Abstract
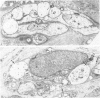
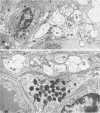
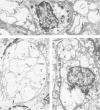
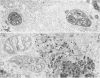
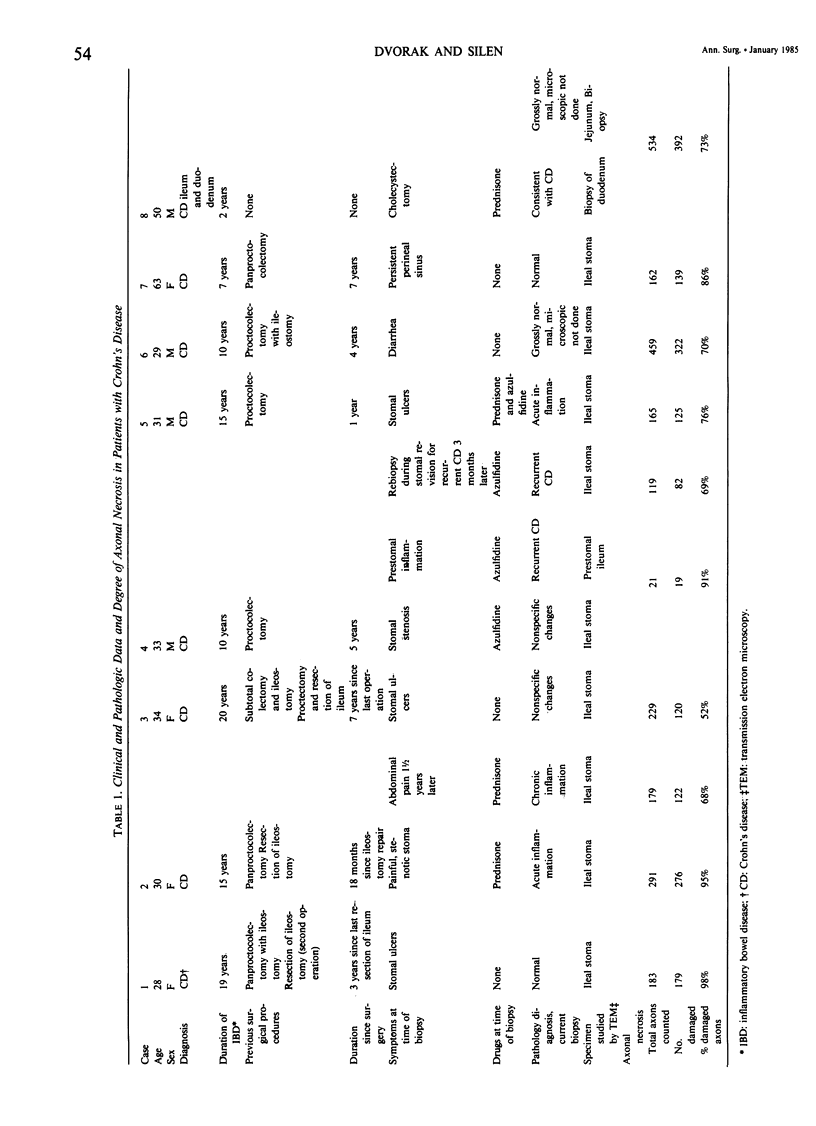
The authors previously have demonstrated axonal necrosis of autonomic nerves in the surgically resected ilea of patients with Crohn's disease both in grossly normal ileal resection margins and in diseased areas. The present study of ileal stomal biopsies was carried out to obviate the possibility that the observed axonal damage might be related to the prolonged surgical manipulations required for ileal resection. The authors present studies of biopsies of ileal stomas and of small bowel from patients with Crohn's disease and various control disorders, including ulcerative colitis. Stomal biopsies were fixed immediately after they were obtained. Widespread, severe axonal necrosis of autonomic nerves was present in all Crohn's disease specimens, regardless of the patient's clinical status or the gross or routine microscopic evaluation of the same specimen. Controls either had no necrosis or displayed a minor degree of focal necrosis involving single axons. The authors conclude that Crohn's disease is accompanied by a severe and extensive necrosis of gut axons, and that such electron microscopic findings may serve to differentiate Crohn's disease from other inflammatory disorders.
