Abstract
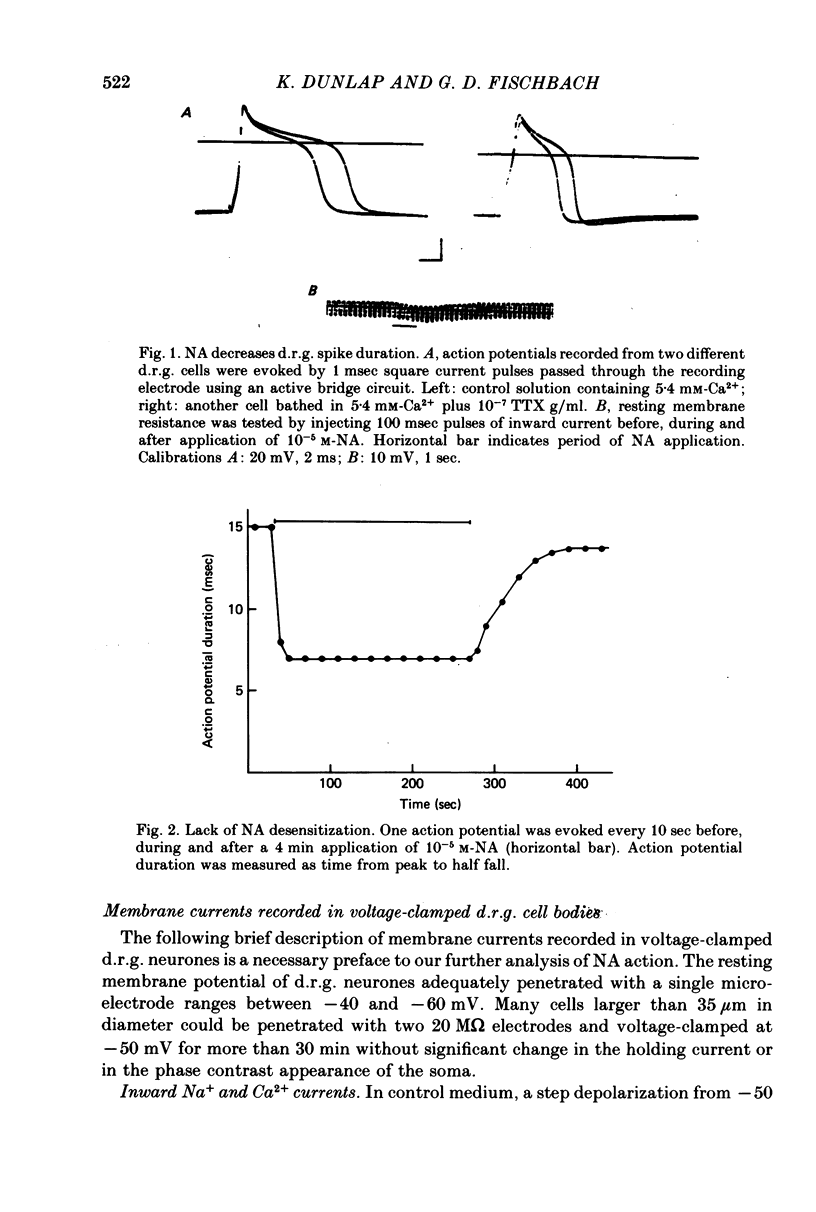
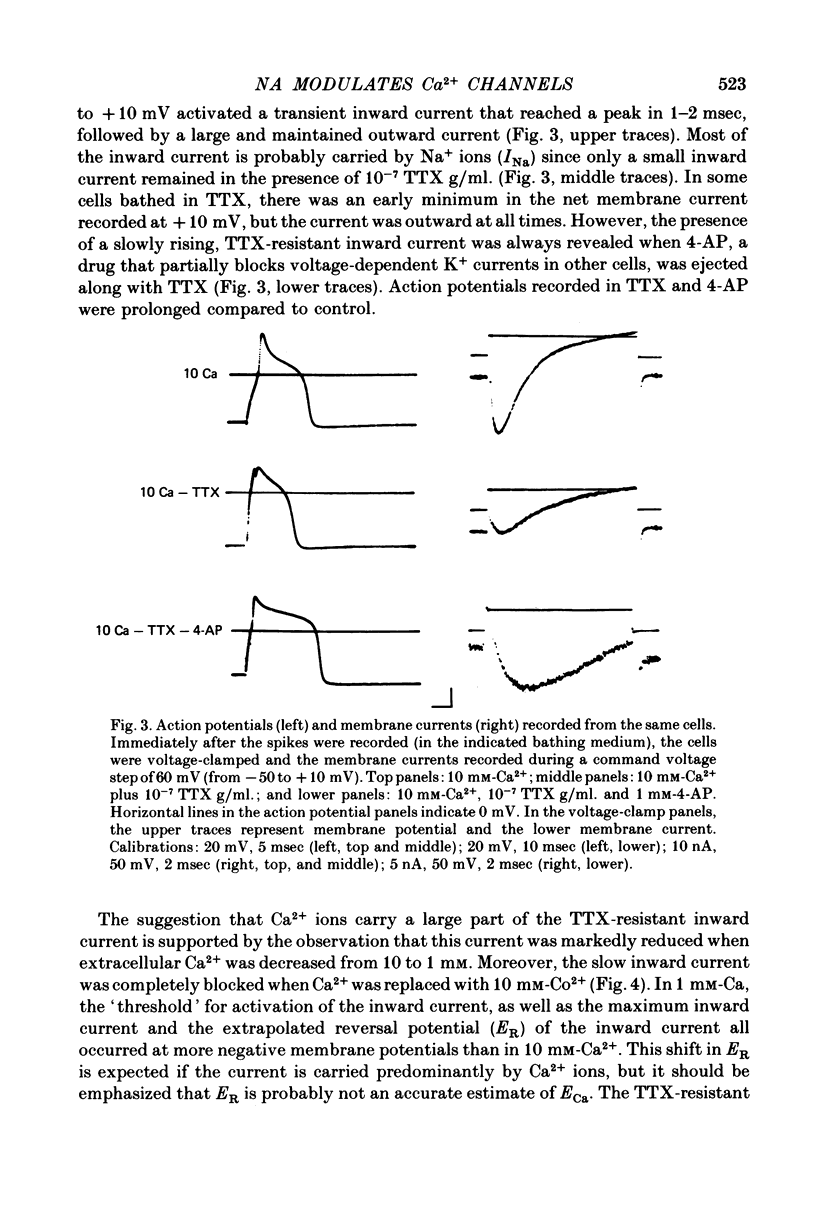
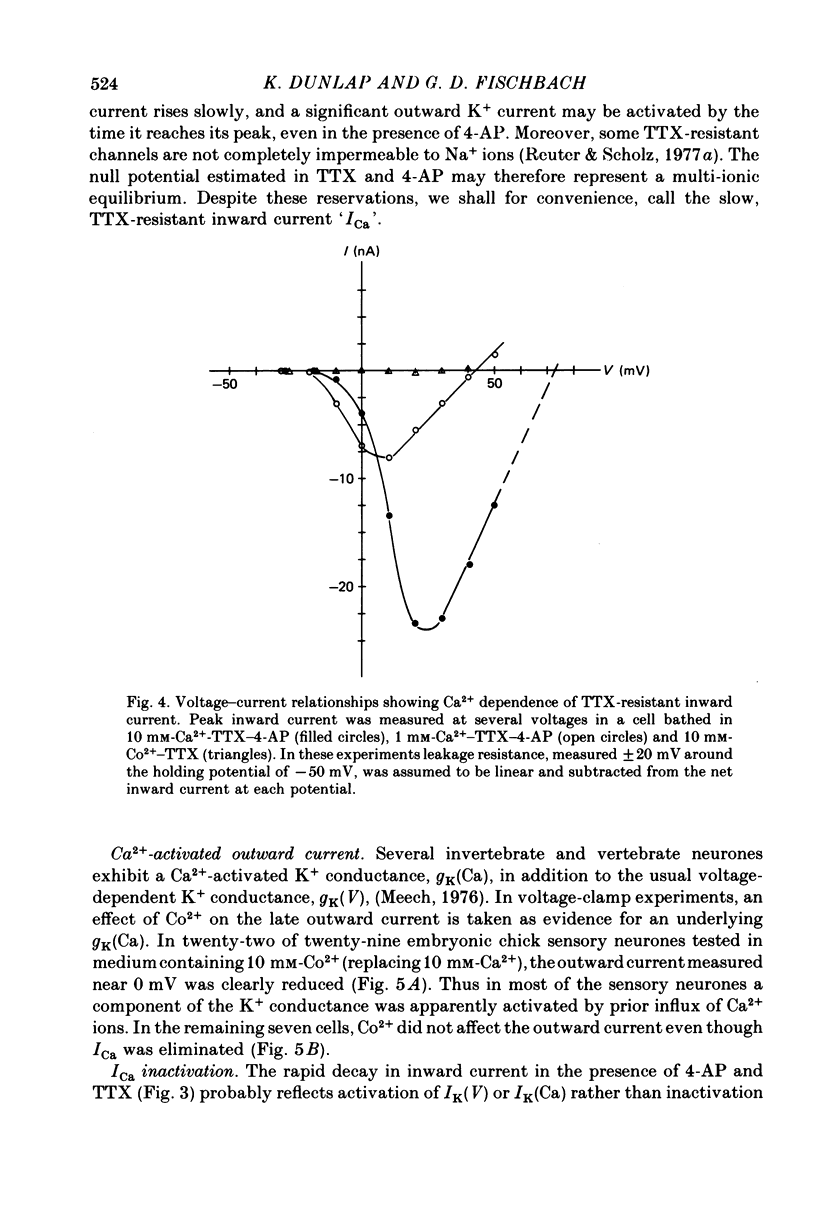
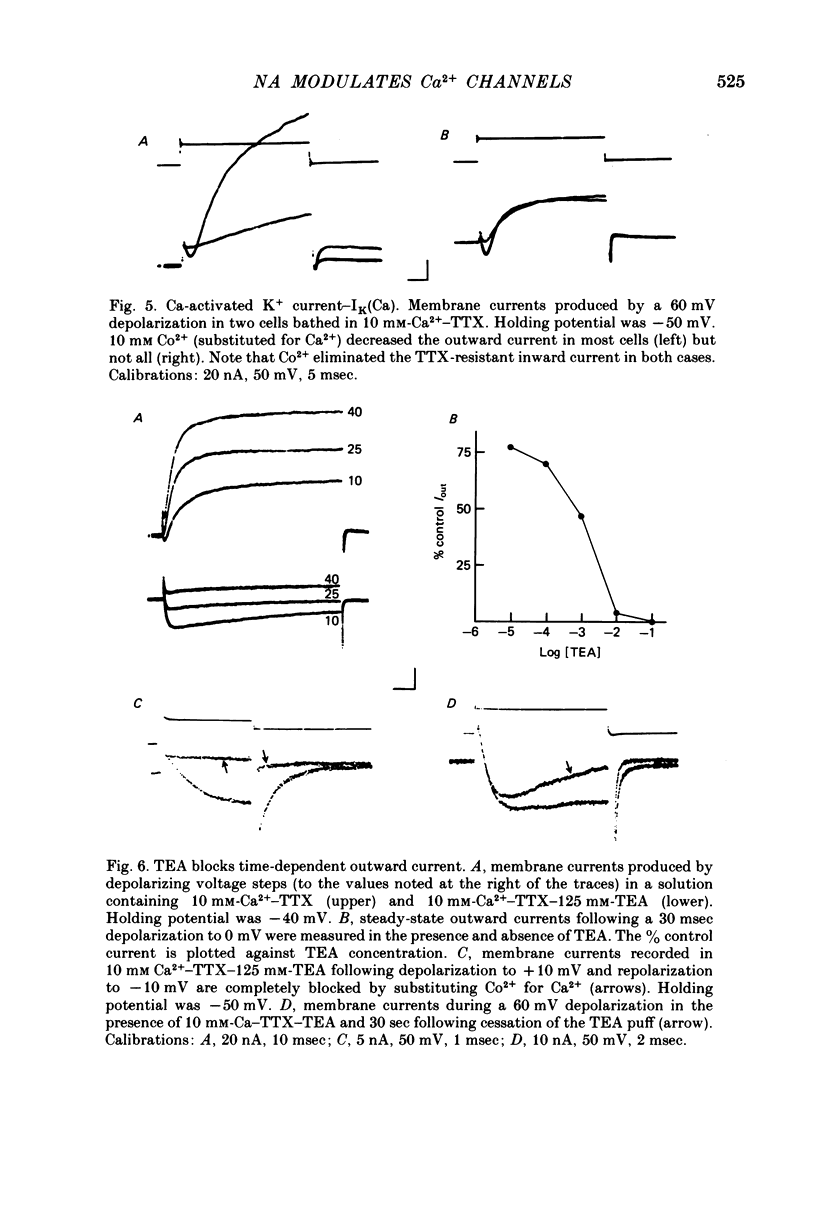
Several neurotransmitters including noradrenaline (NA), gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and serotonin (5-HT), and also certain peptides, decrease the duration of the Na+-Ca2+ action potential recorded in cell bodies of embryonic chick dorsal root ganglion neurones maintained in cell culture. To determine if these agents decreased action potential duration by affecting Ca2+ channels (inward current) or K+ channels (outward current) membrane currents were recorded in voltage-clamped sensory neurone somata. 1. Depolarization produced a prominent inward Na+ current and a smaller and slower inward Ca2+ current (ICa). The inactivation of ICa was not simply dependent on membrane potential but apparently required prior entry of Ca2+. Two components of outward current, voltage-activated and Ca2+-activated, were evident in most cells. 