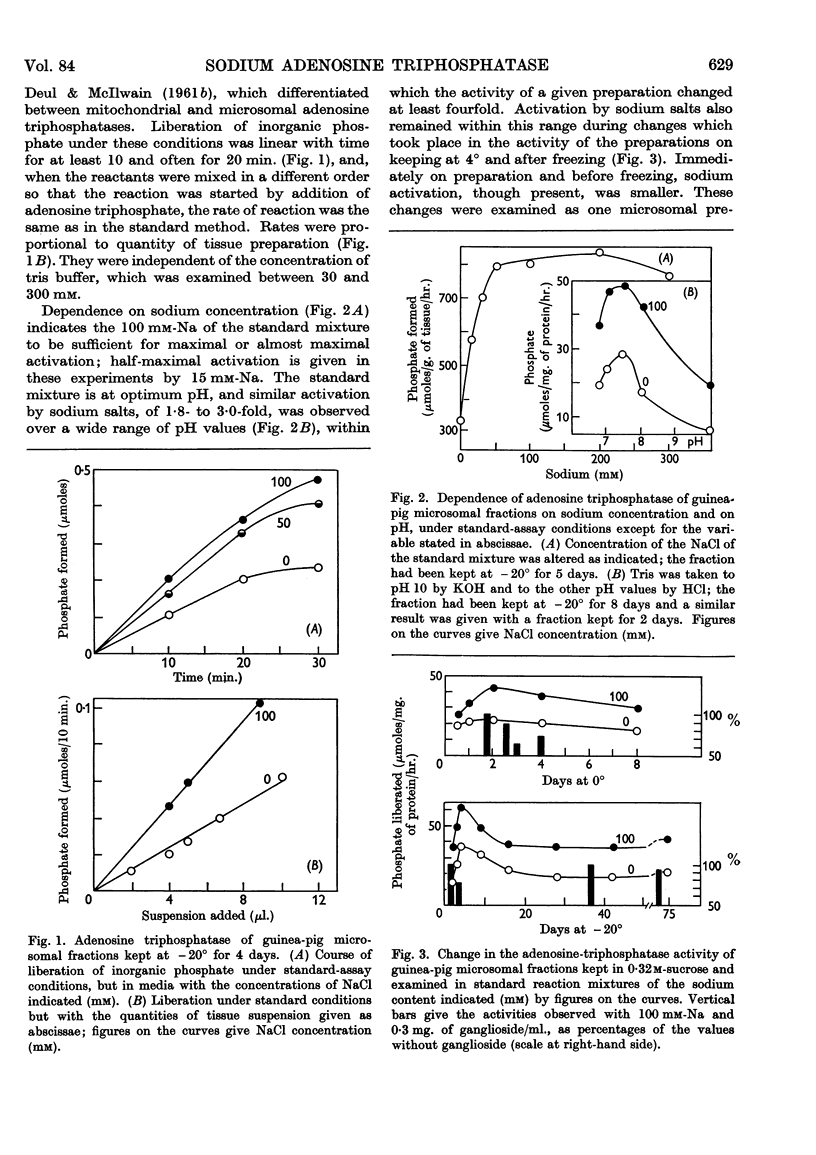
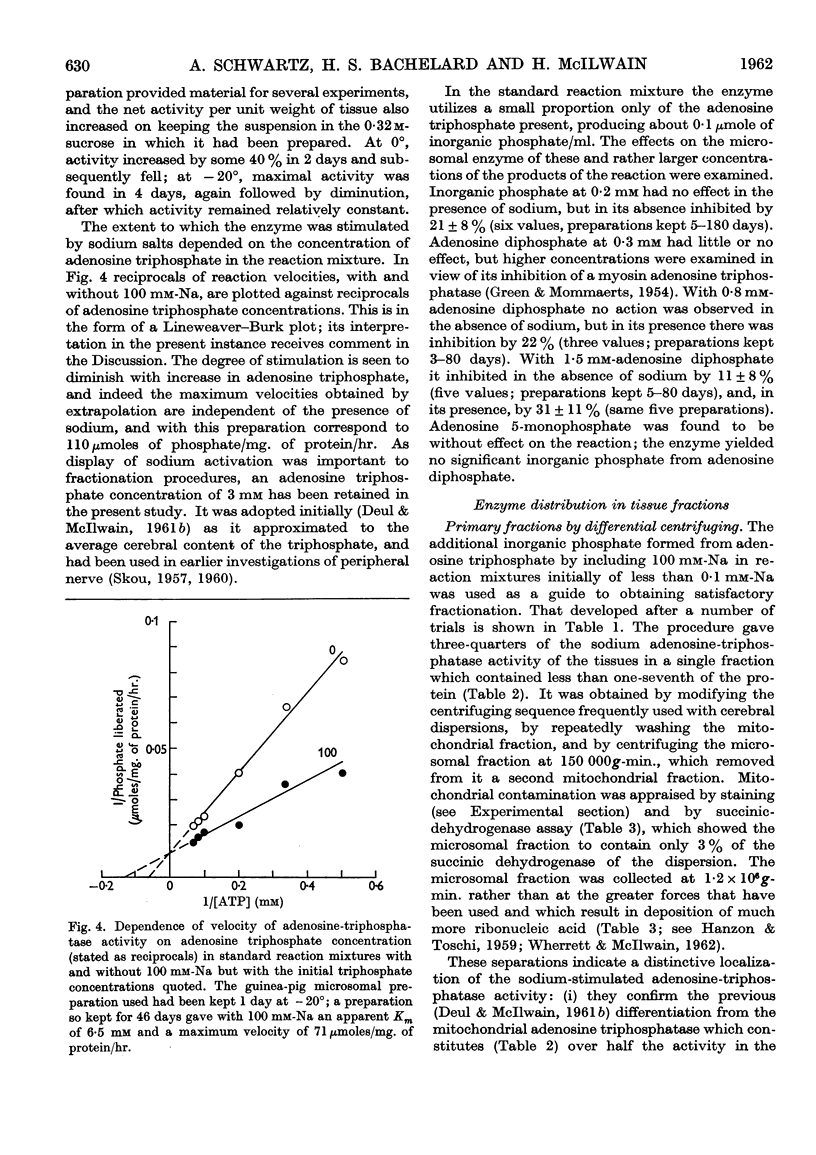
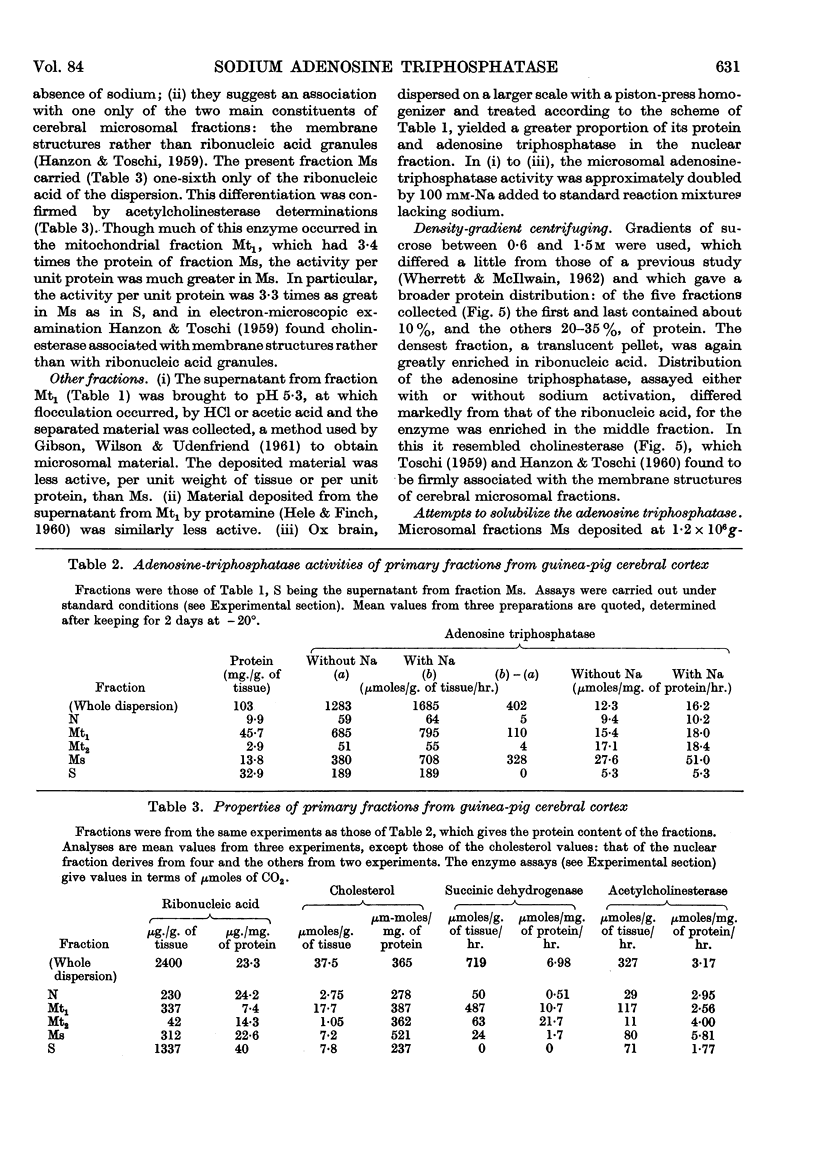
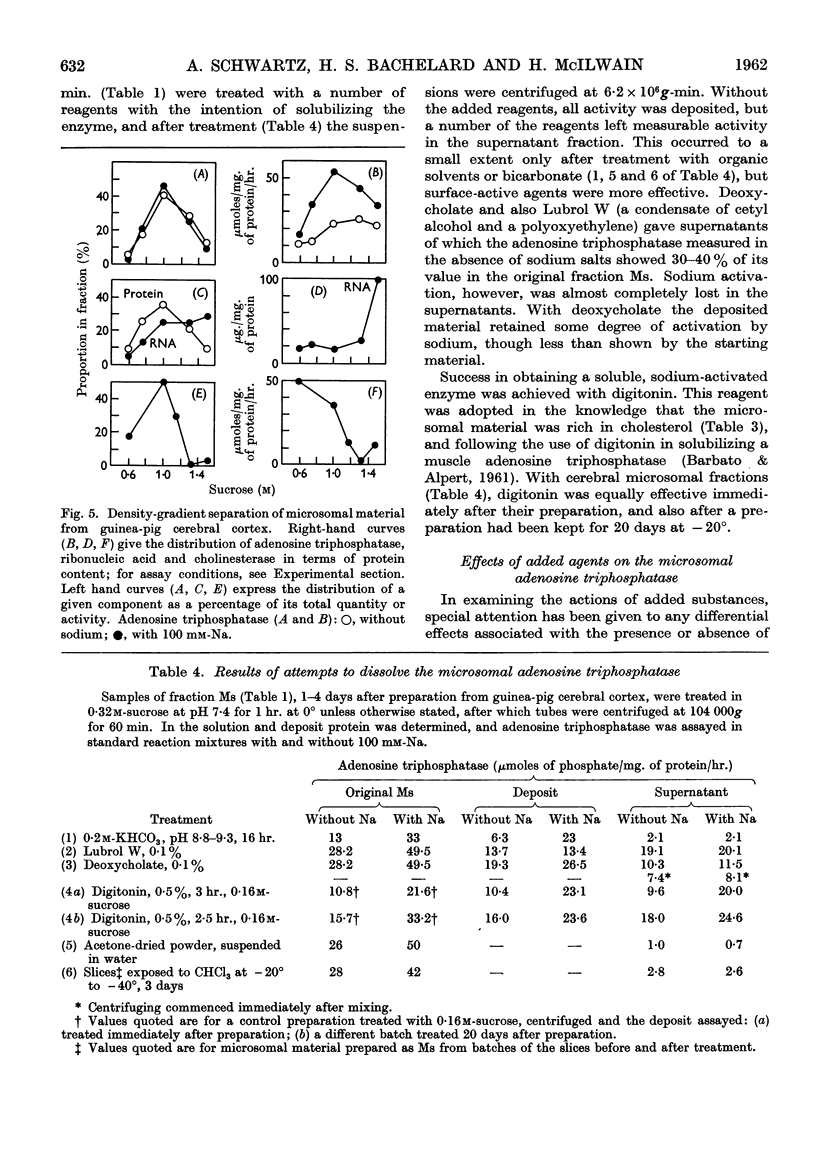
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N. Adenosine triphosphatase in the microsomal fraction from rat brain. Biochem J. 1962 Jun;83:527–533. doi: 10.1042/bj0830527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALDRIDGE W. N., JOHNSON M. K. Cholinesterase, succinic dehydrogenase, nucleic acids, esterase and glutathione reductase in sub-cellular fractions from rat brain. Biochem J. 1959 Oct;73:270–276. doi: 10.1042/bj0730270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBATO I. M., ALPERT N. R. The preparation and characteristics of a purified muscle adenosinetriphosphatase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 May;93:255–261. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONTING S. L., SIMON K. A., HAWKINS N. M. Studies on sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase. I. Quantitative distribution in several tissues of the cat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Dec;95:416–423. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOOTH D. A. The isolation and assay of gangliosides and their interactions with basic proteins. J Neurochem. 1962 May-Jun;9:265–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1962.tb09448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALLANAN M. J., CARROLL W. R., MITCHELL E. R. Physical and chemical properties of protamine from the sperm of salmon (Oncorhynchus tschawytscha). J Biol Chem. 1957 Nov;229(1):279–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARROLL W. R., CALLANAN M. J., SAROFF H. A. Physical and chemical properties of protamine from the sperm of salmon (Oncorhynchus tschawytscha). II. Anion binding characteristics. J Biol Chem. 1959 Sep;234:2314–2316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEUL D. H., McILWAIN H. Activation and inhibition of adenosine triphosphatases of subcellular particles from the brain. J Neurochem. 