Abstract
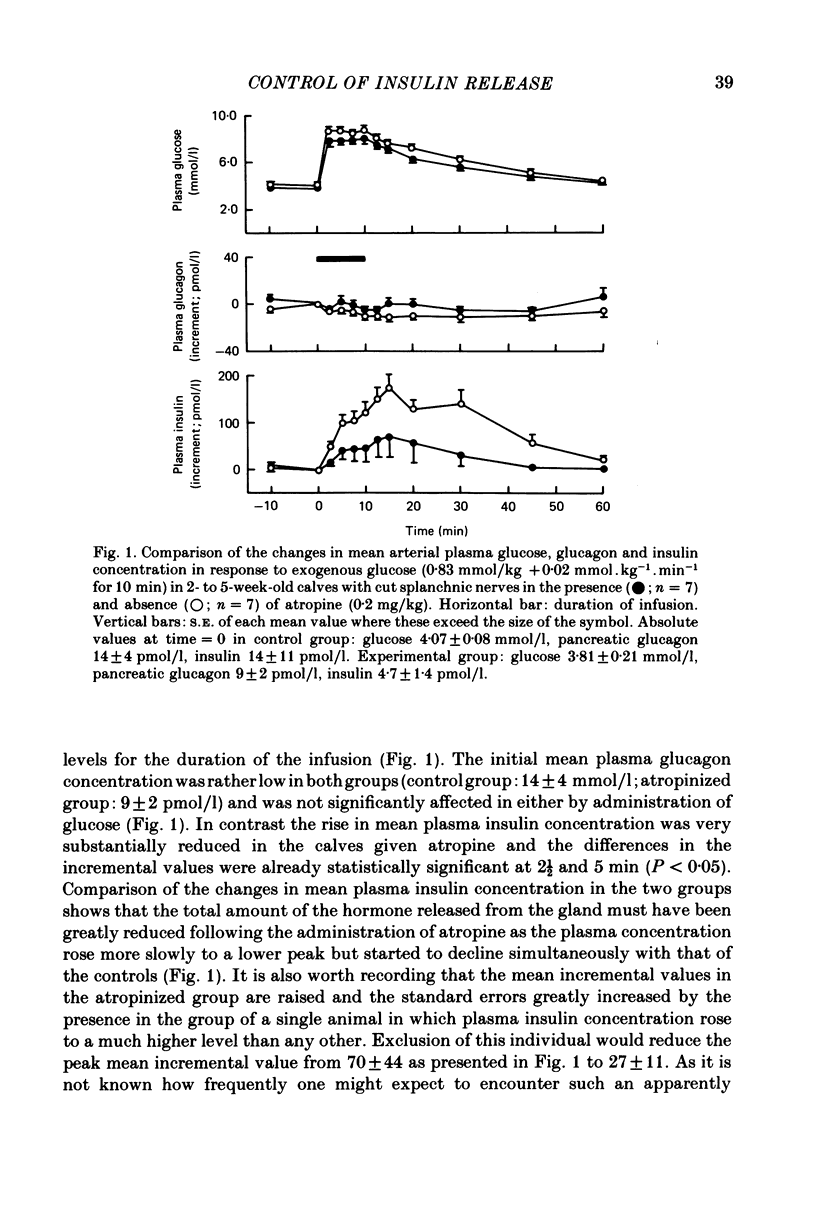
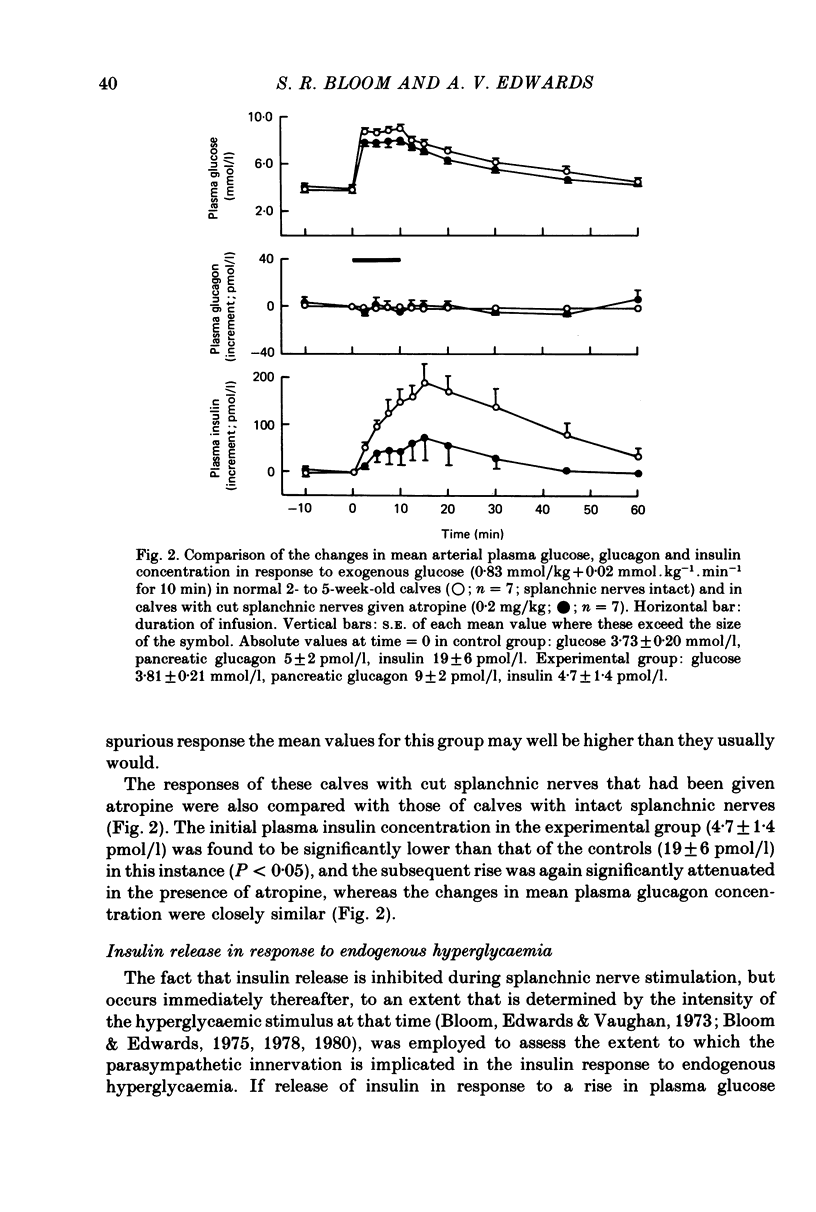
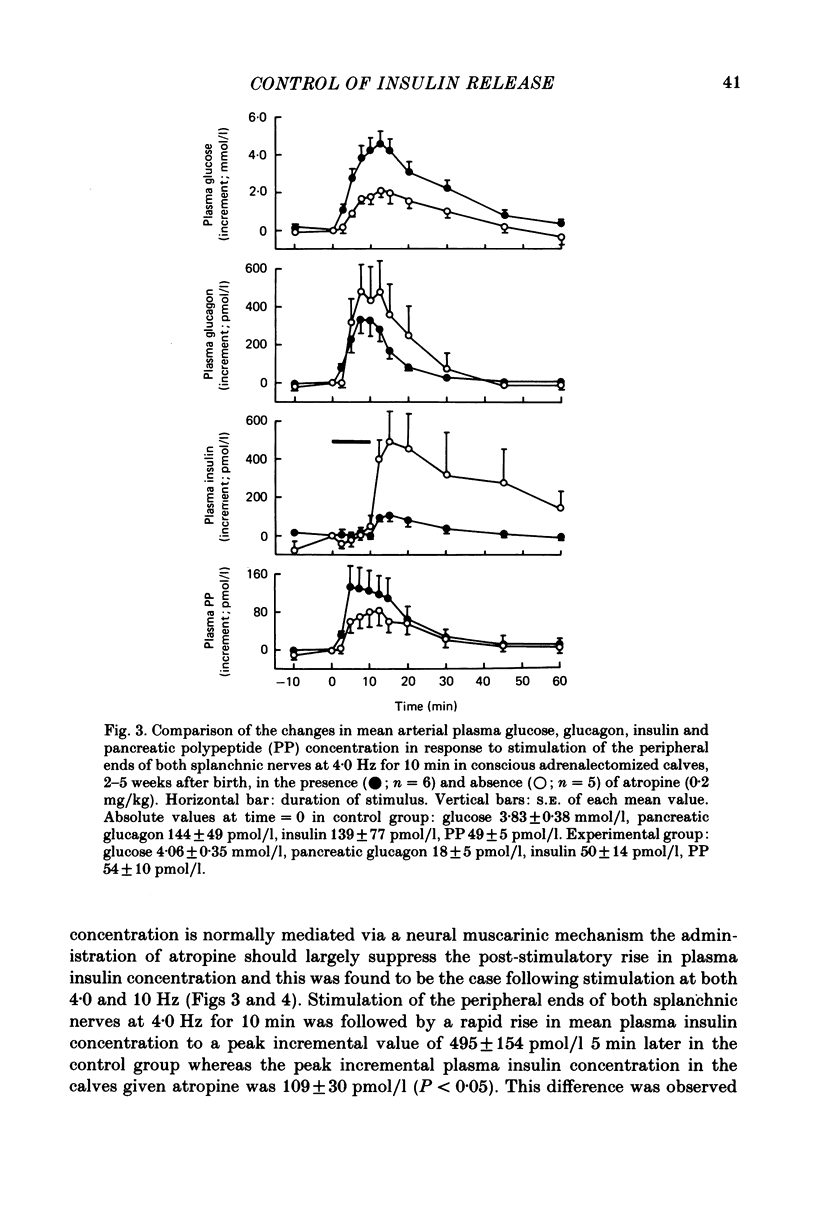
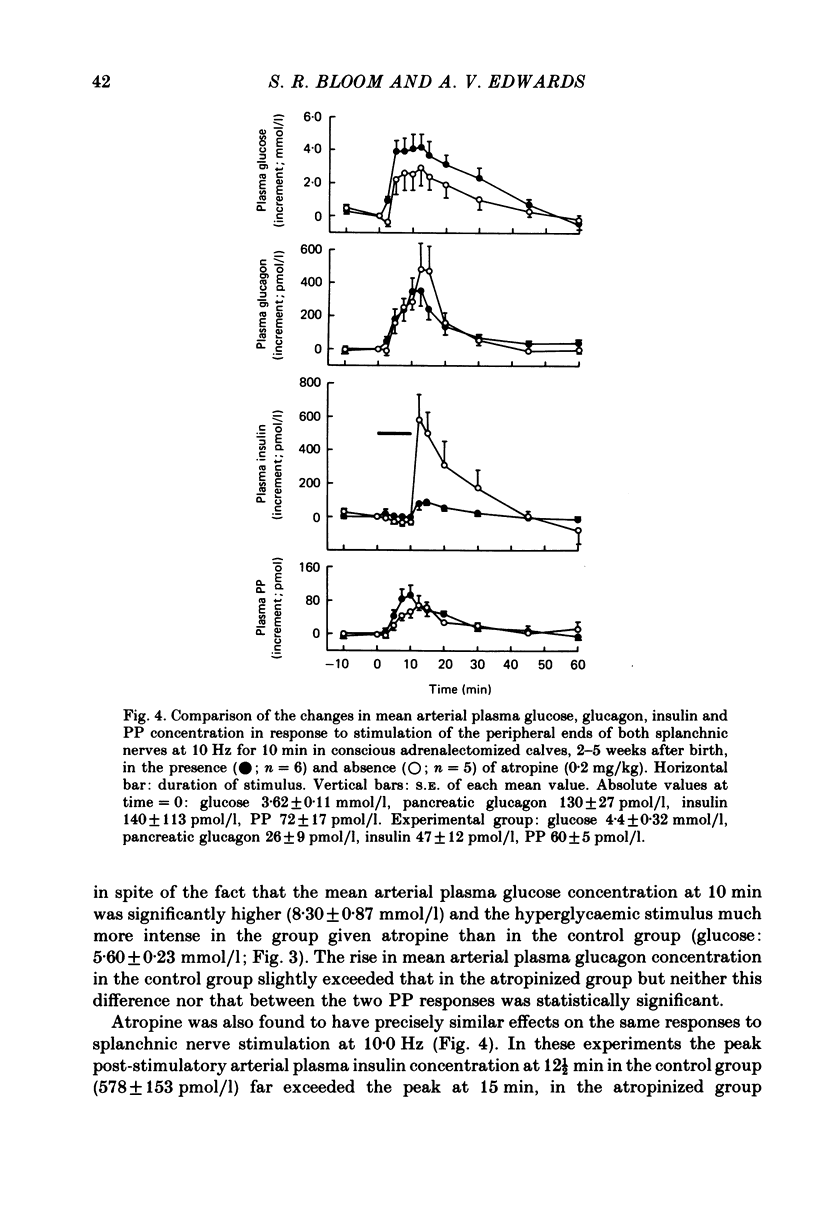
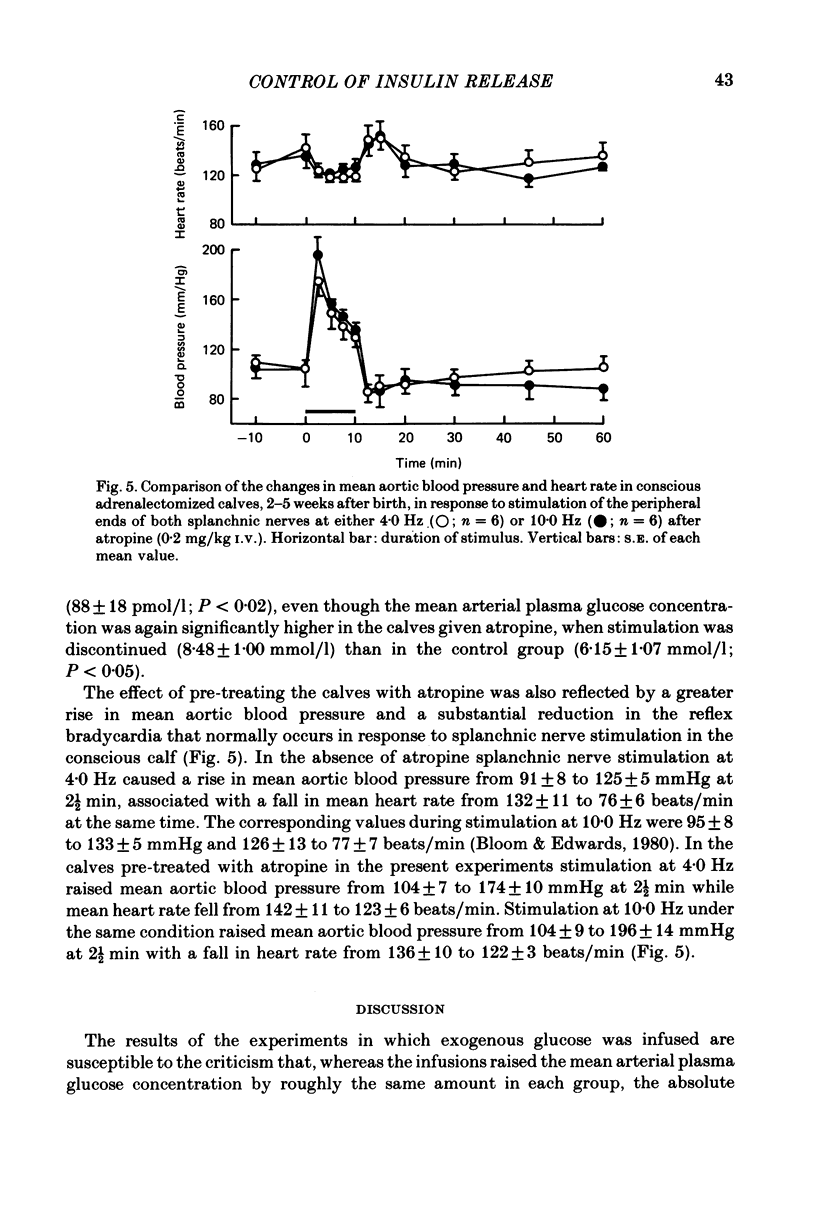
1. The effect of atropine (0.2 mg/kg) on the release of insulin from the pancreas, in response to both exogenous and endogenous hyperglycaemia, has been investigated in conscious 2- to 5-week-old calves. 2 The rise in mean plasma insulin concentration in response to infusions of glucose, which raised the concentration of glucose in the plasma by about 4.0 mmol/l, was significantly depressed in calves with cut splanchnic nerves by prior administration of atropine. 3. The rise in plasma insulin concentration, which normally follows stimulation of the splanchnic nerves in the conscious calf (Bloom & Edwards, 1980), was almost completely suppressed by prior administration of atropine. 4. These findings are discussed in relation to those of other workers with other species. The results indicate that the parasympathetic innervation to the pancreas plays an important part in the control of insulin release in response to hyperglycaemia.