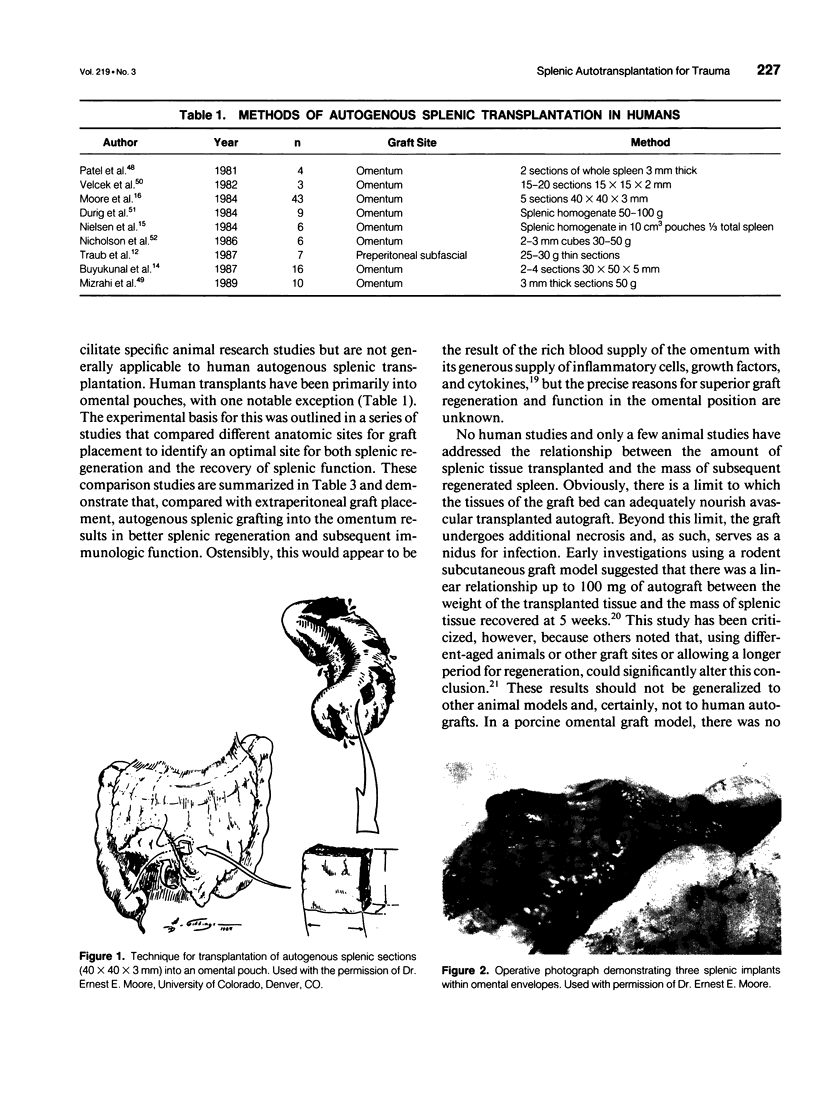
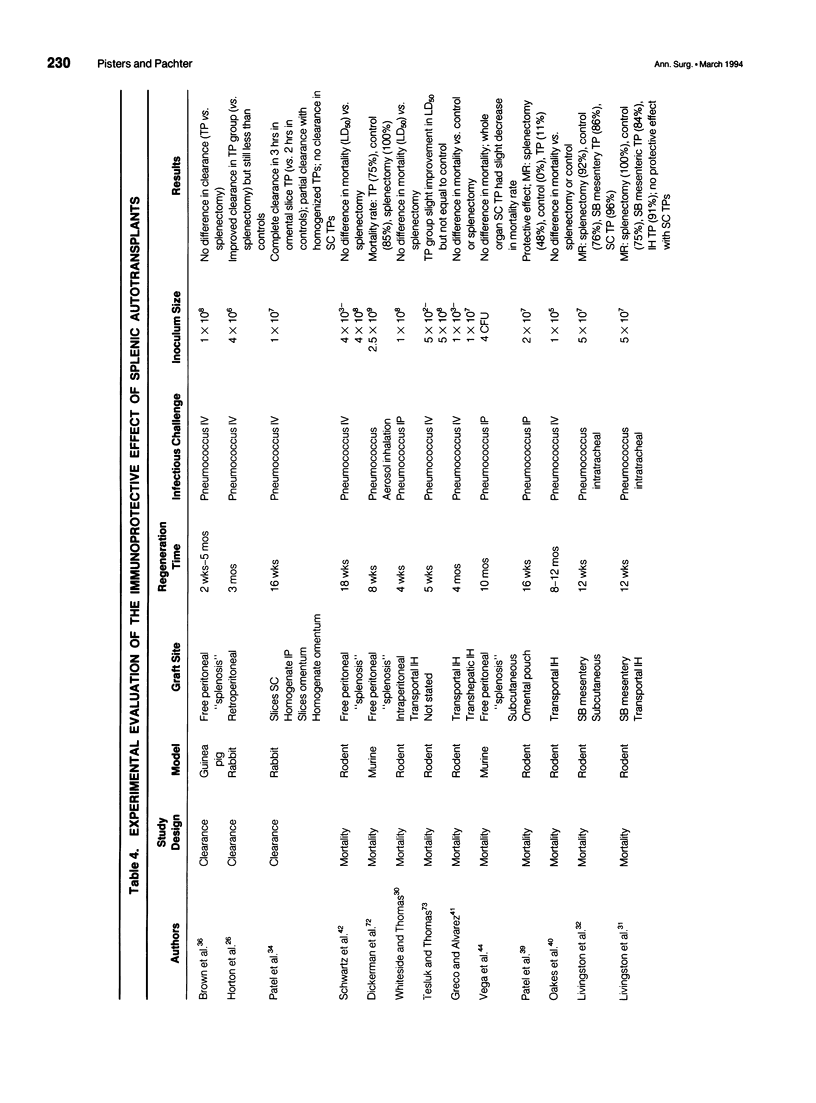
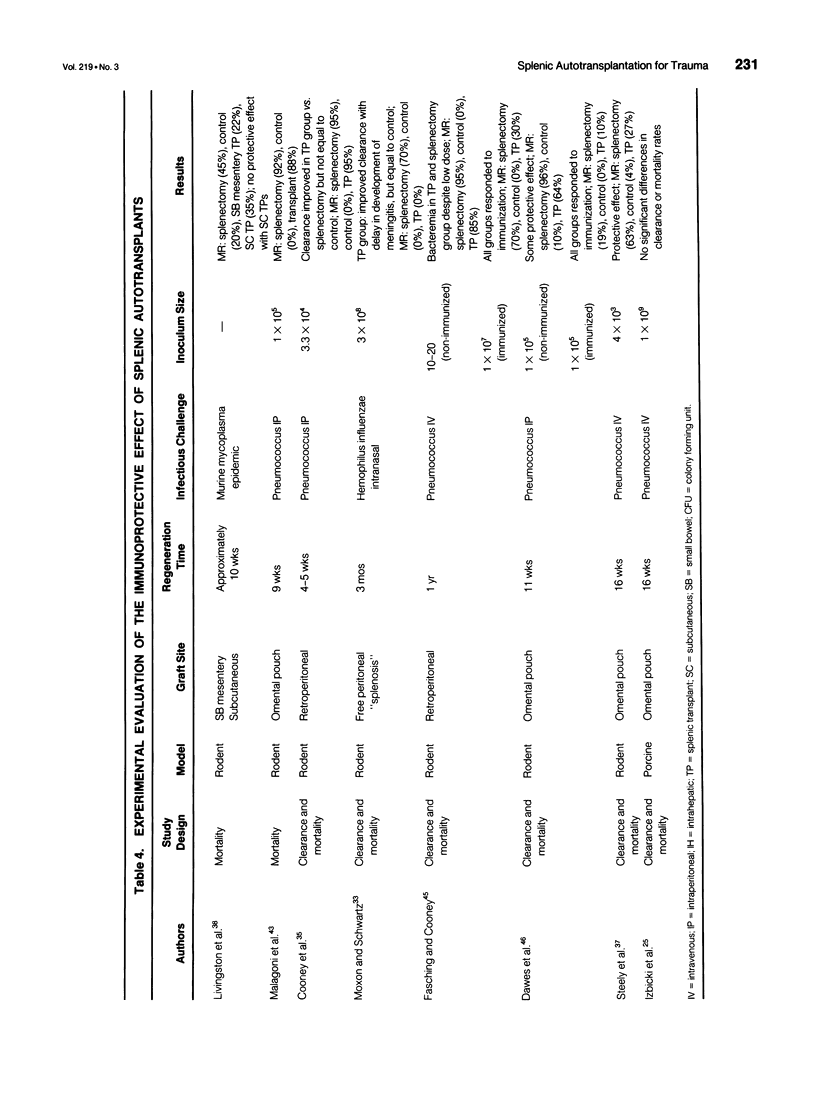
Abstract
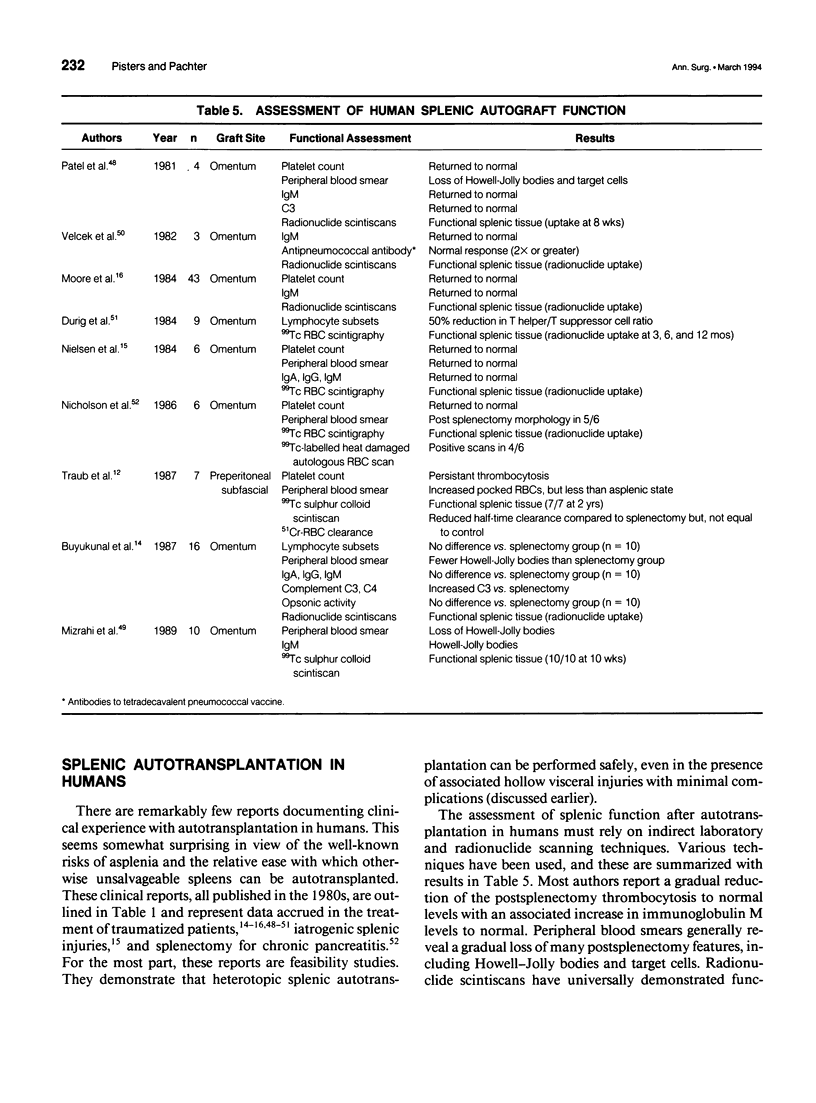
OBJECTIVE: The authors reviewed the experimental evidence, surgical technique, complications, and results of clinical trials evaluating the role of autologous splenic transplantation for splenic trauma. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Splenorrhaphy and nonoperative management of splenic injuries have now become routine aspects in the management of splenic trauma. Unfortunately, not all splenic injuries are readily amenable to conventional spleen-conserving approaches. Heterotopic splenic autotransplantation has been advocated for patients with severe grade IV and V injuries that would otherwise mandate splenectomy. For this subset of patients, splenic salvage by autotransplantation would theoretically preserve the critical role the spleen plays in the host's defense against infection. METHODS: The relevant literature relating to experimental or clinical aspects of splenic autotransplantation was identified and reviewed. Data are presented on the experimental evaluation of autogenous splenic transplantation, methods and complications of autotransplantation, choice of anatomic site and autograft size, and results of clinical trials in humans. RESULTS: The most commonly used technique of autotransplantation in humans involves implanting tissue homogenates or sections of splenic parenchyma into pouches created in the gastrocolic omentum. Most authors have observed evidence of splenic function with normalization of postsplenectomy thrombocytosis, immunoglobulin M levels, and peripheral blood smears. Some degree of immune function of transplanted grafts has been demonstrated with in vivo assays, but the full extent of immunoprotection provided by human splenic autotransplants is currently unknown. CONCLUSIONS: Multiple human and animal studies have established that splenic autotransplantation is a relatively safe and easily performed procedure that results in the return of some hematologic and immunologic parameters to baseline levels. Some aspects of reticuloendothelial function are also preserved. Whether this translates into a real reduction in the morbidity or mortality rates from overwhelming bacterial infection is unknown and requires further investigation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bem C., Echun D. Regeneration of the spleen and splenic autotransplantation. Br J Surg. 1991 Oct;78(10):1276–1276. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800781049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C. A., Van Wyck D. B., Witte M. H., Witte C. L. Antibody formation by subcutaneous and omental splenic autotransplants in rats. J Am Med Womens Assoc. 