Full text
PDF
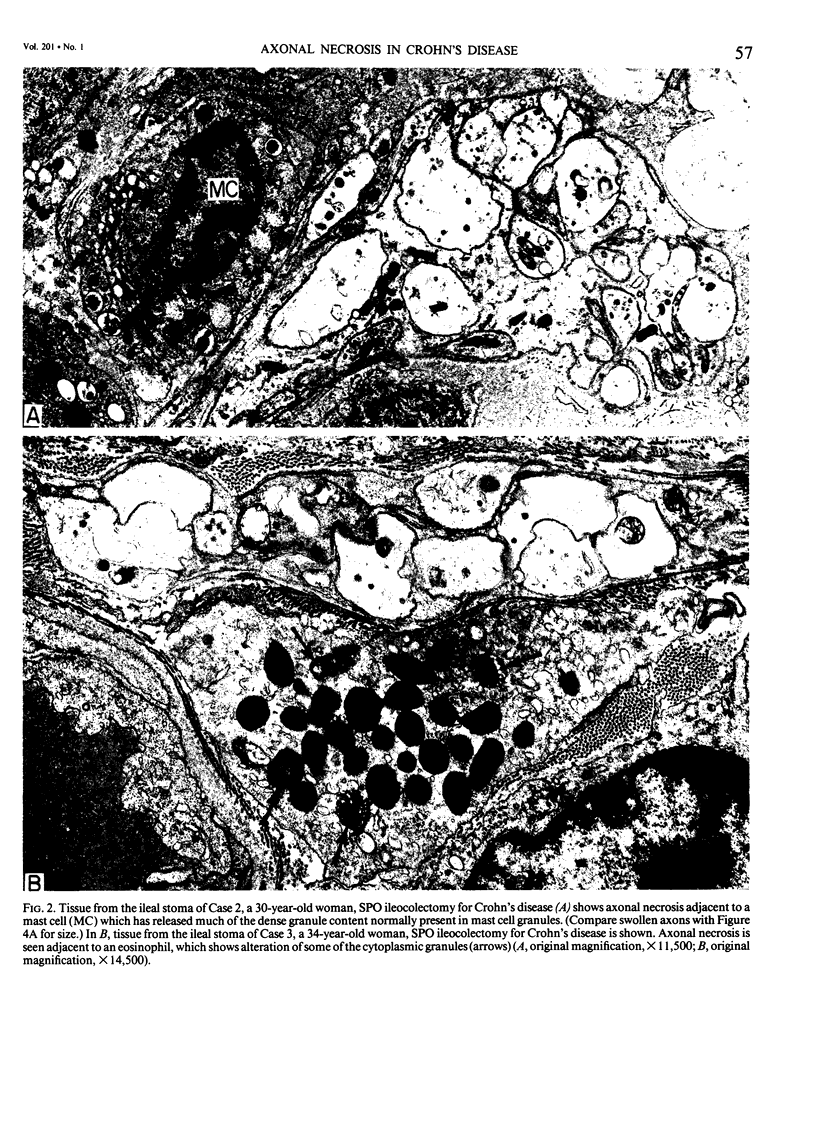
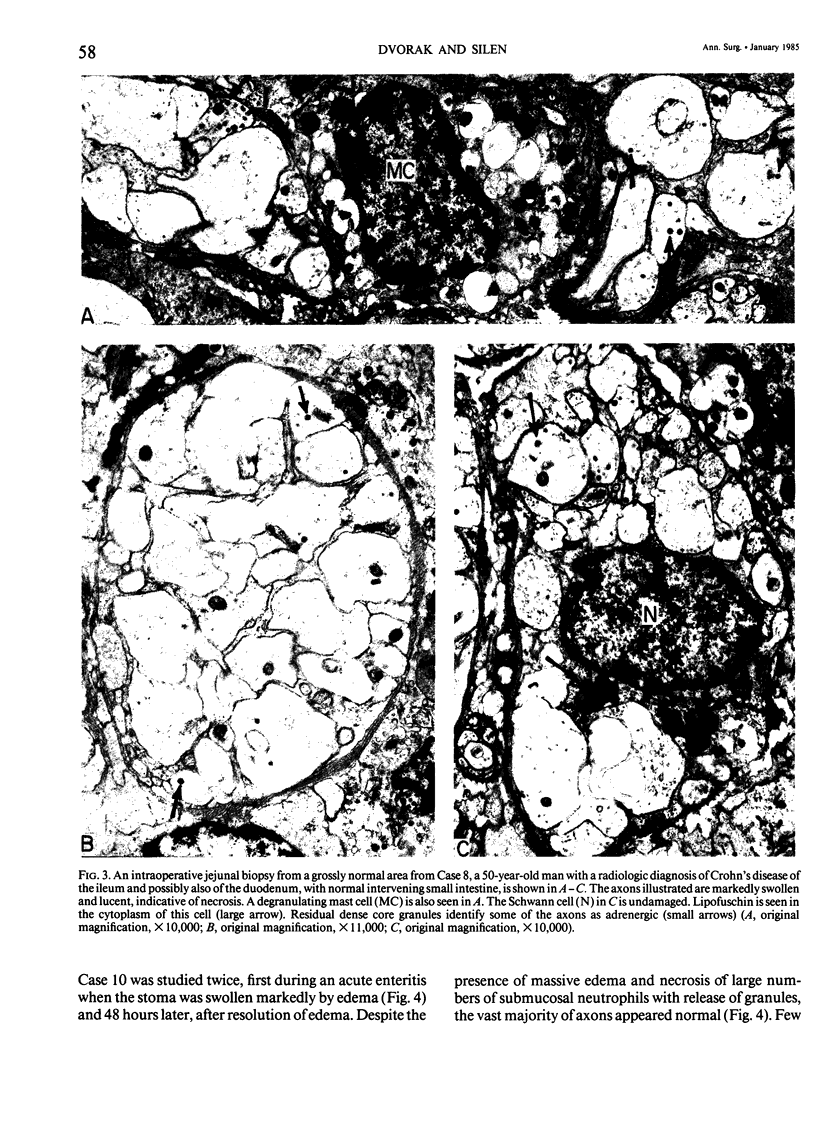
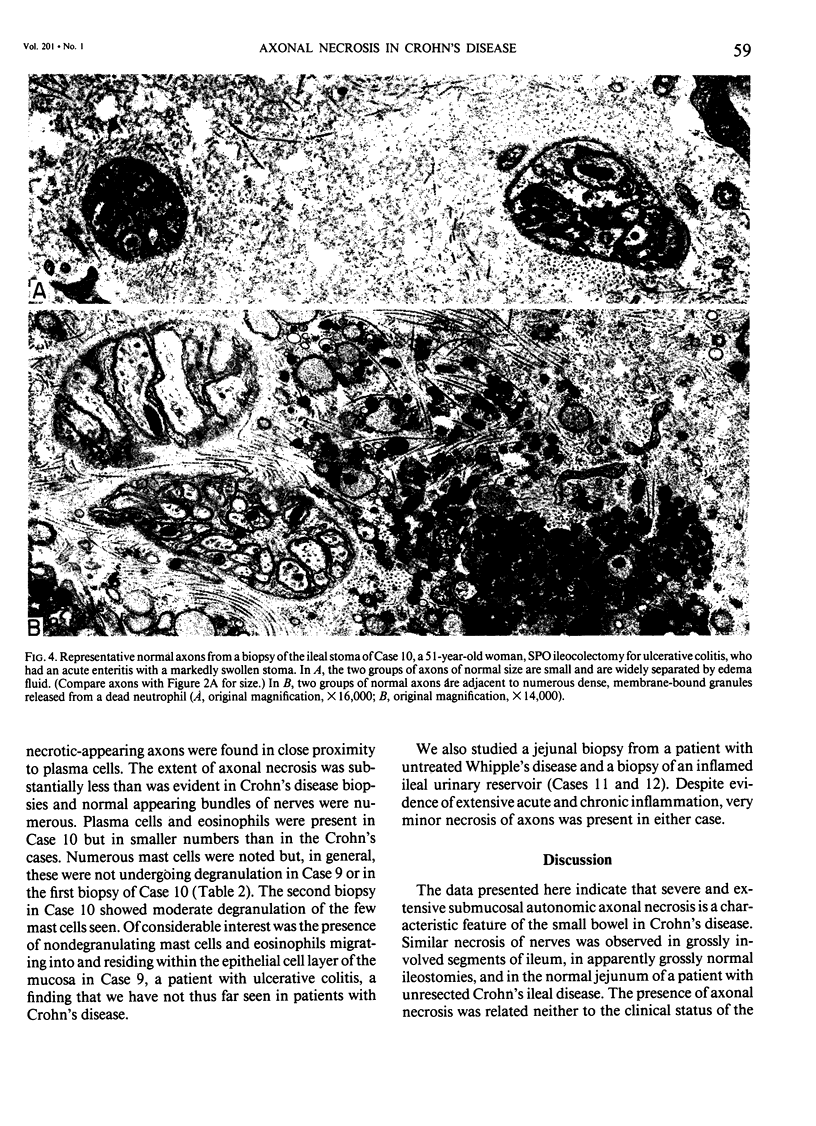
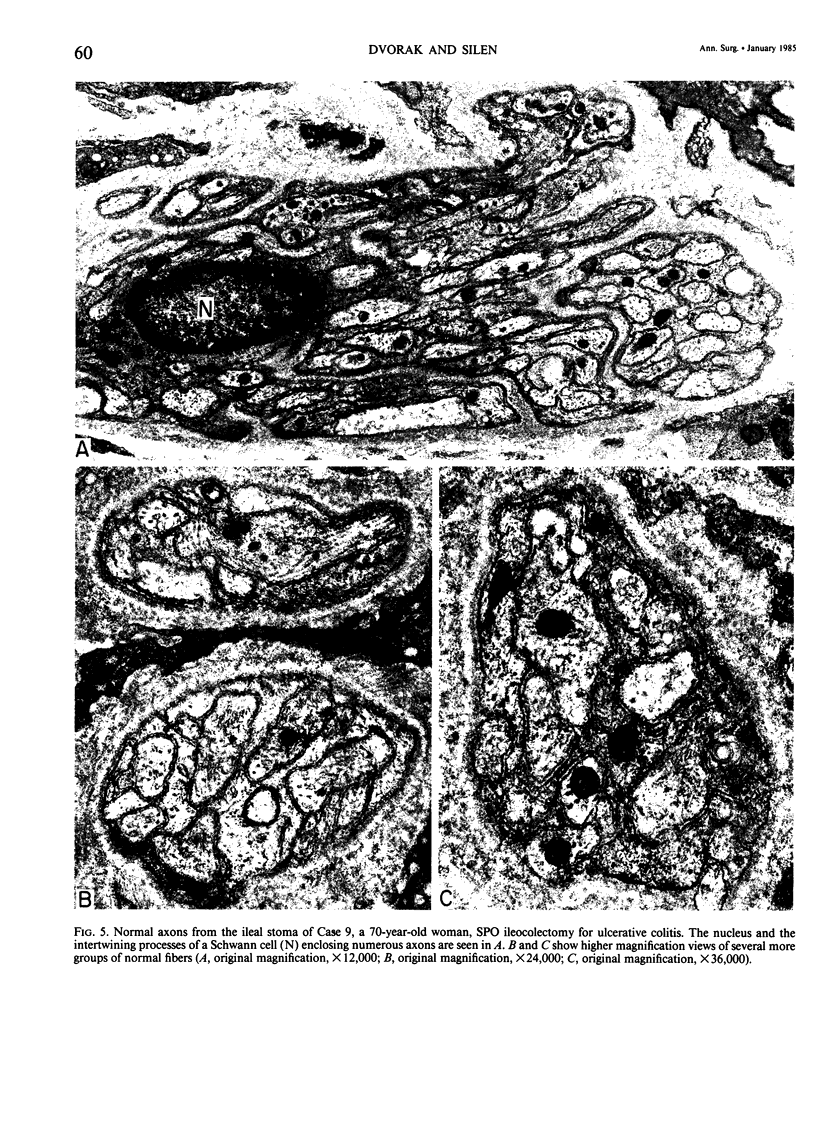



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTONIUS J. I., GUMP F. E., LATTES R., LEPORE M. A study of certain microscopic features in regional enteritis, and their possible prognostic significance. Gastroenterology. 1960 Jun;38:889–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustine G. J., Jr, Levitan H. Neurotransmitter release from a vertebrate neuromuscular synapse affected by a food dye. Science. 1980 Mar 28;207(4438):1489–1490. doi: 10.1126/science.6244619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignami A., Forno L. S. Status spongiosus in Jakob-Creutzfeldt disease. Electron microscopic study of a cortical biopsy. Brain. 1970;93(1):89–94. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop A. E., Polak J. M., Bryant M. G., Bloom S. R., Hamilton S. Abnormalities of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-containing nerves in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1980 Nov;79(5 Pt 1):853–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouldin T. W., Cavanagh J. B. Organophosphorous neuropathy. II. A fine-structural study of the early stages of axonal degeneration. Am J Pathol. 1979 Feb;94(2):253–270. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challa V. R., Jona J. Z., Markesbery W. R. Ultrastructural observations of the myenteric plexus of the pylorus in infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Am J Pathol. 1977 Aug;88(2):309–322. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. PURIFICATION OF A NERVE-GROWTH PROMOTING PROTEIN FROM THE MOUSE SALIVARY GLAND AND ITS NEURO-CYTOTOXIC ANTISERUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Mar;46(3):302–311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.3.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS D. R., DOCKERTY M. B., MAYO C. W. The myenteric plexus in regional enteritis: a study of the number of ganglion cells in the ileum in 24 cases. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1955 Aug;101(2):208–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Ackerman S. J., Loegering D. A., Gleich G. J. Purification of human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5165–5169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Dickersin G. R. Crohn's disease: transmission electron microscopic studies. I. Barrier function. Possible changes related to alterations of cell coat, mucous coat, epithelial cells, and Paneth cells. Hum Pathol. 