Abstract
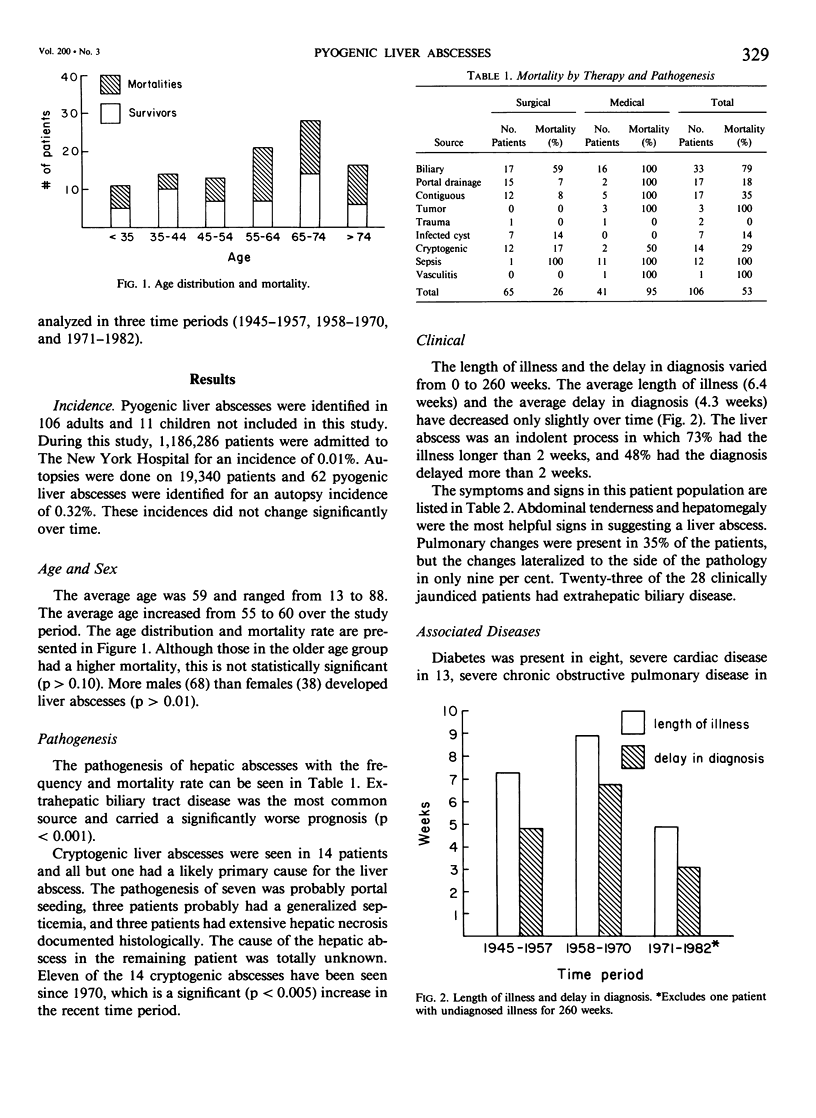
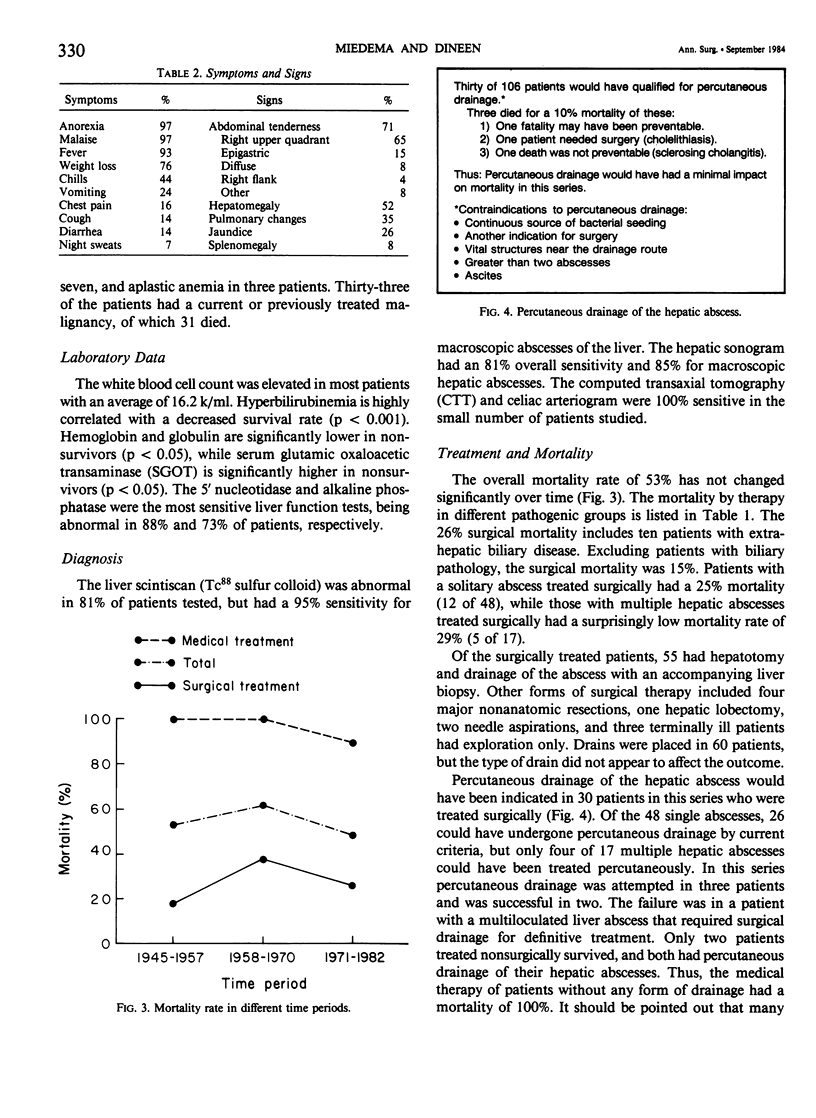
Pyogenic liver abscesses in 106 adult patients at The New York Hospital were reviewed to define optimum treatment. Mortality in the surgically treated patients was 26% (17/65), while those treated nonsurgically had a fatality rate of 95% (39/41). Multiple abscesses treated surgically had a surprisingly low mortality of 29% (5/17). Modern noninvasive tests are highly sensitive in diagnosing liver lesions greater than 2 cm. Difficulty remains in identifying small hepatic abscesses and differentiating large abscesses from tumor. Most liver abscesses have an identifiable source outside the liver. The most common source (31%) was cholangitis secondary to extrahepatic biliary obstruction. Multiple abscesses, mixed organisms, hyperbilirubinemia, and abscess complications are all associated with a significantly increased mortality. However, the lethality of the primary disease process was the most important factor determining survival. Most patients who have the underlying pathogenesis of the abscess controlled will survive surgical treatment. Transperitoneal surgical drainage and antibiotics remain the mainstay of treatment. Percutaneous drainage is recommended for high risk patients only.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altemeier W. A., Schowengerdt C. G., Whiteley D. H. Abscesses of the liver: surgical considerations. Arch Surg. 1970 Aug;101(2):258–266. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1970.01340260162025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOCK M. A., SCHUMAN B. M., EYLER W. R., TRUANT J. P., DUSAULT L. A. SURGERY OF LIVER ABSCESSES. USE OF NEWER TECHNIQUES TO REDUCE MORTALITY. Arch Surg. 1964 Apr;88:602–610. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1964.01310220092015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOURNE W. A. The diagnosis of pyogenic liver abscess. Lancet. 1954 Nov 27;267(6848):1093–1094. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(54)90651-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasegaram M. Management of hepatic abscess. Curr Probl Surg. 1981 May;18(5):282–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaver D. C. Granulomatous Abscess of the Liver of Pyogenic Origin. Am J Pathol. 1931 May;7(3):259–276.5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodine W. N., Schwartz S. I. Pyogenic hepatic abscess. N Y State J Med. 1973 Jun 15;73(12):1657–1661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T. J., McCarthy C. F. Pyogenic liver abscess. Gut. 1969 May;10(5):389–399. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.5.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRONIN K. Pyogenic abscess of the liver. Gut. 1961 Mar;2:53–59. doi: 10.1136/gut.2.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON G., Jr, GLENN F. Multiple liver abscesses following biliary tract surgery. Ann Surg. 1954 Aug;140(2):227–233. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195408000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph W. L., Kahn A. M., Longmire W. P., Jr Pyogenic liver abscess. Changing patterns in approach. Am J Surg. 1968 Jan;115(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(68)90130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlson K. B., Martin E. C., Fankuchen E. I., Schultz R. W., Casarella W. J. Percutaneous abscess drainage. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1982 Jan;154(1):44–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERMAN B., GARLOCK J. H., JANOWITZ H. D. Suppurative pylephlebitis with multiple liver abscesses complicating regional ileitis: review of literature--1940-1960. Ann Surg. 1962 Mar;155:441–448. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196203000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarchick J., De Souza e Silva N. A., Nichols D. R., Washington J. A., 2nd Pyogenic liver abscess. Mayo Clin Proc. 1973 May;48(5):349–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. F., Block G. E. The changing clinical pattern of hepatic abscesses. Arch Surg. 1972 Apr;104(4):465–470. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1972.04180040079014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher J. A., Jr, Reynolds T. B., Yellin A. E. Successful medical treatment of pyogenic liver abscess. Gastroenterology. 1979 Oct;77(4 Pt 1):618–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGDEN W. W., HUNTER P. R., RIVES J. D. Liver abscess. Postgrad Med. 1961 Jul;30:11–19. doi: 10.1080/00325481.1961.11694318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt H. A., Zuidema G. D. Factors influencing mortality in the treatment of pyogenic hepatic abscess. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1975 Feb;140(2):228–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg L., Rees A. M., Kronick D. A. An investigation of the educational needs of health sciences library manpower. IV. Characteristics of manpower in health sciences libraries. Bull Med Libr Assoc. 1971 Jan;59(1):31–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. H., Swartz M. N., Malt R. Hepatic abscess: changes in clinical, bacteriologic and therapeutic aspects. Am J Med. 1974 Oct;57(4):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERMAN J. D., ROBBINS S. L. Changing trends in the casuistics of hepatic abscess. Am J Med. 1960 Jun;28:943–950. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90203-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheinfeld A. M., Steiner A. E., Rivkin L. B., Dermer R. H., Shemesh O. N., Dolberg M. S. Transcutaneous drainage of abscesses of the liver guided by computed tomography scan. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1982 Nov;155(5):662–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparberg M., Gottschalk A., Kirsner J. B. Liver abscess complication regional enteritis: report of two cases. Gastroenterology. 1965 Nov;49(5):548–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR F. W. Regional enteritis complicated by pylephlebitis and multiple liver abscesses. Am J Med. 1949 Dec;7(6):838-40, illust. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(49)90423-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


