Abstract
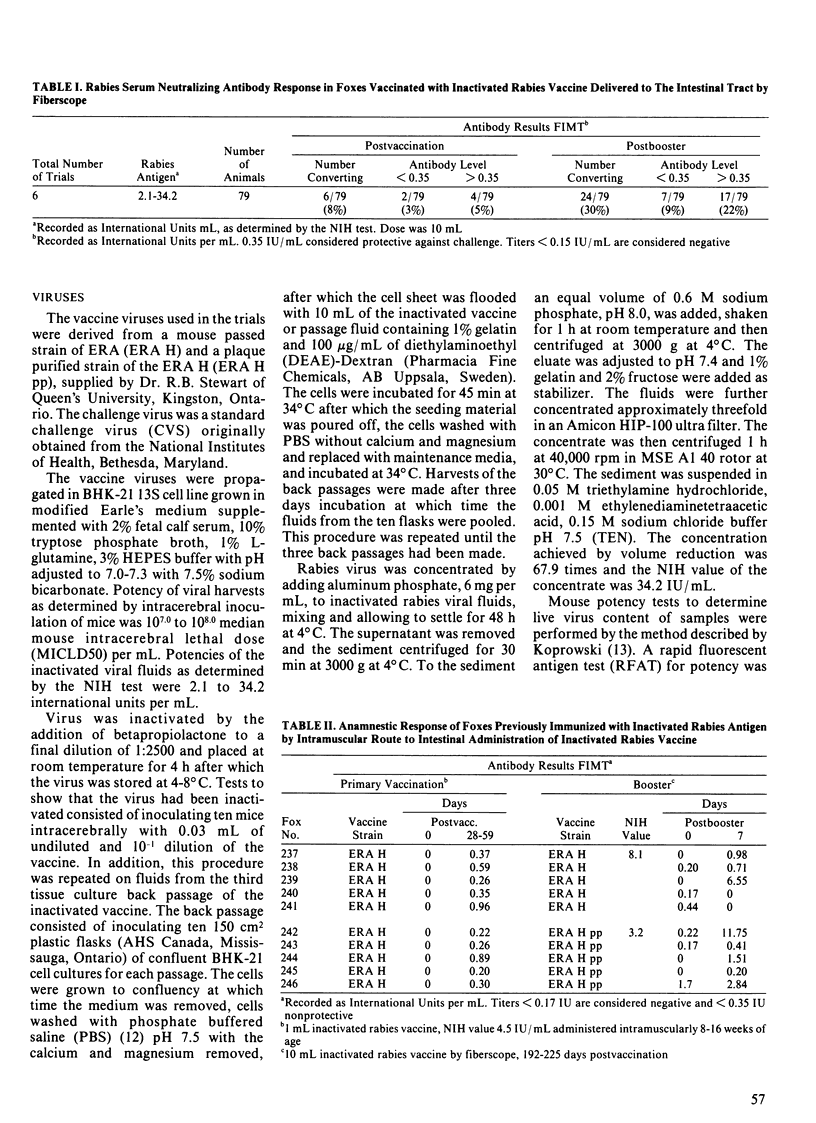
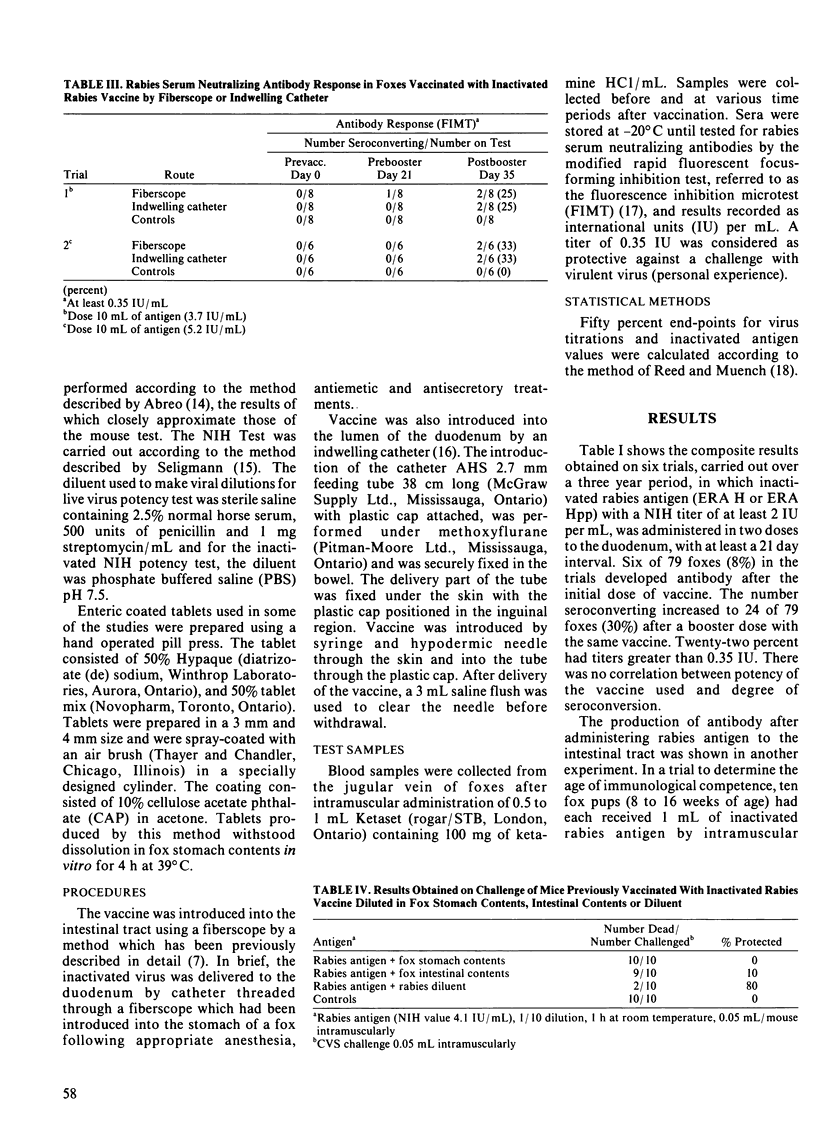
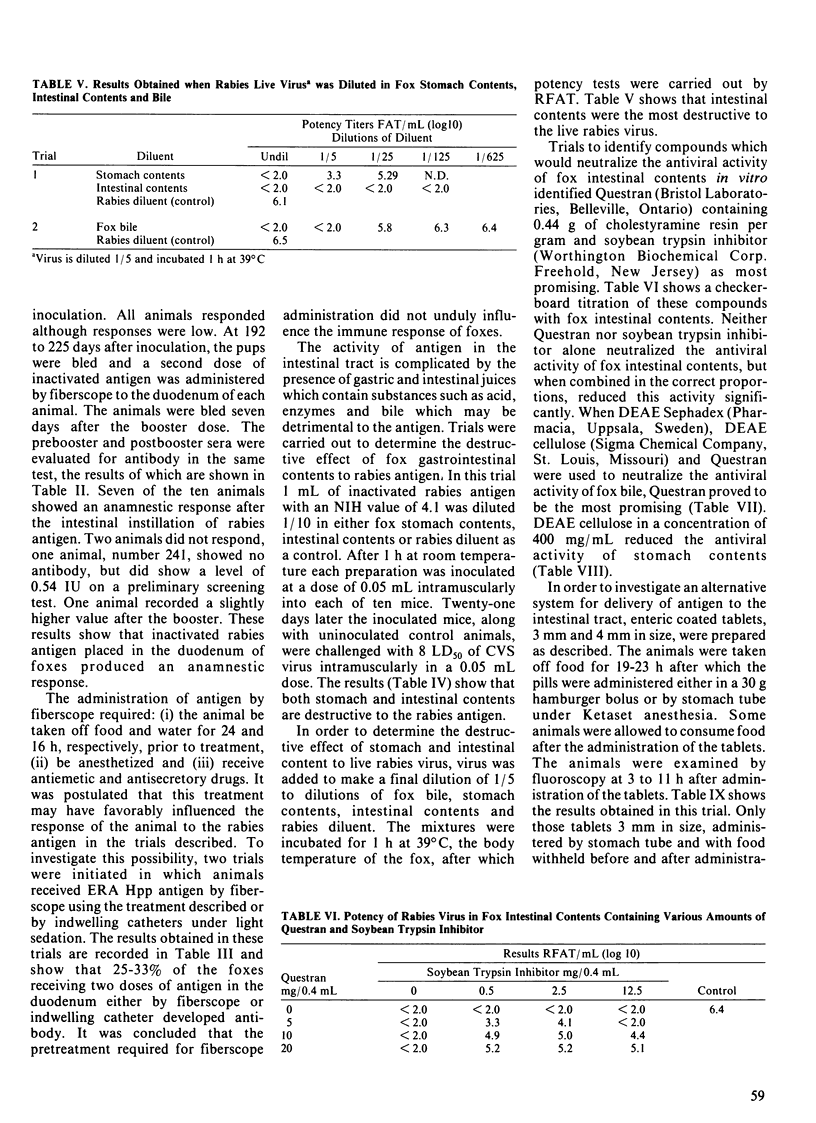
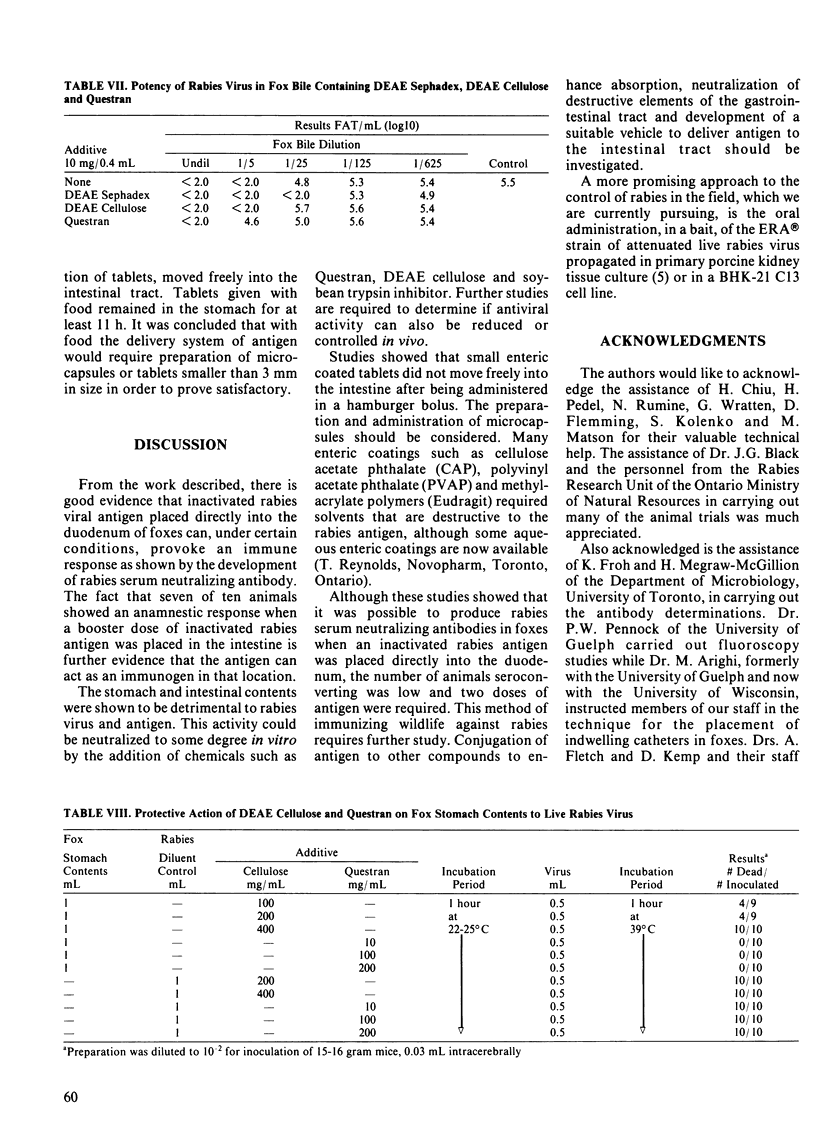
Approximately 30% of foxes given two doses of an inactivated rabies antigen delivered directly into the intestinal tract developed an immune response as measured by rabies serum neutralizing antibodies. Seven of ten previously immunized foxes showed an anamnestic response following a booster dose of inactivated rabies antigen delivered to the intestinal lumen. Stomach and particularly intestinal contents were destructive to rabies antigen and virus. This effect could be partially neutralized in vitro by the addition of Questran and soybean trypsin inhibitor. Small enteric coated tablets fed to foxes in a hamburger bolus remained in the stomach for up to 13 hours and therefore would provide a poor vehicle for the delivery of antigen to the intestinal tract.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black J. G., Lawson K. F. Further studies of sylvatic rabies in the fox (Vulpes vulpes). Vaccination by the oral route. Can Vet J. 1973 Sep;14(9):206–211. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blancou J., Kieny M. P., Lathe R., Lecocq J. P., Pastoret P. P., Soulebot J. P., Desmettre P. Oral vaccination of the fox against rabies using a live recombinant vaccinia virus. Nature. 1986 Jul 24;322(6077):373–375. doi: 10.1038/322373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler D. G., Gall D. G., Kelly M. H., Hamilton J. R. Transmissible gastroenteritis. Mechanisms responsible for diarrhea in an acute viral enteritis in piglets. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1335–1342. doi: 10.1172/JCI107681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton K. M., Webster W. A., Casey G. A., Rhodes A. J., Macinnes C. D., Lawson K. F. Recent advances in rabies diagnosis and research. Can Vet J. 1986 Feb;27(2):85–89. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kathol R. G., Cox T. A., Corbett J. J., Thompson H. S., Clancy J. Functional visual loss: II. Psychiatric aspects in 42 patients followed for 4 years. Psychol Med. 1983 May;13(2):315–324. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700050935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H. Laboratory techniques in rabies: the mouse inoculation test. Monogr Ser World Health Organ. 1973;(23):85–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson K. F., Black J. G., Charlton K. M., Johnston D. H., Rhodes A. J. Safety and immunogenicity of a vaccine bait containing ERA strain of attenuated rabies virus. Can J Vet Res. 1987 Oct;51(4):460–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson K. F., Johnston D. H., Patterson J. M., Black J. G., Rhodes A. J., Zalan E. Immunization of foxes Vulpes vulpes by the oral and intramuscular routes with inactivated rabies vaccines. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Oct;46(4):382–385. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson K. G., Bauer S. P. Enteric inoculation with ERA rabies virus: evaluation of a candidate wildlife vaccine in laboratory rodents. Arch Virol. 1981;67(1):51–56. doi: 10.1007/BF01314601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupprecht C. E., Wiktor T. J., Johnston D. H., Hamir A. N., Dietzschold B., Wunner W. H., Glickman L. T., Koprowski H. Oral immunization and protection of raccoons (Procyon lotor) with a vaccinia-rabies glycoprotein recombinant virus vaccine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7947–7950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann E. B., Jr Laboratory techniques in rabies: the NIH test for potency. Monogr Ser World Health Organ. 1973;(23):279–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck F., Wandeler A., Bichsel P., Capt S., Häfliger U., Schneider L. Oral immunization of foxes against rabies. Laboratory and field studies. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1982;5(1-3):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(82)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolson N. D., Charlton K. M., Lawson K. F., Campbell J. B., Stewart R. B. Studies of ERA/BHK-21 rabies vaccine in skunks and mice. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Jan;52(1):58–62. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler W. G., Shaddock J. H., Williams L. W. Oral rabies vaccine: evaluation of its infectivity in three species of rodents. Am J Epidemiol. 1976 Sep;104(3):294–298. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalan E., Wilson C., Pukitis D. A microtest for the quantitation of rabies virus neutralizing antibodies. J Biol Stand. 1979 Jul;7(3):213–220. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(79)80024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