1980 Sep;11(5 Suppl):561–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Dickersin G. R., Osage J. E., Monahan R. A. Absence of virus structures in Crohn's disease tissues studied by electron microscopy. Lancet. 1978 Feb 11;1(8059):328–328. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90098-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Monahan R. A., Osage J. E., Dickersin G. R. Crohn's disease: transmission electron microscopic studies. II. Immunologic inflammatory response. Alterations of mast cells, basophils, eosinophils, and the microvasculature. Hum Pathol. 1980 Nov;11(6):606–619. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(80)80072-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Osage J. E., Monahan R. A., Dickersin G. R. Crohn's disease: transmission electron microscopic studies. III. Target tissues. Proliferation of and injury to smooth muscle and the autonomic nervous system. Hum Pathol. 1980 Nov;11(6):620–634. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(80)80073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M. Ultrastructural evidence for release of major basic protein-containing crystalline cores of eosinophil granules in vivo: cytotoxic potential in Crohn's disease. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):460–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frigas E., Loegering D. A., Gleich G. J. Cytotoxic effects of the guinea pig eosinophil major basic protein on tracheal epithelium. Lab Invest. 1980 Jan;42(1):35–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Campbell G. R., Gillard S. M., Malmfors T., Cobb J. L., Burnstock G. Cellular studies of sympathetic denervation produced by 6-hydroxydopamine in the vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Jul;174(1):111–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek D. C. Unconventional viruses and the origin and disappearance of kuru. Science. 1977 Sep 2;197(4307):943–960. doi: 10.1126/science.142303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. W., Price D. L. Demyelination in experimental beta, beta'-iminodipropionitrile and hexacarbon neuropathies. Evidence for an axonal influence. Lab Invest. 1981 Aug;45(2):130–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper C. G., Gonatas J. O., Mizutani T., Gonatas N. K. Retrograde transport and effects of toxic ricin in the autonomic nervous system. Lab Invest. 1980 Apr;42(4):396–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herndon R. M., Coyle J. T. Selective destruction of neurons by a transmitter agonist. Science. 