Abstract
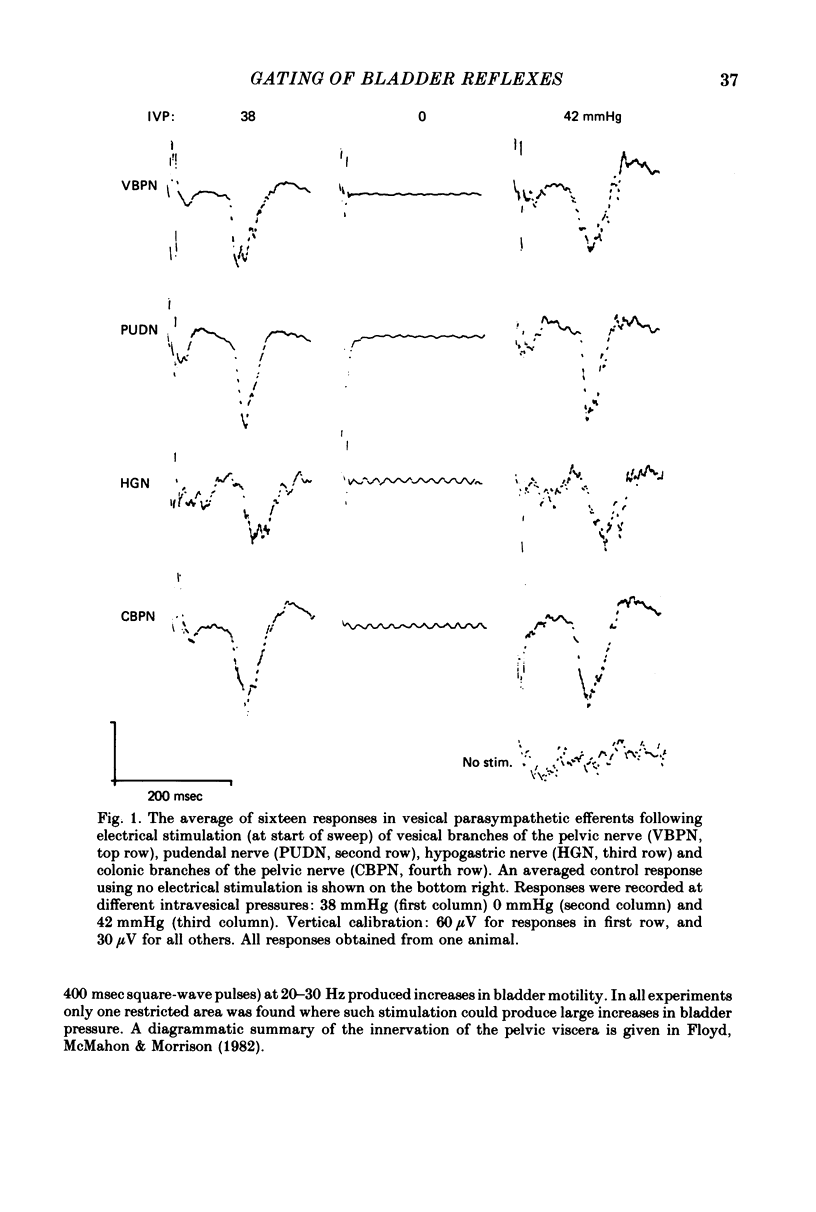
1. Spino-bulbo-spinal reflex responses could be recorded from the vesical branches of the pelvic nerve following electrical stimulation of afferents in the vesical or colonic branches of the pelvic nerves, the hypogastric or pudendal nerves. The latencies of responses from these different sources were similar.
