Abstract
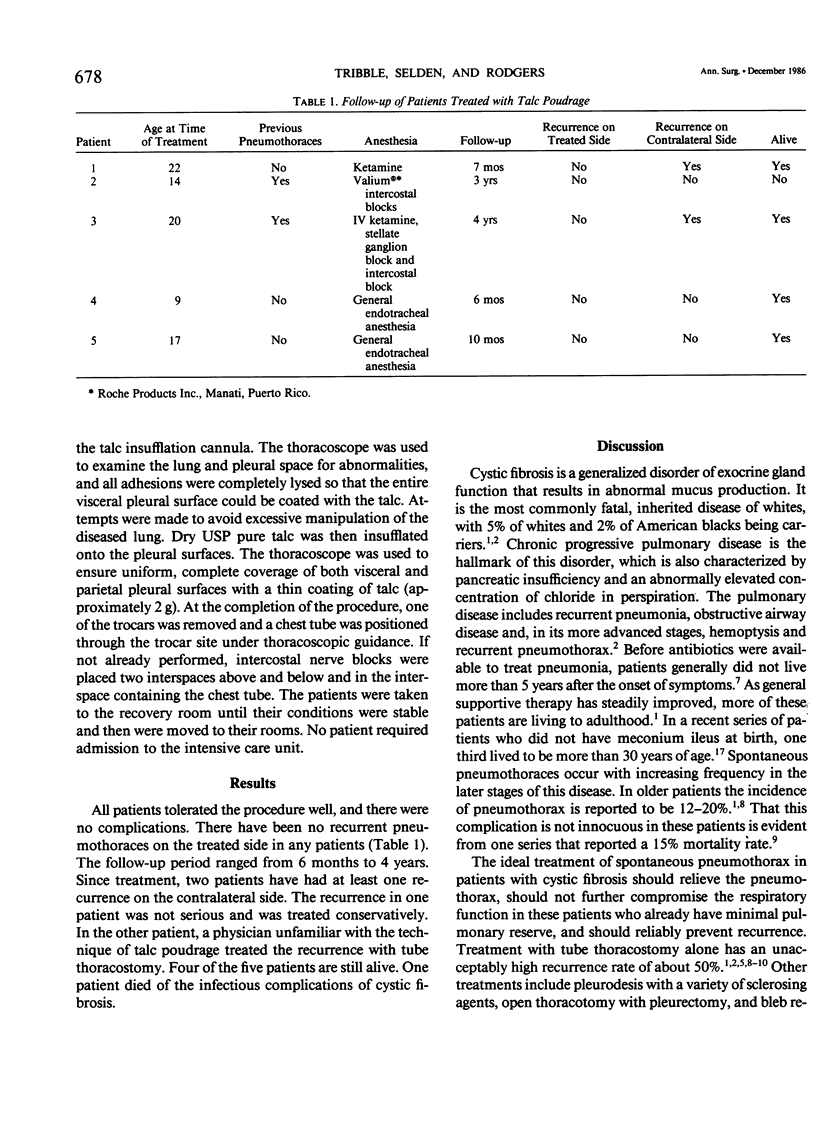
As patients with cystic fibrosis live longer, spontaneous pneumothoraces are seen with increasing frequency. Severe underlying pulmonary disease in these patients makes them particularly susceptible to life-threatening respiratory distress. Several modalities, including chemical sclerosis and open thoracotomy with pleurectomy, have been used to treat pneumothoraces in these patients. In the past 4 years, pneumothoraces in five patients (ages 9-22 years) with cystic fibrosis have been treated with thoracoscopy and talc poudrage. All procedures were performed under either regional or general anesthesia, depending on the age of the patient. Thoracoscopy was performed with a rod lens system and a 5.5-mm trocar, using biopsy forceps to lyse pleural adhesions, all of which ensures access to the entire pleural surface. United States Pharmacopeia-certified talc was insufflated to cover the entire pleural surface. There were no complications, and the patients had minimal pleural pain. Follow-up ranged from 6 months to 4 years. No patient has had a recurrent pneumothorax on the treated side. Thoracoscopy with talc poudrage is a preferable alternative to chemical sclerosis or thoracotomy for treating pneumothoraces in patients with cystic fibrosis. The procedure may be performed under regional anesthesia and allows rapid and complete sclerosis of the pleural cavity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler R. H., Rappole B. W. Recurrent malignant pleural effusions and talc powder aerosol treatment. Surgery. 1967 Dec;62(6):1000–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomberg A. E. Thoracoscopy in perspective. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1978 Sep;147(3):433–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boat T. F., Di Sant' Agnese P. A., Warwick W. J., Handwerger S. A. Pneumothorax in cystic fibrosis. JAMA. 1969 Sep 8;209(10):1498–1504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. B., di Sant'Agnese P. A. Diagnosis and treatment of cystic fibrosis. An update. Chest. 1984 Jun;85(6):802–809. doi: 10.1016/s0012-3692(16)62421-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camp P. T., Moseley P. W., Scott M. L., Hatch H. B., Jr Diagnostic thoracoscopy. Ann Thorac Surg. 1973 Jul;16(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)65814-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dler R. H. A talc powder aerosol method for the prevention of recurrent spontaneous pneumothorax. Ann Thorac Surg. 1968 May;5(5):474–477. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)66384-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKEL A., KRASNA I., BARONOFSKY I. D. An experimental study of pleural symphysis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1961 Jul;42:43–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAENSLER E. A. Parietal pleurectomy for recurrent spontaneous pneumothorax. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1956 Mar;102(3):293–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R., Gutersohn J., Herzog H. Die Behandlung des persistierenden Pneumothorax durch thorakoskopische Massnahmen. Thoraxchir Vask Chir. 1974 Oct;22(5):457–460. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1102811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrieu A. J., Tyers G. F., Williams E. H., O'Neill M. J., Derrick J. R. Intrapleural instillation of quinacrine for treatment of recurrent spontaneous pneumothorax. Ann Thorac Surg. 1979 Aug;28(2):146–150. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)63772-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luck S. R., Raffensperger J. G., Sullivan H. J., Gibson L. E. Management of pneumothorax in children with chronic pulmonary disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1977 Dec;74(6):834–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews L. W., Drotar D. Cystic fibrosis--a challenging long-term chronic disease. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1984 Feb;31(1):133–152. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)34541-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandi P. Recurrent spontaneous pneumothorax; an effective method of talc poudrage. Chest. 1980 Apr;77(4):493–495. doi: 10.1378/chest.77.4.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes D. D., Sherck J. P., Brodsky J. B., Mark J. B. Therapeutic thoracoscopy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1984 Feb;87(2):269–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofoegbu R. O. Pleurodesis for spontaneous pneumothorax. Experience with intrapleural olive oil in high risk patients. Am J Surg. 1980 Nov;140(5):679–681. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penketh A. R., Knight R. K., Hodson M. E., Batten J. C. Management of pneumothorax in adults with cystic fibrosis. Thorax. 1982 Nov;37(11):850–853. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.11.850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers B. M., Moazam F., Talbert J. L. Thoracoscopy in children. Ann Surg. 1979 Feb;189(2):176–180. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197902000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster S. R., McLaughlin F. J., Matthews W. J., Jr, Strieder D. J., Khaw K. T., Shwachman H. Management of pneumothorax in cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr Surg. 1983 Aug;18(4):492–497. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(83)80207-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shwachman H., Kowalski M., Khaw K. T. Cystic fibrosis: a new outlook. 70 patients above 25 years of age. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977 Mar;56(2):129–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shwachman H., Kulczycki L. L., Khaw K. T. A report on sixty-five patients over 17 years of age. Pediatrics. 1965 Nov;36(5):689–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swierenga J., Wagenaar J. P., Bergstein P. G. The value of thoracoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases affecting the pleura and lung. Pneumonologie. 1974 Sep;151(1):11–18. doi: 10.1007/BF02101140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabachnik N. F. Surgical treatment and the patient with cystic fibrosis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1981 Jun;152(6):837–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomashefski J. F., Jr, Bruce M., Stern R. C., Dearborn D. G., Dahms B. Pulmonary air cysts in cystic fibrosis: relation of pathologic features to radiologic findings and history of pneumothorax. Hum Pathol. 1985 Mar;16(3):253–261. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(85)80011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderschueren R. G. Le talcage pleural dans le pneumothorax spontané. Poumon Coeur. 1981;37(4):273–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissberg D., Kaufman M., Zurkowski Z. Pleuroscopy in patients with pleural effusion and pleural masses. Ann Thorac Surg. 1980 Mar;29(3):205–208. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)61868-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wied U., Halkier E., Hoeier-Madsen K., Plucnar B., Rasmussen E., Sparup J. Tetracycline versus silver nitrate pleurodesis in spontaneous pneumothorax. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1983 Oct;86(4):591–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. E., Boat T. F., Doershuk C. F. Cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jun;113(6):833–878. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


