Abstract
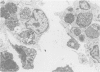
A single bolus of either Escherichia coli endotoxin, sonicated suspension of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae, or pyrogen-free normal saline was intratracheally instilled in six week old specific-pathogen-free pigs. Pigs exposed to E. coli endotoxin developed fever, leukopenia followed by leukocytosis, and endotoxemia. Leukocytosis was the only clinical abnormality noted in pigs receiving the sonicated suspension of H. pleuropneumoniae. At one day postexposure, focal areas of atelectasis and consolidation were observed in the caudal lung lobes of animals receiving either E. coli endotoxin or the sonicated suspension of H. pleuropneumoniae. Lesions were characterized by a neutrophilic bronchitis and bronchiolitis with alveolitis in the surrounding tissue. Increased numbers of alveolar macrophages and evidence of phagocytosis were observed by light and electron microscopy. No clinical abnormalities or lesions were observed in animals receiving normal saline. Lesions typical of acute porcine Haemophilus pleuropneumonia were not produced by either E. coli endotoxin or sonicated suspension of H. pleuropneumoniae, indicating that multiple virulence factors are probably involved in lesion development.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baluyut C. S., Simonson R. R., Bemrick W. J., Maheswaran S. K. Interaction of Pasteurella haemolytica with bovine neutrophils: identification and partial characterization of a cytotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Nov;42(11):1920–1926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendixen P. H., Shewen P. E., Rosendal S., Wilkie B. N. Toxicity of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae for porcine lung macrophages, peripheral blood monocytes, and testicular cells. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):673–676. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.673-676.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. N., Nausley C. A., Riegle L. Heat extraction of animal plasma in preparation for endotoxin testing with the limulus amebocyte lysate test. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Jul;40(7):1048–1049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. B., Barsoum I. S., Ramwell P. W., Yeager H., Jr Human alveolar macrophages: effects of endotoxin in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):753–758. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.753-758.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Harker L. A., Reidy M. A., Gajdusek C. M., Schwartz S. M., Striker G. E. Lipopolysaccharide-mediated bovine endothelial cell injury in vitro. Lab Invest. 1983 Mar;48(3):269–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson A. R., Kilburn K. H., Halprin G. M., McKenzie W. N. Granulocyte recruitment to airways exposed to endotoxin aerosols. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Jan;115(1):89–95. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häni H., König H., Nicolet J., Scholl E. Zur Haemophilus-Pleuropneumonie beim Schwein. V. Pathomorphologie. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1973 May;115(5):191–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häni H., König H., Nicolet J., Scholl E. Zur Haemophilus-Pleuropneumonie beim Schwein. VI. Pathogenese. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1973 May;115(5):205–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz H. J., Quast J. Effects of continuous intravenous infusion of Escherichia coli endotoxin into swine. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Feb;43(2):262–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell E. M., Trump B. F. Histologic fixatives suitable for diagnostic light and electron microscopy. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1976 Aug;100(8):405–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordstoga K., Fjolstad M. The generalized Shwartzman reaction and Haemophilus infections in pigs. Pathol Vet. 1967;4(3):245–253. doi: 10.1177/030098586700400304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimsay R. L., Coyle-Dennis J. E., Lauerman L. H., Squire P. G. Purification and biological characterizationof endotoxin fractions from Pasteruella haemolytica. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Dec;42(12):2134–2138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOPE R. E. PORCINE CONTAGIOUS PLEUROPNEUMONIA. I. EXPERIMENTAL TRANSMISSION, ETIOLOGY, AND PATHOLOGY. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:357–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford S. E., Josephson G. K. Porcine Haemophilus pleuropneumonia epizootic in southwestern Ontario: clinical, microbiological, pathological and some epidemiological findings. Can J Comp Med. 1981 Jan;45(1):2–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiefer B., Moffatt R. E., Greenfield J., Agar J. L., Majka J. A. Porcine Hemophilus parahemolyticus pneumonia in Saskatchewan. I. Natural occurrence and findings. Can J Comp Med. 1974 Apr;38(2):99–104. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebunya T. N., Saunders J. R., Osborne A. D. A model aerosol exposure system for induction of porcine Haemophilus pleuropneumonia. Can J Comp Med. 1983 Jan;47(1):48–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner K. W. Hematoxylin toluidine blue-phloxinate staining of glycol methacrylate sections of retina and other tissues. Stain Technol. 1980 Jul;55(4):229–233. doi: 10.3109/10520298009067245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]