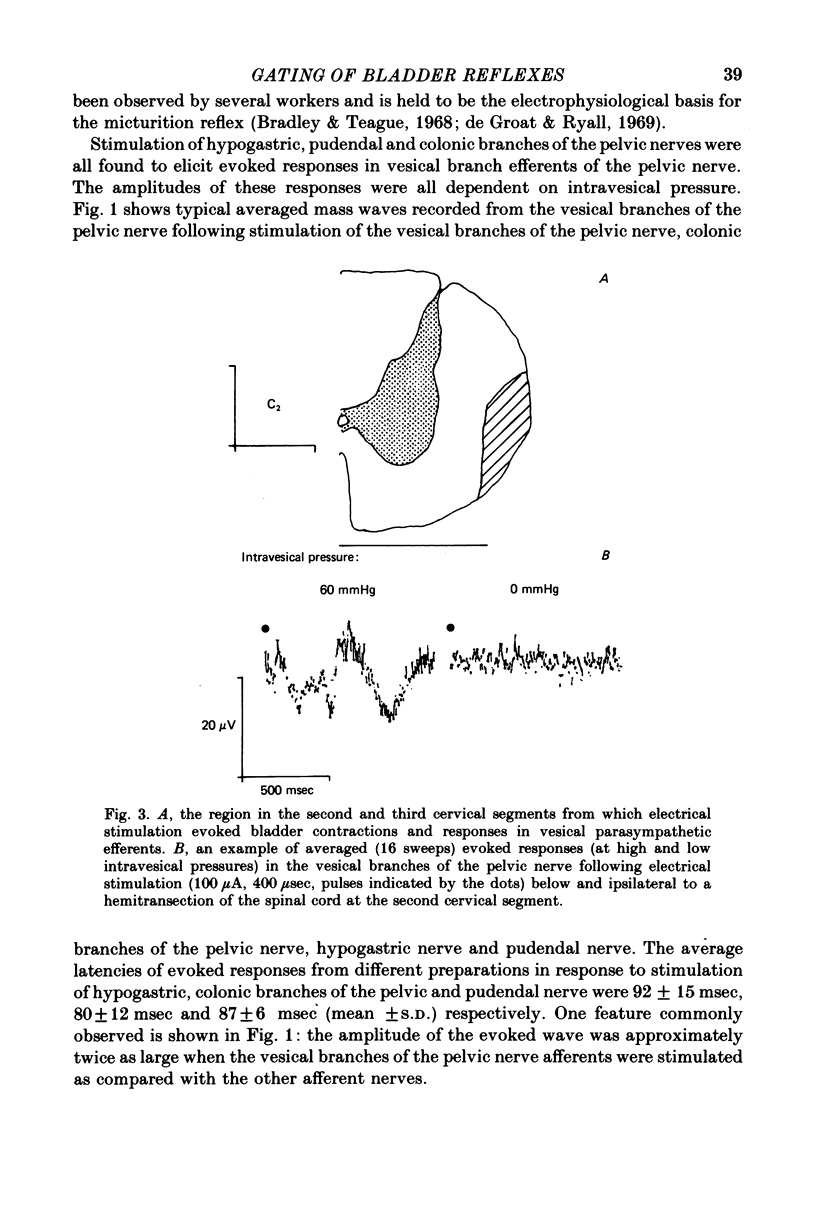
2. Short latency responses could be recorded from the vesical branches of the pelvic nerve on electrical stimulation of descending pathways in the spinal cord and ipsilateral to and just below a hemitransection at the second cervical segment.