1977 Oct 7;198(4312):71–72. doi: 10.1126/science.197604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Ghatak N. R., Johnson A. B., Partnow M. J., Gomori A. J. Argentophilic plaques in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch Neurol. 1972 Jun;26(6):530–542. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490120070008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson G., Hallman H. Substance P counteracts neurotoxin damage on norepinephrine neurons in rat brain during ontogeny. Science. 1982 Jan 1;215(4528):75–77. doi: 10.1126/science.6171883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. J. The ultrastructural basis of capillary permeability studied with peroxidase as a tracer. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):213–236. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger D. T., Martin J. B. Brain peptides (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1981 Apr 16;304(16):944–951. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198104163041605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger L., Maxwell D. S. Wallerian degeneration in the optic nerve of a reptile: an electron microscopic study. Am J Anat. 1969 Jul;125(3):247–269. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001250302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMPERT P., BLUMBERG J. M., PENTSCHEW A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF DYSTROPHIC AXONS IN THE GRACILE AND CUNEATE NUCLEI OF VITAMIN E-DEFICIENT RATS. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1964 Jan;23:60–77. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196401000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W., Earle K. M., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Experimentak kuru encephalopathy in chimpanzees and spider monkeysElectron microscopic studies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1969 Jul;28(3):353–370. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196907000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr Experimental spongiform encephalopathy (Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease) in chimpanzees. Electron microscopic studies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1971 Jan;30(1):20–32. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197101000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeWitt P. A. The neurotoxicity of the rat poison vacor. A clinical study of 12 cases. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 10;302(2):73–77. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001103020202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Booker B. DESTRUCTION OF THE SYMPATHETIC GANGLIA IN MAMMALS BY AN ANTISERUM TO A NERVE-GROWTH PROTEIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Mar;46(3):384–391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.3.