Abstract
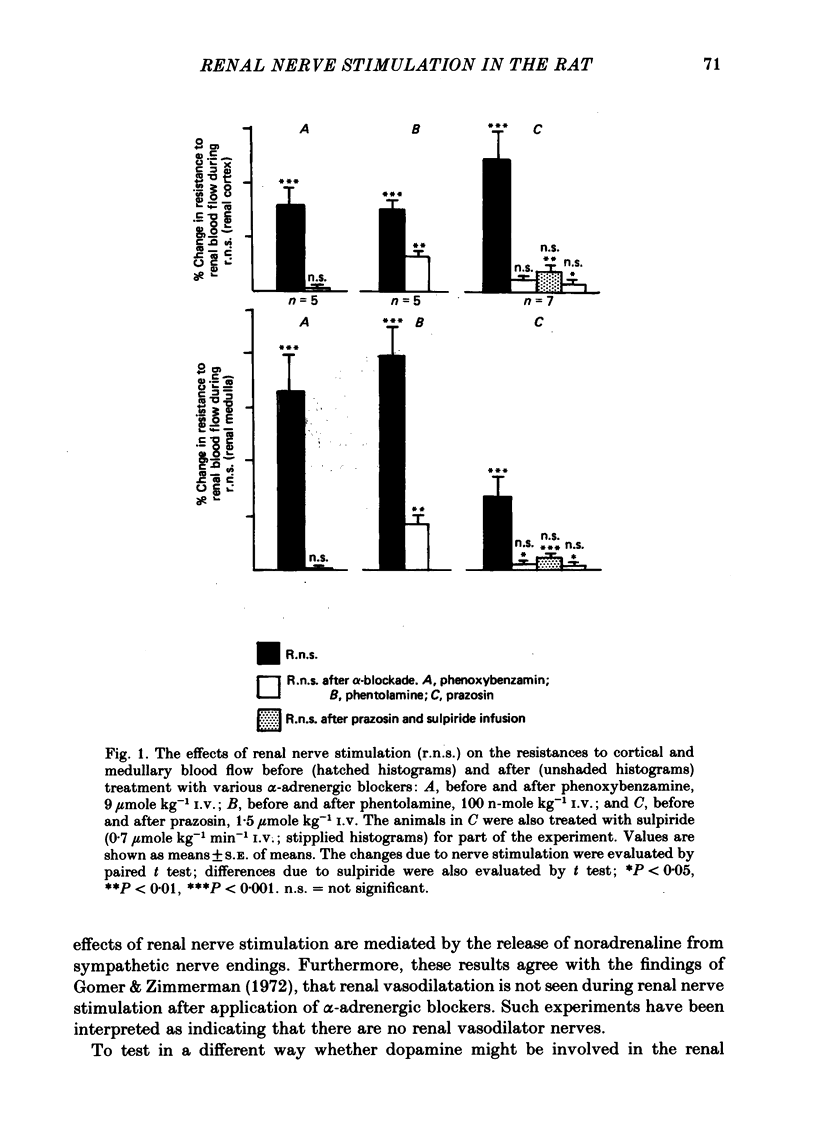
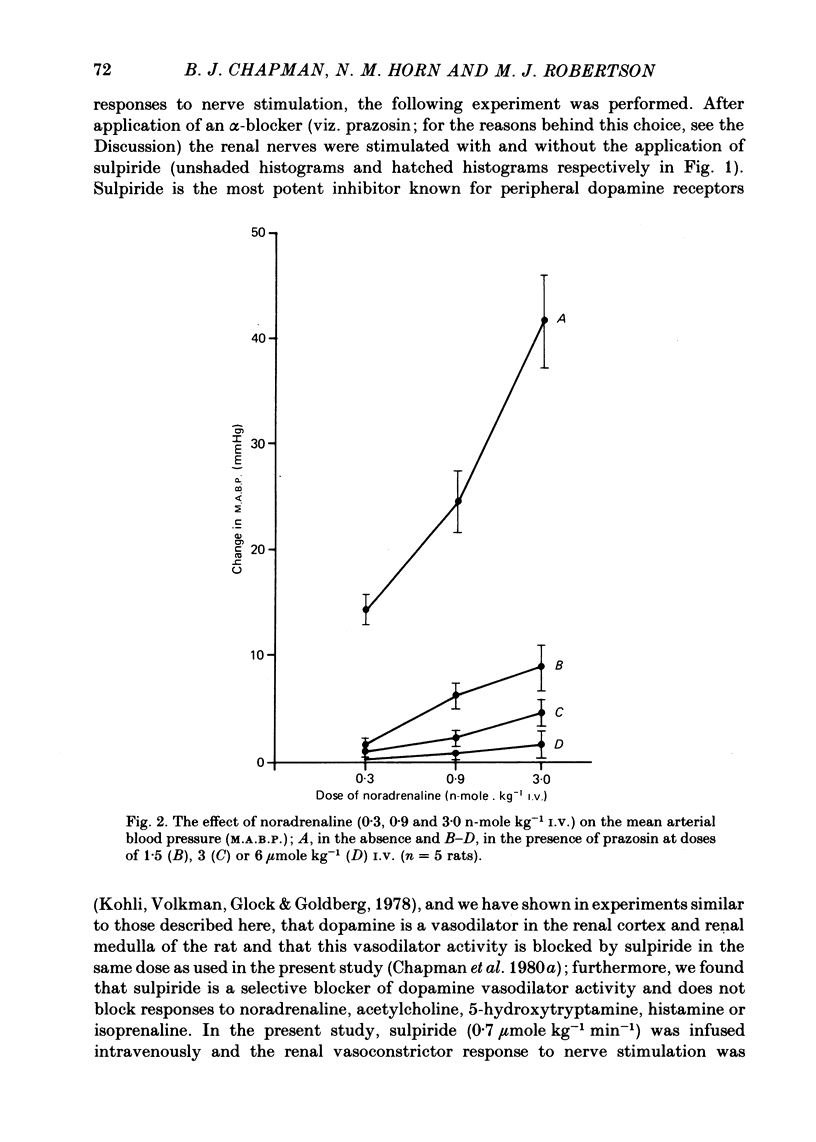
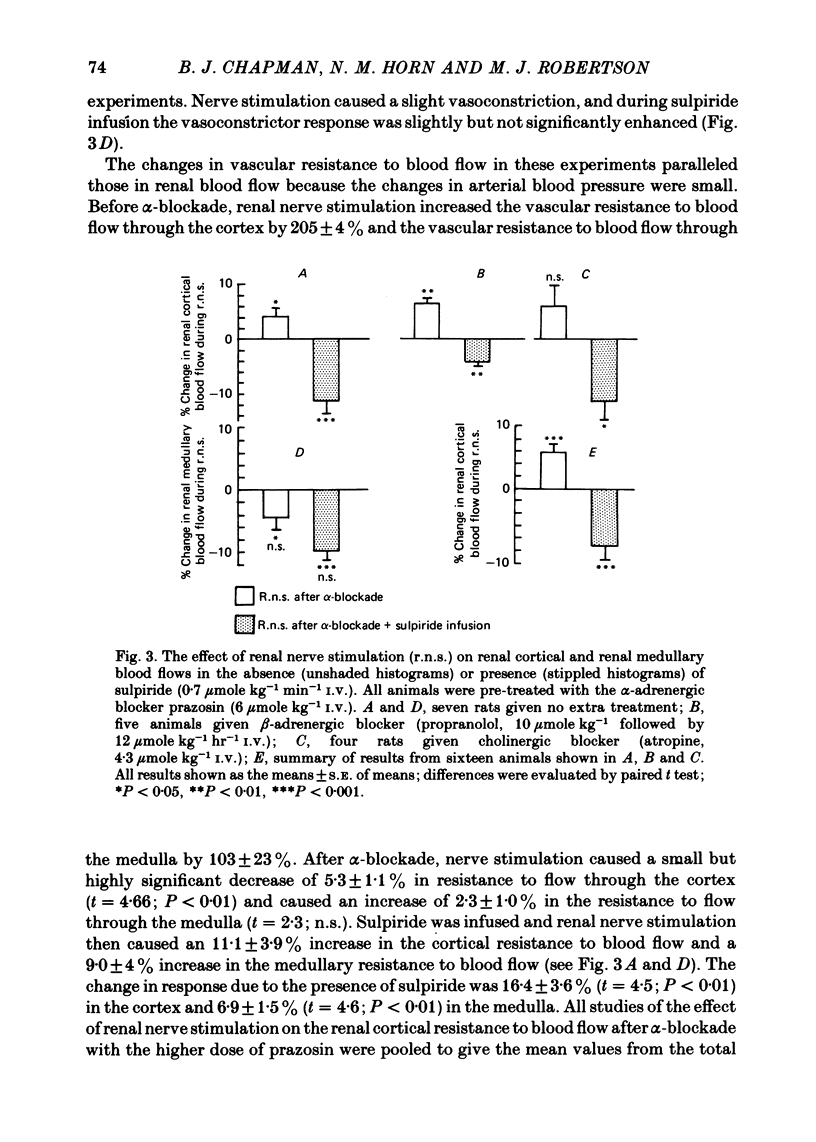
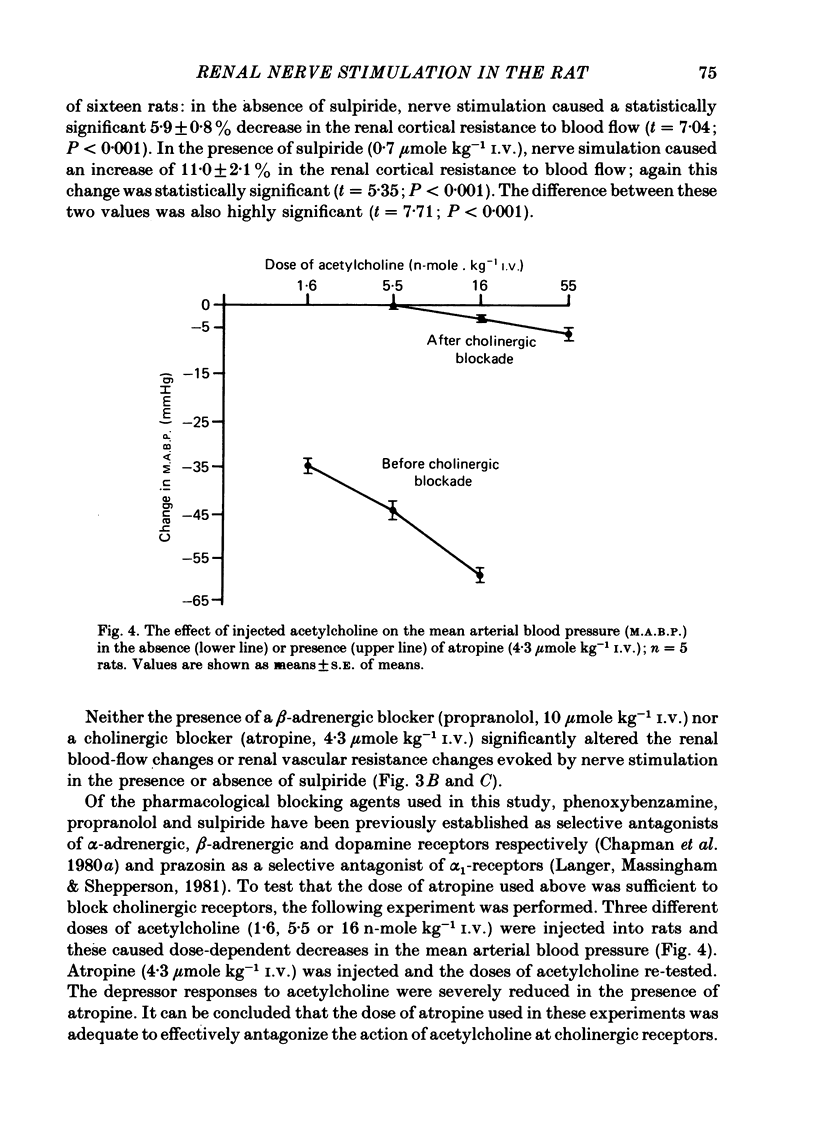
1. Blood flow through the inner cortex and outer medulla of the rat kidney was measured by the hydrogen wash-out technique. 2. Renal nerve stimulation caused vasoconstriction in both cortex and medulla. This constriction was abolished or reduced by phenoxybenzamine (9 mumole/kg I.V.), phentolamine (100 n-mole/kg) or prazosin (1.5 mumole/kg). 3. After prazosin (6 mumole/kg I.V.), renal nerve stimulation caused small but significant renal cortical vasodilatation. This vasodilatation was reversed by sulpiride (0.7 mumole kg-1 min-1), but was unaffected by propranolol (10 mumole/kg) or atropine (4.3 mumole/kg). 4. These results indicate the existence of dopaminergic vasodilator nerves to the renal cortex of the rat.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTON A. H., SAYRE D. F. THE DISTRIBUTION OF DOPAMINE AND DOPA IN VARIOUS ANIMALS AND A METHOD FOR THEIR DETERMINATION IN DIVERSE BIOLOGICAL MATERIAL. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Sep;145:326–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander R. W., Gill J. R., Jr, Yamabe H., Lovenberg W., Keiser H. R. Effects of dietary sodium and of acute saline infusion on the interrelationship between dopamine excretion and adrenergic activity in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jul;54(1):194–200. doi: 10.1172/JCI107743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball S. G., Lee M. R. The effect of carbidopa administration on urinary sodium excretion in man. Is dopamine an intrarenal natriuretic hormone? Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1977 Apr;4(2):115–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1977.tb00681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C., Lang W. J., Laska F. Dopamine-containing vasomotor nerves in the dog kidney. J Neurochem. 1978 Jul;31(1):77–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb12435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C., Lang W. J. Neural dopaminergic vasodilator control in the kidney. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 7;246(149):27–29. doi: 10.1038/newbio246027a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman B. J., Horn N. M., Munday K. A., Robertson M. J. Changes in renal blood flow in the rat during renal nerve stimulation: the effects of alphs-adrenergic blockers and a dopaminergic blocker [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Jun;291:64P–65P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman B. J., Horn N. M., Munday K. A., Robertson M. J. The actions of dopamine and of sulpiride on regional blood flows in the rat kidney. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:437–452. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. H., Johns E. J., Macleod V. H., Singer B. Effect of renal nerve stimulation, renal blood flow and adrenergic blockade on plasma renin activity in the cat. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(1):15–36. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuche J. L., Kuchel O., Barbeau A., Boucher R., Genest J. Relationship between the adrenergic nervous system and renin during adaptation to upright posture: a possible role for 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine (dopamine). Clin Sci. 1972 Oct;43(4):481–491. doi: 10.1042/cs0430481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinerstein R. J., Vannice J., Henderson R. C., Roth L. J., Goldberg L. I., Hoffmann P. C. Histofluorescence techniques provide evidence for dopamine-containing neuronal elements in canine kidney. Science. 1979 Aug 3;205(4405):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.451614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN H. D., KEPCHAR J. H. Control of peripheral resistance in major systemic vascular beds. Physiol Rev. 1959 Jul;39(3):617–686. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1959.39.3.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN H. D., KEPCHAR J. H. Control of peripheral resistance in major systemic vascular beds. Physiol Rev. 1959 Jul;39(3):617–686. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1959.39.3.