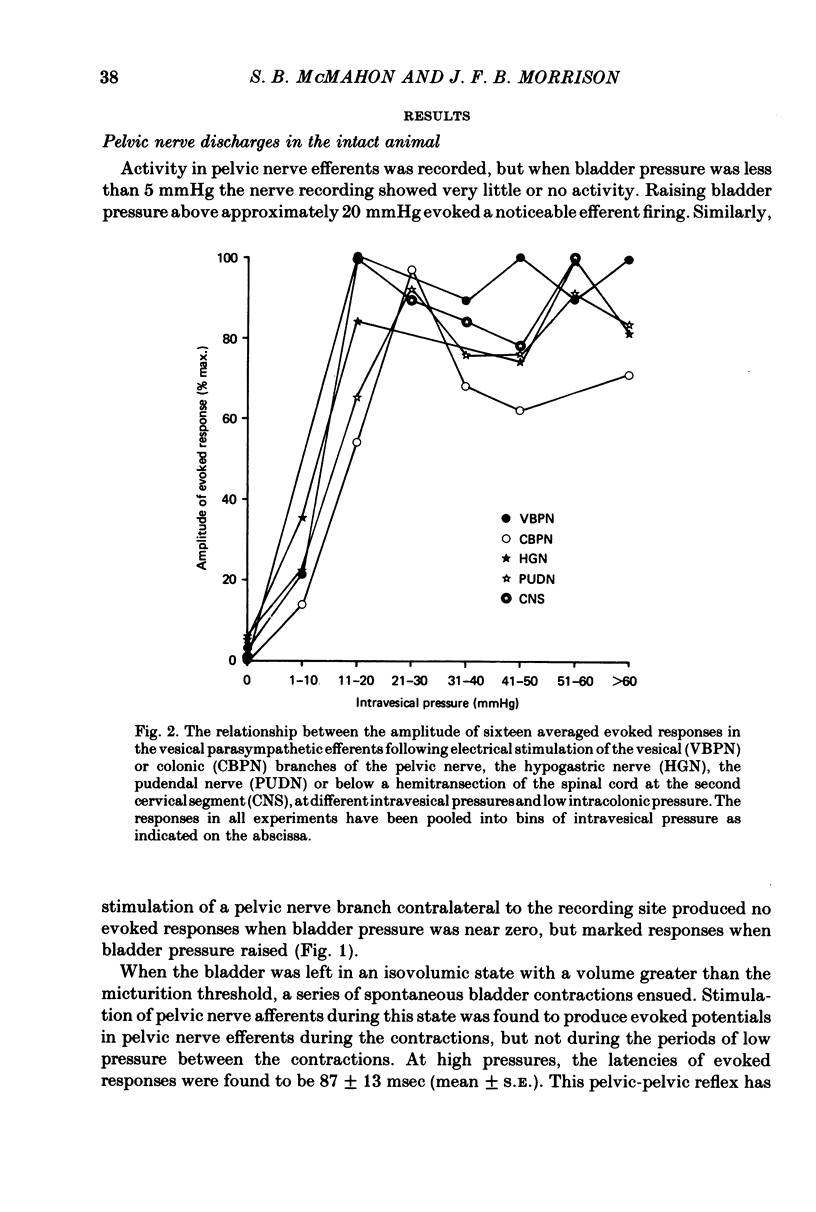
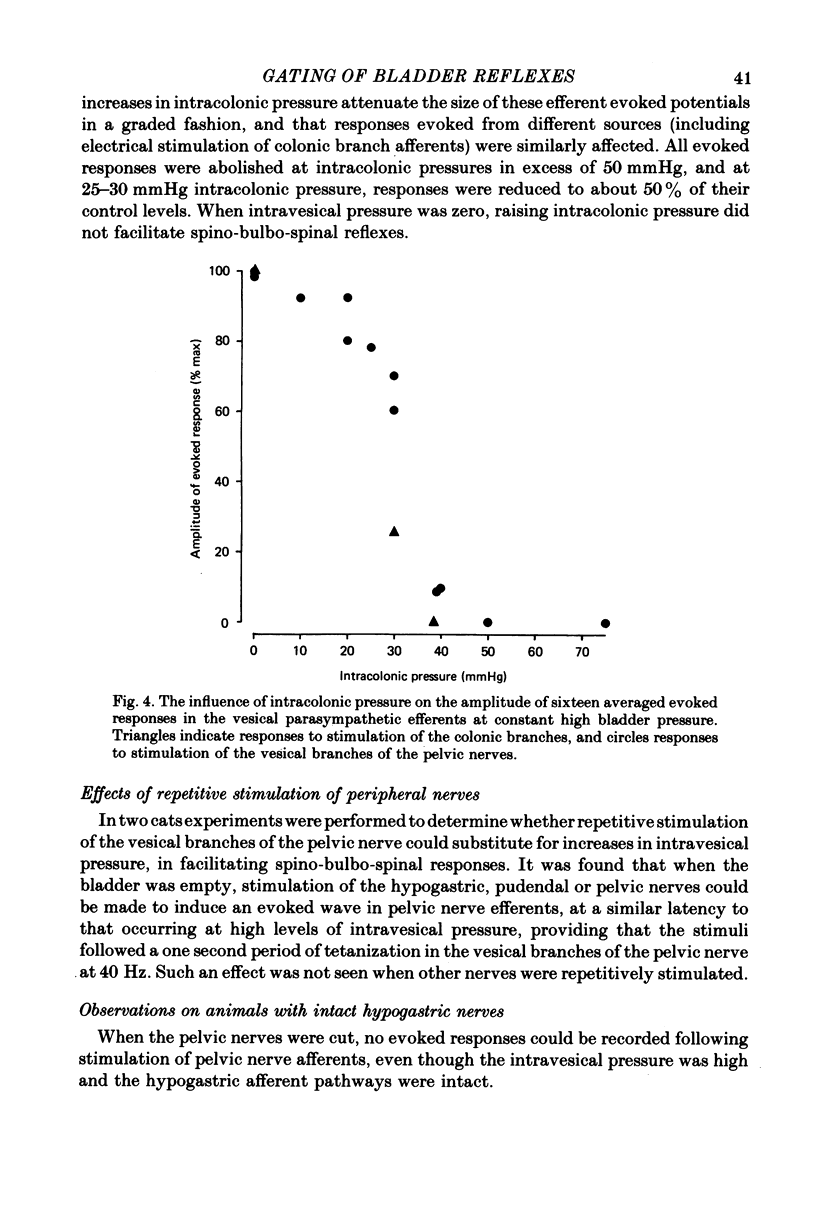
3. These responses were facilitated by increases in intravesical pressure, maximal facilitation occurring at about 30 mmHg. Conversely, increases in intracolonic pressure inhibited these parasympathetic evoked responses, the maximum effect being seen with intracolonic pressures of 40-50 mmHg.
4. These results suggest that the spino-bulbo-spinal responses that are recorded from the vesical parasympathetic efferents can be elicited from nerves innervating viscera other than the bladder, and also somatic structures. The effects of these spino-bulbo-spinal pathways on vesical parasympathetic efferents are dependent on antagonistic influences of intravesical and intracolonic pressure.
5. The pathways that mediate the changes in excitability in these reflexes appear to act at least in part at the termination of the bulbo-spinal limb of the reflex, and involve afferents in the pelvic nerves but not the hypogastric or lumbar colonic nerves.
6. It is proposed that the neurones that mediate this `gating' action on the excitability of pelvic nerve reflexes are located in the sacral cord, and form a proportion of the population of interneurones described by McMahon & Morrison (1982b). In addition it is proposed that the neurones which mediate the ascending limb of the spino-bulbo-spinal reflexes are the long ascending neurones described by McMahon & Morrison (1982a).
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley W. E., Teague C. T. Spinal cord organization of micturition reflex afferents. Exp Neurol. 1968 Dec;22(4):504–516. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(68)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd K., McMahon S. B., Morrison J. F. Inhibitory interactions between colonic and vesical afferents in the micturition reflex of the cat. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:45–52. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCK N. G., POMPEIUS R. INHIBITION OF VESICAL MOTOR ACTIVITY INDUCED BY ANAL STIMULATION. Acta Chir Scand. 1963 Sep;126:244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon S. B., Morrison J. F. Spinal neurones with long projections activated from the abdominal viscera of the cat. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:1–20. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon S. B., Morrison J. F. Two group of spinal interneurones that respond to stimulation of the abdominal viscera of the cat. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:21–34. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson A. The effects of somatic stimuli on the bladder in the cat. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(1):185–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato A., Sato Y., Schmidt P. F. Effects on reflex bladder activity of chemical stimulation of small diameter afferents from skeletal muscle in the cat. Neurosci Lett. 1979 Jan;11(1):13–17. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(79)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundin T., Carlsson C. A., Kock N. G. Detrusor inhibition induced from mechanical stimulation of the anal region and from electrical stimulation of pudendal nerve afferents. An experimental study in cats. Invest Urol. 1974 Mar;11(5):374–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groat W. C., Ryall R. W. Reflexes to sacral parasympathetic neurones concerned with micturition in the cat. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):87–108. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


