Abstract
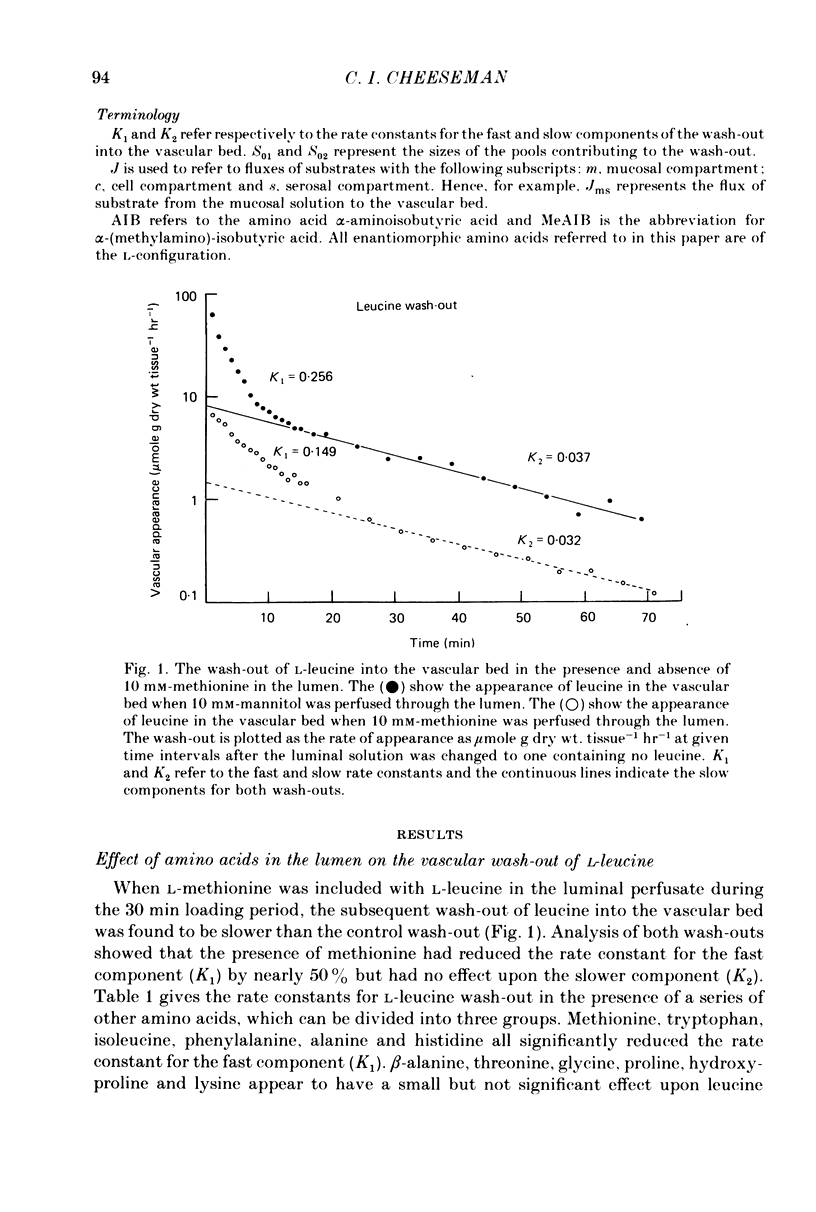
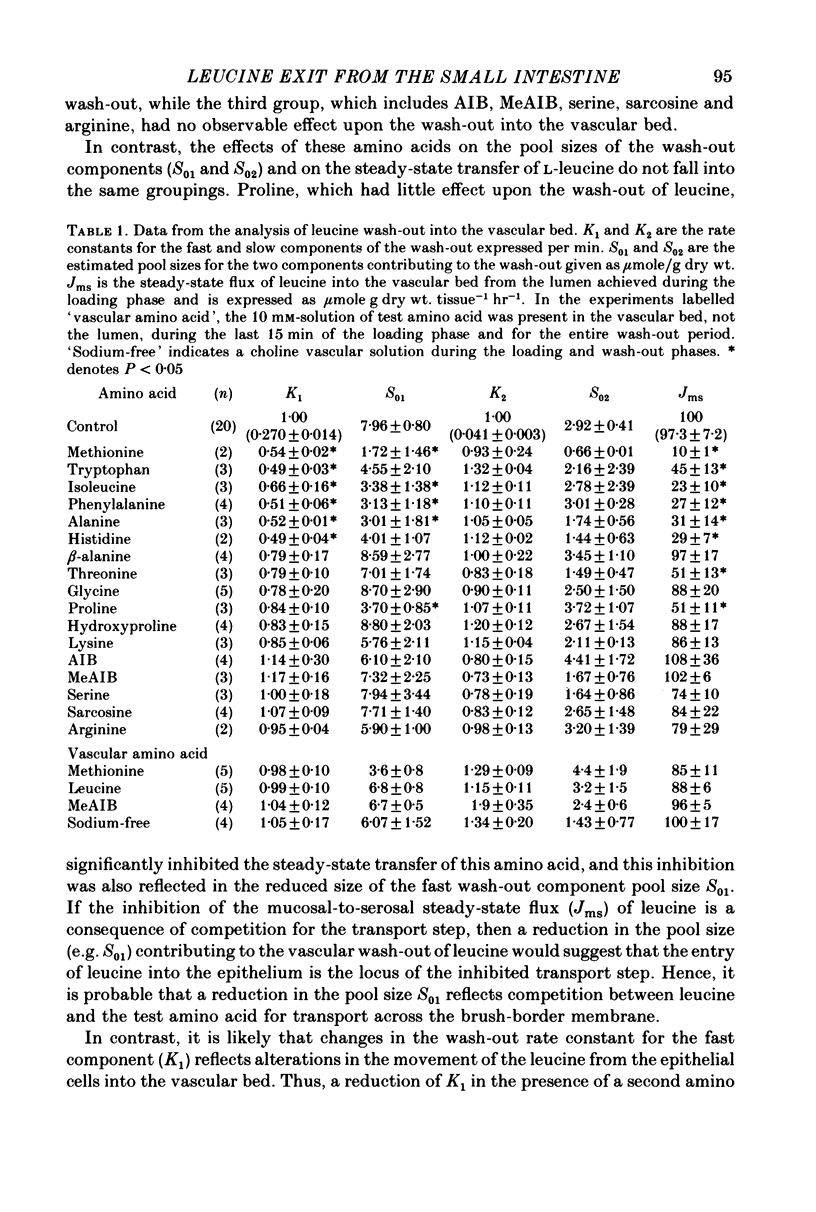
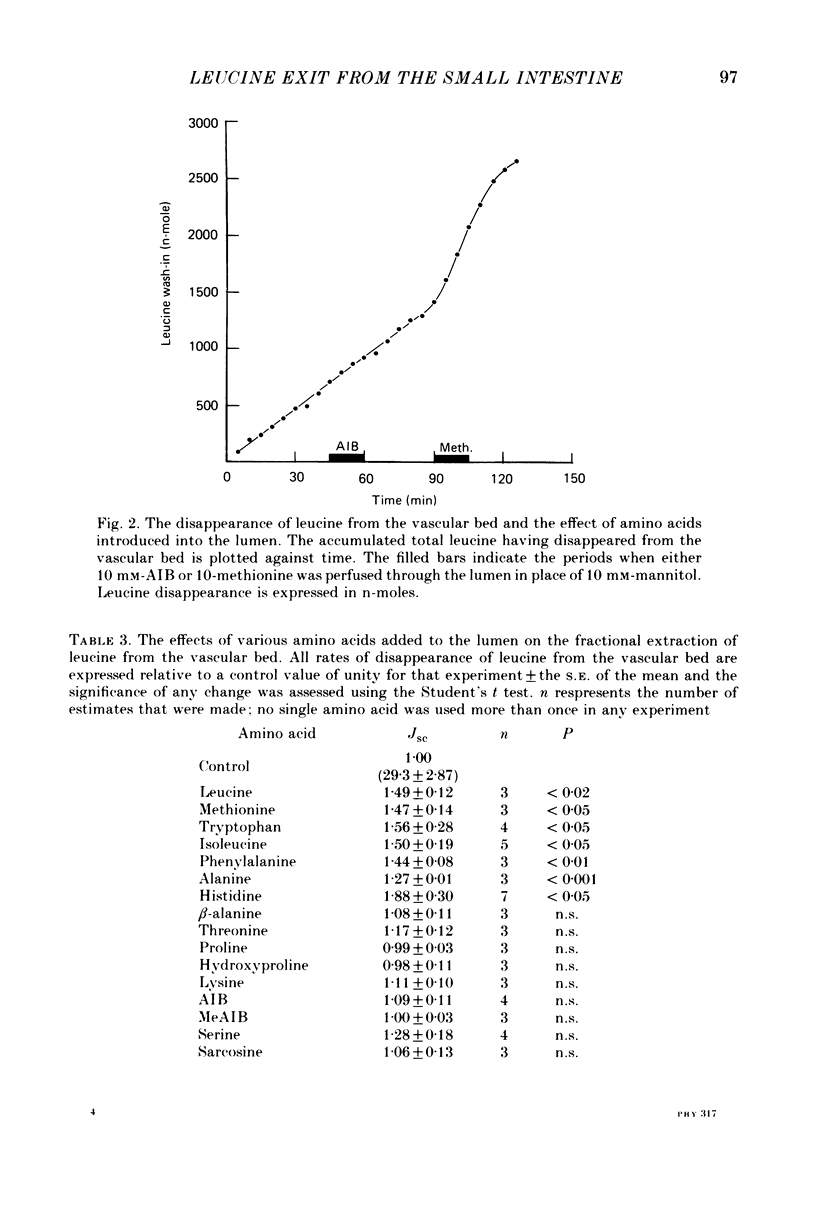
1. The vascularly perfused small intestine of Rana pipiens was used to investigate the movement of the amino acid L-leucine from the epithelium into the vascular bed. It was found that only a few amino acids when present in the lumen inhibited the wash-out leucine into the vascular bed. The series of amino acids which had this effect belonged to the group previously shown to be transported by 'L-type' carrier systems. 2. Nearly all amino acids when present in the lumen accelerated the flux of leucine from the vascular bed to the lumen and there was little correlation between the amino acids which caused this effect and those which inhibited leucine wash-out into the vascular bed. Replacement of luminal sodium also promoted serosal-to-mucosal leucine flux. 3. The effect of the presence of amino acids in the lumen on the uptake of leucine from the vascular bed was measured using a fractional extraction technique; sucrose was the extracellular marker. There was complete correlation between the amino acids which promoted the extraction of leucine from the vascular bed and those which inhibited leucine wash-out into the vascular bed. 4. In contrast, the wash-out of leucine into the vascular bed was not accelerated by the addition of amino acids to the vascular perfusate, and the presence of 10 mM-leucine in the vascular bed had very little effect upon the mucosal-to-serosal flux of leucine. 