Abstract
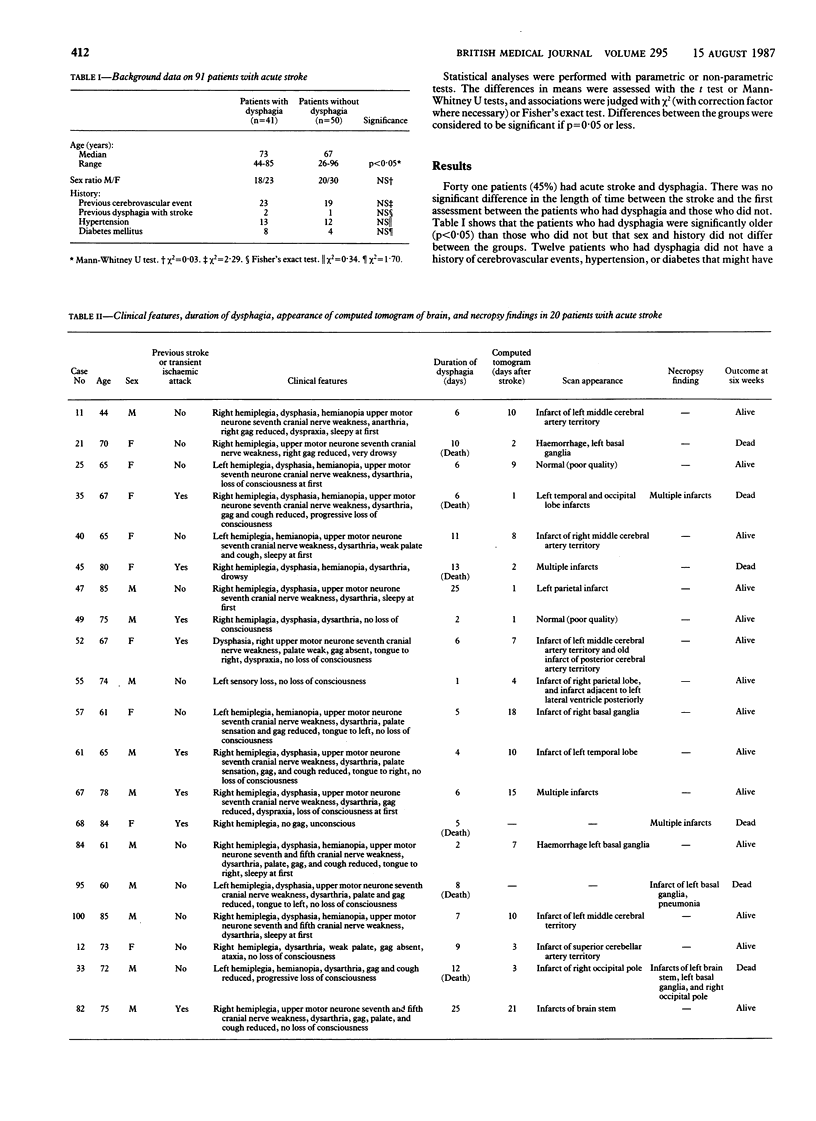
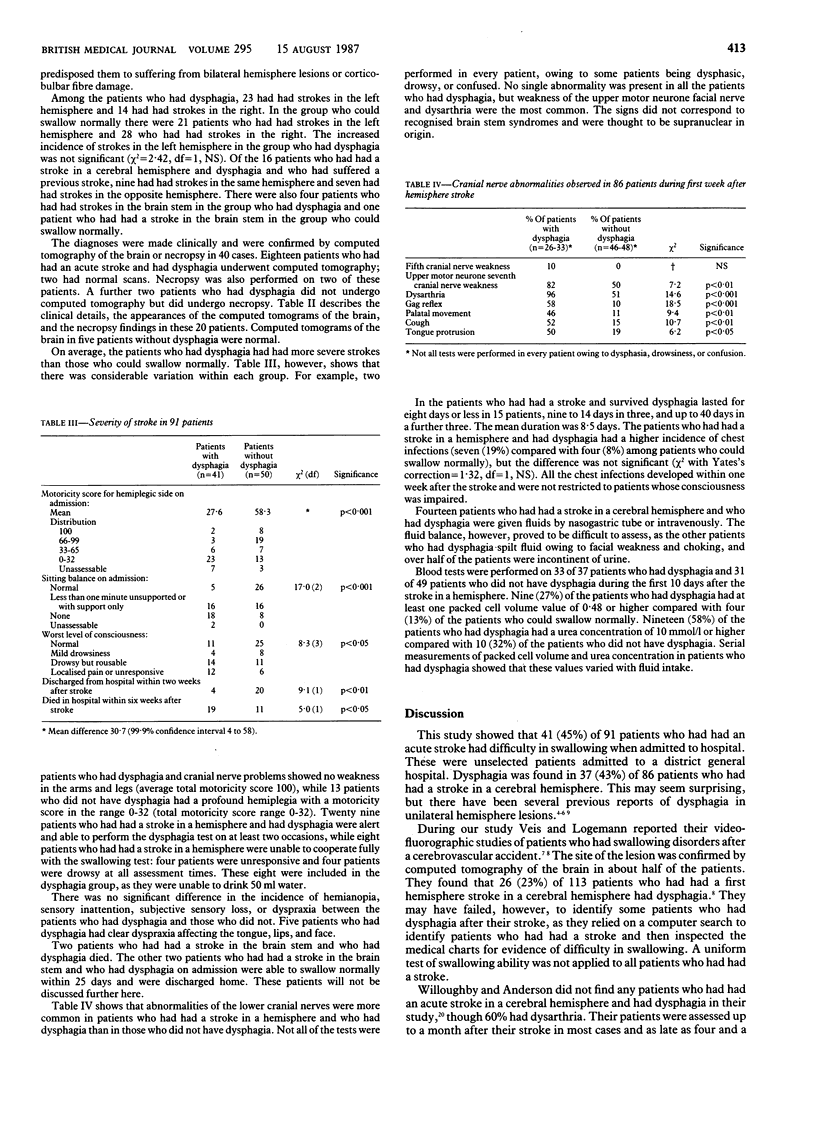
A prospective study was undertaken to define the incidence, duration, and consequences of dysphagia in an unselected group of 91 consecutive patients who had suffered acute stroke. The site of the present lesion and of any previous stroke was determined clinically and was confirmed by computed tomography of the brain or necropsy in 40 cases. Of 41 patients who had dysphagia on admission, 37 had had a stroke in one cerebral hemisphere. Only seven patients showed evidence of lesions in both hemispheres. Nineteen of 22 patients who survived a stroke in a hemisphere regained their ability to swallow within 14 days. Dysphagia in patients who had had a stroke in a cerebral hemisphere was associated in this study with a higher incidence of chest infections, dehydration, and death.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho K., Harmsen P., Hatano S., Marquardsen J., Smirnov V. E., Strasser T. Cerebrovascular disease in the community: results of a WHO collaborative study. Bull World Health Organ. 1980;58(1):113–130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieger D., Hockman C. H. Suprabulbar modulation of reflex swallowing. Exp Neurol. 1976 Aug;52(2):311–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(76)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demeurisse G., Demol O., Robaye E. Motor evaluation in vascular hemiplegia. Eur Neurol. 1980;19(6):382–389. doi: 10.1159/000115178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockman C. H., Bieger D., Weerasuriya A. Supranuclear pathways of swallowing. Prog Neurobiol. 1979;12(1):15–32. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(79)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadows J. C. Dysphagia in unilateral cerebral lesions. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Oct;36(5):853–860. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.5.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veis S. L., Logemann J. A. Swallowing disorders in persons with cerebrovascular accident. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1985 Jun;66(6):372–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby E. W., Anderson N. E. Lower cranial nerve motor function in unilateral vascular lesions of the cerebral hemisphere. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Sep 29;289(6448):791–794. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6448.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winstein C. J. Neurogenic dysphagia. Frequency, progression, and outcome in adults following head injury. Phys Ther. 1983 Dec;63(12):1992–1997. doi: 10.1093/ptj/63.12.1992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


