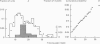Abstract
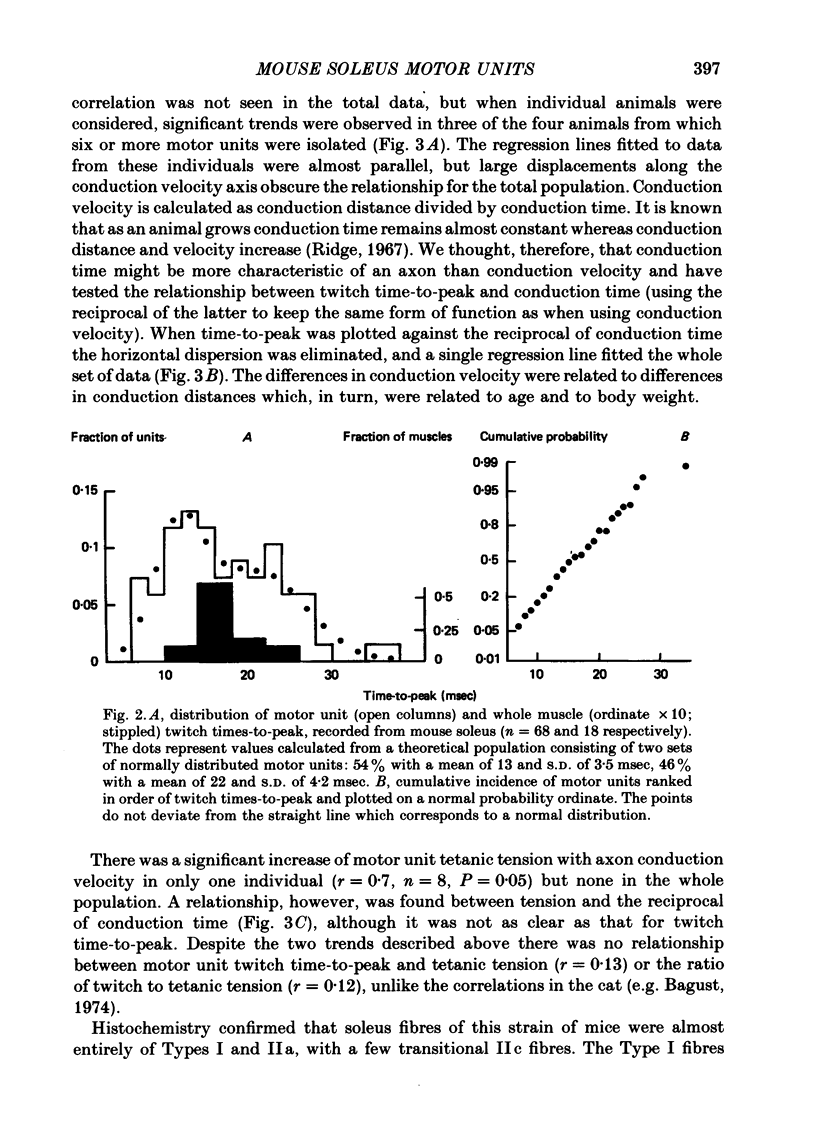
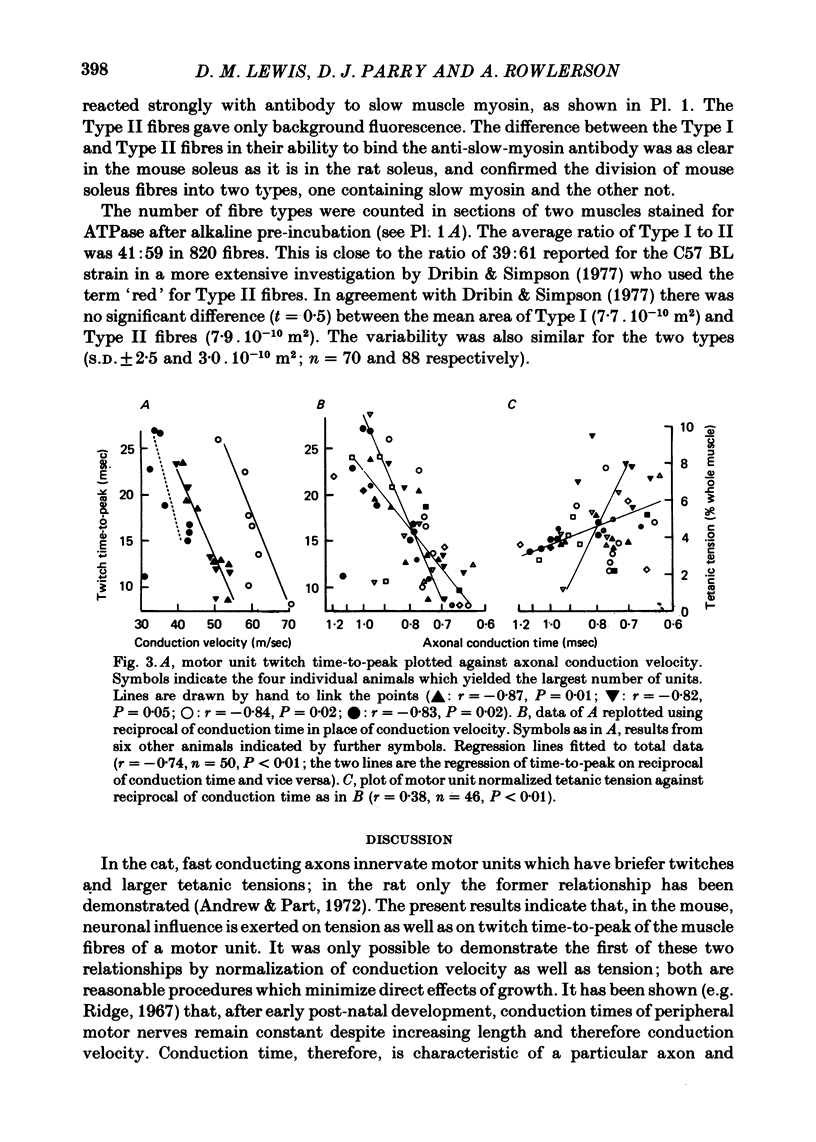
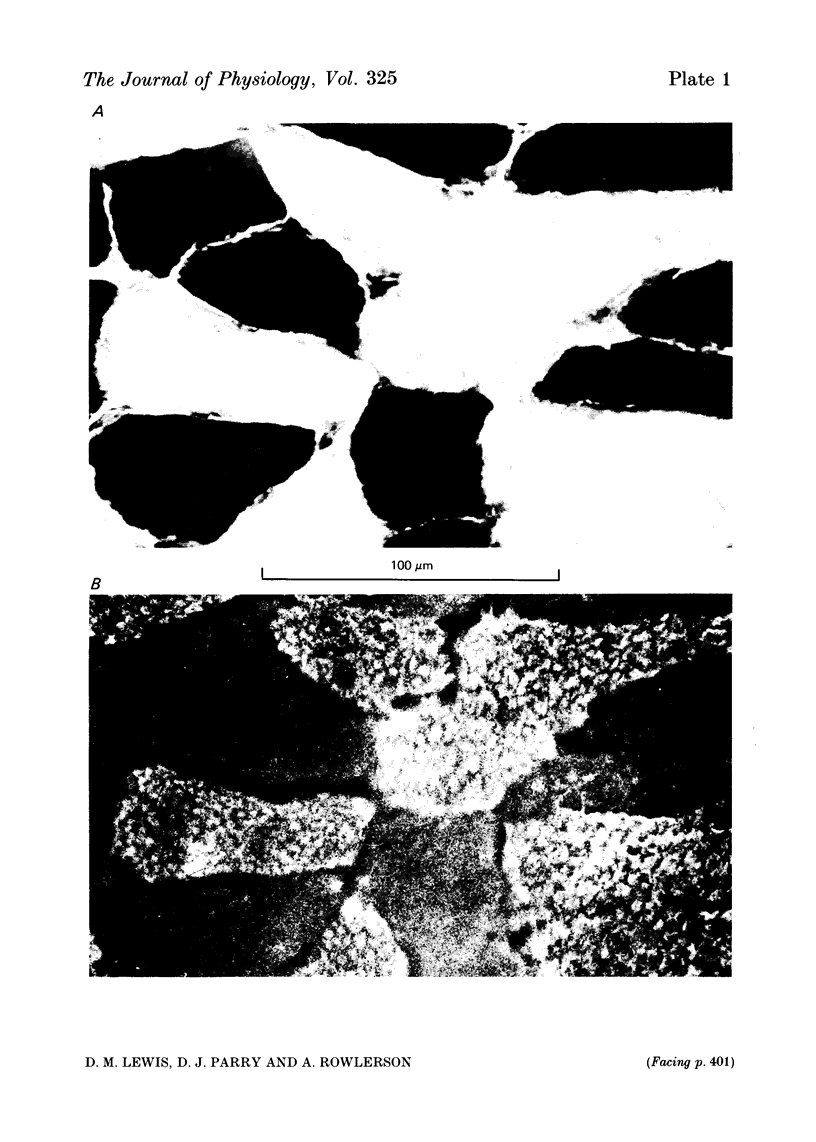
1. Isometric contractions of motor units, isolated functionally by ventral root splitting in vivo, were recorded from mouse soleus muscle. 2. Motor unit tensions varied over a narrow symmetrical range and averaged 4.7% of whole muscle tension, corresponding to twenty-one motor units per muscle. 3. There was considerable variation between muscles in isometric twitch times-to-peak and even greater variation for the motor units. The distribution of motor unit times-to-peak was apparently unimodal and could be fitted by a single normal population. A slightly better fit was, however, obtained with two normal populations, as suggested by the histochemistry. 4. Twitch time-to-peak decreased in proportion to axonal conduction velocity in individual animals. The whole population of motor units could be fitted by a linear relation between time-to-peak and the reciprocal of conduction time in the motor axon. Motor unit tension was also linearly related to the reciprocal of conduction time. 5. Histochemistry showed clear division between Type I and Type IIa fibres. Type I fibres reacted strongly with antibody against slow myosin of cat soleus muscle; Type IIa gave a reaction no stronger than the background. The division was as clear as in the cat or rat.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew B. L., Part N. J. Properties of fast and slow motor units in hind limb and tail muscles of the rat. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1972 Apr;57(2):213–225. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1972.sp002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagust J. Relationships between motor nerve conduction velocities and motor unit contraction characteristics in a slow twitch muscle of the cat. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(2):269–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Kaiser K. K. Muscle fiber types: how many and what kind? Arch Neurol. 1970 Oct;23(4):369–379. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480280083010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Ironton R. Sprouting and regression of neuromuscular synapses in partially denervated mammalian muscles. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:325–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Levine D. N., Tsairis P., Zajac F. E., 3rd Physiological types and histochemical profiles in motor units of the cat gastrocnemius. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):723–748. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Tsairis P. Trophic functions of the neuron. II. Denervation and regulation of muscle. The correlation of physiological properties with histochemical characteristics in single muscle units. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Mar 22;228(0):145–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb20507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bárány M. ATPase activity of myosin correlated with speed of muscle shortening. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6 Suppl):197–218. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.6.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. Properties of motor units in fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(1):45–55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dribin L. B., Simpson S. B., Jr Histochemical and morphological study of dystrophic (C57BL/6J dy2j/dy2j) and normal muscle. Exp Neurol. 1977 Sep;56(3):480–497. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(77)90316-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eusebi F., Miledi R., Takahashi T. Calcium transients in mammalian muscles. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):560–561. doi: 10.1038/284560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. M., Luck J. C., Knott S. A comparison of isometric contractions of the whole muscle with those of motor units in a fast-twitch muscle of the cat. Exp Neurol. 1972 Oct;37(1):68–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(72)90227-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. M., Parry D. J. Properties of motor units in mouse soleus [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Oct;295:90P–90P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luff A. R., Atwood H. L. Membrane properties and contraction of single muscle fibers in the mouse. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jun;222(6):1435–1440. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.6.1435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luff A. R. Dynamic properties of the inferior rectus, extensor digitorum longus, diaphragm and soleus muscles of the mouse. J Physiol. 1981;313:161–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz H., Ermini M., Jenny E. The size of the fibre populations in rabbit skeletal muscles as revealed by indirect immunofluorescence with anti-myosin sera. Histochemistry. 1978 Sep 15;57(3):223–235. doi: 10.1007/BF00492082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. J., Parslow H. G. Fiber type susceptibility in the dystrophic mouse. Exp Neurol. 1981 Sep;73(3):674–685. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(81)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow H. G., Parry D. J. Slowing of fast-twitch muscle in the dystrophic mouse. Exp Neurol. 1981 Sep;73(3):686–699. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(81)90205-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridge R. M. The differentiation of conduction velocities of slow twitch and fast twitch muscle motor innervations in kittens and cats. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1967 Jul;52(3):293–304. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1967.sp001915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan H. S., Aziz-Ullah, Goldspink G., Nowell N. W. Sex and stock differences in the histochemical myofibrillar adenosine triphosphatase reaction in the soleus muscle of the mouse. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Mar;22(3):155–159. doi: 10.1177/22.3.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- te Kronnie G., Pool C. W., Scholten G., van Raamsdonk W. Myofibrillar differences among mammalian skeletal muscle fibres at the ultrastructural level. A comparison of immunocytochemical and morphometrical parameters. Eur J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;22(2):772–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]