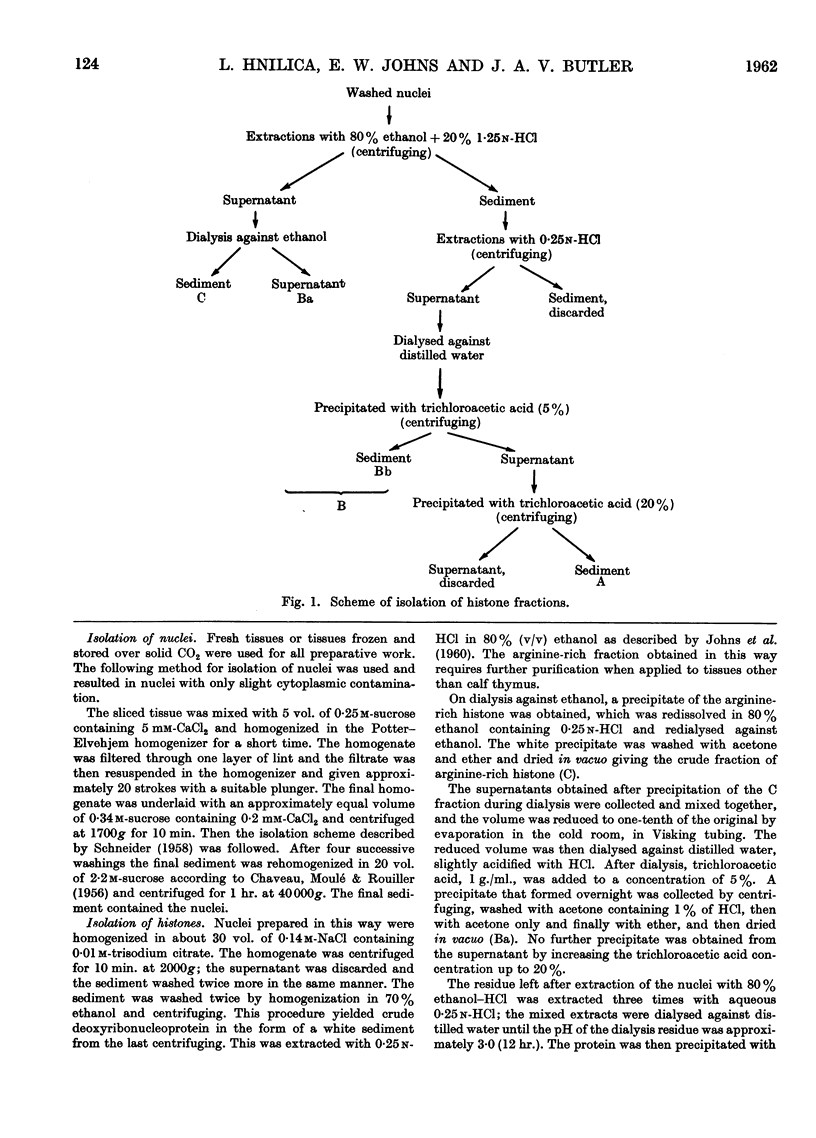
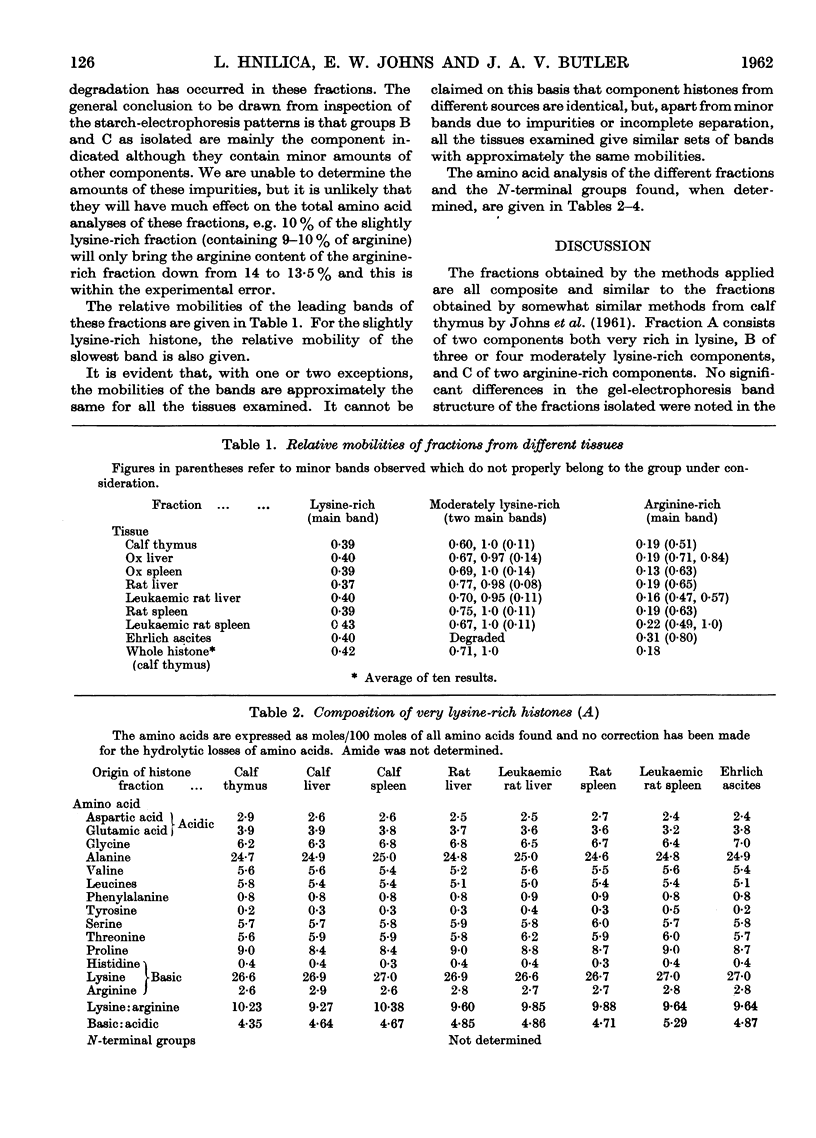
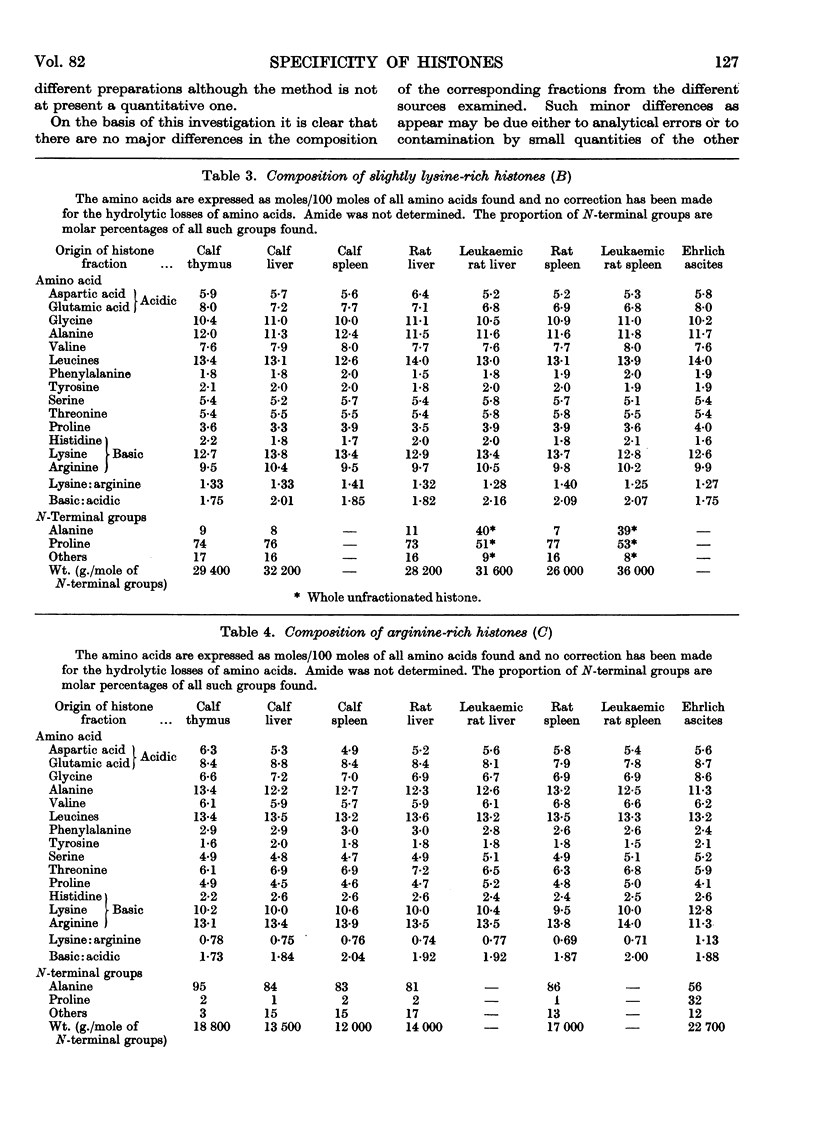
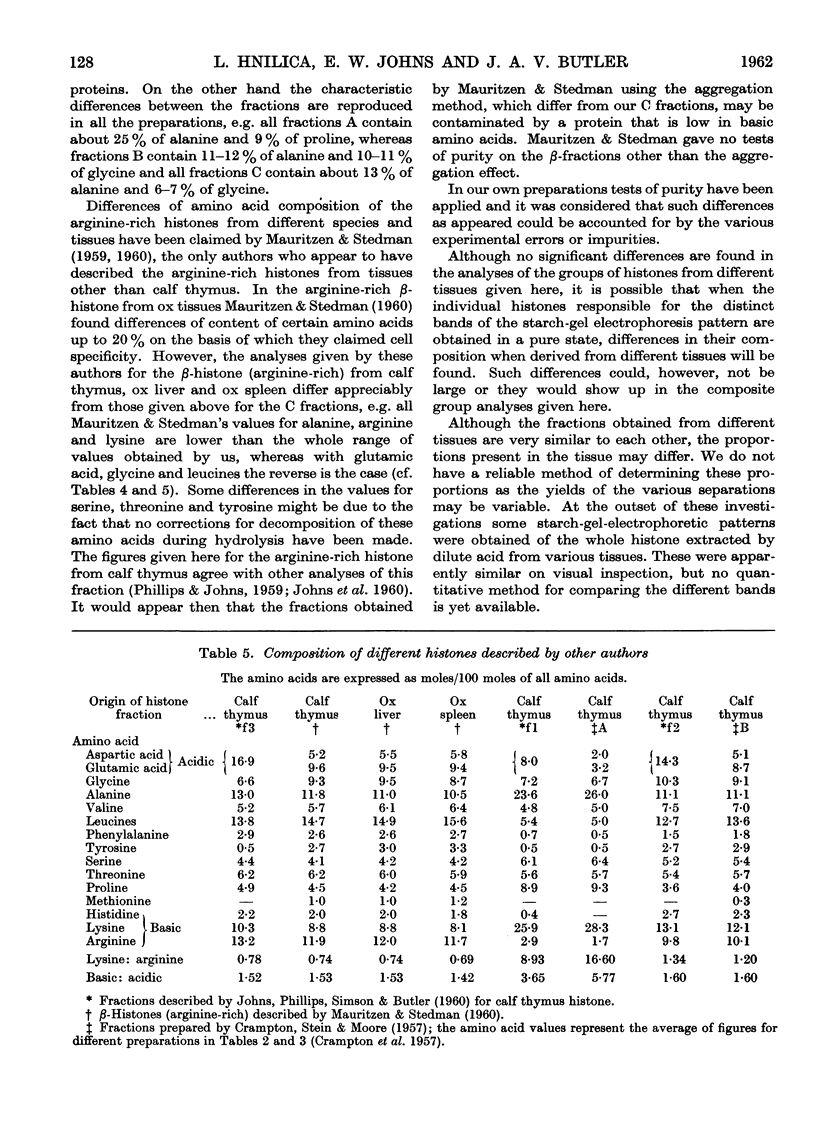
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTLER J. A., DAVISON P. F., JAMES D. W., SHOOTER K. V. The histones of calf thymus deoxyribonucleoprotein. I. Preparation and homogeneity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Feb;13(2):224–232. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90307-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAUVEAU J., MOULE Y., ROUILLER C. Isolation of pure and unaltered liver nuclei morphology and biochemical composition. Exp Cell Res. 1956 Aug;11(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(56)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAMPTON C. F., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. Chromatographic fractionation of calf thymus histone. J Biol Chem. 1955 Aug;215(2):787–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAMPTON C. F., STEIN W. H., MOORE S. Comparative studies on chromatographically purified histones. J Biol Chem. 1957 Mar;225(1):363–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUFT H. J., MAURITZEN C. M., STEDMAN E. Abnormal properties of histones from malignant cells. Nature. 1954 Sep 25;174(4430):580–585. doi: 10.1038/174580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUFT H. J., MAURITZEN C. M., STEDMAN E. The isolation of beta-histone from calf thymocytes and the factors affecting its aggregation. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1958 Jul 1;149(934):21–35. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1958.0048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALY M. M., MIRSKY A. E. Histones with high lysine content. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Jan 20;38(3):405–413. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.3.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON P. F., BUTLER J. A. The fractionation and composition of histones from thymus nucleoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Nov;15(3):439–440. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON P. F. Chromatography of histones. Biochem J. 1957 Aug;66(4):708–712. doi: 10.1042/bj0660708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNS E. W., PHILLIPS D. M., SIMSON P., BUTLER J. A. Improved fractionations of arginine-rich histones from calf thymus. Biochem J. 1960 Dec;77:631–636. doi: 10.1042/bj0770631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNS E. W., PHILLIPS D. M., SIMSON P., BUTLER J. A. The electrophoresis of histones and histone fractions on starch gel. Biochem J. 1961 Jul;80:189–193. doi: 10.1042/bj0800189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUCK J. M., RASMUSSEN P. S., SATAKE K., TSVETIKOV A. N. Further studies on the fractionation of calf thymus histone. J Biol Chem. 1958 Dec;233(6):1407–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAURITZEN C. M., STEDMAN E. Cell specificity of beta-histones in the domestic fowl. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1959 Apr 21;150(940):299–311. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1959.0023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEELIN J. M., BUTLER G. C. A comparison of histones from chicken tissues by zone electrophoresis in starch gel. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1961 Mar;39:485–491. doi: 10.1139/o61-046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEELIN J. M., BUTLER G. C. The fractionation of the histones of calf thymus and chicken erythrocytes by cation-exchange chromatography with sodium salts. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Jul;37(7):843–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEELIN J. M., CONNELL G. E. Zone electrophoresis of chicken-erythrocyte histone in starch gel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Feb;31(2):539–541. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEELIN J. M., NEELIN E. M. Zone electrophoresis of calf thymus histone in starch gel. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1960 Apr;38:355–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS D. M., JOHNS E. W. A study of the proteinase content and the chromatography of thymus histones. Biochem J. 1959 Jul;72:538–544. doi: 10.1042/bj0720538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS D. M. The N-terminal groups of calf-thymus histones. Biochem J. 1958 Jan;68(1):35–40. doi: 10.1042/bj0680035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER J. H., POTTER V. R. Nucleotide metabolism. VIII. Heterogeneous labeling in ribonucleic acid of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jul;233(1):154–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. Zone electrophoresis in starch gels: group variations in the serum proteins of normal human adults. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):629–641. doi: 10.1042/bj0610629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARBUCK W. C., BUSCH H. Kinetics of incorporation of L-arginine-U-C14 into nuclear proteins of tumors and other tissues in vitro. Cancer Res. 1960 Jul;20:891–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F. The free amino groups of insulin. Biochem J. 1945;39(5):507–515. doi: 10.1042/bj0390507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UI N. Preparation, fractionation and properties of calf thymus histone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Sep;25(3):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90519-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENDRELY R., KNOBLOCH A., MATSUDAIRA H. A comparative biochemical study of nucleohistones from different vertebrates. Nature. 1958 Feb 1;181(4605):343–343. doi: 10.1038/181343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


