Abstract
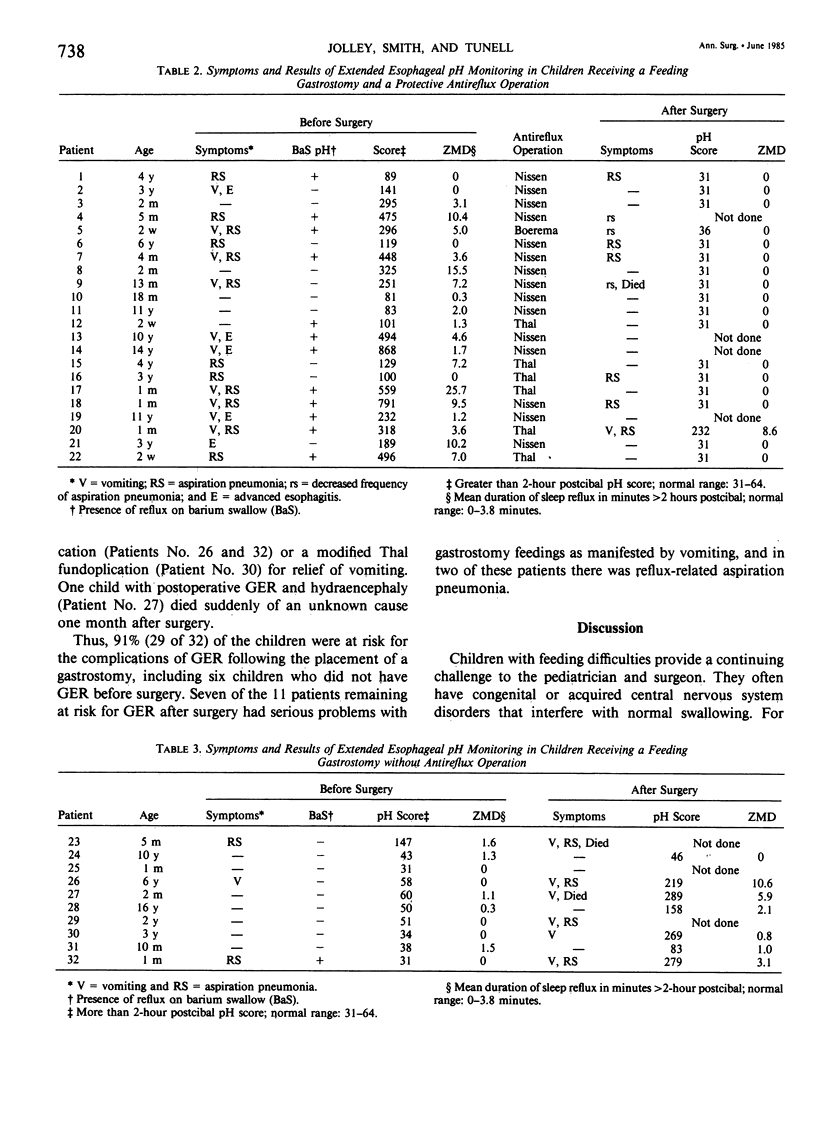
Regurgitation and aspiration of feedings is a significant problem in children with impaired oral intake fed via gastrostomy. Using extended (18-24 hour) esophageal pH monitoring to assess gastroesophageal reflux (GER), we studied prospectively 32 children (aged 2 to 16 years) referred for feeding gastrostomy. Twenty-five patients had repeat esophageal pH monitoring after surgery. Prior to surgery, GER was documented in 23 (72%) of the 32 children. Twenty-two of the 23 children with GER before surgery had an antireflux operation performed in conjunction with the feeding gastrostomy. Gastroesophageal reflux was clinically significant in the single failed antireflux operation and in the child with GER before surgery who only had a gastrostomy performed. All nine patients without GER only had gastrostomy performed. Six of these developed GER by pH monitoring after surgery, with significant vomiting in four. Of our 11 patients remaining at risk for GER after surgery, seven (64%) had persistent vomiting with gastrostomy feedings. Thus, 91% (29 of 32) of the children were potentially at risk for GER if a gastrostomy only was performed. We believe these data support the need for a "protective" antireflux operation in children referred for feeding gastrostomy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcraft K. W., Holder T. M., Amoury R. A. Treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in children by Thal fundoplication. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1981 Nov;82(5):706–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne W. J., Campbell M., Ashcraft E., Seibert J. J., Euler A. R. A diagnostic approach to vomiting in severely retarded patients. Am J Dis Child. 1983 Mar;137(3):259–262. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1983.02140290045012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne W. J., Euler A. R., Ashcraft E., Nash D. G., Seibert J. J., Golladay E. S. Gastroesophageal reflux in the severely retarded who vomit: criteria for and results of surgical intervention in twenty-two patients. Surgery. 1982 Jan;91(1):95–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G., Jolley S. G. Gastroesophageal reflux in infants and children. Recognition and treatment. Surg Clin North Am. 1981 Oct;61(5):1101–1115. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)42534-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolley S. G., Herbst J. J., Johnson D. G., Matlak M. E., Book L. S. Esophageal pH monitoring during sleep identifies children with respiratory symptoms from gastroesophageal reflux. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jun;80(6):1501–1506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolley S. G., Johnson D. G., Herbst J. J., Pena A., Garnier R. An assessment of gastroesophageal reflux in children by extended pH monitoring of the distal esophagus. Surgery. 1978 Jul;84(1):16–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolley S. G., Tunell W. P., Carson J. A., Smith E. I., Grunow J. The accuracy of abbreviated esophageal pH monitoring in children. J Pediatr Surg. 1984 Dec;19(6):848–854. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(84)80383-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raventos J. M., Kralemann H., Gray D. B. Mortality risks of mentally retarded and mentally ill patients after a feeding gastrostomy. Am J Ment Defic. 1982 Mar;86(5):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sondheimer J. M., Morris B. A. Gastroesophageal reflux among severely retarded children. J Pediatr. 1979 May;94(5):710–714. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80135-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunell W. P., Smith E. I., Carson J. A. Gastroesophageal reflux in childhood. The dilemma of surgical success. Ann Surg. 1983 May;197(5):560–565. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198305000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesley J. R., Coran A. G., Sarahan T. M., Klein M. D., White S. J. The need for evaluation of gastroesophageal reflux in brain-damaged children referred for feeding gastrostomy. J Pediatr Surg. 1981 Dec;16(6):866–871. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(81)80836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. D., Dudgeon D. L., Sondheimer J. M. A comparison of medical and surgical treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in severely retarded children. J Pediatr. 1981 Aug;99(2):202–205. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80450-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


