Abstract
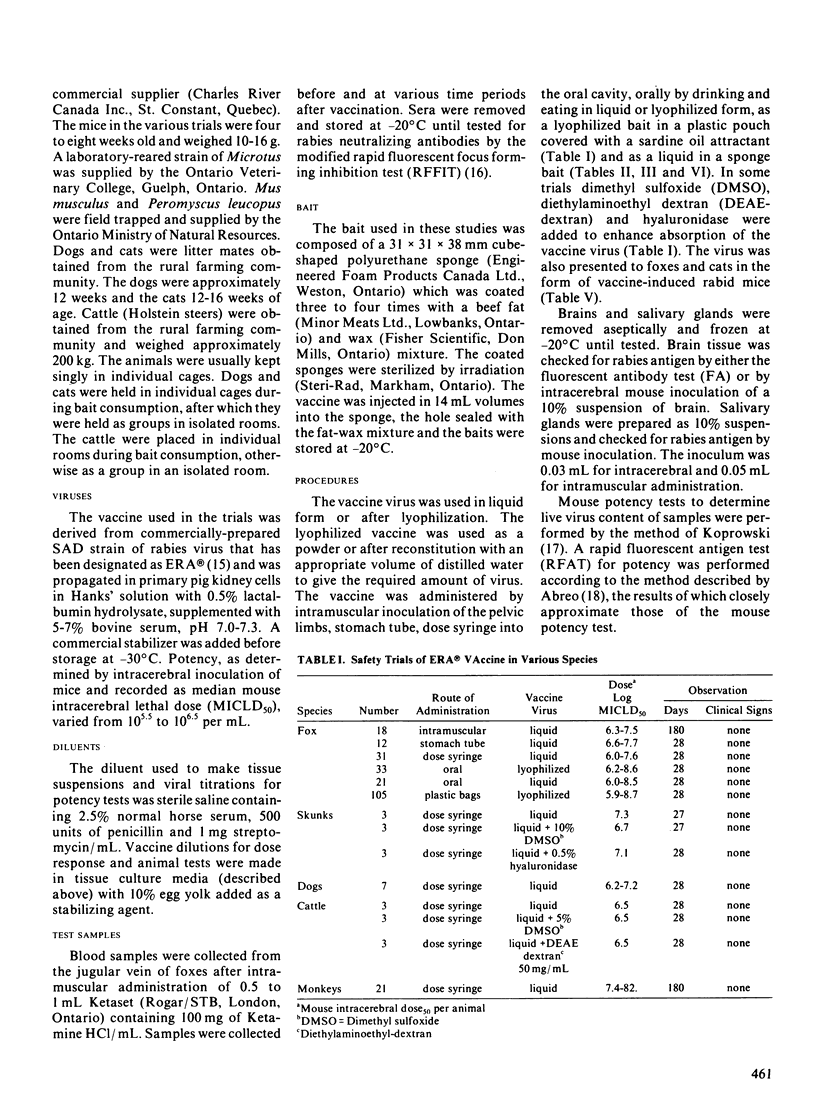
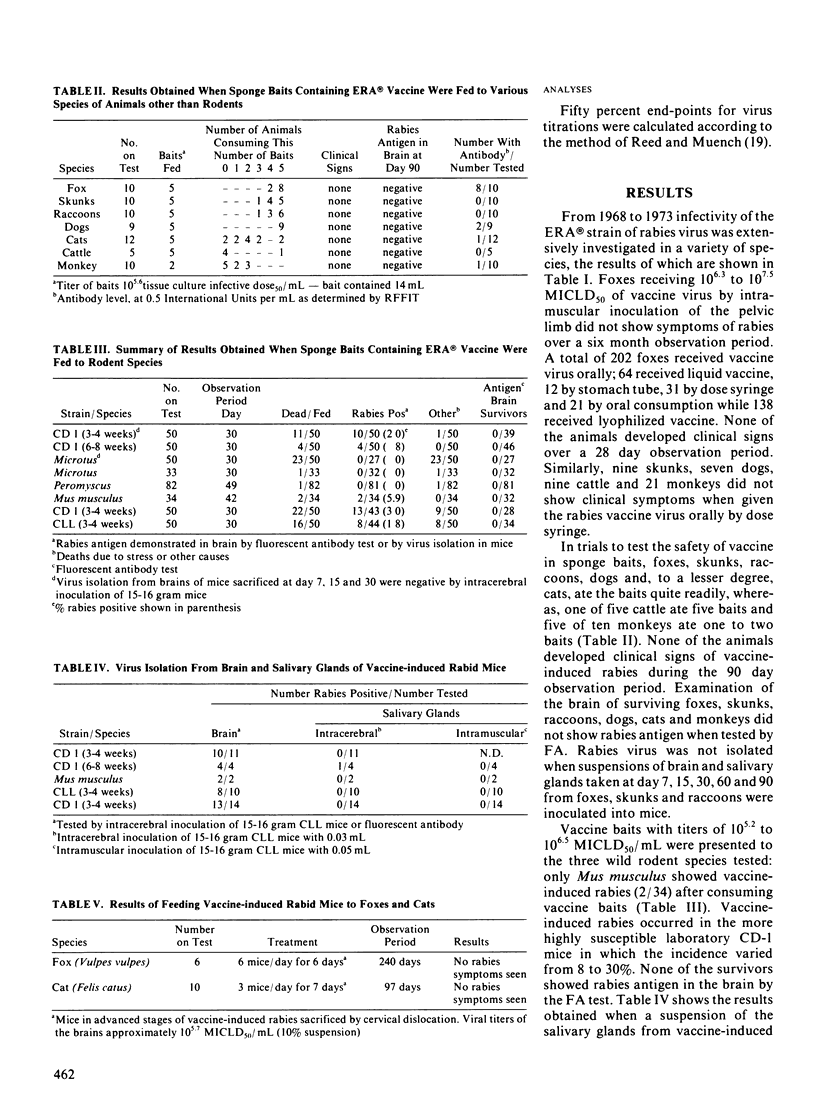
Ninety percent of foxes fed commercial ERA vaccine in a specially designed bait developed rabies serum neutralizing antibodies. The vaccine bait did not cause clinical signs of rabies when consumed by foxes, raccoons, skunks, dogs, cats, cattle and monkeys. When presented, in the laboratory, to wild rodents of the species Microtus, Mus musculus and Peromyscus, the vaccine baits caused vaccine-induced rabies only in Mus musculus. Laboratory mice of the CD-1 and CLL strain were susceptible to vaccine-induced rabies; however, studies showed that transmission of virus to other animals did not occur. These studies suggest that the vaccine bait described could be useful in a rabies control program in areas where foxes and wild dogs are the principal vectors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelseth M. K. An Attenuated Rabies Vaccine for Domestic Animals Produced in Tissue Culture. Can Vet J. 1964 Nov;5(11):279–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abreo C. B. A rapid quantitative microtest for live, attenuated rabies vaccine. J Biol Stand. 1985 Jul;13(3):255–260. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(85)80009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer G. M., Abelseth M. K., Debbie J. G. Oral vaccination of foxes against rabies. Am J Epidemiol. 1971 Jun;93(6):487–490. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. G., Lawson K. F. Further studies of sylvatic rabies in the fox (Vulpes vulpes). Vaccination by the oral route. Can Vet J. 1973 Sep;14(9):206–211. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. G., Lawson K. F. Sylvatic rabies studies in the silver fox (Vulpes vulpes). Susceptibility and immune response. Can J Comp Med. 1970 Oct;34(4):309–311. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. G., Lawson K. F. The safety and efficacy of immunizing foxes (Vulpes vulpes) using bait containing attenuated rabies virus vaccine. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Apr;44(2):169–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debbie J. G., Abelseth M. K., Baer G. M. The use of commercially available vaccines for the oral vaccination of foxes against rabies. Am J Epidemiol. 1972 Sep;96(3):231–235. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esh J. B., Cunningham J. G., Wiktor T. J. Vaccine-induced rabies in four cats. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1982 Jun 1;180(11):1336–1339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H. Laboratory techniques in rabies: the mouse inoculation test. Monogr Ser World Health Organ. 1973;(23):85–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson K. F., Crawley J. F. ERA strain rabies vaccine--intracerebral passage in dogs. Can Vet J. 1973 Jun;14(6):125–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayr A., Kraft H., Jaeger O., Haacke H. Orale Immunisierung von Füchsen gegen Tollwut. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1972 Sep;19(8):615–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck F., Wandeler A., Bichsel P., Capt S., Häfliger U., Schneider L. Oral immunization of foxes against rabies. Laboratory and field studies. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1982;5(1-3):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(82)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler W. G., McLean R. G., Cowart J. C. Vaccination of foxes against rabies using ingested baits. J Wildl Dis. 1975 Jul;11(3):382–388. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-11.3.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler W. G., Shaddock J. H., Williams L. W. Oral rabies vaccine: evaluation of its infectivity in three species of rodents. Am J Epidemiol. 1976 Sep;104(3):294–298. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalan E., Wilson C., Pukitis D. A microtest for the quantitation of rabies virus neutralizing antibodies. J Biol Stand. 1979 Jul;7(3):213–220. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(79)80024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