2. The effect of NA, and also of GABA and 5-HT, was shown to result from a direct effect on ICa because: NA decreased the TTX-resistant tail current recorded at EK and also the inward current recorded in the presence of 125 mM-TEA and TTX (in which Na+ and K+ currents were blocked). 3. The decrease in ICa is most likely due to an effect on the number of available Ca2+ channels and/or the single Ca2+ channel conductance rather than to a shift in either the kinetics of channel activation or the Ca2+ equilibrium potential. 4. No effect of the several transmitters on the voltage-dependent Na+ and K+ currents was observed. 5. Implications of ICa modulation for the phenomenon of presynaptic inhibition are discussed.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber R. P., Vaughn J. E., Saito K., McLaughlin B. J., Roberts E. GABAergic terminals are presynaptic to primary afferent terminals in the substantia gelatinosa of the rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1978 Feb 3;141(1):35–55. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90615-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
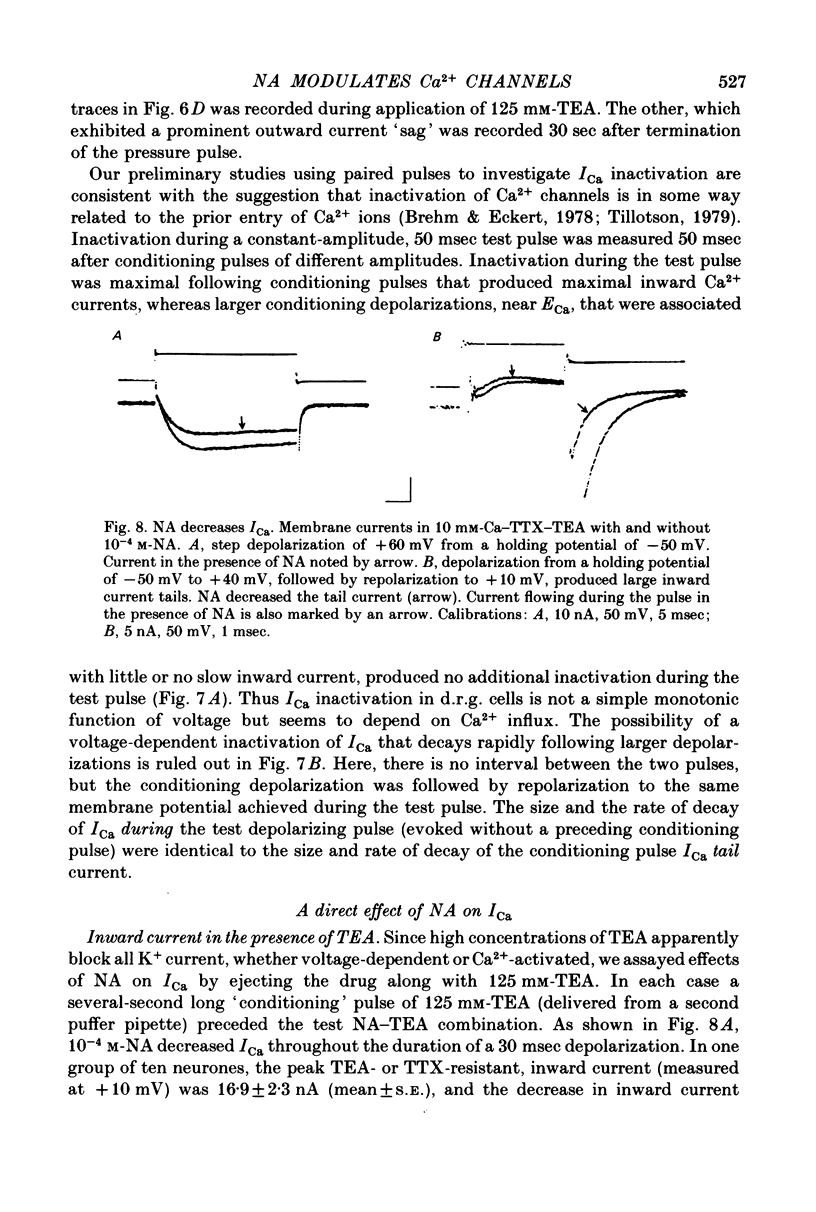
- Basbaum A. I., Clanton C. H., Fields H. L. Opiate and stimulus-produced analgesia: functional anatomy of a medullospinal pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4685–4688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm P., Eckert R. Calcium entry leads to inactivation of calcium channel in Paramecium. Science. 1978 Dec 15;202(4373):1203–1206. doi: 10.1126/science.103199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
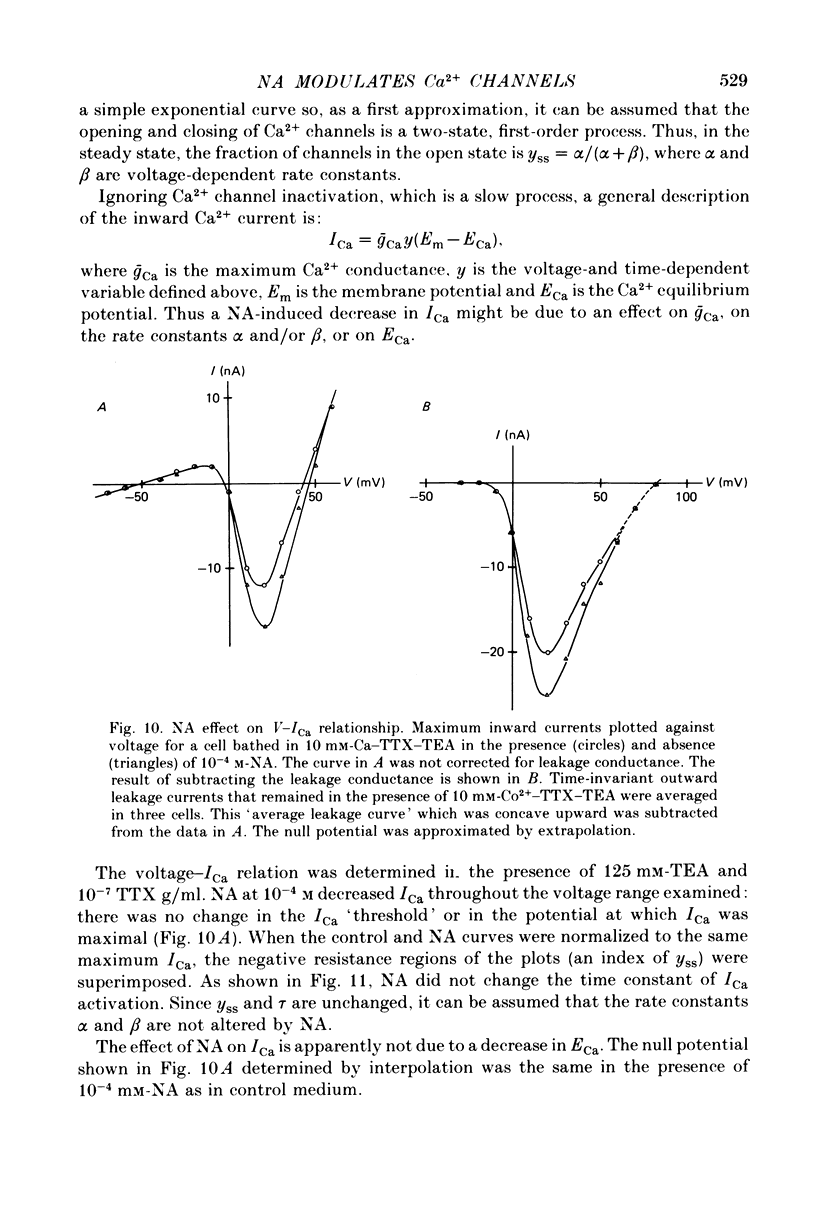
- CARLSSON A., FALCK B., FUXE K., HILLARP N. A. CELLULAR LOCALIZATION OF MONOAMINES IN THE SPINAL CORD. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Jan-Feb;60:112–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb02874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
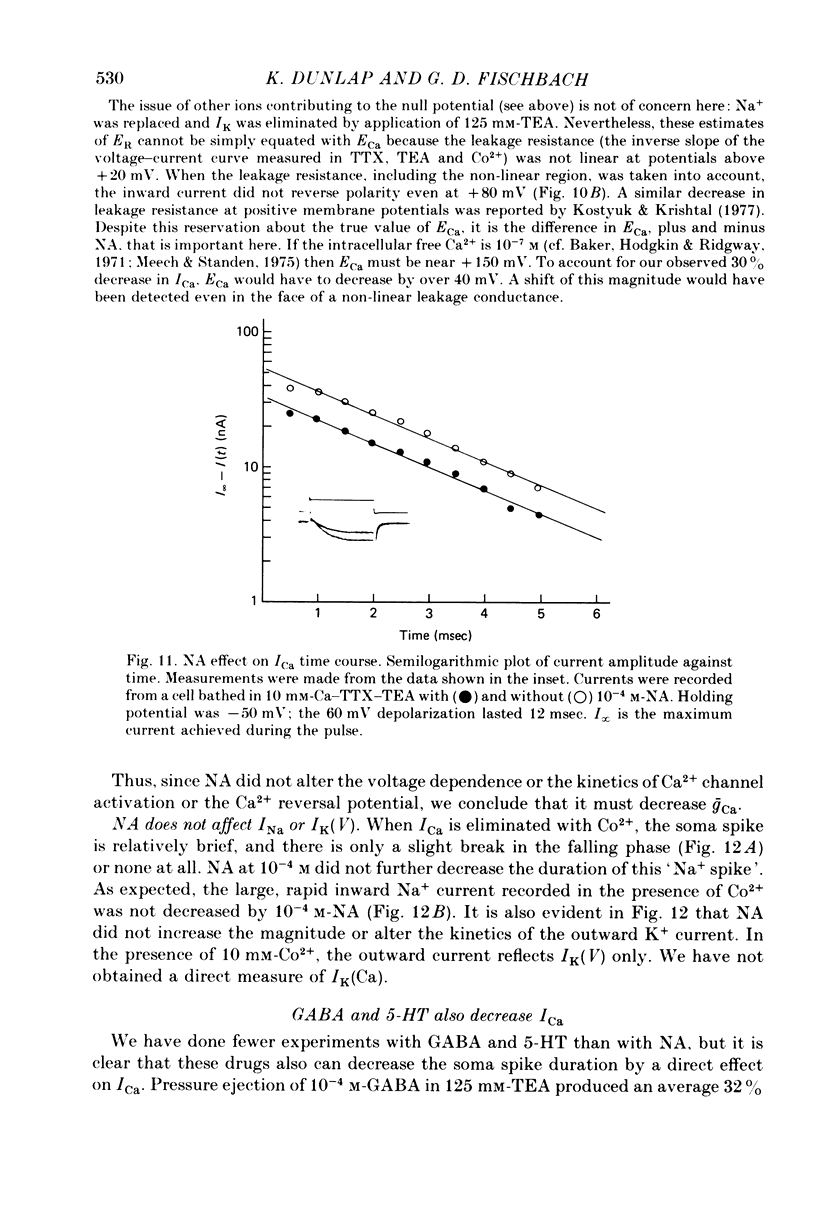
- Choi D. W., Farb D. H., Fischbach G. D. Chlordiazepoxide selectively augments GABA action in spinal cord cell cultures. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):342–344. doi: 10.1038/269342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