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor: its mode of action on sensory and sympathetic nerve cells. Harvey Lect. 1966;60:217–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley W. C., Server A. C., Ishii D. N., Riopelle R. J., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor (second of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 24;297(21):1149–1158. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711242972105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oki M., Daniel E. E. Effects of vagotomy on the ultrastructure of the nerves of dog stomach. Gastroenterology. 1977 Nov;73(5):1029–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parhad I. M., Griffin J. W., Price D. L., Clark A. W., Cork L. C., Miller N. R., Hoffman P. N. Intoxication with beta, beta' -iminodipropionitrile: a model of optic disc swelling. Lab Invest. 1982 Feb;46(2):186–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaitakis A., Berl S., Yahr M. D. Abnormal glutamate metabolism in an adult-onset degenerative neurological disorder. Science. 1982 Apr 9;216(4542):193–196. doi: 10.1126/science.6121377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prineas J. The pathogenesis of dying-back polyneuropathies. II. An ultrastructural study of experimental acrylamide intoxication in the cat. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1969 Oct;28(4):598–621. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196910000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum J. L., Keating J. P., Prensky A. L., Nelson J. S. A progressive neurologic syndrome in children with chronic liver disease. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 26;304(9):503–508. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102263040902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth C. D., Richardson K. C. Electron microscopical studies on axonal degeneration in the rat iris following ganglionectomy. Am J Anat. 1969 Mar;124(3):341–359. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001240305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI M. T., PELLEGRINODEIRALDI A., DEROBERTIS E. EARLY EFFECTS OF ANTISERUM AGAINST THE NERVE GROWTH FACTOR ON FINE STRUCTURE OF SYMPATHETIC NEURONS. Exp Neurol. 1965 Aug;12:370–383. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(65)90079-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. E., Nelson J. S., Johnson E. M., Jr Experimental diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Am J Pathol. 