Abstract
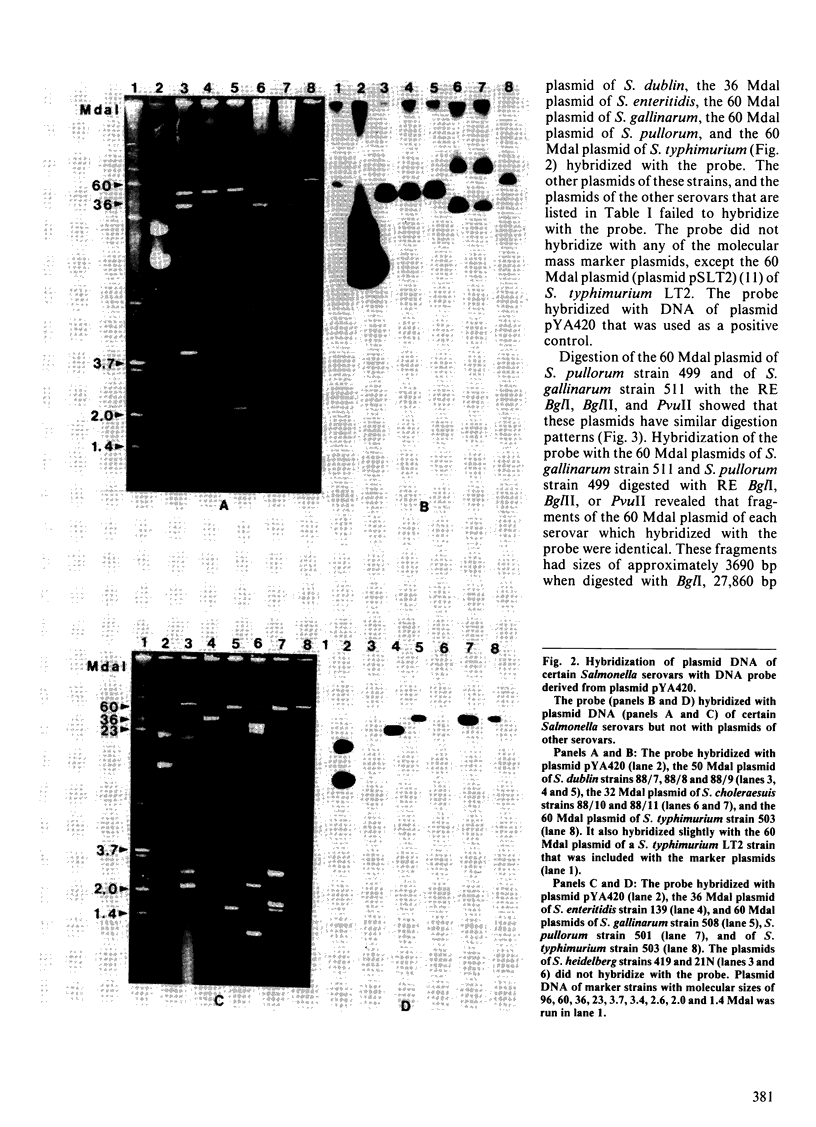
Plasmid DNA of 68 strains of Salmonella that belonged to 18 serovars and exhibited 48 different plasmid profiles was examined for hybridization with a 32P-labelled DNA probe which consisted of a 3750 base pairs (bp) HindIII-HindIII fragment derived from the virulence region of the 60 megadalton (Mdal) plasmid of Salmonella typhimurium. The 32 Mdal plasmid of S. cholerae-suis, the 50 Mdal plasmid of S. dublin, the 36 Mdal plasmid of S. enteritidis, the 60 Mdal plasmid of S. gallinarum, the 60 Mdal plasmid of S. pullorum, and the 60 Mdal plasmid of S. typhimurium, plasmids that have been associated with virulence, all hybridized with the probe. Digestion of plasmid DNA of these strains with PvuII and hybridization with the probe revealed that the plasmids of strains of all six serovars contained fragments of approximately 2520 and 1520 bp that hybridized with the probe. Similarly, hybridization with BglI digests of DNA of the virulence-associated plasmids of strains of these six serovars showed that all six plasmids contained a fragment of approximately 3690 bp that hybridized with the probe. No other plasmids of these strains nor any plasmids of 12 other Salmonella serovars hybridized with the probe. Chromosomal DNA did not hybridize with the probe. The 60 Mdal plasmids of S. gallinarum and S. pullorum showed similar digestion patterns with restriction endonucleases BglI, BglII and PvuII.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird G. D., Manning E. J., Jones P. W. Evidence for related virulence sequences in plasmids of Salmonella dublin and Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jul;131(7):1815–1823. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-7-1815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrow P. A., Simpson J. M., Lovell M. A., Binns M. M. Contribution of Salmonella gallinarum large plasmid toward virulence in fowl typhoid. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):388–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.388-392.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beninger P. R., Chikami G., Tanabe K., Roudier C., Fierer J., Guiney D. G. Physical and genetic mapping of the Salmonella dublin virulence plasmid pSDL2. Relationship to plasmids from other Salmonella strains. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1341–1347. doi: 10.1172/JCI113461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Curtiss R., 3rd Cloning and transposon insertion mutagenesis of virulence genes of the 100-kilobase plasmid of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3262–3271. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3262-3271.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Curtiss R., 3rd Plasmid-associated virulence of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2891–2901. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2891-2901.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett J., Kotlarski I., Mathan V., Francki K., Rowley D. The colonization of Peyer's patches by a strain of Salmonella typhimurium cured of the cryptic plasmid. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1119–1125. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rabert D. K., Svinarich D. M., Whitfield H. J. Association of adhesive, invasive, and virulent phenotypes of Salmonella typhimurium with autonomous 60-megadalton plasmids. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):476–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.476-486.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels T., Popoff M. Y., Durviaux S., Coynault C., Cornelis G. A new method for the physical and genetic mapping of large plasmids: application to the localisation of the virulence determinants on the 90 kb plasmid of Salmonella typhimurium. Microb Pathog. 1987 Aug;3(2):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M. Y., Miras I., Coynault C., Lasselin C., Pardon P. Molecular relationships between virulence plasmids of Salmonella serotypes typhimurium and dublin and large plasmids of other Salmonella serotypes. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1984 May-Jun;135A(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(84)80080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppe C., Gyles C. L. Relation of plasmids to virulence and other properties of salmonellae from avian sources. Avian Dis. 1987 Oct-Dec;31(4):844–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel A. F., Chabbert Y. A. Taxonomy and epidemiology of gram-negative bacterial plasmids studied by DNA-DNA filter hybridization in formamide. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Feb;104(2):269–276. doi: 10.1099/00221287-104-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Kadam S. K., MacLachlan P. R. Derepression of F factor function in Salmonella typhimurium. Can J Microbiol. 1983 Sep;29(9):1205–1212. doi: 10.1139/m83-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The relationship between different transmissible plasmids introduced by F into the same strain of Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Aug;62(3):227–285. doi: 10.1099/00221287-62-3-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson C. M., Baird G. D., Manning E. J. A common virulence region on plasmids from eleven serotypes of Salmonella. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Apr;134(4):975–982. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-4-975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