1961 Dec;8:246–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1961.tb13550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMANUEL C. F., CHAIKOFF I. L. An hydraulic homogenizer for the controlled release of cellular components from various tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 May;24(2):254–261. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90191-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON K. D., WILSON J. D., UDENFRIEND S. The enzymatic conversion of phospholipid ethanolamine to phospholipid choline in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:673–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORE M. B. R. Adenosinetriphosphatase activity of brain. Biochem J. 1951 Nov;50(1):18–24. doi: 10.1042/bj0500018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN I., MOMMAERTS W. F. Adenosinetriphosphatase systems of muscle. IV. Kinetics of myosin adenosinetriphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1954 Oct;210(2):695–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANZON V., TOSCHI G. Centrifugation of brain microsomes in a density gradient. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Nov;21:332–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90265-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELE P., FINCH L. R. Amino acid-activating systems from pig liver. Biochem J. 1960 May;75:352–363. doi: 10.1042/bj0750352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JARNEFELT J. The relative rates of adenosinetriphosphatase and phosphatidic acid synthesis in microsomes from rat brain. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Oct;25:211–213. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90329-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSHLAND D. E., Jr The active site and enzyme action. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1960;22:45–97. doi: 10.1002/9780470122679.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUBO S., TOKURA S., TONOMURA Y. On the active site of myosin A-adenosine triphosphatase. I. Reaction of the enzyme with trinitrobenzenesulfonate. J Biol Chem. 1960 Oct;235:2835–2839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W., KELLER E. B., GROSS J., ZAMECNIK P. C. Studies on cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein particles from the liver of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1955 Nov;217(1):111–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWENSTEIN J. M. The stimulation of transphosphorylation by alkali-metal ions. Biochem J. 1960 May;75:269–274. doi: 10.1042/bj0750269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., WU M. L., HIXON W. S., CRAWFORD E. J. The quantitative histochemistry of brain. II. Enzyme measurements. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):19–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCILWAIN H. Characterization of naturally occurring materials which restore excitability to isolated cerebral tissues. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:24–32. doi: 10.1042/bj0780024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlwain H. Protein interactions and metabolic response to stimulating agents in isolated cerebral tissues: histones as inhibitors. Biochem J. 1959 Nov;73(3):514–521. doi: 10.1042/bj0730514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlwain H., Woodman R. J., Cummins J. T. Basic proteins and the potassium movements and phosphates of cerebral tissues. Biochem J. 1961 Oct;81(1):79–83. doi: 10.1042/bj0810079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY S. V., CHAPPELL J. B. The action of 2:4-dinitrophenol on myosin and mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase systems. Biochem J. 1957 Mar;65(3):469–476. doi: 10.1042/bj0650469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quastel J. H., Wheatley A. H. Anaerobic oxidations. On ferricyanide as a reagent for the manometric investigation of dehydrogenase systems. Biochem J. 1938 May;32(5):936–943. doi: 10.1042/bj0320936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ A. The effect of ouabain on potassium content, phosphoprotein metabolism and oxygen consumption of guinea pig cerebral tissue. Biochem Pharmacol. 1962 Apr-May;11:389–391. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(62)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELA M., KATCHALSKI E. Biological properties of poly-alpha-amino acids. Adv Protein Chem. 1959;14:391–478. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60614-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOWACRE J. L., DUBUY H. G. On the enzymic nature of mitochondrial characterization by Janus green B and the detection of Krebs-cycle dehydrogenases with Janus green B. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1955 Aug;16(1):173–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOU J. C. The influence of some cations on an adenosine triphosphatase from peripheral nerves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Feb;23(2):394–401. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90343-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMSON C. G., McILWAIN H. An attachment of protamines to cerebral tissues, studied in relation to gangliosides, suramin and tissue excitability. Biochem J. 1961 May;79:342–347. doi: 10.1042/bj0790342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOSCHI G. A biochemical study of brain microsomes. Exp Cell Res. 1959 Feb;16(2):232–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(59)90252-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHERRETT J. R., McILWAIN H. Gangliosides, phospholipids, protein and ribonucleic acid in subfractions of cerebral microsomal material. Biochem J. 1962 Aug;84:232–237. doi: 10.1042/bj0840232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAM R. Active cation transport as a pace-maker of respiration. Nature. 1961 Aug 5;191:603–604. doi: 10.1038/191603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