5. These results are discussed with regard to the specificity of an exit system for leucine, in the intestinal epithelium, which appears to have an energy requirement.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd C. A., Cheeseman C. I., Parsons D. S. Amino acid movements across the wall of anuran small intestine perfused through the vascular bed. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;250(2):409–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd C. A., Parsons D. S. Movements of monosaccharides between blood and tissues of vascularly perfused small intestine. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:371–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter G. W., Van Dyke K. A superior counting solution for water-soluble tritiated compounds. Clin Chem. 1971 Jul;17(7):576–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman C. I. The transport of dipeptides by the small intestine. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;58(11):1326–1333. doi: 10.1139/y80-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N., de Cespedes C., Handlogten M. E., Ronquist G. Energization of amino acid transport, studied for the Ehrlich ascites tumor cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 28;300(4):487–522. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(73)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danisi G., Tai Y. H., Curran P. F. Mucosal and serosal fluxes of alanine in rabbit ileum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 11;455(1):200–213. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy A. A., Nowacki J. A. Stoicheiometrical proton and potassium ion movements accompanying the absorption of amino acids by the yeast Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(5):701–711. doi: 10.1042/bj1220701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito G., Faelli A., Capraro V. Sugar and electrolyte absorption in the rat intestine perfused "in vivo". Pflugers Arch. 1973 Jun 4;340(4):335–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00592311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar J. J., Khuri R. N., Curran P. F. Alanine efflux across the serosal border of turtle intestine. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Dec;60(6):720–734. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.6.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mircheff A. K., van Os C. H., Wright E. M. Pathways for alanine transport in intestinal basal lateral membrane vesicles. J Membr Biol. 1980 Jan 31;52(1):83–92. doi: 10.1007/BF01869009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWEY H., SMYTH D. H. Cellular mechanisms in intestinal transfer of amino acids. J Physiol. 1962 Dec;164:527–551. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons D. S., Prichard J. S. A preparation of perfused small intestine for the study of absorption in amphibia. J Physiol. 1968 Sep;198(2):405–434. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. W. The question of counter-transport in the intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 10;367(1):88–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