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg L. I., Kohli J. D., Kotake A. N., Volkman P. H. Characteristics of the vascular dopamine receptor: comparison with other receptors. Fed Proc. 1978 Aug;37(10):2396–2402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomer S. K., Zimmerman B. G. Determination of sympathetic vasodilator responses during renal nerve stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Apr;181(1):75–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCDONALD R. H., Jr, GOLDBERG L. I., MCNAY J. L., TUTTLE E. P., Jr EFFECT OF DOPAMINE IN MAN: AUGMENTATION OF SODIUM EXCRETION, GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE, AND RENAL PLASMA FLOW. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jun;43:1116–1124. doi: 10.1172/JCI104996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Burns R. B., Blumenthal M. R. Role of acetylcholine in the renal vasoconstrictor response to sympathetic nerve stimulation in the dog. Circ Res. 1967 Jun;20(6):616–629. doi: 10.1161/01.res.20.6.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oates N. S., Ball S. G., Perkins C. M., Lee M. R. Plasma and urine dopamine in man given sodium chloride in the diet. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Mar;56(3):261–264. doi: 10.1042/cs0560261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi J., Aoki S., Nomura G., Mizumura Y., Shimizu H. Nervous control of renal circulation--on the existence of sympathetic cholinergic fibers. J Appl Physiol. 1971 Nov;31(5):686–692. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.31.5.686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


