Abstract
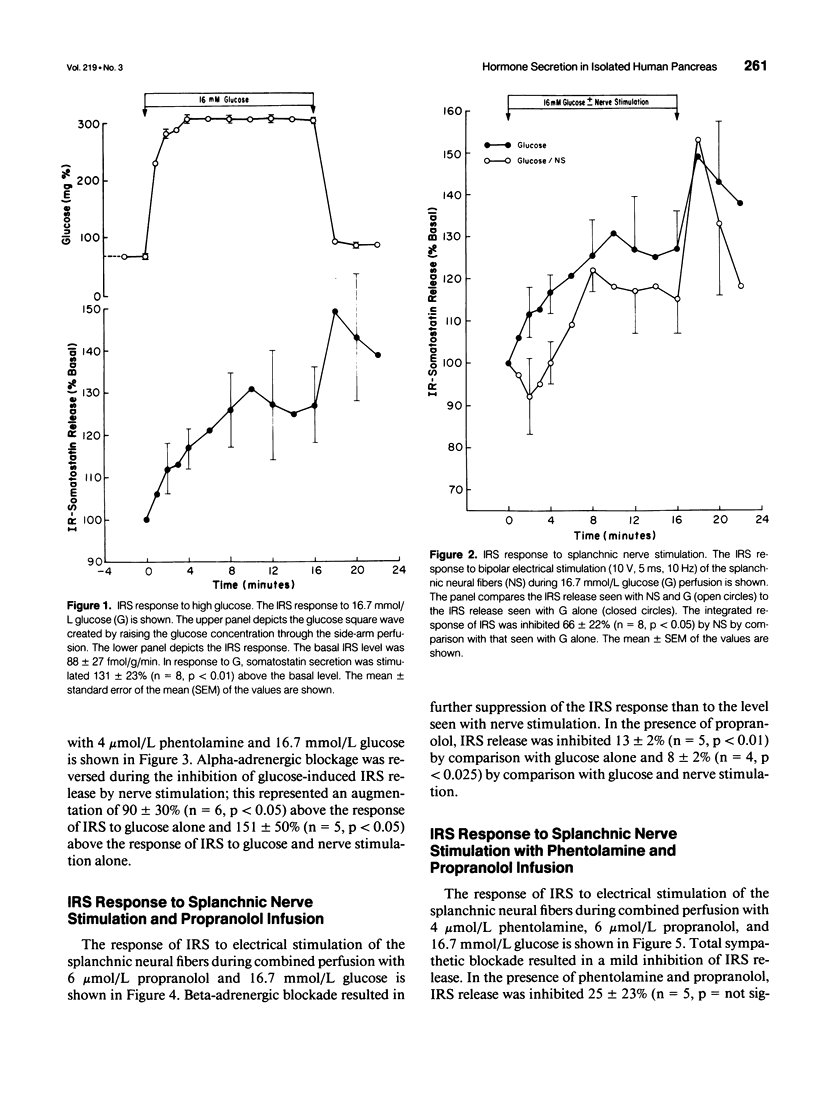
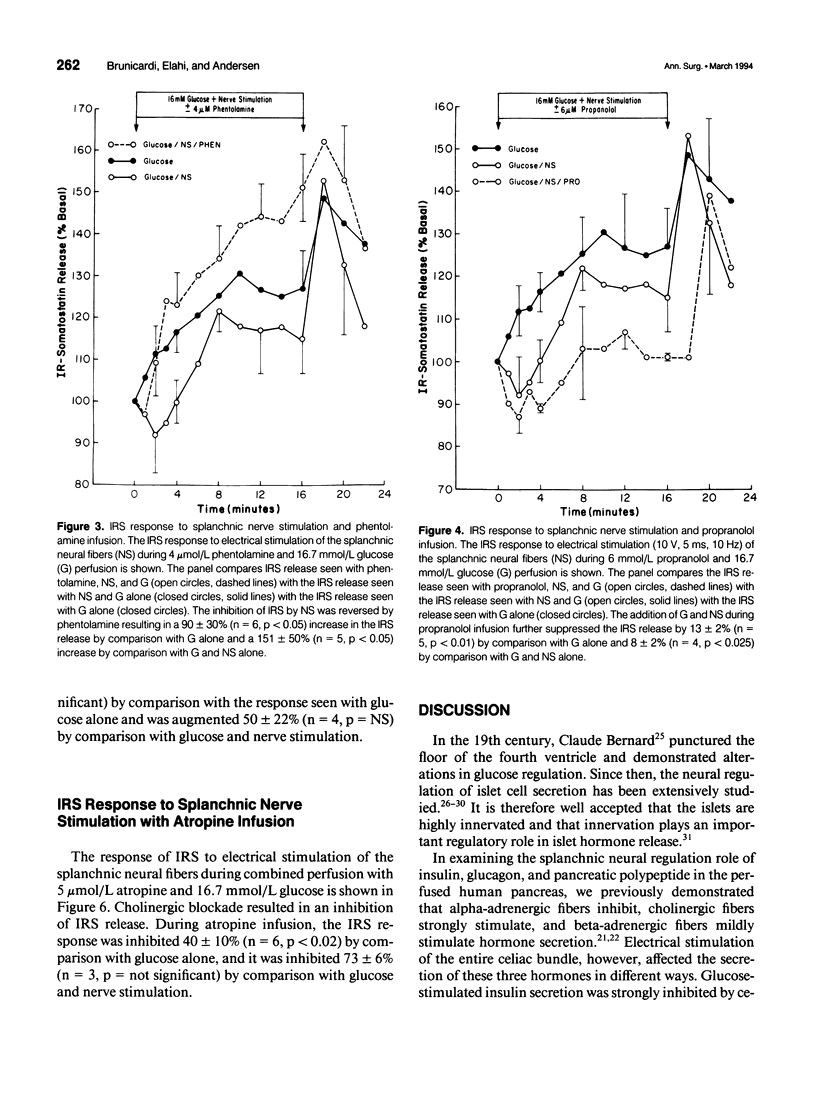
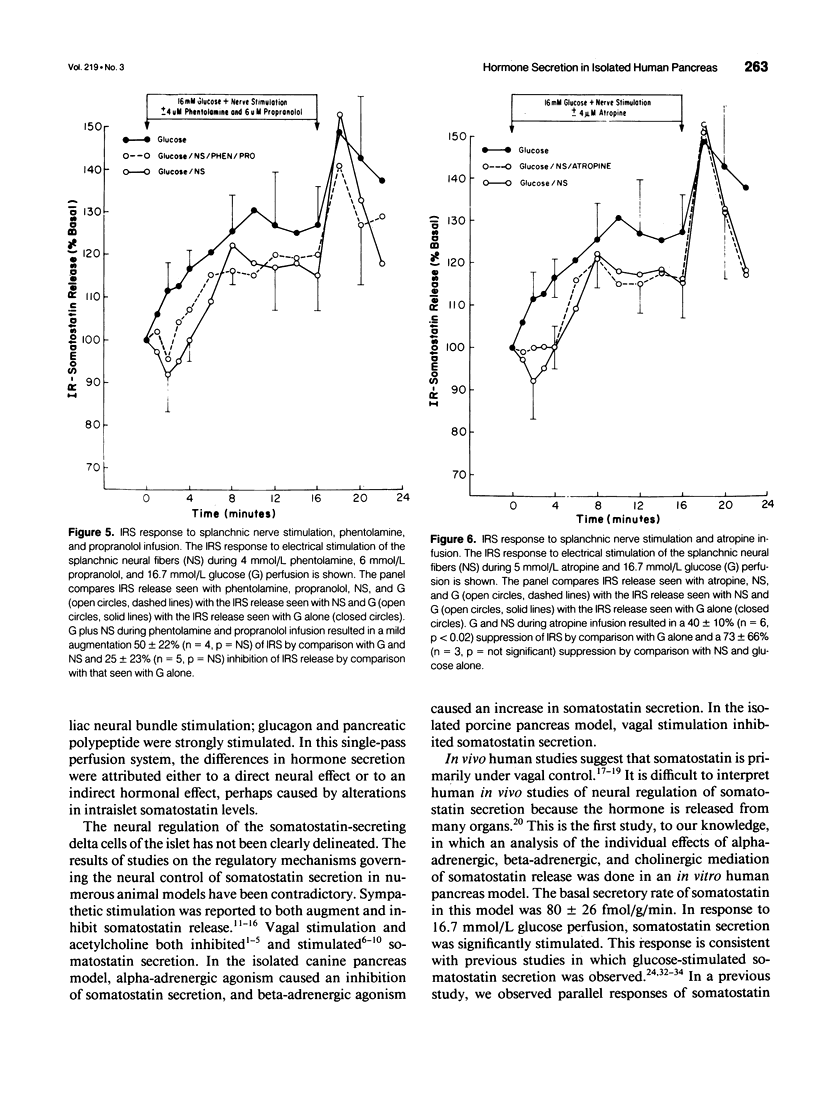
OBJECTIVE: The somatostatin-secreting delta cells in the islets of Langerhans appear to be regulated by neural mechanisms that have not been defined clearly. In this study, the celiac neural bundle of the human pancreas was electrically stimulated in the presence and absence of selective neural antagonists. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: The authors previously reported on studies of the splanchnic neural regulation of insulin, glucagon, and pancreatic polypeptide secretion. In these studies, alpha-adrenergic fibers appeared to have a predominant effect, strongly inhibiting the secretion of insulin, glucagon, and pancreatic polypeptide secretion. Cholinergic fibers appeared to stimulate strongly, although beta-adrenergic fibers weakly stimulated, the secretion of these hormones. Investigations of neural regulatory mechanisms governing human somatostatin release in vitro have not been previously reported. METHODS: Pancreata were obtained from eight cadaveric organ donors. The isolated perfused human pancreas technique was used to assess the regulation of somatostatin secretion by the various neural fibers contained within the celiac plexus. The secretory response of somatostatin was examined in the presence of 16.7 mmol/L glucose, with and without neural stimulation, and specific neural antagonists. RESULTS: The basal somatostatin secretion was 88 +/- 26 fmol/g/min and increased 131 +/- 23% (n = 8, p < 0.01) in response to 16.7 mmol/L glucose. The augmentation seen with glucose was inhibited 66 +/- 22% (n = 8, p < 0.05) during celiac neural bundle stimulation. Alpha-adrenergic blockade resulted in a 90 +/- 30% (n = 6, p < 0.01) augmentation of somatostatin release. Beta-adrenergic blockade caused a 13 +/- 2% (n = 6, p < 0.05) suppression of somatostatin release. Complete adrenergic blockade resulted in a 25 +/- 23% (n = 5, p = not significant) inhibition of somatostatin release. Cholinergic blockade resulted in a 40 +/- 10% (n = 6, p < 0.02) suppression of somatostatin release. CONCLUSIONS: The predominant effect of celiac neural bundle stimulation was inhibition of somatostatin secretion through an alpha-adrenergic effect. Beta-adrenergic fibers stimulate somatostatin secretion; cholinergic fibers have a negligible effect on somatostatin secretion. These data suggest that the splanchnic innervation of the pancreas has a potent regulatory role in somatostatin release in this in vitro human model.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahrén B., Veith R. C., Paquette T. L., Taborsky G. J., Jr Sympathetic nerve stimulation versus pancreatic norepinephrine infusion in the dog: 2). Effects on basal release of somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide. Endocrinology. 1987 Jul;121(1):332–339. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-1-332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunicardi F. C., Druck P., Seymour N. E., Sun Y. S., Gingerich R. L., Elahi D., Andersen D. K. Splanchnic neural regulation of pancreatic polypeptide release in the isolated perfused human pancreas. Am J Surg. 1989 Jan;157(1):50–57. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(89)90419-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunicardi F. C., Druck P., Sun Y. S., Elahi D., Gingerich R. L., Andersen D. K. Regulation of pancreatic polypeptide secretion in the isolated perfused human pancreas. Am J Surg. 1988 Jan;155(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(88)80259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunicardi F. C., Sun Y. S., Druck P., Goulet R. J., Elahi D., Andersen D. K. Splanchnic neural regulation of insulin and glucagon secretion in the isolated perfused human pancreas. Am J Surg. 1987 Jan;153(1):34–40. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(87)90198-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterhuizen A. C., Spriggs T. L., Lever J. D. Nature of islet-cell innervation in the cat pancreas. Diabetes. 1968 Jan;17(1):33–36. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J., Greene K., Hara M., Rizza R., Patton G. Radioimmunoassay of somatostatin and its application in the study of pancreatic somatostatin secretion in vitro. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Jun;93(6):1009–1017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser B., Vinik A. I., Valtysson G., Zoghlin G. Truncal vagotomy abolishes the somatostatin response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Apr;52(4):823–825. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-4-823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermansen K., Christensen S. E., Orskov H. Characterisation of somatostatin release from the pancreas: the role of calcium and acetylcholine. Diabetologia. 1979 Apr;16(4):261–266. doi: 10.1007/BF01221953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermansen K. Effects of substance P and other peptides on the release of somatostatin, insulin, and glucagon in vitro. Endocrinology. 1980 Jul;107(1):256–261. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-1-256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermansen K. Secretion of somatostatin from the normal and diabetic pancreas. Studies in vitro. Diabetologia. 1980;19(6):492–504. doi: 10.1007/BF00253175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst J. J., Jensen S. L., Knuhtsen S., Nielsen O. V. Autonomic nervous control of pancreatic somatostatin secretion. Am J Physiol. 1983 Dec;245(6):E542–E548. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.245.6.E542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst J. J., Jensen S. L., Knuhtsen S., Nielsen O. V., Rehfeld J. F. Effect of vagus, gastric inhibitory polypeptide, and HCl on gastrin and somatostatin release from perfused pig antrum. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):G515–G522. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.244.5.G515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst J. J., Jensen S. L., Nielsen O. V., Schwartz T. W. Oxygen supply, oxygen consumption, and endocrine and exocrine secretions of the isolated, perfused, porcine pancreas. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 May;109(1):7–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honey R. N., Weir G. C. Acetylcholine stimulates insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin release in the perfused chicken pancreas. Endocrinology. 1980 Oct;107(4):1065–1068. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-4-1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipp E., Dobbs R. E., Arimura A., Vale W., Harris V., Unger R. H. Release of immunoreactive somatostatin from the pancreas in response to glucose, amino acids, pancreozymin-cholecystokinin, and tolbutamide. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):760–765. doi: 10.1172/JCI108829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh M., Gerich J. E. Adrenergic modulation of pancreatic somatostatin, insulin, and glucagon secretion: evidence for differential sensitivity of islet A, B, and D cells. Metabolism. 1982 Jul;31(7):715–720. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90203-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson L., Hellerström C. Stimulation by glucose of the blood flow to the pancreatic islets of the rat. Diabetologia. 1983 Jul;25(1):45–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00251896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneto A., Kosaka K., Nakao K. Effects of stimulation of the vagus nerve on insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 1967 Mar;80(3):530–536. doi: 10.1210/endo-80-3-530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly W. D., Lillehei R. C., Merkel F. K., Idezuki Y., Goetz F. C. Allotransplantation of the pancreas and duodenum along with the kidney in diabetic nephropathy. Surgery. 1967 Jun;61(6):827–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., Katagiri K., Ohno T., Harada N., Imanishi H., Iwasaki M., Ito M., Takeuchi T. Effect of acetylcholine and new cholinergic derivative on amylase output, insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin secretions from perfused isolated rat pancreas. Horm Metab Res. 1982 Jul;14(7):356–360. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1019016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaff L. J., Taborsky G. J., Jr Role of pancreatic somatostatin in determining glucagon response to arginine and morphine. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jun;252(6 Pt 1):E751–E755. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.6.E751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucey M. R., Wass J. A., Fairclough P., Webb J., Webb S., Medbak S., Rees L. H. Autonomic regulation of postprandial plasma somatostatin, gastrin, and insulin. Gut. 1985 Jul;26(7):683–688. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.7.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin S. Somatostatin. N Engl J Med. 1983 Dec 15;309(24):1495–1501. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198312153092406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy M. W., Jones M. S., Miller R. E. Pancreatic somatostatin secretion is suppressed by splanchnic nerve stimulation. Diabetologia. 1981 Feb;20(2):102–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00262009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samols E., Stagner J. I. Islet somatostatin--microvascular, paracrine, and pulsatile regulation. Metabolism. 1990 Sep;39(9 Suppl 2):55–60. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90212-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samols E., Stagner J. I., Weir G. C. Autonomic function and control of pancreatic somatostatin. Diabetologia. 1981 Mar;20 (Suppl):388–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samols E., Weir G. C. Adrenergic modulation of pancreatic A, B, and D cells alpha-Adrenergic suppression and beta-adrenergic stimulation of somatostatin secretion, alpha-adrenergic stimulation of glucagon secretion in the perfused dog pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):230–238. doi: 10.1172/JCI109294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson R. L., Elde R. P., Seybold V. Effect of norepinephrine on insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin secretion in isolated perifused rat islets. Diabetes. 1979 Oct;28(10):899–904. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.10.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternini C., De Giorgio R., Brunicardi F. C., Widdison A. L., Reber H. A., Go V. L. CGRP immunoreactivity in the mammalian pancreas. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Jun 30;657:487–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb22808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uvnäs-Wallensten K., Efendic S., Roovete A., Johansson C. Decreased release of somatostatin into the portal vein following electrical vagal stimulation in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Aug;109(4):393–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasada T., Dobbs R. E., Harris V., Unger R. H. Effect of 2-deoxy-D-glucose on plasma somatostatin levels in conscious dogs. Endocrinology. 1981 Apr;108(4):1222–1227. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-4-1222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. C., Porte D., Jr Neural control of the endocrine pancreas. Physiol Rev. 1974 Jul;54(3):596–619. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.3.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


