Abstract
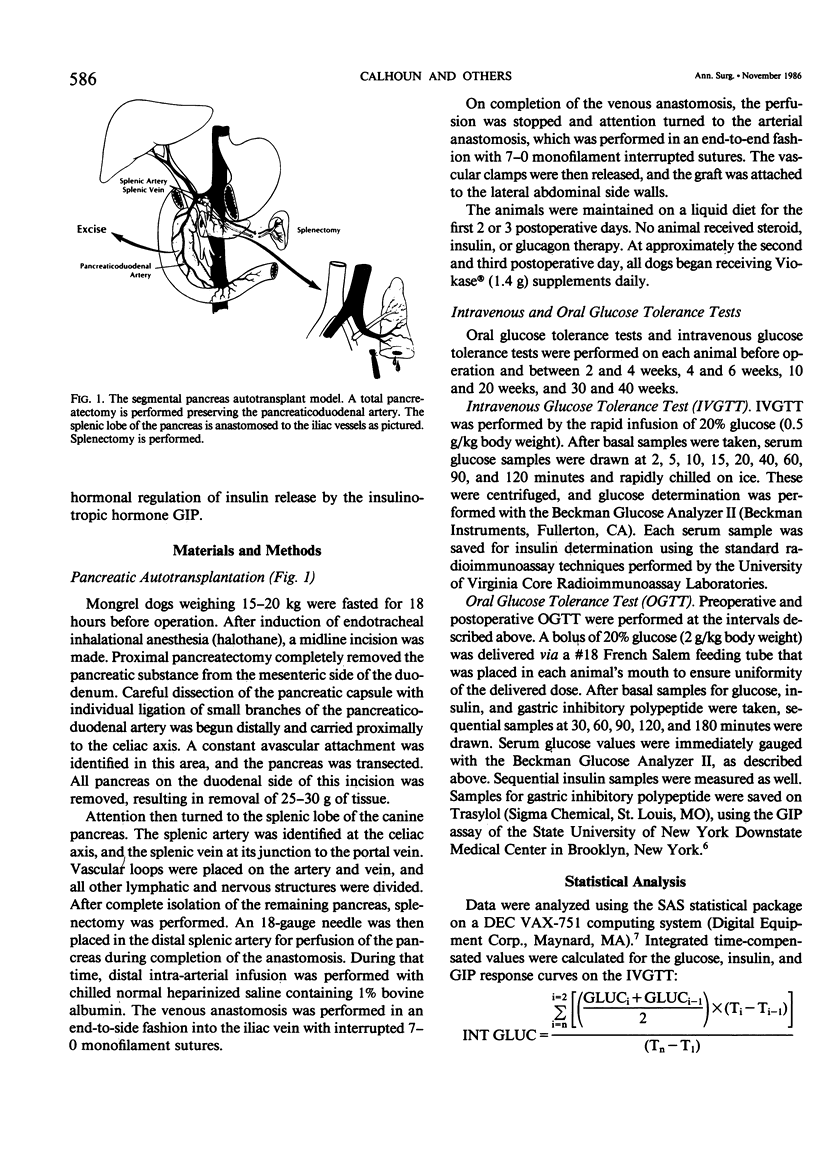
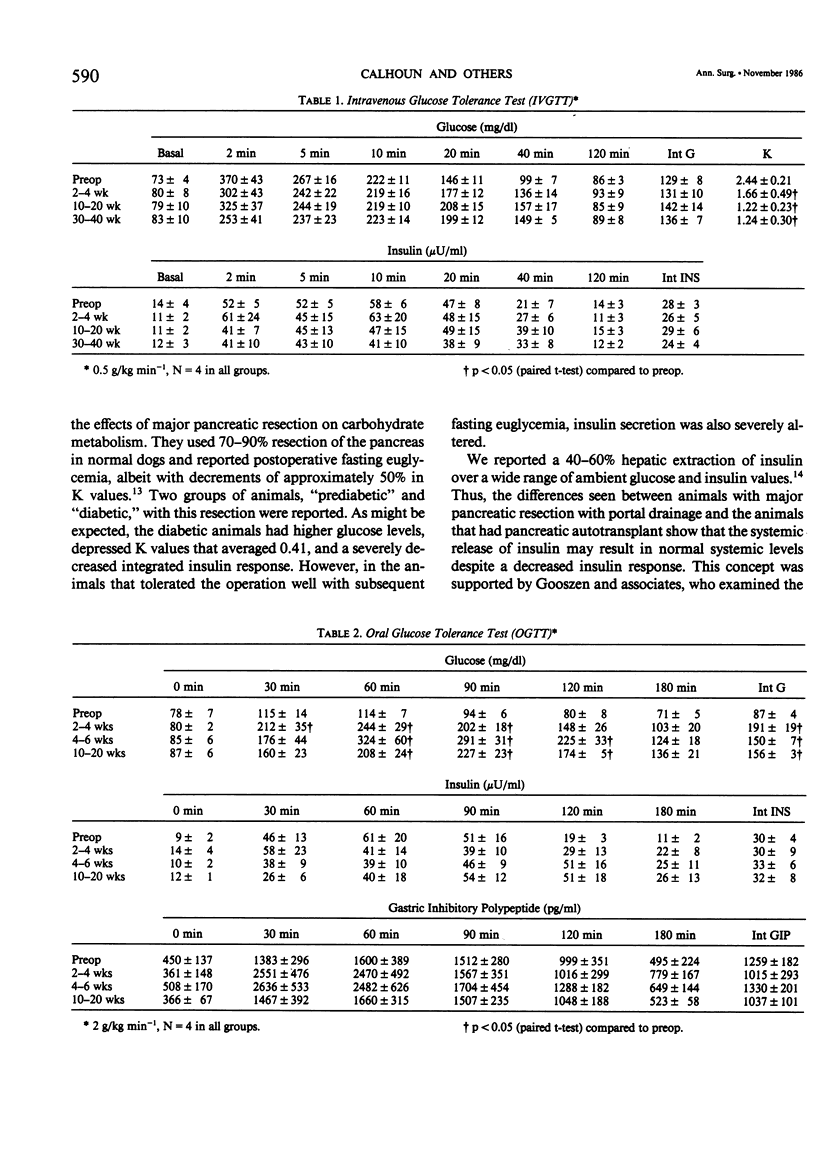
Segmental pancreatic autotransplantation is accompanied by surgical alterations to the pancreas that may have consequences for carbohydrate metabolism. Four mongrel dogs were evaluated before operation and sequentially until 40 weeks after total pancreatectomy and autotransplantation of the splenic lobe of the pancreas with bolus intravenous and oral administration. Intravenous glucose tolerance test (IVGTT) (0.5 g/kg) revealed maintenance of fasting euglycemia for as long as 40 weeks after operation. Peak glucose and integrated glucose values did not show significant changes as a result of autotransplantation. Following transplantation, a delayed peak insulin response was seen; however, basal, peak, and integrated insulin values were largely unaltered. Only K values, a measure of glucose disposal, showed severe alterations (2.44 +/- 0.21 before operation to 1.24 +/- 0.30 at 40 weeks after operation). Oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT) (2.0 g/kg) demonstrated an increased peak hyperglycemic response after autotransplantation with increased integrated glucose responses. Insulin levels remained at those levels seen before operation, and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) responses were unchanged during the OGTT as late as 20 weeks after operation. In conclusion, pancreas autotransplantation after total pancreatectomy results in significant metabolic alterations that the IVGTT fails to detect with absolute glucose or insulin levels. However, K values are significantly lowered, which indicates alterations in cellular glucose transport. The OGTT demonstrates hyperglycemia without increased insulin or GIP levels, which suggests an altered beta cell response to the enteric stimulus of insulin release. These changes are nonetheless well tolerated by animals that have remained clinically healthy and euglycemic in the basal state.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abumrad N. N., Cherrington A. D., Williams P. E., Lacy W. W., Rabin D. Absorption and disposition of a glucose load in the conscious dog. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jun;242(6):E398–E406. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.242.6.E398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen D. K., Elahi D., Brown J. C., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Oral glucose augmentation of insulin secretion. Interactions of gastric inhibitory polypeptide with ambient glucose and insulin levels. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):152–161. doi: 10.1172/JCI109100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bewick M., Mundy A. R., Eaton B., Watson F. Endocrine function of the heterotopic pancreatic allotransplant in dogs. II. Immediate post-transplant period. Transplantation. 1981 Jan;31(1):19–22. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198101000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. C., Dryburgh J. R., Ross S. A., Dupré J. Identification and actions of gastric inhibitory polypeptide. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1975;31:487–532. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571131-9.50017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. C., Pederson R. A., Jorpes E., Mutt V. Preparation of highly active enterogastrone. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;47(1):113–114. doi: 10.1139/y69-020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A. D., Chiasson J. L., Liljenquist J. E., Jennings A. S., Keller U., Lacy W. W. The role of insulin and glucagon in the regulation of basal glucose production in the postabsorptive dog. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1407–1418. doi: 10.1172/JCI108596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church D. B. A comparison of intravenous and oral glucose tolerance tests in the dog. Res Vet Sci. 1980 Nov;29(3):353–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleator I. G., Gourlay R. H. Release of immunoreactive gastric inhibitory polypeptide (IR-GIP) by oral ingestion of food substances. Am J Surg. 1975 Aug;130(2):128–135. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(75)90360-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupre J., Ross S. A., Watson D., Brown J. C. Stimulation of insulin secretion by gastric inhibitory polypeptide in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Nov;37(5):826–828. doi: 10.1210/jcem-37-5-826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyse E. J., Kiene S., Brinckmann W., Fischer U. Plasma insulin and glucose tolerance in pancreatectomized dogs after autologous partial pancreas transplantation. Loss of the insulinogenic reflex after oGTT and meal feeding. Horm Metab Res. 1982 Oct;14(10):521–525. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1019066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooszen H. G., van Schilfgaarde R., Frölich M., Van der Burg M. P. The effects of duct obliteration and of autotransplantation on the endocrine function of canine pancreatic segments. Diabetes. 1985 Oct;34(10):1008–1013. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.10.1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks J. B., Andersen D. K., Wise J. E., Putnam W. S., Meyers W. C., Jones R. S. The hepatic extraction of gastric inhibitory polypeptide and insulin. Endocrinology. 1984 Sep;115(3):1011–1018. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-3-1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings A. S., Cherrington A. D., Liljenquist J. E., Keller U., Lacy W. W., Chiasson J. L. The roles of insulin and glucagon in the regulation of gluconeogenesis in the postabsorptive dog. Diabetes. 1977 Sep;26(9):847–856. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.9.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzio M., Dryburgh J. R., Malloy K. M., Brown J. C. Radioimmunoassay for gastric inhibitory polypeptide. Gastroenterology. 