Diagnostik und Therapie von "grossen" Leberhämangiomen. Helv Chir Acta. 1987 Dec;54(4):387–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conter R. L., Longmire W. P., Jr Recurrent hepatic hemangiomas. Possible association with estrogen therapy. Ann Surg. 1988 Feb;207(2):115–119. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198802000-00001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs K. E. Hepatic hemangiomas. World J Surg. 1990 Jul-Aug;14(4):468–471. doi: 10.1007/BF01658669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson W. J., DelGuercio L. R. Preliminary experience in liver surgery using the ultrasonic scalpel. Surgery. 1984 Feb;95(2):230–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishak K. G., Rabin L. Benign tumors of the liver. Med Clin North Am. 1975 Jul;59(4):995–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31998-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki S., Starzl T. E. Personal experience with 411 hepatic resections. Ann Surg. 1988 Oct;208(4):421–434. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198810000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. M., Sheedy P. F., 2nd, Stanson A. W., Stephens D. H., Hattery R. R., Adson M. A. Computed tomography and angiography of cavernous hemangiomas of the liver. Radiology. 1981 Jan;138(1):115–121. doi: 10.1148/radiology.138.1.7455071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno González E., Landa Garcia I., Calleja Kempin J., Santoyo Santoyo J., Gomez Gutierrez M., Jover Navalón J. M., Arias Diaz J., Manrique A., Vorwald Kuborn P. Indikationen und Resultate der chirurgischen Behandlung von cavernösen Hämangiomen der Leber. Chirurg. 1988 May;59(5):338–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OCHSNER J. L., HALPERT B. Cavernous hemangioma of the liver. Surgery. 1958 Apr;43(4):577–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. I., Husser W. C. Cavernous hemangioma of the liver. A single institution report of 16 resections. Ann Surg. 1987 May;205(5):456–465. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198705000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark D. D., Felder R. C., Wittenberg J., Saini S., Butch R. J., White M. E., Edelman R. R., Mueller P. R., Simeone J. F., Cohen A. M. Magnetic resonance imaging of cavernous hemangioma of the liver: tissue-specific characterization. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985 Aug;145(2):213–222. doi: 10.2214/ajr.145.2.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Koep L. J., Weil R., 3rd, Fennell R. H., Iwatsuki S., Kano T., Johnson M. L. Excisional treatment of cavernous hemangioma of the liver. Ann Surg. 1980 Jul;192(1):25–27. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198007000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trastek V. F., van Heerden J. A., Sheedy P. F., 2nd, Adson M. A. Cavernous hemangiomas of the liver: resect or observe? Am J Surg. 1983 Jan;145(1):49–53. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(83)90165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



