Abstract
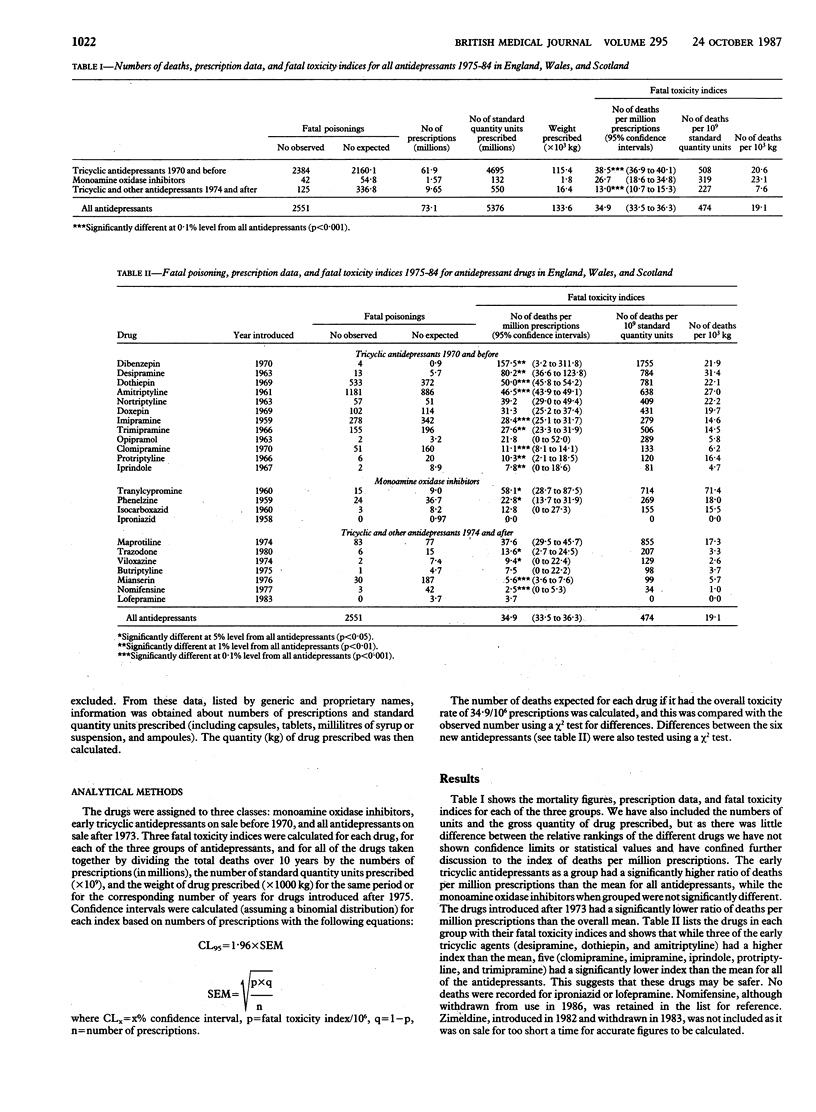
A fatal toxicity index (deaths per million National Health Service prescriptions) was calculated for antidepressant drugs on sale during the years 1975-84 in England, Wales, and Scotland. The tricyclic drugs introduced before 1970 had a higher index than the mean for all the drugs studied (p less than 0.001). In this group the toxicity of amitriptyline, dibenzepin, desipramine, and dothiepin was significantly higher, while that of clomipramine, imipramine, iprindole, protriptyline, and trimipramine was lower. The monoamine oxidase inhibitors had intermediate toxicity, and the antidepressants introduced since 1973, considered as a group, had significantly lower toxicity than the mean (p less than 0.001). Of these newer drugs, maprotiline had a fatal toxicity index similar to that of the older tricyclic antidepressants, while the other newly introduced drugs had lower toxicity indices, with those for mianserin, nomifensine, trazodone, and viloxazine reaching significance. Provided that these drugs are equally effective clinically, serious consideration should be given to prescribing antidepressants with a lower fatal toxicity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali C. J., Henry J. A. Trazodone overdosage: experience over 5 years. Neuropsychobiology. 1986;15 (Suppl 1):44–45. doi: 10.1159/000118286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barraclough B. M. Are there safer hypnotics than barbiturates? Lancet. 1974 Jan 12;1(7846):57–58. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)93055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer C., Farmer R. Self poisoning in 1984: a prediction that didn't come true. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Feb 2;290(6465):391–391. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6465.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callaham M., Kassel D. Epidemiology of fatal tricyclic antidepressant ingestion: implications for management. Ann Emerg Med. 1985 Jan;14(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(85)80725-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crome P., Newman B. The problem of tricyclic antidepressant poisoning. Postgrad Med J. 1979 Sep;55(646):528–532. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.55.646.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crome P., Newman B. Why patients die from tricyclic antidepressant poisoning. Vet Hum Toxicol. 1979;21 (Suppl):56–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King L. A. Ferguson's principle and the prediction of fatal drug levels in blood. Hum Toxicol. 1985 May;4(3):273–278. doi: 10.1177/096032718500400307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King L. A., Moffat A. C. A possible index of fatal drug toxicity in humans. Med Sci Law. 1983 Jul;23(3):193–198. doi: 10.1177/002580248302300307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulig K. Management of poisoning associated with "newer" antidepressant agents. Ann Emerg Med. 1986 Sep;15(9):1039–1045. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(86)80126-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard B. E. Toxicity of antidepressants. Lancet. 1986 Nov 8;2(8515):1105–1105. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90511-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickander R. C., Emmerson J. L., Hynes M. D., Steinberg M. I., Sullivan H. R. Pharmacologic and toxic effects in animals of dextropropoxyphene and its major metabolite norpropoxyphene: a review. Hum Toxicol. 1984 Aug;3 (Suppl):13S–36S. doi: 10.1177/096032718400300103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osselton M. D., Blackmore R. C., King L. A., Moffat A. C. Poisoning-associated deaths for England and Wales between 1973 and 1980. Hum Toxicol. 1984 Jun;3(3):201–221. doi: 10.1177/096032718400300305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentel P. R., Benowitz N. L. Tricyclic antidepressant poisoning. Management of arrhythmias. Med Toxicol. 1986 Mar-Apr;1(2):101–121. doi: 10.1007/BF03259831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls W. N. Trazodone (Desyrel, Mead-Johnson Pharmaceutical Division). Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1982 Jan;16(1):7–13. doi: 10.1177/106002808201600102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakeling A. Efficacy and side effects of mianserin, a tetracyclic antidepressant. Postgrad Med J. 1983 Apr;59(690):229–231. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.59.690.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedin G. P., Oderda G. M., Klein-Schwartz W., Gorman R. L. Relative toxicity of cyclic antidepressants. Ann Emerg Med. 1986 Jul;15(7):797–804. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(86)80375-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuhara H., Matsuo H., Sakamoto K., Ueda I. Mechanism of membrane stabilizing and lytic effects of tricyclic antidepressants. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;30(3):397–401. doi: 10.1254/jjp.30.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuhara H., Tonooka M., Kamei K., Sakamoto K. Membrane effects of various drugs on isolated rat hepatocytes and erythrocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1985 Jul;79(3):453–460. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(85)90142-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