1974 Mar;66(3):357–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakides G. K., Rabinovitch A., Mintz D., Olson L., Rapaport F. T., Miller J. Long-term study of vascularized free-draining intraperitoneal pancreatic segmental allografts in beagle dogs. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):292–303. doi: 10.1172/JCI110026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizumoto R., Kawarada Y., Goshima H., Tamaki H., Sekoguchi T., Tomikawa I. Carbohydrate metabolism and endocrine function in the pancreas remnant after major pancreatic resection. Am J Surg. 1982 Feb;143(2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(82)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore B. On the treatment of Diabetus mellitus by acid extract of Duodenal Mucous Membrane. Biochem J. 1906;1(1):28–38. doi: 10.1042/bj0010028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munda R., Berlatzky Y., Jonung M., Murphy R. F., Brackett K., Joffe S. N., Alexander J. W. Studies on segmental pancreatic autotransplants in dogs. Arch Surg. 1983 Nov;118(11):1310–1315. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1983.01390110058013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M. J., Kipnis D. M. Plasma insulin responses to oral and intravenous glucose: studies in normal and diabetic sujbjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1954–1962. doi: 10.1172/JCI105685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottiers R., Mattheeuws D., Kaneko J. J., Vermeulen A. Glucose uptake and insulin secretory responses to intravenous glucose loads in the dog. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Jan;42(1):155–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strubbe J. H. Effects of pancreas transplantation on insulin secretion in the rat during ingestion of varying glucose loads. Diabetologia. 1982 May;22(5):354–357. doi: 10.1007/BF00253581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y. S., Brunicardi F. C., Druck P., Walfisch S., Berlin S. A., Chance R. E., Gingerich R. L., Elahi D., Andersen D. K. Reversal of abnormal glucose metabolism in chronic pancreatitis by administration of pancreatic polypeptide. Am J Surg. 1986 Jan;151(1):130–140. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(86)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland D. E., Goetz F. C., Najarian J. S. One hundred pancreas transplants at a single institution. Ann Surg. 1984 Oct;200(4):414–440. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198410000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland D. E., Najarian J. S., Greenberg B. Z., Senske B. J., Anderson G. E., Francis R. S., Goetz F. C. Hormonal and metabolic effects of a pancreatic endocrine graft. Vascularized segmental transplantation in insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Nov;95(5):537–541. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-5-537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