1977 Nov;32(11):409-13, 419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Hosea S. W., Frank M. M. The role of the spleen in experimental pneumococcal bacteremia. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):975–982. doi: 10.1172/JCI110148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrington J. D. Surgical repair of a ruptured spleen in children: report of eight cases. Arch Surg. 1977 Apr;112(4):417–419. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1977.01370040069011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büyükünal C., Danişmend N., Yeker D. Spleen-saving procedures in paediatric splenic trauma. Br J Surg. 1987 May;74(5):350–352. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800740507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callery M. P., Bennett J. A., McKneally M. F. Evaluation of the subrenal capsular space as a potential site for splenic autoimplantation. Curr Surg. 1989 May-Jun;46(3):207–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee S. N., Eckles D., Gershwin M. E. Preferential B-cell reconstitution following splenic autotransplantation in mice. Transplant Proc. 1979 Jun;11(2):1458–1459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney D. R., Dearth J. C., Swanson S. E., Dewanjee M. K., Telander R. L. Relative merits of partial splenectomy, splenic reimplantation, and immunization in preventing postsplenectomy infection. Surgery. 1979 Oct;86(4):561–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney D. R., Swanson S. E., Dearth J. C., Dewanjee M. K., Telander R. L. Heterotopic splenic autotransplantation in prevention of overwhelming postsplenectomy infection. J Pediatr Surg. 1979 Jun;14(3):337–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes L. G., Malangoni M. A., Spiegel C. A., Schiffman G. Response to immunization after partial and total splenectomy. J Surg Res. 1985 Jul;39(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(85)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerman J. D., Horner S. R., Coil J. A., Gump D. W. The protective effect of intraperitoneal splenic autotransplants in mice exposed to an aerosolized suspension of type III Streptococcus pneumoniae. Blood. 1979 Aug;54(2):354–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürig M., Landmann R. M., Harder F. Lymphocyte subsets in human peripheral blood after splenectomy and autotransplantation of splenic tissue. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Jul;104(1):110–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasching M. C., Cooney D. R. Reimmunization and splenic autotransplantation: a long-term study of immunologic response and survival following pneumococcal challenge. J Surg Res. 1980 May;28(5):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(80)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greco R. S., Alvarez F. E. Intraportal and intrahepatic splenic autotransplantation. Surgery. 