1981 May;103(2):210–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuffler M. D., Jonak Z. Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction caused by a degenerative disorder of the myenteric plexus: the use of Smith's method to define the neuropathology. Gastroenterology. 1982 Mar;82(3):476–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemers P. T., Dobbins W. O., 3rd The Meissner plexus in Crohn's disease of the colon. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1974 Jan;138(1):39–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sima A. A., Robertson D. M. Peripheral neuropathy in the diabetic mutant mouse. An ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1979 Jun;40(6):627–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M., Steinberg M. C. Wallerian degeneration: a reevaluation based on transected and colchicine-poisoned nerves in the Amphibian, Triturus. Am J Anat. 1972 Jan;133(1):51–83. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001330105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. Disorders of the myenteric plexus. Gut. 1970 Mar;11(3):271–274. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo J., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Autoantibodies against axonal neurofilaments in patients with Kuru and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Science. 1980 Oct 10;210(4466):190–193. doi: 10.1126/science.6997994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P. S., Sterman A. B., Horoupian D. S., Foulds M. M. Neurotoxic fragrance produces ceroid and myelin disease. Science. 1979 May 11;204(4393):633–635. doi: 10.1126/science.432669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P. S., Thomas P. K. Ultrastructural studies of the dying-back process. II. The sequestration and removal by Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes of organelles from normal and diseases axons. J Neurocytol. 1974 Dec;3(6):763–783. doi: 10.1007/BF01097197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Tranzer J. P. Chemical sympathectomy by selective destruction of adrenergic nerve endings with 6-Hydroxydopamine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1968;261(3):271–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00536990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley R. G., Blessing W. W., Reis D. J. Suicide transport: destruction of neurons by retrograde transport of ricin, abrin, and modeccin. Science. 1982 May 21;216(4548):889–890. doi: 10.1126/science.6177039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]