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian T. E., Bloom S. R., Bryant M. G., Polak J. M., Heitz P. H., Barnes A. J. Distribution and release of human pancreatic polypeptide. Gut. 1976 Dec;17(12):940–944. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.12.940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Maritz G., Turner R. C. A sensitive, precise radioimmunoassay of serum insulin relying on charcoal separation of bound and free hormone moieties. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1972 Jul;70(3):487–509. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0700487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assan R., Slusher N. Structure-function and structure-immunoreactivity relationships of the glucagon molecule and related synthetic peptides. Diabetes. 1972 Aug;21(8):843–855. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.8.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V. Certain pharmacological characteristics of the release of pancreatic glucagon in response to stimulation of the splanchnic nerves. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:25–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V. Developmental changes in pancreatic endocrine function in the young calf. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:23–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Hardy R. N. The role of the autonomic nervous system in the control of pancreatic endocrine responses to milk ingestion in the calf. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:37–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Järhult J. The effect of somatostatin on pancreatic endocrine responses mediated via the parasympathetic innervation in the conscious calf. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:29–38. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V. Pancreatic endocrine responses to stimulation of the peripheral ends of the splanchnic nerves in the conscious adrenalectomized calf. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:39–48. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V. The release of pancreatic glucagon and inhibition of insulin in response to stimulation of the sympathetic innervation. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(1):157–173. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Vaughan N. J. The role of the autonomic innervation in the control of glucagon release during hypoglycaemia in the calf. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;236(3):611–623. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Vaughan N. J. The role of the sympathetic innervation in the control of plasma glucagon concentration in the calf. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(2):457–466. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. A. Interrelation of parathyroids, suprarenals and pancreas. J Physiol. 1924 Mar 14;58(4-5):294–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1924.sp002130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. A. The influence of the vagus on the islets of Langerhans: Part I. Vagus hypoglycaemia. J Physiol. 1925 Mar 31;59(6):466–471. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1925.sp002206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Henderson J. R. The effect of atropine on insulin release caused by intravenous glucose in the rhesus monkey. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1975 Apr;78(4):736–745. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0780736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Henderson J. R. The effect of vagal stimulation on plasma insulin and glucose levels in the baboon. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):317–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman L. A., Ezdinli E. Z., Javid R. Effect of vagotomy and vagal stimulation on insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1967 Jul;16(7):443–448. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.7.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hell N. S., de Aguiar Pupo A. Influence of the vagus and splanchnic nerves on insulin secretion and glycemia. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1979 Oct;1(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(79)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneto A., Kosaka K., Nakao K. Effects of stimulation of the vagus nerve on insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 1967 Mar;80(3):530–536. doi: 10.1210/endo-80-3-530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niijima A. An electrophysiological study on the regulatory mechanism of blood sugar level in the rabbit. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 11;87(2-3):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90416-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