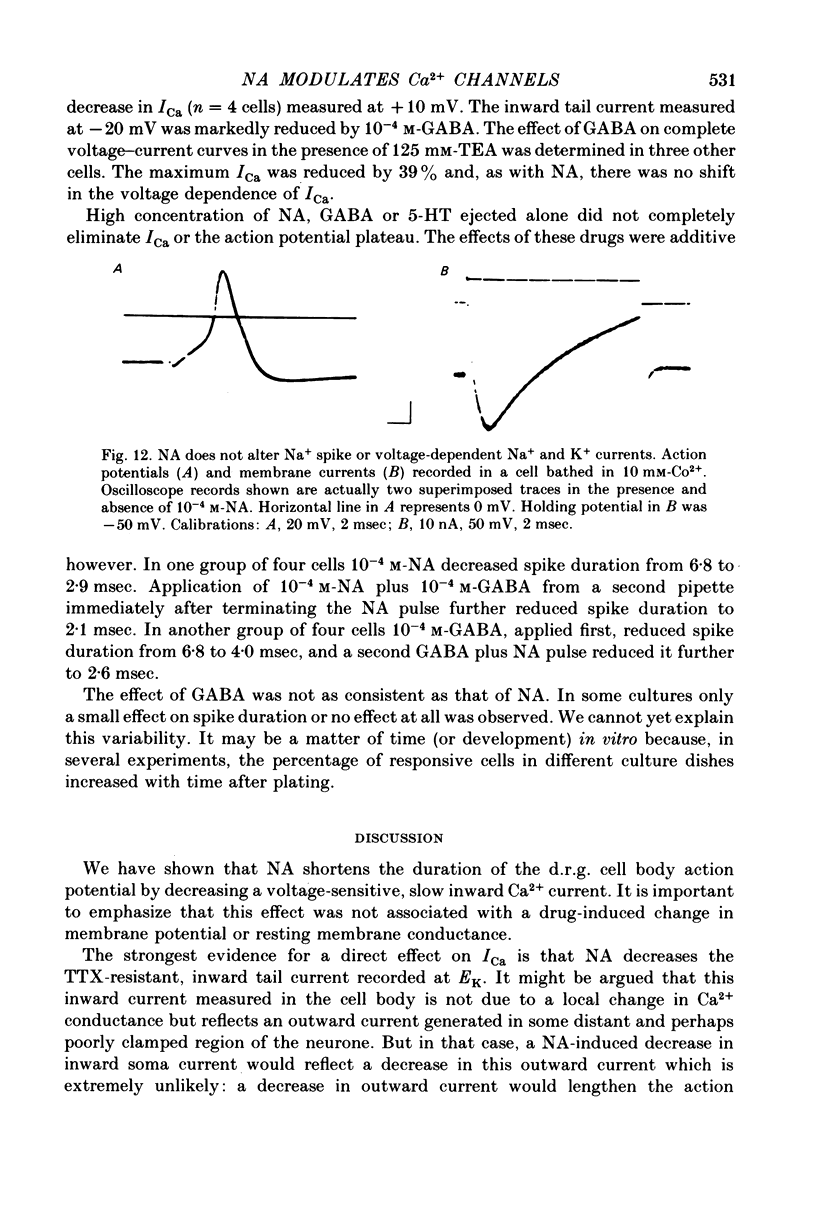
- De Groat W. C. GABA-depolarization of a sensory ganglion: antagonism by picrotoxin and bicuculline. Brain Res. 1972 Mar 24;38(2):429–432. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90726-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichter M. A., Fischbach G. D. The action potential of chick dorsal root ganglion neurones maintained in cell culture. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):281–298. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap K., Fischbach G. D. Neurotransmitters decrease the calcium ocmponent of sensory neurone action potentials. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):837–839. doi: 10.1038/276837a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elde R., Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Terenius L. Immunohistochemical studies using antibodies to leucine-enkephalin: initial observations on the nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience. 