1981 Sep;90(3):535–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORAN M., COLEBATCH J. H. Relation between splenectomy and subsequent infection. A clinical study. Arch Dis Child. 1962 Aug;37:398–414. doi: 10.1136/adc.37.194.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert J. C., Fisher J. M., Ershler W. B. Serum antibody responses to pneumococcal vaccine after splenic autotransplantation. J Trauma. 1989 Mar;29(3):355–359. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198903000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth R. J., McKenzie H., Parratt D., Irving A. D., Cuschieri A. The role of the spleen in the immune response following naturally acquired exposure to encapsulated bacteria. Int J Exp Pathol. 1990 Dec;71(6):835–843. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth R. J. Regeneration of the spleen and splenic autotransplantation. Br J Surg. 1991 Mar;78(3):270–278. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton J., Ogden M. E., Williams S., Coln D. The importance of splenic blood flow in clearing pneumococcal organisms. Ann Surg. 1982 Feb;195(2):172–176. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198202000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izbicki J. R., Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W., Raedler C., Kastl S., Bauhuber W., Wilker D. K., Lütticken R., Ruckdeschel G., Schlunck T., Anke A. Splenectomy does not influence outcome of pneumococcal septicemia in a porcine model. J Trauma. 1991 Feb;31(2):189–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING H., SHUMACKER H. B., Jr Splenic studies. I. Susceptibility to infection after splenectomy performed in infancy. Ann Surg. 1952 Aug;136(2):239–242. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195208000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasna I. H., Thompson D. A. Failure of autotransplantation of the spleen in dogs: an anatomic, radionuclide imaging, and pathologic study. J Pediatr Surg. 1985 Feb;20(1):30–33. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(85)80387-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanng Nielsen J., Saksø P., Hanberg Sørensen F., Hvid Hansen H. Demonstration of splenic functions following splenectomy and autologous spleen implantation. Acta Chir Scand. 1984;150(6):469–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston C. D., Levine B. A., Sirinek K. R. Improved survival rate for intraperitoneal autotransplantation of the spleen following pneumococcal pneumonia. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1983 Jun;156(6):761–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston C. D., Levine B. A., Sirinek K. R. Intraperitoneal splenic autotransplantation. Protection afforded in a naturally occurring epidemic of murine mycoplasmosis. Arch Surg. 1983 Apr;118(4):458–461. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1983.01390040068014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston C. D., Levine B. A., Sirinek K. R. Site of splenic autotransplantation affects protection from sepsis. Am J Surg. 1983 Dec;146(6):734–737. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(83)90329-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malangoni M. A., Dawes L. G., Droege E. A., Almagro U. A. The influence of splenic weight and function on survival after experimental pneumococcal infection. Ann Surg. 1985 Sep;202(3):323–328. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198509000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malangoni M. A., Dawes L. G., Droege E. A., Rao S. A., Collier B. D., Almagro U. A. Splenic phagocytic function after partial splenectomy and splenic autotransplantation. Arch Surg. 1985 Mar;120(3):275–278. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1985.01390270015003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malangoni M. A., Evers B. M., Peyton J. C., Wellhausen S. R. Reticuloendothelial clearance and splenic mononuclear cell populations after resection and autotransplantation. Am J Surg. 1988 Feb;155(2):298–302. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(88)80720-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi S., Bickel A., Haj M., Lunski I., Shtamler B. Posttraumatic autotransplantation of spleen tissue. Arch Surg. 1989 Jul;124(7):863–865. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1989.01410070123025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore E. E., Shackford S. R., Pachter H. L., McAninch J. W., Browner B. D., Champion H. R., Flint L. M., Gennarelli T. A., Malangoni M. A., Ramenofsky M. L. Organ injury scaling: spleen, liver, and kidney. J Trauma. 1989 Dec;29(12):1664–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore F. A., Moore E. E., Moore G. E., Millikan J. S. Risk of splenic salvage after trauma. Analysis of 200 adults. Am J Surg. 1984 Dec;148(6):800–805. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(84)90441-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. E., Stevens R. E., Moore E. E., Aragon G. E. Failure of splenic implants to protect against fatal postsplenectomy infection. Am J Surg. 1983 Sep;146(3):413–414. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Schwartz A. D. Heterotropic splenic autotransplantation in the prevention of Haemophilus influenza meningitis and fatal sepsis in Sprague-Dawley rats. Blood. 1980 Nov;56(5):842–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson S., Hutchinson G. H., Hawkins T., Venables C. W. Successful splenosis following autologous splenic implantation. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1986 Apr;31(2):67–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes D. D., Froehlich J. P., Charters A. C. Intraportal splenic autotransplantation in rats: feasibility and effectiveness. J Surg Res. 1982 Jan;32(1):7–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(82)90178-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst R., Kamran D. Autotransplantation of splenic tissue. J Pediatr Surg. 1986 Feb;21(2):120–124. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(86)80062-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst R., Westermann J., Rothkötter H. J. Immunoarchitecture of regenerated splenic and lymph node transplants. Int Rev Cytol. 1991;128:215–260. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60500-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachter H. L., Hofstetter S. R., Spencer F. C. Evolving concepts in splenic surgery: splenorrhaphy versus splenectomy and postsplenectomy drainage: experience in 105 patients. Ann Surg. 1981 Sep;194(3):262–269. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198109000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel J. M., Williams J. S., Naim J. O., Hinshaw J. R. The effect of site and technique of splenic tissue reimplantation on pneumococcal clearance from the blood. J Pediatr Surg. 1986 Oct;21(10):877–880. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(86)80012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel J., Williams J. S., Naim J. O., Hinshaw J. R. Protection against pneumococcal sepsis in splenectomized rats by implantation of splenic tissue into an omental pouch. Surgery. 1982 Jun;91(6):638–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel J., Williams J. S., Shmigel B., Hinshaw J. R. Preservation of splenic function by autotransplantation of traumatized spleen in man. Surgery. 1981 Oct;90(4):683–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson H. A., Gallagher D., Chilcote R., Sullivan E., Wilimas J., Espeland M., Ritchey A. K. Developmental pattern of splenic dysfunction in sickle cell disorders. Pediatrics. 1985 Sep;76(3):392–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson H. A., Johnston D., Smith K. A., Touloukian R. J. The born-again spleen. Return of splenic function after splenectomy for trauma. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 22;298(25):1389–1392. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806222982504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimpl W., Dapunt O., Kaindl H., Thalhamer J. Incidence of septic and thromboembolic-related deaths after splenectomy in adults. Br J Surg. 1989 May;76(5):517–521. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800760528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimpl W., Thalhamer J., Pattermann M. Perfusion of autologous splenic grafts in correlation with specific immunological functions--an experimental study in pigs. Eur Surg Res. 1987;19(1):53–61. doi: 10.1159/000128680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilmann H., Pabst R., Creutzig H. Regeneration and function of autologous splenic grafts in pigs. Eur Surg Res. 1983;15(3):168–175. doi: 10.1159/000128349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M. Physiology and physiopathology of the reticuloendothelial system. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Dec;126(6):1031–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K. Vascular structure of splenic autografts in the rat kidney. Anat Anz. 1988;166(1-5):297–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A. D., Dadash-Zadeh M., Goldstein R., Luck S., Conway J. J. Antibody response to intravenous immunization following splenic tissue autotransplantation in Sprague-Dawley rats. Blood. 1977 May;49(5):779–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A. D., Goldthorn J. F., Winkelstein J. A., Swift A. J. Lack of protective effect of autotransplanted splenic tissue to pneumococcal challenge. Blood. 1978 Mar;51(3):475–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackford S. R., Molin M. Management of splenic injuries. Surg Clin North Am. 1990 Jun;70(3):595–620. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)45132-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shokouh-Amiri M. H., Rahimi-Saber S., Hansen C. P., Olsen P. S., Jensen S. L. Does survival depend on the amount of autotransplanted splenic tissue? Arch Surg. 1990 Nov;125(11):1472–1474. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1990.01410230066011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer D. B. Postsplenectomy sepsis. Perspect Pediatr Pathol. 1973;1:285–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steely W. M., Satava R. M., Brigham R. A., Setser E. R., Davies R. S. Splenic autotransplantation: determination of the optimum amount required for maximum survival. J Surg Res. 1988 Sep;45(3):327–332. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(88)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steely W. M., Satava R. M., Harris R. W., Quispe G. Comparison of omental splenic autotransplant to partial splenectomy. Protective effect against septic death. Am Surg. 1987 Dec;53(12):702–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavassoli M., Ratzan R. J., Crosby W. H. Studies on regeneration of heterotopic splenic autotransplants. Blood. 1973 May;41(5):701–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesluk G. C., Thomas C. G., Jr Prevention of postsplenectomy pneumococcal sepsis in rats. Surg Forum. 1979;30:35–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thalhamer J., Lenglachner C., Grillenberger W., Pimpl W. Alteration of proliferation and subtle changes of protein synthesis in autologous transplanted spleens. Ann Surg. 1989 Nov;210(5):630–636. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198911000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thalhamer J., Liaunigg A., Bergmann E., Leitner W., Kurz M., Seifriedsberger M., Weinlich D., Kaindl H., Pimpl W. Autotransplantation der Milz an Ratten: Entwicklung, Funktion und Cytokin-Expression in intraomentalen und subkutanen Regeneraten. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1992;104(15):461–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thalhamer J., Pimpl W., Pattermann M. The role of the spleen and splenic autotransplants in clearing experimental bacteremia caused by the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Res Exp Med (Berl) 1986;186(3):229–238. doi: 10.1007/BF01852049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timens W., Leemans R. Splenic autotransplantation and the immune system. Adequate testing required for evaluation of effect. Ann Surg. 1992 Mar;215(3):256–260. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199203000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub A., Giebink G. S., Smith C., Kuni C. C., Brekke M. L., Edlund D., Perry J. F. Splenic reticuloendothelial function after splenectomy, spleen repair, and spleen autotransplantation. N Engl J Med. 1987 Dec 17;317(25):1559–1564. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198712173172503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega A., Howell C., Krasna I., Campos J., Heyman S., Ziegler M., Koop C. E. Splenic autotransplantation: optimal functional factors. J Pediatr Surg. 1981 Dec;16(6):898–904. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(81)80843-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcek F. T., Jongco B., Shaftan G. W., Klotz D. H., Rao S. P., Schiffman G., Kottmeier P. K. Posttraumatic splenic replantation in children. J Pediatr Surg. 1982 Dec;17(6):879–883. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(82)80460-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. E., Govin G. G., Rice C. L., Virgilio R. W. Splenorrhaphy for splenic trauma. J Trauma. 1979 Sep;19(9):692–697. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197909000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermann J., Pabst R. Autotransplantation of splenic fragments: lymphocyte subsets in blood, lymph nodes and splenic tissue. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Apr;64(1):188–194. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermann J., Schwinzer R., Jecker P., Pabst R. Lymphocyte subsets in the blood. The influence of splenectomy, splenic autotransplantation, ageing, and the site of blood sampling on the number of B, T, CD4+, and CD8+ lymphocytes in the rat. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Mar;31(3):327–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02775.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteside D. C., Thomas C. G., Jr Effect of splenectomy and autologous splenic implantation on a Streptococcus pneumoniae challenge. Surg Forum. 1979;30:32–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]