Abstract
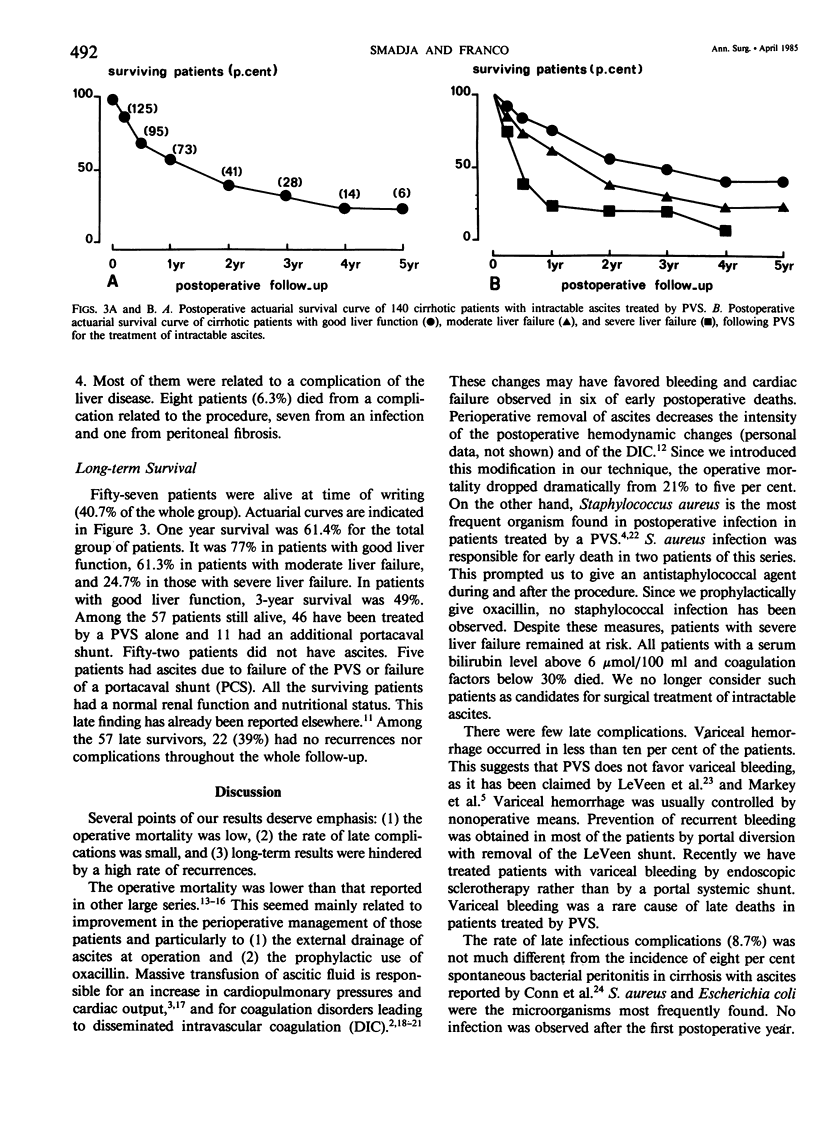
One hundred and forty patients with an intractable ascites complicating a chronic liver disease received a peritoneovenous shunt (PVS) using the LeVeen valve. Operative mortality was ten per cent but was 25% in patients with severe liver failure. Intraoperative drainage of ascites sharply decreased postoperative complications and mortality. One-year actuarial survival rate was 81.4%, respectively 77.7%, 61.3%, and 24.7% in patients with good liver function and moderate or severe liver failure. Variceal hemorrhage occurred in 11 patients and late infection in another 11 patients. Thirty-eight patients (30.5%) had recurrence of ascites. This was mostly due to an obstruction on the venous side of the shunt. An elective portacaval shunt had to be done in 23 patients for recurrence of ascites or variceal bleeding. Among the 57 patients still alive at time of writing, 51 were free of ascites. These results suggest that PVS is an efficient operation. This procedure may be largely indicated in the selected and small group of cirrhotic patients with true intractable ascites and moderate or no liver insufficiency.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernhoft R. A., Pellegrini C. A., Way L. W. Peritoneovenous shunt for refractory ascites: operative complications and long-term results. Arch Surg. 1982 May;117(5):631–635. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1982.01380290081014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blendis L. M., Greig P. D., Langer B., Baigrie R. S., Ruse J., Taylor B. R. The renal and hemodynamic effects of the peritoneovenous shunt for intractable hepatic ascites. Gastroenterology. 1979 Aug;77(2):250–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capone R. R., Buhac I., Kohberger R. C., Balint J. A. Resistant ascites in alcoholic liver cirrhosis: course and prognosis. Am J Dig Dis. 1978 Oct;23(10):867–871. doi: 10.1007/BF01072457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn H. O. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Multiple revisitations. Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):455–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darsee J. R., Fulenwider J. T., Rikkers L. F., Ansley J. D., Nordlinger B. F., Ivey G., Heymsfield S. B. Hemodynamics of LeVeen shunt pulmonary edema. Ann Surg. 1981 Aug;194(2):189–192. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198108000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupas J. L., Remond A., Vermynck J. P., Capron J. P., Lorriaux A. Superior vena cava thrombosis as a complication of peritoneovenous shunt. Gastroenterology. 1978 Nov;75(5):899–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhauser F. E., Strodel W. E., Knol J. A., Turcotte J. G. Superior vena caval obstruction associated with long-term peritoneovenous shunting. Ann Surg. 1979 Dec;190(6):758–760. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197912000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. Peritoneovenous shunt in the management of ascites and the hepatorenal syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1982 Apr;82(4):790–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco D., Charra M., Jeambrun P., Belghiti J., Cortesse A., Sossler C., Bismuth H. Nutrition and immunity after peritoneovenous drainage of intractable ascites in cirrhotic patients. Am J Surg. 1983 Nov;146(5):652–657. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(83)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco D., Cortesse A., Castro e Sousa F., Bismuth H. Dérivation péritonéo-jugulaire dans le traitement de l'ascite irréductible du cirrhotique : résultats chez 88 malades. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1981 Apr;5(4):393–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco D. Traitement de l'ascite irréductible du cirrhotique par la dérivation portale. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1983 May;7(5):533–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano J. L., Reinhardt G. F., Howell H. S., Hacker L. C., Stanley M. M. Clinical experience with autogenous ascitic fluid infusion for cirrhotic ascites. Am Surg. 1977 Aug;43(8):520–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee H. B., Stanley M. M., Reinhardt G. F. Intractable ascites treated with peritoneovenous shunts (LeVeen). A 24- to 64-month follow-up of results in 52 alcoholic cirrhotics. Arch Surg. 1981 May;116(5):518–524. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1981.01380170016003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig P. D., Langer B., Blendis L. M., Taylor B. R., Glynn M. F. Complications after peritoneovenous shunting for ascites. Am J Surg. 1980 Jan;139(1):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon D. C., Demirjian Z., Ellman L., Fischer J. E. Disseminated intravascular coagulation with the peritoneovenous shunt. Ann Intern Med. 1979 May;90(5):774–776. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-5-774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeVeen H. H., Vujic I., d'Ovidio N. G., Hutto R. B. Peritoneovenous shunt occlusion. Etiology, diagnosis, therapy. Ann Surg. 1984 Aug;200(2):212–223. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198408000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeVeen H. H., Wapnick S., Grosberg S., Kinney M. J. Further experience with peritoneo-venous shunt for ascites. Ann Surg. 1976 Nov;184(5):574–581. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197611000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. G., Nelson J. C., Corines P., del Guercio L. R. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Complication of LeVeen peritoneovenous shunts. JAMA. 1978 Nov 3;240(19):2064–2066. doi: 10.1001/jama.240.19.2064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leveen H. H., Christoudias G., Ip M., Luft R., Falk G., Grosberg S. Peritoneo-venous shunting for ascites. Ann Surg. 1974 Oct;180(4):580–591. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197410000-00023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund R. H., Moritz M. W. Complications of Denver peritoneovenous shunting. Arch Surg. 1982 Jul;117(7):924–928. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1982.01380310038009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markey W., Payne J. A., Straus A. Hemorrhage from esophageal varices after placement of the LeVeen shunt. Gastroenterology. 1979 Aug;77(2):341–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matseshe J. W., Beart R. W., Bartholomew L. G., Baldus W. P. Fatal disseminated intravascular coagulation after peritoneovenous shunt for intractable ascites. Mayo Clin Proc. 1978 Aug;53(8):526–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokesch R. C., Rimland D. Infectious complications of the peritoneovenous shunt. Am J Gastroenterol. 1983 Apr;78(4):235–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. L., Swaim W. R., Vogel S. B. Coagulopathy following peritoneovenous shunting. Surgery. 1979 Jun;85(6):671–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawes R. L., Jr, Sydorak G. R., Kennedy P. A., Brown W. H., Scribner R. G., Beare J. P., Harris E. J. Coagulopathy associated with peritoneovenous shunting. Am J Surg. 1981 Jul;142(1):51–55. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(81)80011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wapnick S., Grosberg S. J., Evans M. I. Randomized prospective matched pair study comparing peritoneovenous shunt and conventional therapy in massive ascites. Br J Surg. 1979 Sep;66(9):667–670. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800660924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney P. J., McDonald B. A., Ramsay E. G. Experience with the LeVeen valve shunt. Ariz Med. 1978 Sep;35(9):587–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormser G. P., Hubbard R. C. Peritonitis in cirrhotic patients with LeVeen shunts. Am J Med. 1981 Sep;71(3):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90151-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]