1976 Aug;1(4):349–351. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles W., Noble S. J. Changes in membrane currents in bullfrog atrium produced by acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;261(1):103–123. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F., KATZ B. Measurement of current-voltage relations in the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):424–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann A., Gorman A. L. External and internal effects of tetraethylammonium on voltage-dependent and Ca-dependent K+ currents components in molluscan pacemaker neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1979 Apr;12(1):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(79)91485-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn J. P., McAfee D. A. Alpha-drenergic inhibition of calcium-dependent potentials in rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:191–204. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn J. P., McAfee D. A. Norepinephrine inhibits calcium-dependent potentials in rat sympathetic neurons. Science. 1979 Jun 15;204(4398):1233–1235. doi: 10.1126/science.221979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. A., Lieberman M. Heart: excitation and contraction. Annu Rev Physiol. 1971;33:479–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.33.030171.002403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Kandel E. R. Presynaptic modulation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ current: mechanism for behavioral sensitization in Aplysia californica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3512–3516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A. Effects of calcium and calcium-chelating agents on the inward and outward current in the membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):569–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudge A. W., Leeman S. E., Fischbach G. D. Enkephalin inhibits release of substance P from sensory neurons in culture and decreases action potential duration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):526–530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., Minota S., Karczmar A. G. Primary afferent neurones: the ionic mechanism of GABA-mediated depolarization. Neuropharmacology. 1974 Mar;13(3):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(74)90110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Localization of beta adrenergic receptors, and effects of noradrenaline and cyclic nucleotides on action potentials, ionic currents and tension in mammalian cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(2):429–451. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Scholz H. A study of the ion selectivity and the kinetic properties of the calcium dependent slow inward current in mammalian cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(1):17–47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Scholz H. The regulation of the calcium conductance of cardiac muscle by adrenaline. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(1):49–62. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro E., Castellucci V. F., Kandel E. R. Presynaptic inhibition in Aplysia involves a decrease in the Ca2+ current of the presynaptic neuron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1185–1189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D. Inactivation of Ca conductance dependent on entry of Ca ions in molluscan neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1497–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Giles W., Greengard P. Cyclic AMP mediates the effects of adrenaline on cardiac purkinje fibres. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 6;240(101):181–183. doi: 10.1038/newbio240181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. Z., Oxford G. S., Wu C. H., Narahashi T. Interactions of aminopyridines with potassium channels of squid axon membranes. Biophys J. 1976 Jan;16(1):77–81. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85663-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


